二、数据结构
链表
单链表
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/828/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
//head:头节点的指向 e[i]:当前节点i的值 ne[i]:当前节点i的next指针 idx:当前存储的点
int head, e[N], ne[N], idx;
//初始化
void init(){
head = -1;
idx = 1;
}
//将x插入到头节点
void add_head(int x){
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = head;
head = idx;
idx++;
}
//将x插入到下标是k的后面
void add(int k, int x){
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = ne[k];
ne[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
//删除第k+1个节点
void remove(int k){
ne[k] = ne[ne[k]];
}
int main(){
init();
int m;
cin>>m;
char c;
while(m--){
cin>>c;
int k, x;
if(c == 'H'){
cin>>x;
add_head(x);
}else if(c == 'D'){
cin>>k;
//删除头节点
if(k == 0){
head = ne[head];
}else{
remove(k);
}
}else{
cin>>k>>x;
add(k, x);
}
}
for(int i = head; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
cout<<e[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
双链表
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/829/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int e[N], l[N], r[N], idx;
//初始化,0表示左端点,1表示右端点,下标从2开始
void init(){
r[0] = 1;
l[1] = 0;
idx = 2;
}
//在第k个点的右边插入x
void add(int k, int x){
e[idx] = x;
r[idx] = r[k];
l[idx] = k;
l[r[k]] = idx;
r[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
//删除第k个点
void remove(int k){
r[l[k]] = r[k];
l[r[k]] = l[k];
}
int main(){
init();
int m;
cin>>m;
string s;
while(m--){
cin>>s;
int k, x;
if(s == "L"){
cin>>x;
add(0, x);
}else if(s == "R"){
cin>>x;
add(l[1], x);
}else if(s == "D"){
cin>>k;
//下标从2开始
remove(k + 1);
}else if(s == "IL"){
cin>>k>>x;
add(l[k + 1], x);
}else{
cin>>k>>x;
add(k + 1, x);
}
}
for(int i = r[0]; i != 1; i = r[i]){
cout<<e[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}
栈
先进后出
模拟栈
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/830/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int st[N], tt;
//栈顶插入一个元素
void push(int x){
st[++tt] = x;
}
//删除栈顶
void pop(){
tt--;
}
//判断栈是否为空
void empty(){
cout<<(tt > 0 ? "NO" : "YES")<<endl;
}
//查询栈顶元素
void query(){
cout<<st[tt]<<endl;
}
int main(){
int m;
cin>>m;
string s;
while(m--){
int x;
cin>>s;
if(s == "push"){
cin>>x;
push(x);
}else if(s == "pop"){
pop();
}else if(s == "empty"){
empty();
}else{
query();
}
}
return 0;
}
表达式求值
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/3305/
中缀表达式,需要括号;后缀表达式,不需要括号
#include<iostream>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int st1[N], tt1, tt2; //存储数字
char st2[N]; //存储运算符
unordered_map<char, int> mp{{'+', 1}, {'-', 1}, {'*', 2}, {'/', 2}}; //运算符优先级
string s;
void f(){
int x1 = st1[tt1];
tt1--;
int x2 = st1[tt1];
tt1--;
char c = st2[tt2];
tt2--;
int res = 0;
if(c == '-'){
res = x2 - x1;
}else if(c == '+'){
res = x2 + x1;
}else if(c == '*'){
res = x2 * x1;
}else{
res = x2 / x1;
}
st1[++tt1] = res;
}
