Android12蓝牙框架
参考:
https://evilpan.com/2021/07/11/android-bt/
https://source.android.com/docs/core/connect/bluetooth?hl=zh-cn
https://developer.android.com/guide/topics/connectivity/bluetooth?hl=zh-cn
https://developer.android.com/guide/components/intents-filters?hl=zh-cn
文章目录
- AIDL Server
- btm_ble_set_discoverability
- btsnd_hcic_write_cur_iac_lap
- HCI 子系统
- 接收数据
- 发送数据
- BTIF: Bluetooth Interface
- BTU : Bluetooth Upper Layer
- BTM: Bluetooth Manager
- BTE: Bluetooth embedded system
- BTA :Blueetooth application layer
- CO: call out
- CI: call in
- HF : Handsfree Profile
- HH: HID Host Profile
- HL: Health Device Profile
- av: audio/vidio
- ag: audio gateway
- ar: audio/video registration
- gattc: GATT client
- HIDL: HAL Interface Definition Language
Android4.2 之后采用 bluedroid 作为协议;整体由 bluetooth.apk,bluedroid ,libbt-vendor 三个 部 分 组 成 。
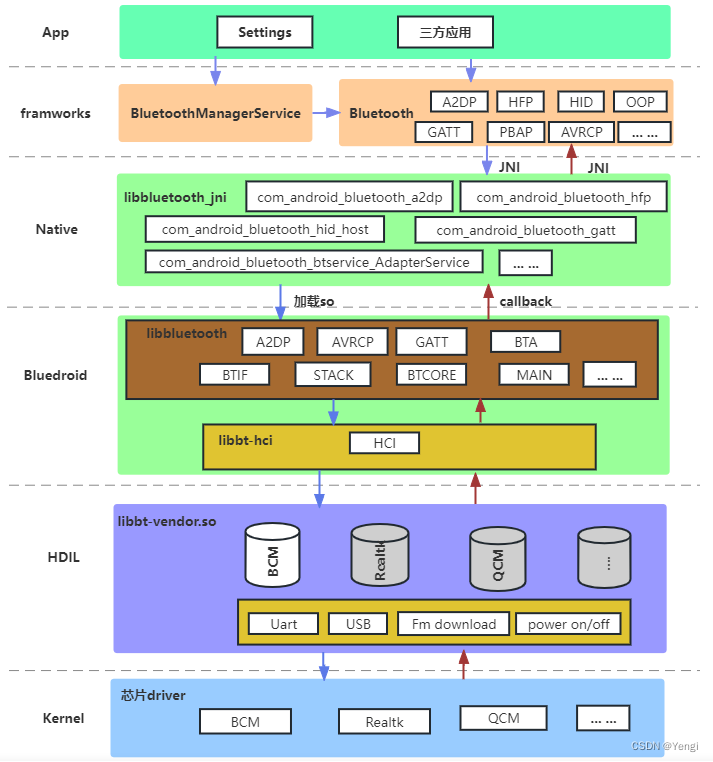
蓝牙协议栈一方面是以系统服务的方式提供接口,另一方面也以client的方式给应用程序提供SDK,不管怎样,最终都是需要经过HCI协议去与Controller进行交互
对于BlueDroid而言,协议栈是在用户层实现的,内核只暴露出HCI(USB/UART)的接口。因此,我们可以从HCI出发,自底向上进行分析,也可以参考上面的框架图,从用户应用程序开始,自顶向下进行分析
AIDL Server
bool SetScanMode(int scan_mode) system/bt/service/adapter.cc
SetAdapterProperty
hal::BluetoothInterface::Get()->GetHALInterface()->set_adapter_property
set_adapter_property system/bt/btif/src/bluetooth.cc
do_in_main_thread
btif_set_adapter_property system/bt/btif/src/btif_core.cc
BTA_DmSetVisibility system/bt/bta/dm/bta_dm_act.cc
android12/system/bt/stack/btm/btm_inq.cc
这其中涉及了几个API:
btm_ble_set_discoverability
btsnd_hcic_write_cur_iac_lap
btsnd_hcic_write_inqscan_cfg
btsnd_hcic_write_scan_enable
btm_ble_set_discoverability
第一个API是BLE相关,内部实际上最终也调用了btsnd_hcic_xxx的类似接口。IAC意为Inquiry Access Code,蓝牙baseband定义了几个固定IAC,分别是LIAC和GIAC(见baseband)。LAP是蓝牙地址的一部分,如下图所示:
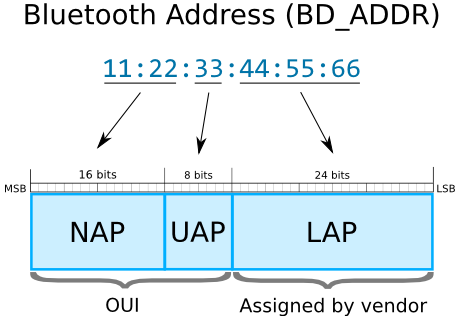
- NAP: Non-significant Address Part, NAP的值在跳频同步帧中会用到
- UAP: Upper Address Part,UAP的值会参与对蓝牙协议算法的选择
