《PneumoLLM:利用大型语言模型的力量进行尘肺病诊断》|文献速递--基于深度学习的医学影像病灶分割
Title
题目
PneumoLLM: Harnessing the power of large language model for pneumoconiosis diagnosis
《PneumoLLM:利用大型语言模型的力量进行尘肺病诊断》
01
文献速递介绍
在计算机辅助诊断领域,对医学数据的处理和分析能力至关重要。这不仅有助于潜在疾病的诊断,还能够预测未来的临床结果。随着深度学习理论的迅速发展,研究人员设计了复杂的网络架构(He et al., 2016;Dosovitskiy et al., 2020),并整理了大量高质量的数据集(Deng et al., 2009;Wang et al., 2017),以预训练这些强大的网络。预训练策略通过优化权重分布赋予网络宝贵的知识,从而使研究人员能够进一步利用标注数据来针对特定疾病进行模型的微调。当数据丰富且标注准确时,这一经典范式通常能够取得出色的效果,尤其是在常见疾病的诊断上。例如,EchoNet-Dynamic(Ouyang et al., 2020)在心脏功能评估上已经超越了医学专家。
然而,当我们深入探讨如尘肺病等职业病时(Li et al., 2023b;Dong et al., 2022),情形就会发生变化。长期暴露在充满粉尘的环境中且未配备个人防护装备的个体容易患上肺纤维化,这是一种尘肺病的前兆(Qi et al., 2021;Devnath et al., 2022)。尘肺病高发地区通常经济不发达,缺乏医疗资源和基础设施,以及专业的医疗从业者。此外,这些地区对疾病筛查和诊断存在明显的抵触情绪,导致临床数据严重不足(Sun et al., 2023;Huang et al., 2023b)。数据的匮乏使得传统的预训练与微调策略难以奏效。
Abatract
摘要
The conventional pretraining-and-finetuning paradigm, while effective for common diseases with ampledata, faces challenges in diagnosing data-scarce occupational diseases like pneumoconiosis. Recently, largelanguage models (LLMs) have exhibits unprecedented ability when conducting multiple tasks in dialogue,bringing opportunities to diagnosis. A common strategy might involve using adapter layers for vision–language alignment and diagnosis in a dialogic manner. Yet, this approach often requires optimization ofextensive learnable parameters in the text branch and the dialogue head, potentially diminishing the LLMs’efficacy, especially with limited training data. In our work, we innovate by eliminating the text branch andsubstituting the dialogue head with a classification head. This approach presents a more effective methodfor harnessing LLMs in diagnosis with fewer learnable parameters. Furthermore, to balance the retention ofdetailed image information with progression towards accurate diagnosis, we introduce the contextual multitoken engine. This engine is specialized in adaptively generating diagnostic tokens. Additionally, we proposethe information emitter module, which unidirectionally emits information from image tokens to diagnosistokens. Comprehensive experiments validate the superiority of our methods.
传统的预训练和微调范式虽然在数据充足的常见疾病诊断中表现有效,但在诊断如尘肺病等数据稀缺的职业病时面临挑战。近年来,大型语言模型(LLMs)在对话中执行多项任务时展现出前所未有的能力,为疾病诊断带来了新的机遇。常见的策略可能包括使用适配层进行视觉和语言的对齐,并以对话的方式进行诊断。然而,这种方法通常需要优化文本分支和对话头中的大量可学习参数,在训练数据有限的情况下,可能会削弱LLMs的效能。在我们的工作中,我们创新地去除了文本分支,并用分类头替代了对话头。此方法为利用LLMs进行诊断提供了一种更有效的途径,同时减少了可学习参数的数量。此外,为了平衡详细图像信息的保留与准确诊断的推进,我们引入了上下文多重标记引擎。该引擎专门用于自适应生成诊断标记。此外,我们提出了信息发射模块,该模块单向地将信息从图像标记传递到诊断标记。全面的实验验证了我们方法的优越性。
Method
方法
The efficacy of computer-aided diagnosis systems is crucial in processing and analyzing medical data. However, these systems often facea significant shortfall in clinical data availability. Leveraging the richknowledge reservoirs of foundational models is a promising strategyto address this data scarcity. Yet, the conventional pretraining-andfinetuning approach may compromise the representation capabilities ofLLMs, due to substantial changes in their parameter spaces, leading toincreased training time and memory overhead (Touvron et al., 2023a,b;OpenAI, 2023b).
