数据结构的美之链表和树
有种感觉叫做,不同的场景,应用不同的数据结构和算法,可以大大滴优化增删改查以及存储方面等等的性能。笔者这里呢也是在最近复习准备面试的时候,去阅读源码,觉得设计这种数据结构和引用的人真的是非常牛逼,也是心血来潮,于是乎写一篇我对数据结构的理解和对数据结构之间设计的心得。
首先先介绍一下这里登场的数据结构。之后的pk会在另一篇文章中出现。
数据机构
链表系列
LinkedList
这个双端链表相信大家都很熟悉了,前后指针嘛,用这个双端链表可以实现栈,队列包括hashtable部分的数据结构都是可以的。但是这样的链表总会有一个指向前或后的指针,至于怎么实现大家可以看看java/redis中的源码这个比较典型就不再列举代码了。那么这个指针其实是非常占用空间的。比较典型的影响就是在redis中。大家也都知道redis其实以内存为基础的,非常快对吧,因此,内存资源也就是非常宝贵的。
那么如何能去进一步去节省能存呢,能否把这个指针给省略呢?其实是可以的,也就是我们下面讲到的zipList。
ZipList
zipList是一种特殊的双端链表,特殊就特殊在他是没有指向前后的指针的。并且这个压缩链表在内存中还是连续组成的,可以在任意一端进行压入和弹出。并且如果只是修改最前和最后的话,它的实践复杂度还是O(1).嘎嘎快。
在redis里,一个指针占用8个字节,省略两个指针就能省略16个内存了,这样节点一多,节省出来的内存空间也是相当可观的。

这个可以说是zipList的简略组成。
zlbytes达标整个压缩列表占用内存的总字节数,
ztail记录压缩列表表尾节点距离压缩列表的起始地址有多少字节,通过这个偏移量,可以快速确定表尾节点的地址。也正是通过这个设计可以满足任意端压入弹出。
zlen是记录压缩表中的节点数量,如果没有超过这个数量,就可以通过这个字段得出,但是这个字段只有2个字节,也就是说记录的个数是有限的,如果超过了65535的话,就需要遍历整个表了,所以不建议存储太多的数据。
entry就是实际的节点,而zlend就是记录末端。
Entry
除了基本的标识常量以外,redis的entry节点设计的也是非常巧妙地。大家可以注意到这个redis中除了巧妙地数据结构意外,还有就是编码:encoding.这个编码地作用我一上来也是听蒙蔽地啊,但是看细看之后觉得还是很牛逼地。
编码体现地作用可以和操作系统内存管理中地连续内存管理中的块式内存管理作类比。读起来很绕口啊,笔者简单介绍一下,假设无论需要多大地内存,如果把整体划分成固定大小地块,就会造成很大地浪费。打个比方:如果是小学生,中学生,高中生,分别能吃1,2,3块蛋糕。但是一共有12块,我们把他们分成等大小地4块给他们,是不是小学生浪费地就比较严重?因此这里块式管理就采取了一个伙伴系统算法,也就是说是动态给你分配的,它的分配大小是2的n次幂,如果你是1,如果是2就给你2的1次,3就给你2的二次,这样可以相对节省了内存空间。当然也是由一些缺点的,比如要是需要65的内存,就必须分配128的了。当然举这个例子也只是希望大家更加轻松地理解编码的意义。

previous_entry_length:前一节点的长度,占1个或5个字节。 如果前一节点的长度小于254字节,则采用1个字节来保存这个长度值,如果前一节点的长度大于254字节,则采用5个字节来保存这个长度值,第一个字节为0xfe,后四个字节才是真实长度数据,这么看是不是和伙伴算法大同小异。
而encoding就是编码属性,记录content数据类型和长度,占用1/2/5字节。编码可以决定存储内容占有的字节数,也可以按照上面说的伙伴算法理解。
整个节点占有的字节数是确定的。
这也是为什么ziplist称之为压缩表,当然,这种动态变化字节的方式还是有问题的,比如说这个previous_entry_length。
现在,假设我们有N个连续的、长度为250~253字节之间的entry,因此entry的previous_entry_length属性用1个字节即可表示,如果大量的这些结点发生增删操作,就会导致记录节点的length大量变化,导致连锁更新的问题,不过这类问题非常非常小,几乎遇不到。
写到这里笔者突然想到一个锁的设计也和这个zipList有些异曲同工之妙,那就是CLH锁,他可以说是aqs阻塞框架的前辈了。
CLH 锁是一种隐式的链表队列,没有显式的维护前驱或后继指针。因为每个等待获取锁的线程只需要轮询前一个节点的状态就够了,而不需要遍历整个队列。在这种情况下,只需要使用一个局部变量保存前驱节点,而不需要显式的维护前驱或后继指针。
做个小总结
-
压缩列表的可以看做一种连续内存空间的"双向链表"
-
列表的节点之间不是通过指针连接,而是记录上一节点和本节点长度来寻址,内存占用较低
-
如果列表数据过多,导致链表过长,可能影响查询性能因为只能从头到尾或者从尾到头部查询。
-
增或删较大数据时有可能发生连续更新问题,连锁更新可能会导致频繁的内存申请
QuickList
有读者可能好奇,为什么有了zipList还不够,还要再来一种数据结构?因为我们的zipList还是存在几个问题。
1.实际的内存里想要申请一大块连续的内存空间是有一定难度的。在内存占用比较多的情况下申请内存的效率是很低的,我们往往要限制zipList的长度和entry节点的大小才能缓解一些。
2.如果要存储大量数据,zipList存储到上限了怎么办?这个比较好像,数据拆分呗。
3.你说拆分就拆分啊?那微服务拆分了还要远程调用联系呢,你这个怎么联系啊?