- LAP: Lower Address Part,由设备厂商分配,LAP的值作为Access Code的一部分,唯一确定某个蓝牙设备
- SAP (significant address part) = UAP + LAP
btsnd_hcic_write_cur_iac_lap
// system/bt/stack/hcic/hcicmds.cc
void btsnd_hcic_write_cur_iac_lap(uint8_t num_cur_iac, LAP* const iac_lap) {
btu_hcif_send_cmd(LOCAL_BR_EDR_CONTROLLER_ID, p);
}
/UINTx_TO_STREAM(pp, n)的作用是将整数以小端的形式写入p->data中,最终调用btu_hcif_send_cmd函数发送数据
// system/btstack/btu/btu_hcif.cc
void btu_hcif_send_cmd(UNUSED_ATTR uint8_t controller_id, BT_HDR* p_buf) {
uint8_t* stream = p_buf->data + p_buf->offset;
stream++;
btu_hcif_log_command_metrics(opcode, stream,
android::bluetooth::hci::STATUS_UNKNOWN, false);
hci_layer_get_interface()->transmit_command(
p_buf, btu_hcif_command_complete_evt, btu_hcif_command_status_evt,
vsc_callback);
}
//可见p_buf->data中保存的就是HCI数据,前16位为opcode,其中高6字节为ogf,低10字节为ocf,也就是我们平时使用hcitool cmd时的前两个参数
HCI 子系统
继续跟踪transmit_command,就来到了HCI子系统中
transmit_command system/bt/hci/src/hci_layer.cc
enqueue_command
process_command_credits
其调用链路为:
BluetoothHciCallbacks::hciEventReceived system/bt/hci/src/hci_layer_android.cc
hci_event_received system/bt/hci/src/hci_layer.cc
filter_incoming_event
process_command_credits
接收数据
BluetoothHciCallbacks::hciEventReceived 这个函数回调是在HCI初始化的时候调用的
BluetoothHci::initialize(system/bt/vendor_libs/linux/interface/bluetooth_hci.cc):
Return<void> BluetoothHci::initialize system/bt/vendor_libs/linux/interface/bluetooth_hci.cc
openBtHci
fd_watcher_本质上是针对hci_fd文件句柄的读端事件监控,后者由openBtHci函数产生,该函数由厂商实现,接口文件是hardware/interfaces/bluetooth/1.0/IBluetoothHci.hal。在Linux中的参考实现如下:
发送数据
继续回头接着上节之前的内容讲,我们的任务队列是在process_command_credits中被消费的,取出来之后需要进入到hci_thread线程中执行。从接收数据一节中也能看出,hci接口本身使用的是串行总线,因此不能并发地发送数据,所有命令都是在之前的命令响应后再发送。
值得一提的是,enqueue_command实际上绑定的是函数event_command_ready,以包含我们命令内容和对应回调的类型waiting_command_t为参数:
static void enqueue_command(waiting_command_t* wait_entry) {
base::Closure callback = base::Bind(&event_command_ready, wait_entry);
//...
