Compiler Lab1- 自制词法分析器
由于编译原理课的Lab1为自制词法分析器,所以笔者用C++实现了一个极简的C语言词法分析器,用于分析C语言源代码。它可以处理关键字、标识符、整数、实数、浮点数的科学计数法表示、运算符、分隔符、字符串字面量、字符字面量、注释和预处理指令。请注意,此版本的词法分析器不是很完善,但它应该能够处理大多数简单的C语言源代码。
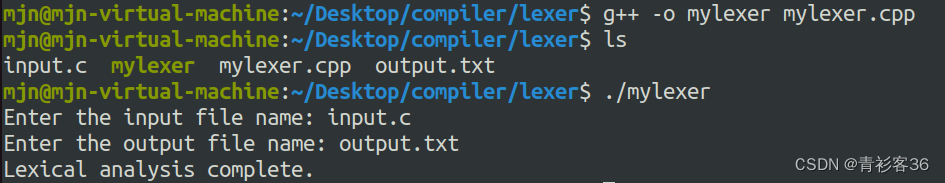
用户输入输入文件名和输出文件名,然后检查这些文件是否可以正确打开。然后,我们从输入文件中读取内容,对其进行词法分析,并将结果写入输出文件中。最后,我们通知用户词法分析已完成,并提示用户查看输出文件以获取结果。
mylexer.cpp文件
词法分析器核心文件
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
enum class TokenType
{
Keyword,
Identifier,
Integer,
Real,
Operator,
Separator,
StringLiteral,
CharLiteral,
Comment,
Preprocessor,
Unknown
};
struct Token
{
TokenType type;
string value;
};
bool isKeyword(const string &value)
{
static const unordered_set<string> keywords = {
"auto", "break", "case", "char", "const", "continue", "default", "do",
"double", "else", "enum", "extern", "float", "for", "goto", "if", "int",
"long", "register", "return", "short", "signed", "sizeof", "static",
"struct", "switch", "typedef", "union", "unsigned", "void", "volatile", "while"};
return keywords.find(value) != keywords.end();
}
bool isOperator(char c)
{
static const unordered_set<char> operators = {
'+', '-', '*', '/', '%', '>', '<', '=', '&', '|', '!', '~', '^', '?', ':'};
return operators.find(c) != operators.end();
}
bool isSeparator(char c)
{
static const unordered_set<char> separators = {
'(', ')', '[', ']', '{', '}', ',', ';', '.', '#'};
return separators.find(c) != separators.end();
}
vector<Token> lex(const string &input)
{
vector<Token> tokens;
string buffer;
auto flushBuffer = [&]()
{
if (!buffer.empty())
{
if (isKeyword(buffer))
{
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Keyword, buffer});
}
else
{
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Identifier, buffer});
}
buffer.clear();
}
};
size_t i = 0;
while (i < input.length())
{
char c = input[i];
if (isalpha(c) || c == '_')
{
buffer.push_back(c);
i++;
}
else
{
flushBuffer();
if (isdigit(c))
{
string number;
number.push_back(c);
i++;
while (i < input.length() && (isdigit(input[i]) || input[i] == '.' || tolower(input[i]) == 'e'))
{
number.push_back(input[i]);
if (tolower(input[i]) == 'e' && i + 1 < input.length() && (input[i + 1] == '+' || input[i + 1] == '-'))
{
number.push_back(input[++i]);
}
i++;
}
while (i < input.length() && (tolower(input[i]) == 'u' || tolower(input[i]) == 'l'))
{
number.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
tokens.push_back({number.find('.') != string::npos || number.find('e') != string::npos || number.find('E') != string::npos ? TokenType::Real : TokenType::Integer, number});
}
else if (isOperator(c))
{
if (c == '/' && i + 1 < input.length())
{
if (input[i + 1] == '/')
{
i += 2;
string comment;
while (i < input.length() && input[i] != '\n')
{
comment.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Comment, comment});
}
else if (input[i + 1] == '*')
{
i += 2;
string comment;
while (i + 1 < input.length() && !(input[i] == '*' && input[i + 1] == '/'))
{
comment.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
if (i + 1 < input.length())
{
// comment.push_back(input[i]);
i += 2;
}
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Comment, comment});
// cout << "here " << endl;
}
}
else
{
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Operator, string(1, c)});
i++;
}
}
else if (isSeparator(c))
{
if (c == '#')
{
string preprocessor;
i++;
while (i < input.length() && (isalnum(input[i]) || input[i] == '_'))
{
preprocessor.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Preprocessor, preprocessor});
}
else
{
tokens.push_back({TokenType::Separator, string(1, c)});
i++;
}
}
else if (c == '\"')
{
string str_literal;
i++;
while (i < input.length() && input[i] != '\"')
{
if (input[i] == '\\' && i + 1 < input.length())
{
str_literal.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
str_literal.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
i++;
tokens.push_back({TokenType::StringLiteral, str_literal});
}
else if (c == '\'')
{
string char_literal;
i++;
if (i < input.length())
{
if (input[i] == '\\' && i + 1 < input.length())
{
char_literal.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
char_literal.push_back(input[i]);
i++;
}
i++;
tokens.push_back({TokenType::CharLiteral, char_literal});
}
else
{
i++;
}
}
}
flushBuffer();
return tokens;
}
int main()
{
string input_filename;
string output_filename;
cout << "Enter the input file name: ";
cin >> input_filename;
cout << "Enter the output file name: ";
cin >> output_filename;
ifstream infile(input_filename);
ofstream outfile(output_filename);
if (!infile)
{
cerr << "Error opening the input file!" << endl;
return 1;
}
if (!outfile)
{
cerr << "Error opening the output file!" << endl;
return 1;
}
string input((istreambuf_iterator<char>(infile)), istreambuf_iterator<char>());
auto tokens = lex(input);
for (const auto &token : tokens)
{
// outfile << "Token type: " << static_cast<int>(token.type) << ", value: " << token.value << endl;
outfile << "Token type: ";
switch (token.type)
{
case TokenType::Keyword:
outfile << "Keyword";
break;
case TokenType::Identifier:
outfile << "Identifier";
break;
case TokenType::Integer:
outfile << "Integer";
break;
case TokenType::Real:
outfile << "Real";
break;
case TokenType::Operator:
outfile << "Operator";
break;
case TokenType::Separator:
outfile << "Separator";
break;
case TokenType::StringLiteral:
outfile << "StringLiteral";
break;
case TokenType::CharLiteral:
outfile << "CharLiteral";
break;
case TokenType::Comment:
outfile << "Comment";
break;
case TokenType::Preprocessor:
outfile << "Preprocessor";
break;
case TokenType::Unknown:
outfile << "Unknown";
break;
}
outfile << ", Value: " << token.value << endl;
}
cout << "Lexical analysis complete." << endl;
return 0;
}
input.c文件
用于词法分析器的输入文件
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 6
int main()
{
// Single-Line Comments
int a = 0;
double b = 1.5;
long c = 100L;
char d = 'd';
char s[6] = "hello";
/*
Multiline comment
Multiline comment
*/
if (a > 0)
{
printf("%s", s);
}
else
{
c = a + N;
}
return 0;
}
output.txt文件
词法分析器的输出结果
Token type: Preprocessor, Value: include
Token type: Operator, Value: <
Token type: Identifier, Value: stdio
Token type: Separator, Value: .
