android so的加载流程(Android 13~14)
序言
分析环境: Android 13~14
其实大佬 << 安卓so加载流程源码分析 >> 已经写得非常好了,我就没必要再写了
建议读者看看这篇文字,比较新,质量很高<< 安卓so加载流程源码分析 >>
为什么要分析 android so的加载流程 ???
我想明白
- so是怎么打开的,
- so的DT_INIT何时执行
- so的DT_INIT_ARRAY何时执行
- JNI_LOAD何时执行
整体的加载流程是怎么样的
通过阅读源码以及文章, 作图如下
看上去还是比较清晰的
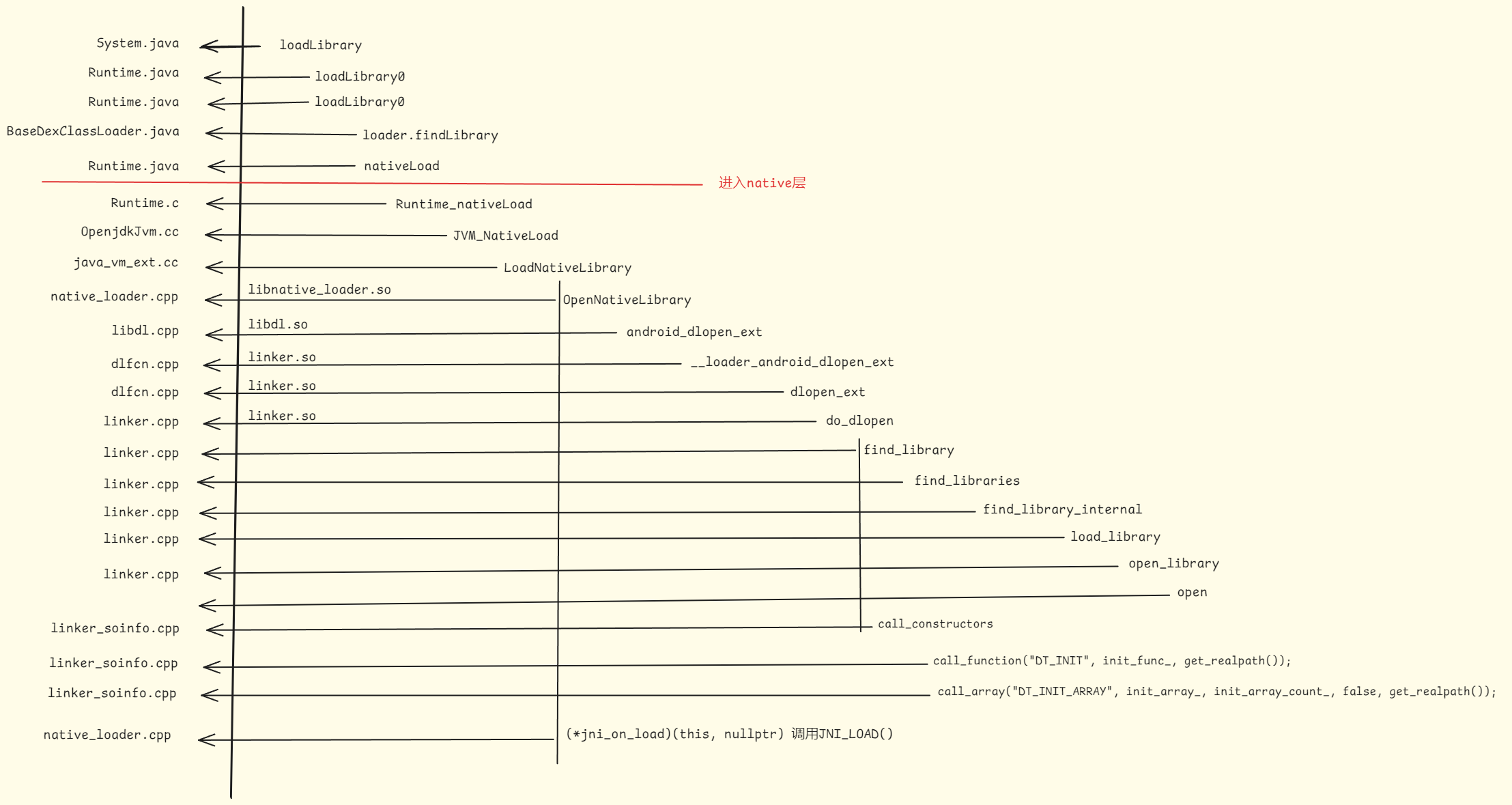
1), so怎么被打开的? 用dlopen吗
从图中我们可以看出
so是在linker.cpp中,通过函数open_libiary调用open函数打开的so文件
于是我们知道so是open打开的,不是dlopen
2), init_array, init 何时被执行的?