int main(){
cin>>s;
int n = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
//如果是数字
if(isdigit(s[i])){
int x = 0, j = i;
//计算数字
while(j < n && isdigit(s[j])){
x = x * 10 + (s[j] - '0');
j++;
}
//存储到数字栈中
st1[++tt1] = x;
//因为for循环i还要++
i = j - 1;
}else if(s[i] == '('){
//存储到运算符栈中
st2[++tt2] = s[i];
}else if(s[i] == ')'){
//当栈顶不等于左括号时,就计算括号里的
while(st2[tt2] != '('){
f();
}
//弹出左括号
tt2--;
}else{
//当运算符栈中有元素,当前元素小于等于栈顶优先级,则先计算之前的
while(tt2 > 0 && mp[st2[tt2]] >= mp[s[i]]){
f();
}
//存储到运算符栈中
st2[++tt2] = s[i];
}
}
//防止算了括号里的就结束了
while(tt2 > 0){
f();
}
cout<<st1[tt1];
return 0;
}
队列
先进先出
模拟队列
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/831/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int q[N], hh, tt = -1;
//插入元素x
void push(int x){
q[++tt] = x;
}
//弹出队头
void pop(){
hh++;
}
//判断队列是否为空
void empty(){
cout<<(hh <= tt ? "NO" : "YES")<<endl;
}
//查询队头
void query(){
cout<<q[hh]<<endl;
}
int main(){
int m;
cin>>m;
string s;
while(m--){
cin>>s;
int x;
if(s == "push"){
cin>>x;
push(x);
}else if(s == "pop"){
pop();
}else if(s == "empty"){
empty();
}else{
query();
}
}
return 0;
}
单调栈
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/832/
存储一个单调递增的序列
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int st[N], tt;
int n, x;
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x;
//如果栈顶大于等于当前元素,那就弹出栈顶
while(tt && st[tt] >= x){
tt--;
}
//如果栈顶小于当前元素,那就输出
if(tt){
cout<<st[tt]<<" ";
}else{
cout<<-1<<" ";
}
//入栈
st[++tt] = x;
}
return 0;
}
单调队列
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/156/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int a[N], q[N]; //q数组存储下标
int n, k, x;
int main(){
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>a[i];
}
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x;
//如果队头已经出窗口了,那就出队
if(hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]){
hh++;
}
//如果队尾大于等于当前元素,那就出队
while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]){
tt--;
}
//存储下标,要放在输出前,防止第三个元素还没进队列
q[++tt] = i;
if(i >= k - 1){
cout<<a[q[hh]]<<" ";
}
}
cout<<endl;
hh = 0, tt = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x;
//如果队头已经出窗口了,那就出队
if(hh <= tt && i - k + 1 > q[hh]){
hh++;
}
//如果队尾小于等于当前元素,那就出队
while(hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i]){
tt--;
}
//存储下标,要放在输出前,防止第三个元素还没进队列
q[++tt] = i;
if(i >= k - 1){
cout<<a[q[hh]]<<" ";
}
}
return 0;
}
KMP
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/833/

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int ne[N];
int n, m;
char s[N], p[N];
int main(){
//下标从1开始
cin >> m >> p + 1 >> n >> s + 1;
//求ne数组
for(int i = 2, j = 0; i <= n; i++){
while(j && p[i] != p[j + 1]){
j = ne[j];
}
if(p[i] == p[j + 1]){
j++;
}
ne[i] = j;
}
//s串和p串匹配
for(int i = 1, j = 0; i <= n; i++){
//如果j没有回到起点,且不相等,那就到标记的位置
while(j && s[i] != p[j + 1]){
j = ne[j];
}
//如果匹配,j向后移