计算机辅助诊断系统在处理和分析医学数据中的有效性至关重要。然而,这些系统往往面临临床数据可用性不足的重大挑战。利用基础模型丰富的知识储备是一种解决数据稀缺的有前途的策略。然而,传统的预训练和微调方法可能会由于其参数空间的显著变化而削弱大型语言模型(LLMs)的表示能力,导致训练时间和内存开销的增加(Touvron et al., 2023a,b;OpenAI, 2023b)。
Conclusion
结论
In this paper, we introduce PneumoLLM, a pioneering approachutilizing large language models for streamlined diagnostic processesin medical imaging. By discarding the text branch and transformingthe dialogue head into a classification head, PneumoLLM simplifies theworkflow for eliciting knowledge from LLMs. This innovation provesparticular effectiveness when only classification labels are available fortraining, rather than extensive descriptive sentences. The streamlinedprocess also significantly reduces the optimization space, facilitatinglearning with limited training data. Ablation studies further underscorethe necessity and effectiveness of the proposed modules, especiallyin maintaining the integrity of source image details while advancingtowards accurate diagnostic outcomes.
在本文中,我们介绍了PneumoLLM,这是一种利用大型语言模型简化医学影像诊断流程的创新方法。通过舍弃文本分支并将对话头转换为分类头,PneumoLLM简化了从大型语言模型中提取知识的工作流程。这一创新在仅有分类标签用于训练而非大量描述性语句的情况下表现出特别的效果。简化的流程也显著减少了优化空间,有助于在有限的训练数据下进行学习。消融研究进一步强调了所提出模块的必要性和有效性,特别是在保持源图像细节完整性的同时,实现准确诊断结果方面。
Figure
图
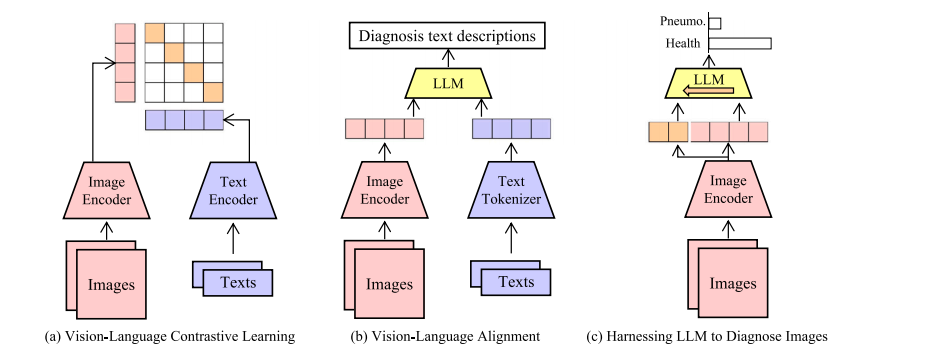
Fig. 1. Representative pipelines to elicit knowledge from large models. (a) Traditional works conduct vision–language contrastive learning to align multimodal representations. (b)To utilize large language models, existing works transform images into visual tokens, and send visual tokens to LLM to generate text descriptions. (c) Our work harnesses LLM todiagnose medical images by proper designs, forming a simple and effective pipeline.