问的好,这就引入了我们这个结构,quickList,同样这也是一个双向链表,不过呢,他又指针并且每个节点变成了zipList。
为了避免QuickList中的每个ZipList中entry过多,Redis提供了一个配置项:list-max-ziplist-size来限制。
源码
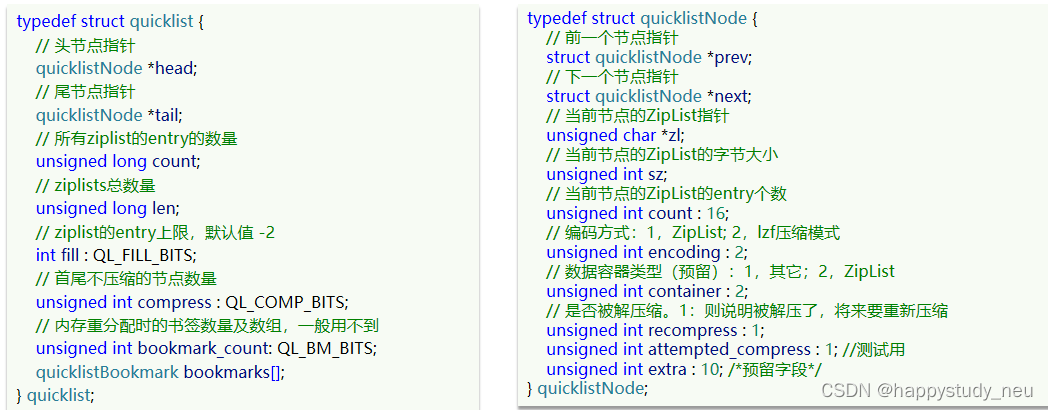
再看这个是不是更清晰一些

wc!这也太复杂了吧,不过我觉得不用记啊,只知道它的有点就好,这样也方便我们设计数据对不对?
小总结一下
-
是一个节点为ZipList的双端链表
-
节点采用ZipList,解决了传统链表的内存占用问题
-
控制了ZipList大小,解决连续内存空间申请效率问题
-
中间节点可以压缩,进一步节省了内存
SkipList
好家伙,qucikList还不够?这又来一个skipList?
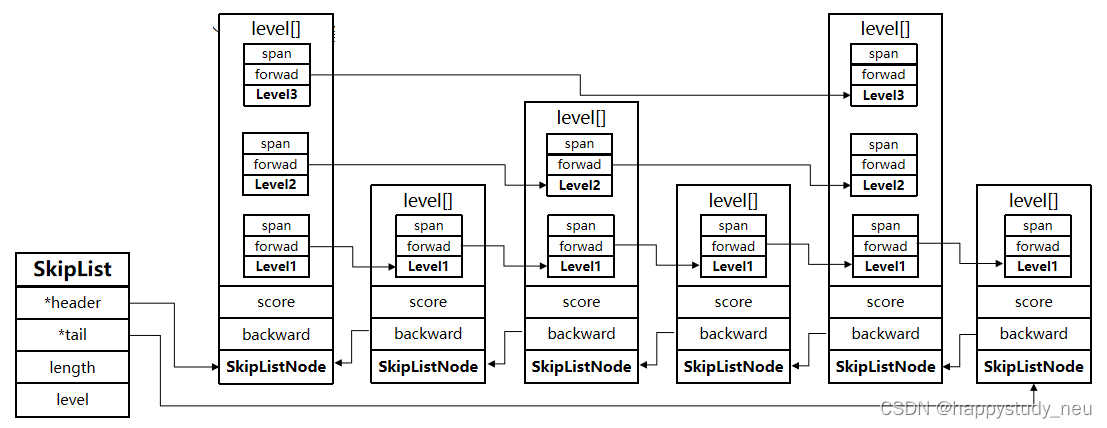
这是什么!跳表,说实话,跳表一上来确实挺蒙蔽的,怎么链表还能跳跃啊?不过看一下图就能理解了,还真能跳,隔山打牛。
相信小伙伴们都听过zset这个数据结构,那么这个它的组成除了hash之外,还有就是这个skipList了。
为了便于理解,我们直接上图:

那么这里呢,也是最好实现设计一下skipList,会更好理解的。
package com.zzm.algorithm.redis;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* @BelongsProject: leet
* @BelongsPackage: com.zzm.algorithm.redis
* @Author: zzm
* @CreateTime: 2024-03-05 16:33
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class SkipList {
static Random r=new Random();
static int randomLevel(int max){
// 50% 25% 12.5%
//return r.nextBoolean()?1:r.nextBoolean()?2:r.nextBoolean()?3:4
int x=1;
while(x<max){
if(r.nextBoolean()){
return x;
}
x++;
}
return x;
}
static class MySkipList{
//next指针的个数
private static final int Max=10; //redis 32,java 64
//跳表的头节点,不回变也不会用来比较
private final Node head=new Node(-1);
static class Node{
int val;//值
Node[] next=new Node[Max];//实际上头节点可以取最大,剩下的节点可以根据实际高度来赋值,这里简化了
public Node(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}
//下楼梯规则
//若next指针为null,或者next指向的节点值>=目标,向下找
//若next指针不为null,且next指向的节点值<目标,向右找
public Node[] find(int val){//返回的是所找节点的前一个节点,层数为0
Node[] path=new Node[Max];//记录经过的路径
Node curr=head;
//需要从高向下找。
for(int level=Max-1;level>=0;level--){
//从上向下找
//拿当前层的next指针,但是向右找并不是找一次,而是一致找到比它大或者等于的才可以停下,所以这里应该用while而不用if
while(curr.next[level]!=null&&curr.next[level].val<val){
curr=curr.next[level];
}
path[level]=curr;
//向下找和向右找的条件互斥,不用再做额外判断了
}
return path;
}
public boolean search(int val){
Node[] path=find(val);
Node node = path[0].next[0];
//要考虑到下一个指针可能为null
return node!=null && node.val==val;
}
public void add(int val){
//1.确定添加位置,把val当作目标查询,精力的路径就可以添加位置
Node[] path = find(val);
//2.创建新的节点随机高度
Node node = new Node(val);//新节点
//随机高度返回,不希望节点的高度一致。希望矮的节点概率更高些,高的节点概率更小些
int level = randomLevel(Max);
//3.修改路径节点的next指针,以及新节点的next指针
//新节点的next指针有多高,就修改
//只负责修改自己高度的指针就可以
for(int i=0;i<level;i++){
//path[i].next[i]同层的next指针
node.next[i]=path[i].next[i];
path[i].next[i]=node;
}
}
//删除的逻辑
public boolean erase(int val){
Node[] path=find(val);
Node node = path[0].next[0];
if(node==null||node.val!=val){
return false;
}
//我们只需要循环到节点的高度就可以了,但是节点的高度我们并没有设置成属性,那么就直接放最大了,可以优化
for(int i=0;i<Max;i++){
//路径节点的next指针指向的不是被删除节点的时候就break
if(path[i].next[i]!=node){
break;
}
path[i].next[i]=node.next[i];
}
return true;
}
}
}
我们可以发现,这个跳表的元素是可以按照升序序列插入的,也就是可以排序,并且指针的跨度不同。这个跳表本身也是一个双向链表。
这个level的高度是不一样的,这个是随机的多层指针,这也可以提高链表查找时候的高效率。
树系列
BSTree
这个呢就是二叉搜索树,二叉搜索树的特点就是中序遍历下来的结果发现是升序排列的,这个看到这里的小伙伴相信对此并不陌生,我也就不再过多赘述。不过这个搜索树有个很明显的缺点就是在某种极端的情况下,他会变成一个链表。这样它的查询效率不就由O(logn)变成O(n)了么。