if(s[i] == p[j + 1]){
j++;
}
//如果完全匹配p串,那就到下一个位置再尝试
if(j == m){
cout << i - m << " ";
j = ne[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
//下标从0开始
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1000010;
int n, m;
char s[N], p[N];
int ne[N];
int main()
{
cin >> m >> p >> n >> s;
ne[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1, j = -1; i < m; i ++ )
{
while (j >= 0 && p[j + 1] != p[i]) j = ne[j];
if (p[j + 1] == p[i]) j ++ ;
ne[i] = j;
}
for (int i = 0, j = -1; i < n; i ++ )
{
while (j != -1 && s[i] != p[j + 1]) j = ne[j];
if (s[i] == p[j + 1]) j ++ ;
if (j == m - 1)
{
cout << i - j << ' ';
j = ne[j];
}
}
return 0;
}
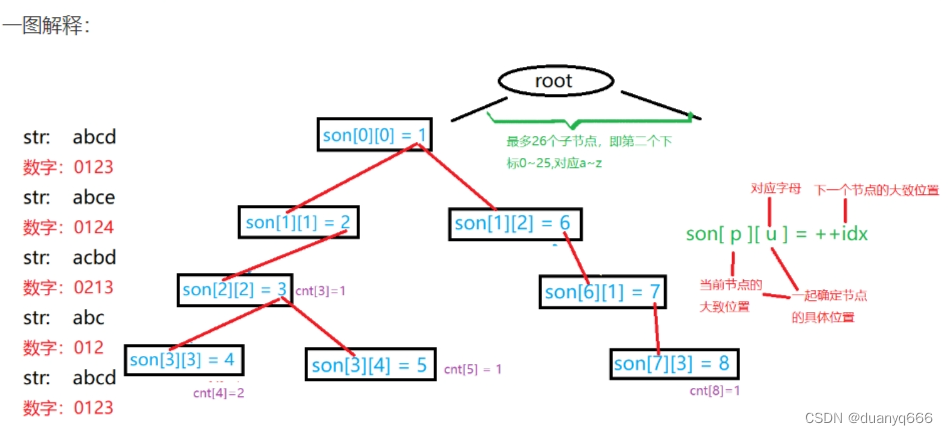
Trie树
高效的存储和查找字符串集合
Trie字符串统计
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/837/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int son[N][26], cnt[N], idx; //0是根节点也是空节点
int n;
//插入字符串
void insert(char str[N]){
int p = 0;
//字符串结尾是'\0'
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i++){
//字母对应成数字
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]){
son[p][u] = ++idx;
}
p = son[p][u];
}
//标记以这个节点结束的字符串有多少个
cnt[p]++;
}
//查询字符串
int query(char str[]){
int p = 0;
for(int i = 0; str[i]; i++){
int u = str[i] - 'a';
if(!son[p][u]){
return 0;
}
p = son[p][u];
}
return cnt[p];
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
char c, s[N];
while(n--){
cin>>c;
if(c == 'I'){
cin>>s;
insert(s);
}else{
cin>>s;
cout<<query(s)<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
最大异或对
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/145/
字典树不单单可以高效存储和查找字符串集合, 还可以存储二进制数字
将每个数以二进制方式存入字典树, 找的时候从最高位去找有无该位的异
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int son[31 * N][2], idx;
int n, x;
int ans, res;
void insert(int x){
int p = 0;
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){
int u = x >> i & 1;
if(!son[p][u]){
son[p][u] = ++idx;
}
p = son[p][u];
}
}
int query(int x){
int p = 0;
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 30; i >= 0; i--){
int u = x >> i & 1;
if(son[p][!u]){
p = son[p][!u];
sum = 2 * sum + !u;
}else{
p = son[p][u];
sum = 2 * sum + u;
}
}
return sum;
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin>>x;
insert(x);
res = query(x);
ans = max(ans, res ^ x);
}
cout<<ans;
return 0;
}
并查集
合并集合
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/838/
开始时每个集合都是一个独立的集合,并且都是等于自己本身下标的数
例如:p[5]=5,p[3]=3;
如果是M操作的话那么就将集合进行合并,合并的操作是:
p[3]=p[5]=5;
所以3的祖宗节点便成为了5
此时以5为祖宗节点的集合为{5,3}
如果要将p[9]=9插入到p[3]当中,应该找到3的祖宗节点,
然后再把p[9]=9插入其中,所以p[9]=find(3);(find()函数用于查找祖宗节点)
也可以是p[find(9)]=find(3),因为9的节点本身就是9
此时以5为祖宗节点的集合为{5,3,9};
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N];
int n, m;
//找到根节点,路径压缩
int find(int x){
if(x != p[x]){
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
//初始化每个节点的根节点
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