从图中可以看出,
在完成so的加载后,do_dlopen函数会调用 soinfo *si->call_constructors() 来实现构造函数
call_constructors中又会执行下面的代码来执行DT_INIT和DT_INIT_ARRAY
// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.
call_function("DT_INIT", init_func_, get_realpath());
call_array("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array_, init_array_count_, false, get_realpath());
3), JNI_LOAD何时被执行的
从图中可以看出 在so加载完毕后,
在java_vm_ext.cc中, 执行了(*jni_on_load), 从而调用了JNI_LOAD
int version = (*jni_on_load)(this, nullptr);
so的路径从哪里查找?
这里只分析一部分, 貌似还有什么mLibPaths可以找so的路径,没去分析…懒了
在 Runtime.java中,有这样的代码
// Runtime.java
private synchronized void loadLibrary0(ClassLoader loader, Class<?> callerClass, String libname)
{
if (libname.indexOf((int)File.separatorChar) != -1) //不能存在路径的`/`,传递进来的只能是xxx
{
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError( "Directory separator should not appear in library name: " + libname);
}
String libraryName = libname;
if (loader != null && !(loader instanceof BootClassLoader))
{
// BootClassLoader 继承了 ClassLoader的 findLibrary(), 但并没有去重写它. ClassLoader.findLibrary()一直返回null
String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName);
if (filename == null && (loader.getClass() == PathClassLoader.class || loader.getClass() == DelegateLastClassLoader.class))
{
filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);//xxx - > libxxx.so
}
if (filename == null)
{
//看上去mapLibraryName不仅仅是字符串的替换
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(loader + " couldn't find \"" + System.mapLibraryName(libraryName) + "\"");
}
String error = nativeLoad(filename, loader);
if (error != null)
{
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
return;
}
// 直接使用mLibPaths的情况, 没有loader
// We know some apps use mLibPaths directly, potentially assuming it's not null.
// Initialize it here to make sure apps see a non-null value. getLibPaths();
String filename = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
String error = nativeLoad(filename, loader, callerClass);
if (error != null)
{
throw new UnsatisfiedLinkError(error);
}
}
其中调用String filename = loader.findLibrary(libraryName); 来获取so_path
PathClassLoader 和 DexClassLoader 都没有实现 findLibrary
BaseDexClassLoader 重写了 ClassLoader.findLibrary
//BaseDexClassLoader.java
@Override
public String findLibrary(String name)
{
return pathList.findLibrary(name); //可以看到它调用了PathList.findLibrary
}
进入DexPathList.java
//DexPathList.java
public String findLibrary(String libraryName)
{
String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
//首先调用System.mapLibraryName拿到so的前缀和后缀名,如libname为hello,那么经过此函数转换后变成了libhello.so
for (NativeLibraryElement element : this.nativeLibraryPathElements) //NativeLibraryElement[] nativeLibraryPathElements
{
String path = element.findNativeLibrary(fileName);
if (path != null)
{
return path;
}
}
return null;
}
关于System.mapLibraryName(libraryName); 的作用
假如so_name = “xxx”, 通过调用mapLibraryName
so_filename = “libxxx.so”
在findLibrary中, 我们会发现这么一个变量 this.nativeLibraryPathElements
this.nativeLibraryPathElements是什么???
这得追溯到DexPathList的构造函数
//DexPathList.java 构造函数中完成..
//记录所有的dexFile文件
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory, suppressedExceptions, definingContext, isTrusted);
// Native libraries may exist in both the system and
// application library paths, and we use this search order:
//
// 1. This class loader's library path for application libraries (librarySearchPath):
// 1.1. Native library directories
// 1.2. Path to libraries in apk-files
// 2. The VM's library path from the system property for system libraries
// also known as java.library.path
//
// This order was reversed prior to Gingerbread; see http://b/2933456.