图1. 从大型模型中获取知识的代表性流程。(a) 传统方法进行视觉-语言对比学习,以对齐多模态表示。(b) 为了利用大型语言模型,现有方法将图像转换为视觉标记,并将视觉标记发送到大型语言模型中生成文本描述。(c) 我们的工作通过适当的设计利用大型语言模型诊断医学图像,形成了一个简单而有效的流程。
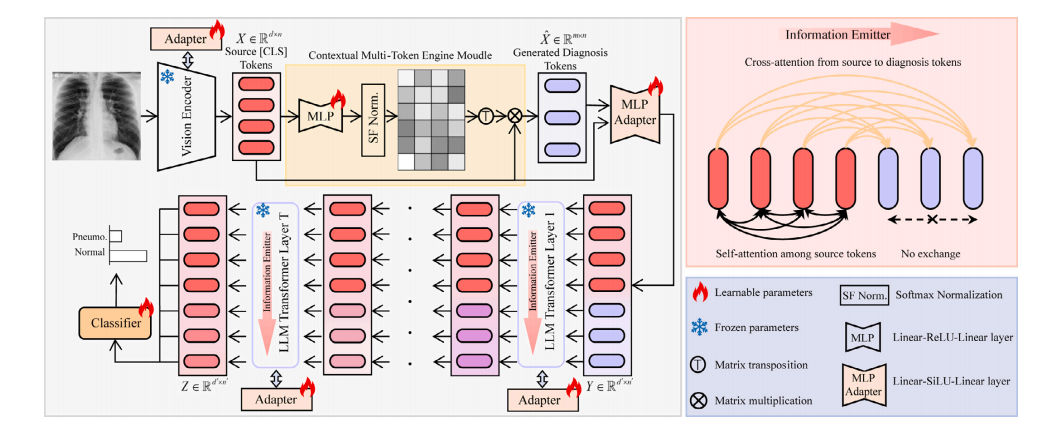
Fig. 2. Diagram of the proposed PneumoLLM. The vision encoder processes chest radiography and extracts source tokens. The contextual multi-token engine generates multiplediagnosis tokens conditioned on source tokens. To elicit in-depth knowledge from the LLM, we design the information emitter module within the LLM Transformer layers, enablingunidirectional information flow from source tokens to diagnosis tokens, preserving complete radiographic source details and aggregating critical diagnostic information.
图2. 所提出的PneumoLLM的示意图。视觉编码器处理胸部X光片并提取源标记。上下文多重标记引擎基于源标记生成多个诊断标记。为了从大型语言模型中获取深入的知识,我们在大型语言模型的Transformer层中设计了信息发射模块,实现了从源标记到诊断标记的单向信息流动,既保留了完整的X光片源细节,又聚合了关键的诊断信息。
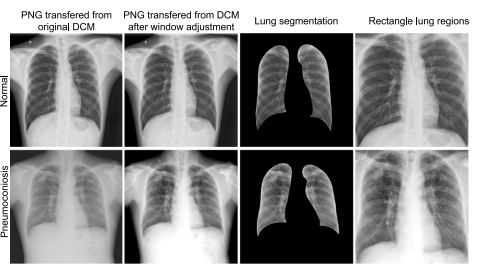
Fig. 3. The illustration examples of dataset preprocessing: two examples labeled as‘‘Normal’’ and ‘‘Pneumoconiosis’’. The window adjustment operation use the defaultwindow level and width (stored in the DICOM tags) to pre-process the original DICOMfiles. The segmentation results are obtained using the CheXmask pipeline, as proposedin the paper by Gaggion et al. (2023). The selection of the rectangular lung regions isbased on the largest external rectangle of the segmentation results.