p[i] = i;
}
char c;
int a, b;
while(m--){
cin>>c;
if(c == 'M'){
cin>>a>>b;
//将a合并到b的集合中
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}else{
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<(find(a) == find(b) ? "Yes" : "No")<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
连通块中点的数量
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/839/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int p[N], cnt[N];
int n, m;
int find(int x){
if(x != p[x]){
p[x] = find(p[x]);
}
return p[x];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
p[i] = i;
cnt[i] = 1;
}
string s;
while(m--){
cin>>s;
int a, b;
if(s == "C"){
cin>>a>>b;
//如果是一个集合,就不用再加了
if(find(a) == find(b)){
continue;
}
cnt[find(b)] += cnt[find(a)];
p[find(a)] = find(b);
}else if(s == "Q1"){
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<(find(a) == find(b) ? "Yes" : "No")<<endl;
}else{
cin>>a;
cout<<cnt[find(a)]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
食物链
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/description/242/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 5e4 + 10;
int p[N], d[N]; //p存储根节点,d存储到根节点的距离
int n, k;
int res;
int find(int x){
if(x != p[x]){
int t = find(p[x]);
d[x] += d[p[x]];
p[x] = t;
}
return p[x];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>k;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
p[i] = i;
}
int c, x, y;
while(k--){
cin>>c>>x>>y;
if(x > n || y > n){
res++;
}else{
//找到x和y的根节点
int px = find(x), py = find(y);
if(c == 1){
//如果父节点相同,但是距离不同,就是假话
if(px == py && (d[x] - d[y]) % 3){
res++;
}else if(px != py){
//不在一个集合,放在一个集合中
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] - d[x]; //d[px] + d[x]和d[y]同余
}
}else{
if(px == py && (d[x] - d[y] - 1) % 3){
res++;
}else if(px != py){
p[px] = py;
d[px] = d[y] - d[x] + 1;
}
}
}
}
cout<<res;
return 0;
}
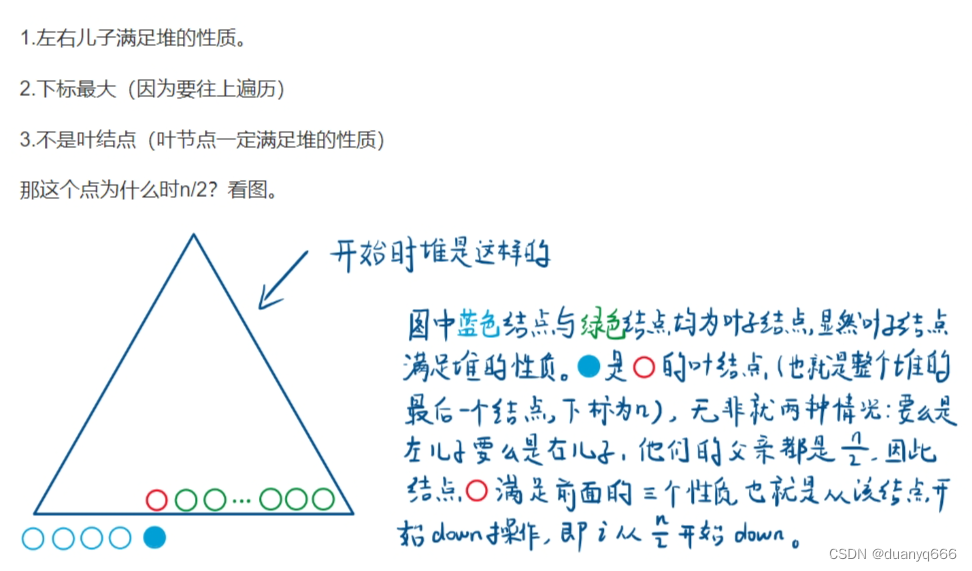
堆
用一个一维数组存储一颗二叉树
1.插入一个元素
2.求集合当中最小值(最大值)
3.删除最小值(最大值)
4.删除任意一个元素
5.修改任意一个元素
小根堆:根节点小于等于左右子节点
堆排序
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/840/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int h[N], cnt;
int n, m;
void down(int u){
int t = u;
//如果根节点大于左右子节点,那就交换下标
if(2 * u <= cnt && h[2 * u] < h[t]){
t = 2 * u;
}
if(2 * u + 1 <= cnt && h[2 * u + 1] < h[t]){
t = 2 * u + 1;
}
//如果已经交换了下标,那就递归子节点,u为根节点,t为子节点
if(h[t] != h[u]){
swap(h[t], h[u]);
down(t);
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m;
cnt = n;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin>>h[i];
}
for(int i = n / 2; i > 0; i--){
down(i);
}
while(m--){
cout<<h[1]<<" ";
h[1] = h[cnt];
cnt--;
down(1);
}
return 0;
}
模拟堆
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/841/
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int h[N], cnt, m; //m:第几个插入的数
int hp[N], ph[N]; //hp[k]:第k个插入的点是几号,ph[j]:j号是第几个插入的点
int n;