AVLTree
由于BSTree的不平衡性,因此有大神就发明了让BSTree平衡的算法,但是这个AVL树是绝对平衡的,平衡条件就是树左右子树高度绝对值不能超过1。
代码放这了,可以看到啊,这添加删除调整的代码也太费劲了,酷酷旋转啊。
package com.zzm.structure.binarytree;
/**
* @BelongsProject: leet
* @BelongsPackage: com.zzm.structure.binarytree
* @Author: zzm
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-26 20:39
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
//AVL树
/*
二叉搜索树在插入和删除的时候,节点可能失衡
如果在插入和删除的时候通过旋转,始终让二叉搜索树保持平衡,撑为自平衡的二叉搜索树
AVL是自平衡二叉搜索树的实现之一
**/
public class AVLTree {
static class AVLNode{
int key;
Object value;
AVLNode left;
AVLNode right;
int height=1;//高度
public AVLNode(int key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public AVLNode(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public AVLNode(int key, Object value, AVLNode left, AVLNode right, int height) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
this.height = height;
}
}
//防止出现null的问题
private int height(AVLNode node){
return node==null?0:node.height;
}
//更新节点高度,(新增,删除,旋转)
private void updateHeight(AVLNode node){
//当前节点的高度等于左右子树的最大高度+1
node.height=Integer.max(height(node.left),height(node.right))+1;
}
//平衡因子 balance factor = 一个节点的 左子树高度-右子树高度 差值没有超过一就是平衡的
private int bf(AVLNode node){
// bf = 0,1,-1 时,表示左右平衡
// bf > 1 时,表示左边太高
// bf < -1 时,表示右边太高
return height(node.left)-height(node.right);
}
//右旋, 传入要旋转的节点,返回旋转后的新的根节点
private AVLNode rightRotate(AVLNode red){
//不用考虑yellow为null,左边比右边高了,左边肯定不能为空
//1,2顺序不能换
AVLNode yellow = red.left; //1
//因为右孩子比父亲节点大,需要需要考虑换爹
AVLNode green = yellow.right;//2
//上位
yellow.right=red;
//换爹
red.left=green;
//更新高度,不能调换顺序,因为父节点的高度是依赖于子节点的高度的
updateHeight(red);
updateHeight(yellow);
return yellow;
}
//左旋,传入的是要旋转的节点,返回旋转后的新的根节点
private AVLNode leftRotate(AVLNode red){
AVLNode yellow=red.right;
AVLNode green=yellow.left;
yellow.left=red;
red.right=green;
updateHeight(red);
updateHeight(yellow);
return yellow;
}
//左右旋,先左旋左子树,再右旋根节点
private AVLNode leftRightRotate(AVLNode node){
node.left=leftRotate(node.left);
return rightRotate(node);
}
//右左旋转
private AVLNode rightLeftRotate(AVLNode node){
node.right=rightRotate(node.right);
return leftRotate(node);
}
//检查节点是否失衡,重新平衡树
private AVLNode balance(AVLNode node){
if(node==null){
return null;
}
int bf = bf(node);
if(bf>1 && bf(node.left)>=0){ //LL,或者
return rightRotate(node);
}else if(bf>1 && bf(node.left)<0){ //LR
return leftRightRotate(node);
} else if (bf<-1 && bf(node.right)>0) { //RL
return rightLeftRotate(node);
} else if (bf<-1 && bf(node.right)<=0) { //RR
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
AVLNode root;
public void put(int key,Object value){
root=doPut(root,key,value);
}
public AVLNode doPut(AVLNode node,int key,Object value){
//1.找到空位,创建新节点
if(node==null){
return new AVLNode(key,value);
}
//2.key在树中已经存在了,更新
if(key==node.key){
node.value=value;
return node;
}
//3.继续查找
if(key<node.key){
node.left=doPut(node.left,key,value);
}else{
node.right=doPut(node.right,key,value);
}
updateHeight(node);//递归回去的过程中一点一点更新的