//app目录的native库
this.nativeLibraryDirectories = splitPaths(librarySearchPath, false); //librarySearchPath是构造函数的参数,从ClassLoader那边传递过来
//系统目录的native库
this.systemNativeLibraryDirectories = splitPaths(System.getProperty("java.library.path"), true);
//记录所有的Native动态库
this.nativeLibraryPathElements = makePathElements(getAllNativeLibraryDirectories());//getAllNativeLibraryDirectories拿到所有的NativeLibrary
于是这里就牵扯出一个问题,so的搜索路径
于是路径有
- 系统会优先查找自己目录的libraries
- 然后再找APK 压缩文件中
- 最后才会查找Android 虚拟机环境变量目录中的libraries
我自己尝试去找一个 classloader 看看
this.nativeLibraryDirectories
/data/app/com.example.myapplication2-YBD_9i86XuDyqMpoEGKHQQ==/lib/arm64
/data/app/com.example.myapplication2-YBD_9i86XuDyqMpoEGKHQQ==/base.apk!/lib/arm64-v8a
this.systemNativeLibraryDirectories
/system/lib64
/system/product/lib64
然后查看 this.nativeLibraryPathElements 是一个什么鬼
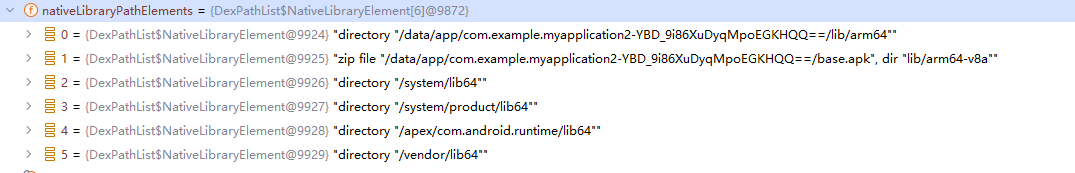
发现是 this.nativeLibraryDirectories + this.systemNativeLibraryDirectories + VM's library 的 NativeLibraryPathElement 对象
this.nativeLibraryPathElements包含了所有要搜索的路径
然后我们抽取一个 DexPathList$NativeLibraryPathElement 对象查看一下
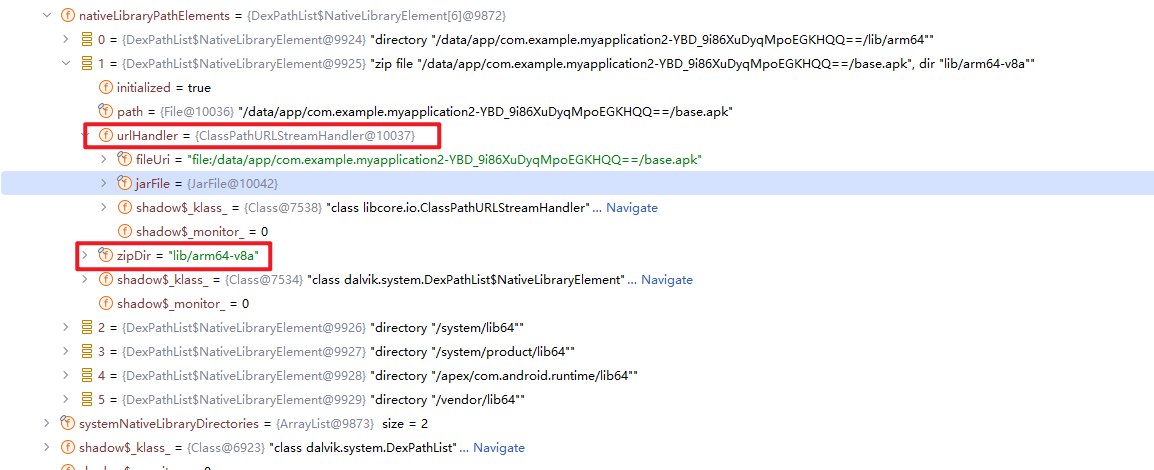
以其中一个 zip 的搜索路径为例,
zipDir = “lib/arm64-v8a”
然后 urlHandle 的 (String)fileUri 指向了当前 app 的安装路径, urlHandle 的 jarfile 也指向了 app 的安装路径
继续回到 DexPathList.findLibrary
//DexPathList.java
public String findLibrary(String libraryName)
{
String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
//首先调用System.mapLibraryName拿到so的前缀和后缀名,如libname为hello,那么经过此函数转换后变成了libhello.so
for (NativeLibraryElement element : this.nativeLibraryPathElements) //NativeLibraryElement[] nativeLibraryPathElements
{
String path = element.findNativeLibrary(fileName);
if (path != null)
{
return path;
}
}
return null;
}
//DexPathList$NativeLibraryElement.findNativeLibrary
public String findNativeLibrary(String name)
{
maybeInit();
if (zipDir == null) //优先会去找非zipDir目录的library, 大概是非apk目录
{
String entryPath = new File(path, name).getPath();
if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(entryPath))
{
return entryPath;
}
}
else if (urlHandler != null) //再去找zipDir目录的library,而这个zipDir 实际上就是APP原本的目录
{
// Having a urlHandler means the element has a zip file.
// In this case Android supports loading the library iff // it is stored in the zip uncompressed. String entryName = zipDir + '/' + name;
if (urlHandler.isEntryStored(entryName)) //这段代码用于判断给定entryName在指定的 JAR 文件中是否存在,并且是否是以“存储”方式存储的。
{
//apk好像被当作jar的形式打开
return path.getPath() + zipSeparator + entryName;
}
}
return null;
}
所以this.nativeLibraryPathElements 记录了所有要查找的目录
然后调用element.findNativeLibrary(fileName) , 在逐个逐个element对应目录下查找so文件是否存在
- 优先会去找非zipDir目录的library,
- 再去找zipDir(也就是apk压缩)目录的library