图3. 数据集预处理的示例说明:“正常”和“尘肺病”两种标签的示例。窗位和窗宽调整操作使用默认的窗位和窗宽(存储在DICOM标签中)对原始DICOM文件进行预处理。分割结果是使用Gaggion等人(2023)论文中提出的CheXmask流程获得的。矩形肺区域的选择基于分割结果的最大外接矩形。
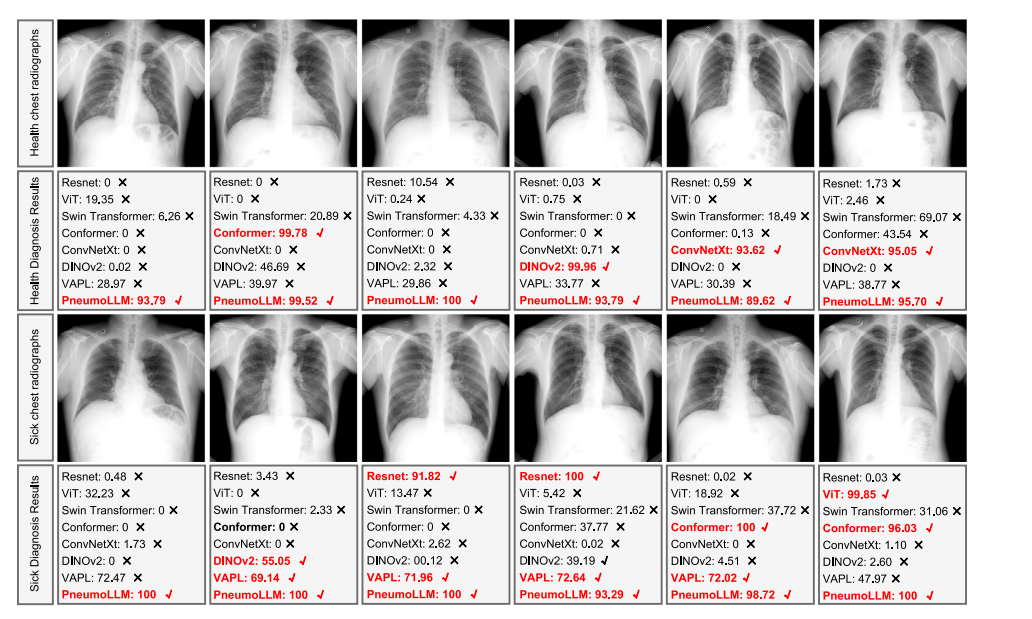
Fig. 4. Pneumoconiosis diagnosis results comparison with recent prestigious methods. The correct diagnosis results are highlighted in red.
图4. 尘肺病诊断结果与近期著名方法的比较。正确的诊断结果以红色突出显示。
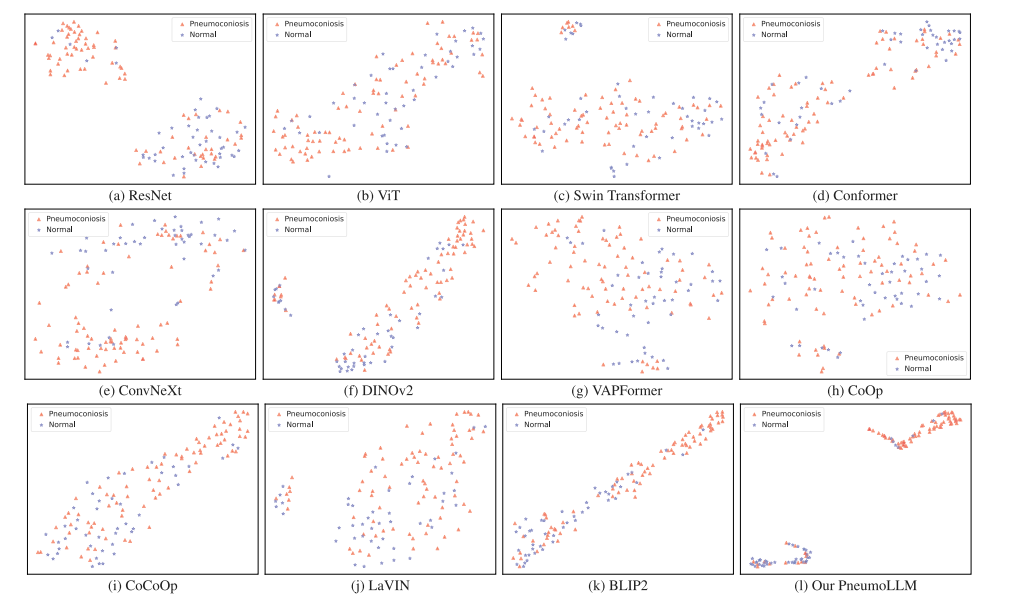
Fig. 5. The t-SNE visualization of feature representation obtained by different networks in comparison experiment.