//返回平衡后的节点
return balance(node);
}
public void remove(int key){
root=doRemove(root,key);
}
private AVLNode doRemove(AVLNode node,int key){
//1.如果node为空直接返回
if(node==null){
return null;
}
//2.没有找到key继续递归
if(key<node.key){
node.left=doRemove(node.left,key);
}else if(key>node.key){
node.right=doRemove(node.right,key);
}else{
//3.找到key,1).没有孩子 2)只有一个孩子 3)有两个孩子
if(node.left==null&&node.right==null) {
//没有孩子,自己也没了,返回null
return null;
}else if(node.left==null) {
node=node.right;
}else if(node.right==null) {
node=node.left;
}else{
//先找到后继节点
AVLNode s=node.right;
while(s.left!=null){
s=s.left;
}
//处理后继节点的后事
s.right=doRemove(node.right,s.key);
s.left=node.left;
node=s;
}
}
//4.更新高度
updateHeight(node);
//5.平衡
return balance(node);
}
}
不过添加删除费劲的好处就是你查询效率保障了呀,O(logn),牛~B。
RedBlackTree
红黑树也是一种自平衡二叉查找树,它的查询性能略微逊色于 AVL 树,但插入和删除效率更高。红黑树的插入、删除和查询的时间复杂度和跳表一样都是 O(log n)。
定义这里就不介绍了,直接上代码
package com.zzm.structure.binarytree;
import static com.zzm.structure.binarytree.RedBlackTree.Color.BLACK;
import static com.zzm.structure.binarytree.RedBlackTree.Color.RED;
/**
* @BelongsProject: leet
* @BelongsPackage: com.zzm.structure.binarytree
* @Author: zzm
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-27 14:13
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
//红黑树
public class RedBlackTree {
enum Color {
RED, BLACK;
}
Node root;
static class Node {
int key;
Object value;
Node left;
Node right;
Node parent; // 父节点
Color color = RED; // 颜色
public Node(int key, Object value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public Node(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
public Node(int key, Color color) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
}
public Node(int key, Color color, Node left, Node right) {
this.key = key;
this.color = color;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
if (left != null) {
left.parent = this;
}
if (right != null) {
right.parent = this;
}
}
// 是否是左孩子
boolean isLeftChild() {
return parent != null && parent.left == this;
}
// 叔叔
Node uncle() {
if (parent == null || parent.parent == null) {
return null;
}
if (parent.isLeftChild()) {
return parent.parent.right;
} else {
return parent.parent.left;
}
}
// 兄弟
Node sibling() {
if (parent == null) {
return null;
}
if (this.isLeftChild()) {
return parent.right;
} else {
return parent.left;
}
}
}
// 判断红
boolean isRed(Node node) {
return node != null && node.color == RED;
}
// 判断黑
boolean isBlack(Node node) {
// return !isRed(node);
return node == null || node.color == BLACK;
}
// 右旋 1. parent 的处理
// 2. 在旋转方法内建立旋转后新根的父子关系
private void rightRotate(Node pink) {
//拿到更上层的节点
Node parent = pink.parent;
Node yellow = pink.left;
Node green = yellow.right;
if (green != null) {
green.parent = pink;
}
yellow.right = pink;
yellow.parent = parent; //pink.parent
pink.left = green;
pink.parent = yellow;
if (parent == null) {
root = yellow;
} else if (parent.left == pink) {
//可能是左子树
parent.left = yellow;