Token type: Identifier, Value: h
Token type: Operator, Value: >
Token type: Preprocessor, Value: define
Token type: Identifier, Value: N
Token type: Integer, Value: 6
Token type: Keyword, Value: int
Token type: Identifier, Value: main
Token type: Separator, Value: (
Token type: Separator, Value: )
Token type: Separator, Value: {
Token type: Comment, Value: Single-Line Comments
Token type: Keyword, Value: int
Token type: Identifier, Value: a
Token type: Operator, Value: =
Token type: Integer, Value: 0
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Keyword, Value: double
Token type: Identifier, Value: b
Token type: Operator, Value: =
Token type: Real, Value: 1.5
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Keyword, Value: long
Token type: Identifier, Value: c
Token type: Operator, Value: =
Token type: Integer, Value: 100L
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Keyword, Value: char
Token type: Identifier, Value: d
Token type: Operator, Value: =
Token type: CharLiteral, Value: d
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Keyword, Value: char
Token type: Identifier, Value: s
Token type: Separator, Value: [
Token type: Integer, Value: 6
Token type: Separator, Value: ]
Token type: Operator, Value: =
Token type: StringLiteral, Value: hello
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Comment, Value:
Multiline comment
Multiline comment
Token type: Keyword, Value: if
Token type: Separator, Value: (
Token type: Identifier, Value: a
Token type: Operator, Value: >
Token type: Integer, Value: 0
Token type: Separator, Value: )
Token type: Separator, Value: {
Token type: Identifier, Value: printf
Token type: Separator, Value: (
Token type: StringLiteral, Value: %s
Token type: Separator, Value: ,
Token type: Identifier, Value: s
Token type: Separator, Value: )
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Separator, Value: }
Token type: Keyword, Value: else
Token type: Separator, Value: {
Token type: Identifier, Value: c
Token type: Operator, Value: =
Token type: Identifier, Value: a
Token type: Operator, Value: +
Token type: Identifier, Value: N
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Separator, Value: }
Token type: Keyword, Value: return
Token type: Integer, Value: 0
Token type: Separator, Value: ;
Token type: Separator, Value: }
注:在mylexer.cpp中,笔者定义了一个名为flushBuffer的Lambda函数,它将buffer中的内容添加到tokens向量,并清空buffer。
下面来详细解释一下这个Lambda函数:
auto flushBuffer:我们使用auto关键字来定义一个名为flushBuffer的变量,它将存储我们的Lambda表达式。auto关键字告诉编译器根据Lambda表达式的类型自动推导flushBuffer的类型。
[&]():这是Lambda表达式的开头部分,方括号[]内表示Lambda函数的捕获说明符。在这个例子中,我们使用&表示按引用捕获所有外部变量。这意味着在Lambda函数内部,我们可以访问并修改外部作用域中的变量,例如buffer和tokens。括号()表示Lambda函数没有参数。
{}:这是Lambda函数的主体,大括号{}内包含了函数的实现。在这个例子中,我们检查buffer是否为空,如果不为空,我们将buffer中的内容添加到tokens向量,并清空buffer。
C++中的lambda表达式是一种创建匿名函数对象的便捷方式。自C++11起,lambda表达式成为了C++的一部分。它们通常用于定义简短的函数,可以直接在需要使用它们的地方定义。Lambda表达式的语法如下:
[capture](parameters) -> return_type { function_body }
- capture:捕获列表,用于捕获来自定义lambda的作用域内的变量。捕获列表可以按值或按引用捕获变量。
- parameters:函数参数列表,与常规函数参数列表类似。
- return_type:返回类型(可选)。如果省略此部分,编译器会自动推导返回类型(通常为void或单个 return 语句的类型)。
- function_body:函数体,包含实现所需功能的代码。
只看上面的概念还是太抽象了,我们举个简单的例子,来直观地感受一下Lambda表达式
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int factor = 3;
// vector数组中每个元素都乘以factor
for_each(numbers.begin(), numbers.end(), [factor](int& number) {
number *= factor;
});
// 打印修改过的number数组
for (const auto& number : numbers) {
cout << number << " ";
}
return 0;
}
输出结果为:
3 6 9 12 15 