command_queue.push(std::move(callback));
}
因此,负责执行HCI发送命令的是event_command_ready函数:
static void event_command_ready(waiting_command_t* wait_entry) {
{
/// Move it to the list of commands awaiting response
std::lock_guard<std::recursive_timed_mutex> lock(
commands_pending_response_mutex);
wait_entry->timestamp = std::chrono::steady_clock::now();
list_append(commands_pending_response, wait_entry);
}
// Send it off
packet_fragmenter->fragment_and_dispatch(wait_entry->command);
update_command_response_timer();
}
首先将command放到一个等待响应的队列里,然后分片发送:
static void fragment_and_dispatch(BT_HDR* packet) {
CHECK(packet != NULL);
uint16_t event = packet->event & MSG_EVT_MASK;
uint8_t* stream = packet->data + packet->offset;
// We only fragment ACL packets
if (event != MSG_STACK_TO_HC_HCI_ACL) {
callbacks->fragmented(packet, true);
return;
}
// ACL/L2CAP fragment...
}
实现中只对ACL类型的HCI数据进行分片发送,不管是不是分片,都对最后一个packet调用callbacks->fragmented(),callbacks的类型是packet_fragmenter_callbacks_t,在packet_fragmenter_t->init中初始化并设置。而packet_fragmenter的初始化发生在hci_module_start_up()中,HCI层定义的回调如下:
static const packet_fragmenter_callbacks_t packet_fragmenter_callbacks = { transmit_fragment, dispatch_reassembled, fragmenter_transmit_finished };
fragmented即对应transmit_fragment,对应定义如下:
// Callback for the fragmenter to send a fragment static void transmit_fragment(BT_HDR* packet, bool send_transmit_finished) { btsnoop->capture(packet, false); // HCI command packets are freed on a different thread when the matching // event is received. Check packet->event before sending to avoid a race. bool free_after_transmit = (packet->event & MSG_EVT_MASK) != MSG_STACK_TO_HC_HCI_CMD && send_transmit_finished; hci_transmit(packet); if (free_after_transmit) { buffer_allocator->free(packet); } }
hci_transmit有不同平台的实现,分别在:
- hci/src/hci_layer_linux.c
- hci/src/hci_layer_android.c
前者是通过write直接向HCI socket的fd写入,后者是调用IBluetoothHci::sendHciCommand去实现,接口定义同样是在hardware/interfaces/bluetooth/1.0/IBluetoothHci.hal文件中。
因为不同手机厂商的SoC中集成蓝牙芯片的接口不同,有的是使用USB连接,有的是使用UART连接,因此需要给安卓提供一个统一的操作接口,这个接口就很适合由HAL(HIDL)来进行抽象。这部分实现通常是使用Linux中已有的UART/USB驱动进行操作,以提高代码的复用性。
在ITX-3588J 中,通过/dev/ttyS6与蓝牙芯片进行通信,通过rfkill控制蓝牙开关
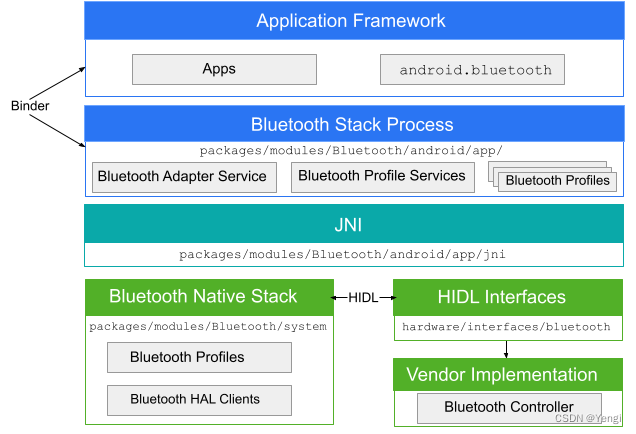
蓝牙协议栈、HIDL interface、 libbt-vendor
-
Bluetooth Native Stack
-
HIDL Interfaces
-
Vendor Implementation
相关源码路径
system/bt
hardware/interfaces/bluetooth/1.0/default
hardware/broadcom/libbt/src
net/rfkill/rfkill-bt.c
drivers/tty