} else {
//但也可能是右子树
parent.right = yellow;
}
}
// 左旋
private void leftRotate(Node pink) {
Node parent = pink.parent;
Node yellow = pink.right;
Node green = yellow.left;
if (green != null) {
green.parent = pink;
}
yellow.left = pink;
yellow.parent = parent;
pink.right = green;
pink.parent = yellow;
if (parent == null) {
root = yellow;
} else if (parent.left == pink) {
parent.left = yellow;
} else {
parent.right = yellow;
}
}
/**
* 新增或更新
* <br>
* 正常增、遇到红红不平衡进行调整
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
public void put(int key, Object value) {
Node p = root;
Node parent = null;
while (p != null) {
parent = p;
if (key < p.key) {
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
p = p.right;
} else {
p.value = value; // 更新
return;
}
}
Node inserted = new Node(key, value);
if (parent == null) {
root = inserted;
} else if (key < parent.key) {
parent.left = inserted;
inserted.parent = parent;
} else {
parent.right = inserted;
inserted.parent = parent;
}
fixRedRed(inserted);
}
//调整平衡,防止两个红色节点相邻
void fixRedRed(Node x) {
// case 1 插入节点是根节点,变黑即可
if (x == root) {
x.color = BLACK;
return;
}
// case 2 插入节点父亲是黑色,无需调整
if (isBlack(x.parent)) {
return;
}
/* case 3 当红红相邻,叔叔为红时
需要将父亲、叔叔变黑、祖父变红,然后对祖父做递归处理
*/
//拿到父亲
Node parent = x.parent;
//拿到叔叔
Node uncle = x.uncle();
//拿到祖父
Node grandparent = parent.parent;
if (isRed(uncle)) {
parent.color = BLACK;
uncle.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
//递归调用
fixRedRed(grandparent);
return;
}
// case 4 当红红相邻,叔叔为黑时
//如果变色不能平衡,那么就需要变色配合旋转
if (parent.isLeftChild() && x.isLeftChild()) { // LL
parent.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
rightRotate(grandparent);
} else if (parent.isLeftChild()) { // LR
leftRotate(parent);
x.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
rightRotate(grandparent);
} else if (!x.isLeftChild()) { // RR
parent.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
leftRotate(grandparent);
} else { // RL
rightRotate(parent);
x.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
leftRotate(grandparent);
}
}
/**
* 删除
* <br>
* 正常删、会用到李代桃僵技巧、遇到黑黑不平衡进行调整
*
* @param key 键
*/
public void remove(int key) {
Node deleted = find(key);
if (deleted == null) {
return;
}
doRemove(deleted);
}
public boolean contains(int key) {
return find(key) != null;
}
// 查找要删除节点
private Node find(int key) {
Node p = root;
while (p != null) {
if (key < p.key) {
p = p.left;
} else if (p.key < key) {
p = p.right;
} else {
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
// 查找剩余节点
private Node findReplaced(Node deleted) {
if (deleted.left == null && deleted.right == null) {
return null;
}
if (deleted.left == null) {
return deleted.right;
}
if (deleted.right == null) {
return deleted.left;
}
Node s = deleted.right;
while (s.left != null) {
s = s.left;
}
return s;
}
// 处理双黑 (case3、case4、case5)
private void fixDoubleBlack(Node x) {
if (x == root) {
return;
}
Node parent = x.parent;
Node sibling = x.sibling();