void head_swap(int a, int b){
swap(hp[ph[a]], hp[ph[b]]);
swap(ph[a], ph[b]);
swap(h[a], h[b]);
}
void down(int u){
int t = u;
if(2 * u <= cnt && h[2 * u] < h[t]){
t = 2 * u;
}
if(2 * u + 1 <= cnt && h[2 * u + 1] < h[t]){
t = 2 * u + 1;
}
if(h[t] != h[u]){
head_swap(t, u);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int u){
while(u / 2 > 0 && h[u / 2] > h[u]){
head_swap(u / 2, u);
u /= 2;
}
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
string s;
while(n--){
cin>>s;
int k, x;
if(s == "I"){
cin>>x;
m++;
cnt++;
hp[m] = cnt;
ph[cnt] = m;
h[cnt] = x;
up(cnt);
}else if(s == "PM"){
cout<<h[1]<<endl;
}else if(s == "DM"){
head_swap(1, cnt);
cnt--;
down(1);
}else if(s == "D"){
cin>>k;
k = hp[k];
head_swap(k, cnt);
cnt--;
down(k);
up(k);
}else{
cin>>k>>x;
k = hp[k];
h[k] = x;
down(k);
up(k);
}
}
return 0;
}
哈希表
模拟散列表
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/842/
//拉链法
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 3; //大于1e5的第一个质数
int h[N], e[N], ne[N], idx;
int n;
void insert(int x){
//加N防止模出来的数是负数
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
e[idx] = x;
ne[idx] = h[k];
h[k] = idx;
idx++;
}
int find(int x){
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
for(int i = h[k]; i != -1; i = ne[i]){
if(e[i] == x){
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
cin>>n;
memset(h, -1, sizeof(h));
char c;
while(n--){
cin>>c;
int x;
if(c == 'I'){
cin>>x;
insert(x);
}else{
cin>>x;
if(find(x)){
cout<<"Yes"<<endl;
}else{
cout<<"No"<<endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
//开放寻地址法
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 3, null = 0x3f3f3f3f; //第一个大于2e5的质数
int h[N];
int n;
int find(int x){
int k = (x % N + N) % N;
//如果k位置不等于x,那就找下一个数
while(h[k] != x && h[k] != null){
k++;
//到结尾也没找到,就从头开始找
if(k == N){
k = 0;
}
}
return k;
}
int main(){
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof(h));
cin>>n;
char c;
while(n--){
cin>>c;
int x;
if(c == 'I'){
cin>>x;
//找到第一个空位置
int k = find(x);
h[k] = x;
}else{
cin>>x;
//查询是否有x存在
int k = find(x);
cout<<(h[k] == x ? "Yes" : "No")<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
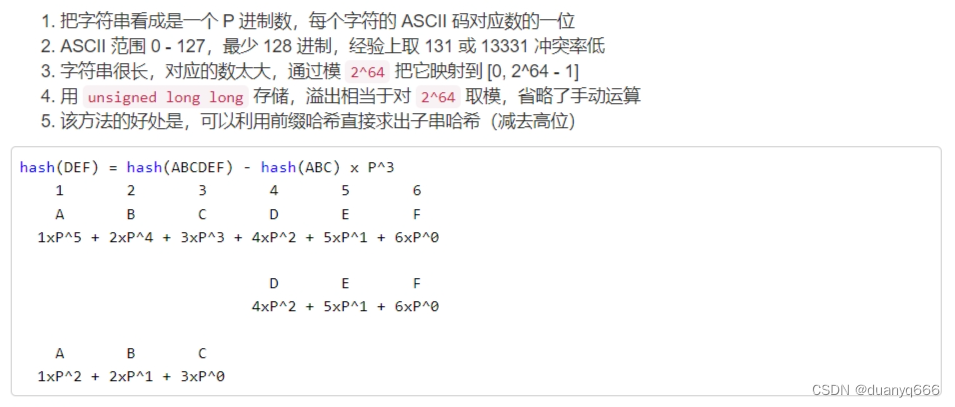
字符串哈希
https://www.acwing.com/problem/content/843/


#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10, p = 131; //p为131或13331,2的64次方,溢出int就等效于取模了
unsigned long long a[N], b[N]; //a存储前缀和,b存储要乘的进位数
char s[N];
int n, m;
//初始化
void init(){
b[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = a[i - 1] * p + s[i];
b[i] = b[i - 1] * p;
}
}
unsigned long long get(int l, int r){
return a[r] - a[l - 1] * b[r - l + 1];
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>m>>s + 1;
init();
int l1, r1, l2, r2;
while(m--){
cin>>l1>>r1>>l2>>r2;
cout<<(get(l1, r1) == get(l2, r2) ? "Yes" : "No")<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