图5. 比较实验中由不同网络获得的特征表示的t-SNE可视化。
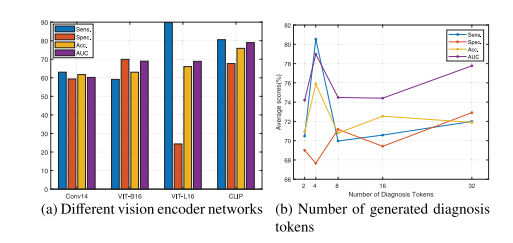
Fig. 6. Illustration on various vision encoder networks and the number of generateddiagnosis tokens. Please zoom in for the best view.
图 6. 各种视觉编码器网络及其生成的诊断标记数量的示意图。请放大查看以获得最佳效果。
Table
表
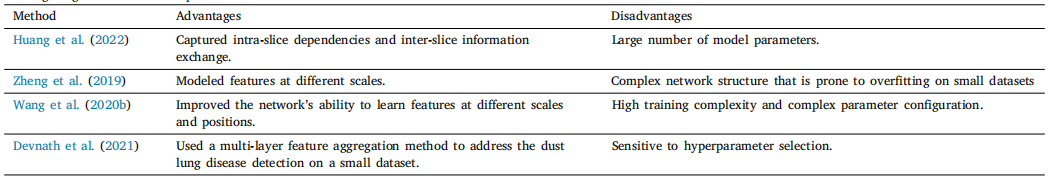
Table 1Existing diagnosis methods for pneumoconiosis.
表1现有的尘肺病诊断方法。
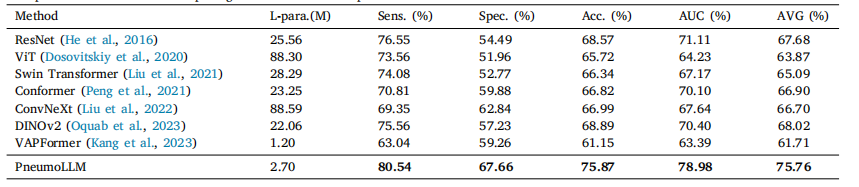
Table 2Comparison results with recent prestigious methods on the pneumoconiosis dataset
表2 尘肺病数据集上与近期著名方法的比较结果
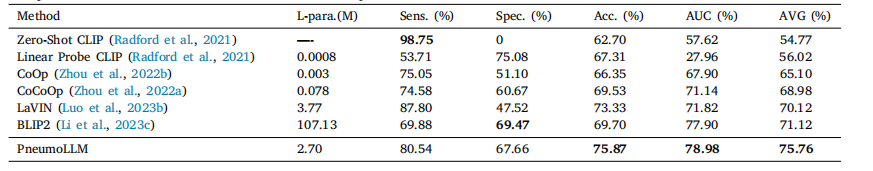
Table 3Comparison results with recent LLM-based methods on the pneumoconiosis dataset.
表3 尘肺病数据集上与近期基于大型语言模型(LLM)方法的比较结果。

Table 4Analysis of LLaMA-7B foundational model in pneumoconiosis diagnosis
表4 LLaMA-7B基础模型在尘肺病诊断中的分析

Table 5Ablation study on eliminating the textual processing branch in LLM.
表5 消除大型语言模型(LLM)中的文本处理分支的消融研究。

Table 6Ablation study on various PneumoLLM components
表6 各种PneumoLLM组件的消融研究