// case 3 兄弟节点是红色
if (isRed(sibling)) {
if (x.isLeftChild()) {
leftRotate(parent);
} else {
rightRotate(parent);
}
parent.color = RED;
sibling.color = BLACK;
fixDoubleBlack(x);
return;
}
//防止空指针
if (sibling != null) {
// case 4 兄弟是黑色, 两个侄子也是黑色
if (isBlack(sibling.left) && isBlack(sibling.right)) {
sibling.color = RED;
if (isRed(parent)) {
parent.color = BLACK;
} else {
fixDoubleBlack(parent);
}
}
// case 5 兄弟是黑色, 侄子有红色
else {
// LL
if (sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.left)) {
rightRotate(parent);
sibling.left.color = BLACK;
sibling.color = parent.color;
}
// LR
else if (sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.right)) {
sibling.right.color = parent.color;
leftRotate(sibling);
rightRotate(parent);
}
// RL
else if (!sibling.isLeftChild() && isRed(sibling.left)) {
sibling.left.color = parent.color;
rightRotate(sibling);
leftRotate(parent);
}
// RR
else {
leftRotate(parent);
sibling.right.color = BLACK;
sibling.color = parent.color;
}
//都需要把父亲节点的颜色变为黑色
parent.color = BLACK;
}
} else {
// @TODO 实际也不会出现,触发双黑后,兄弟节点不会为 null
fixDoubleBlack(parent);
}
}
//执行真正的删除
private void doRemove(Node deleted) {
Node replaced = findReplaced(deleted);
Node parent = deleted.parent;
// 没有孩子
if (replaced == null) {
// case 1 删除的是根节点
if (deleted == root) {
root = null;
} else {
if (isBlack(deleted)) {
// 双黑调整
fixDoubleBlack(deleted);
} else {
// 红色叶子, 无需任何处理
}
if (deleted.isLeftChild()) {
parent.left = null;
} else {
parent.right = null;
}
deleted.parent = null;
}
return;
}
// 有一个孩子
if (deleted.left == null || deleted.right == null) {
// case 1 删除的是根节点
if (deleted == root) {
root.key = replaced.key;
root.value = replaced.value;
//清空根节点的孩子
root.left = root.right = null;
} else {
if (deleted.isLeftChild()) {
parent.left = replaced;
} else {
parent.right = replaced;
}
replaced.parent = parent;
//修改当前删除的节点,便利于垃圾回收
deleted.left = deleted.right = deleted.parent = null;
if (isBlack(deleted) && isBlack(replaced)) {
// @TODO 实际不会有这种情况 因为只有一个孩子时 被删除节点是黑色 那么剩余节点只能是红色不会触发双黑
fixDoubleBlack(replaced);
} else {
// case 2 删除是黑,剩下是红
replaced.color = BLACK;
}
}
return;
}
// case 0 有两个孩子 => 有一个孩子 或 没有孩子
//先保存一下要删除的key和value
int t = deleted.key;
deleted.key = replaced.key;
replaced.key = t;
Object v = deleted.value;
deleted.value = replaced.value;
replaced.value = v;
doRemove(replaced);
}
}
红黑树相对于AVL树在添加和删除操作中的调整平衡效率较高,主要是因为红黑树的平衡条件相对宽松,从而减少了调整平衡所需的旋转次数。然而,AVL树由于其严格的平衡条件,在查找操作上可能会比红黑树更加高效,特别是在那些查找操作远远多于插入和删除操作的场景中。
实现起来是真的费劲啊
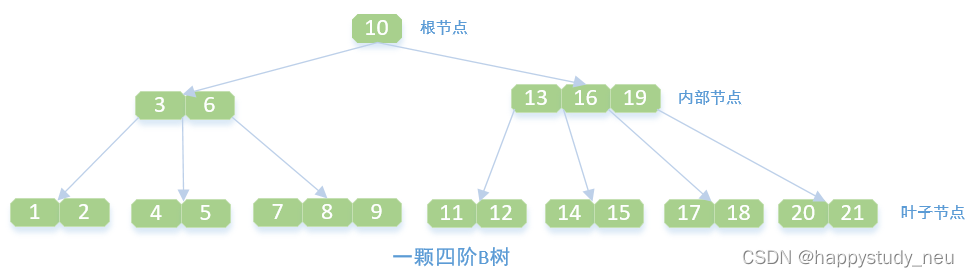
BTree
找了个图片,希望读者知道大概长什么样子就好了。
实现这里也有,不过我觉得理解就好
package com.zzm.structure.binarytree;
import com.sun.source.tree.Tree;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @BelongsProject: leet
* @BelongsPackage: com.zzm.structure.binarytree
* @Author: zzm
* @CreateTime: 2024-01-28 11:54
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
//B树
public class BTree {
Node root;
int t;//树中节点的最小度数
final int MIN_KEY_NUMBER;//最小关键字个数
final int MAX_KEY_NUMBER;//最大关键字个数
static class Node {
boolean leaf = true;//代表节点是否是叶子节点
int keyNumber;//有效关键字数目
int t;//最小度数(这个节点最少有几个孩子)
int[] keys;//关键字
Node[] children;//孩子
public Node(int t) {
this.t = t;//最小孩子数>=2
this.keys = new int[2 * t - 1];//比孩子数少一个
this.children = new Node[2 * t];//最小度数*2(左边+右边)就是可能拥有最多的孩子数
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return Arrays.toString(Arrays.copyOfRange(keys, 0, keyNumber));
}
//多路查找
Node get(int key){
int i=0;
while(i<keyNumber){
if(keys[i]==key){
return this;
}
if(keys[i]>key){
//当前循环没找到
break;
}
i++;
}
//执行到此时,keys[i]>key 或者 i=keyNumber,超出索引范围
if(leaf){
return null;
}
//退出循环时i的值就是要去第i个孩子进行查找,递归调用就可以了
return children[i].get(key);
}
//向keys指定索引处插入key
//[1,3,5]
void insertKey(int key, int index) {
//五个参数:原数组,原数组的起始索引,目标数组,目标数组的起始索引,要复制的长度
System.arraycopy(keys, index, keys, index + 1, keyNumber - index);
keys[index] = key;
keyNumber++;
}
//向children 指定索引处插入child
void insertChild(Node child, int index) {
System.arraycopy(children, index, children, index + 1, keyNumber - index);
children[index] = child;
}
int removeKey(int index) {
int t = keys[index];
System.arraycopy(keys, index + 1, keys, index, --keyNumber - index);
return t;
}
int removeLeftmostKey() {
return removeKey(0);
}
int removeRightmostKey() {
return removeKey(keyNumber - 1);
}
Node removeChild(int index) {
Node t = children[index];
System.arraycopy(children, index + 1, children, index, keyNumber - index);
children[keyNumber] = null;
return t;
}
Node removeLeftmostChild() {
return removeChild(0);
}
Node removeRightmostChild() {
return removeChild(keyNumber);
}
void moveToLeft(Node left) {
int start = left.keyNumber;
if (!leaf) {
for (int i = 0; i <= keyNumber; i++) {
left.children[start + i] = children[i];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < keyNumber; i++) {
left.keys[left.keyNumber++] = keys[i];
}
}
Node leftSibling(int index) {
return index > 0 ? children[index - 1] : null;
}
Node rightSibling(int index) {
return index == keyNumber ? null : children[index + 1];
}
}
//根节点
//默认无参构造
public BTree() {
this(2);
}
public BTree(int t) {
this.t = t;
MIN_KEY_NUMBER=t-1;
MAX_KEY_NUMBER=2*t-1;
root =new Node(t);
}
//1.判断一个key在树中是否存在
public boolean contains(int key){
return root.get(key)!=null;
}
//2.新增
public void put(int key){
doPut(root,key,null,0);
}
private void doPut(Node node,int key,Node parent,int index){
int i=0;
while(i<node.keyNumber){
if(node.keys[i]==key){
return;//更新的逻辑
}
if(node.keys[i]>key){
//当前循环没找到
break;
}
i++;//i的值就是找到了插入位置i
}
//是叶子节点就可以直接插入
if(node.leaf){
node.insertKey(key,i);
//上限
}else{
//在第i个孩子节点完成插入
doPut(node.children[i],key,node,i);
//上限
}
if(node.keyNumber==MAX_KEY_NUMBER){
split(node,parent,index);
}
}
private void split(Node left,Node parent,int index){
if(parent==null){//分裂的是根节点,创建新的节点,把根节点变成新的节点的孩子
Node newRoot=new Node(t);
newRoot.leaf=false;
newRoot.insertChild(left,0);
this.root=newRoot;
parent=newRoot;//创建新的根节点之后,继续走下面代码进行分裂逻辑
}
//1.创建right节点,把left中的t之后的key和children拷贝到right
Node right=new Node(t);//整个树中所有的t值是一样的
right.leaf=left.leaf;
System.arraycopy(left.keys,t,right.keys,0,t-1);
if(!left.leaf){
System.arraycopy(left.children,t,right.children,0,t);//孩子拷贝比key多一个
}
right.keyNumber=t-1;
//2.中间的key(t-1)提升到父节点
int mid=left.keys[t-1];
parent.insertKey(mid,index);
//3.把right设置为parent的孩子
parent.insertChild(right,index+1);
}
//3.删除
public void remove(int key){
doRemove(null,root,0,key);
}
private void doRemove(Node parent,Node node,int index,int key){
int i=0;
while(i<node.keyNumber){
if(node.keys[i]>=key){
break;
}
i++;//两层含义:1)可能找到了:代表待删除key的索引。2)没找到:代表到第i个孩子继续查找
}
//区分两层含义,就看i是否在有效范围内
//抽取方法快捷键:ctrl+alt+m
if(node.leaf){//是不是叶子
if(!found(node, key, i)){//case 1 当前节点是叶子节点,没找到
return ;//不再向下走
}else{//case 2 当前节点是叶子节点,找到了
node.removeKey(i);//删除指定索引处的key
}
}else{
if(!found(node, key, i)){//case 3 当前节点是非叶子节点,没找到
//继续到第i个孩子里面进行查找
doRemove(node,node.children[i],i,key);
}else{//case 4 当前节点是非叶子节点,找到了
//1)找到后继的key
Node s=node.children[i+1];//到比key值大的孩子节点机型查找
while(!s.leaf){
s=s.children[0];//不是叶子节点就一直向左走
}
int skey=s.keys[0];//找到了最小的key
//2)调换待删除的key
node.keys[i]=skey;
//3)删除后继key
doRemove(node,node.children[i+1],i+1,skey);
}
}
if(node.keyNumber<MIN_KEY_NUMBER){
//调整平衡 case 5 case6
balance(parent, node, index);
}
}
private void balance(Node parent,Node x,int i){
//case6 根节点
if(x==root){
if(root.keyNumber==0 && root.children[0]!=null){
root=root.children[0];//根节点的孩子节点变成新的根节点
}
return;
}
Node left=parent.leftSibling(i);//左兄弟
Node right=parent.rightSibling(i);//右兄弟
if(left!=null&&left.keyNumber>MIN_KEY_NUMBER){
//case5-1:左边富裕,右旋
//a) 父节点的key旋转下来
x.insertKey(parent.keys[i-1],0);
if(!left.leaf){
//b)处理一下左边兄弟的最右边的孩子,转移到自己的最左侧
x.insertChild(left.removeRightmostChild(),0);
}
//c)将兄弟节点的key移到父节点
parent.keys[i-1]=left.removeRightmostKey();
return;
}
if(right!=null&&right.keyNumber>MIN_KEY_NUMBER){
//case5-2:右边富裕,左旋
//a) 父节点中的后继的key旋转下来
x.insertKey(parent.keys[i],x.keyNumber);
//b)right最小的孩子换爹
if(!right.leaf){
//处理一下右边兄弟的最左边的孩子,转移到自己的最右侧
x.insertChild(right.removeLeftmostChild(),x.keyNumber);
}
//c)将兄弟节点的最小的key移到父节点
parent.keys[i]=right.removeLeftmostKey();
return;
}
//case5-3:左右都穷,合并
//有左兄弟,就和左兄弟合并
if(left!=null){
//把被调整节点从父节点移除
parent.removeChild(i);
//从父节点移动一个索引为i-1的key到左兄弟
left.insertKey(parent.removeKey(i-1),left.keyNumber);
//把自己的key和children都拷贝到左兄弟
x.moveToLeft(left);
}else{
//向自己合并
parent.removeChild(i+1);
x.insertKey(parent.removeKey(i),x.keyNumber);
right.moveToLeft(x);
}
}
private static boolean found(Node node, int key, int i) {
return i < node.keyNumber && node.keys[i] == key;
}
}
B+Tree
有了对B树的认识,我们对B+树只需要知道长什么样子就可以了,具体的细节实现可以去这个博客里面查找。

B树和B+树详解-CSDN博客
LSMTree
LSM 树的全称是 Log-structured merge-tree,它也被mongodb的wireTiger引擎作为底层的索引数据结构之一。
LSM 树是一个基于磁盘的数据结构,它设计的主要目的是为长期需要高频率写入操作的文件提供低成本的索引机制。无论是 B 树还是 B+ 树,向这些数据结构组成的索引文件中写入记录都需要执行的磁盘随机写,LSM 树的优化逻辑就是牺牲部分的读性能,将随机写转换成顺序写以优化数据的写入。
这里也不具体介绍LSMTree的实现,只需要记住它的特点就好。
