OrionX vGPU 研发测试场景下最佳实践之Jupyter模式
在上周的文章中,我们讲述了OrionX vGPU研发测试场景下最佳实践之SSH模式,今天,让我们走进 Jupyter模式下的最佳实践。
-
• Jupyter模式:Jupyter是最近几年算法人员使用比较多的一种工具,很多企业已经将其改造集成开发工具,将Jupyter部署在容器或者虚机给算法人员使用。
环境准备
环境包含物理机器或者虚机,网络环境、GPU卡,操作系统以及容器平台。
硬件环境
本次POC环境准备三台虚机,其中一台CPU节点,两台GPU节点,每台GPU节点有一块T4卡。
操作系统为ubuntu 18.04
管理网络:千兆TCP
远程调用网络:100G RDMA
Kubernetes环境
三个节点安装k8s环境,可以使用kubeadm来安装,或者一些部署工具:
-
• kubekey
-
• KUBOARD 喷雾
当前部署kubernetes环境如下:
root@sc-poc-master-1:~# kubectl get node
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
sc-poc-master-1 Ready control-plane,master,worker 166d v1.21.5
sc-poc-worker-1 Ready worker 166d v1.21.5
sc-poc-worker-2 Ready worker 166d v1.21.5其中master为CPU节点,worker节点为2个T4 GPU节点。
OrionX vGPU 池化环境
参考趋动科技《OrionX 实施方案-k8s版》
部署完之后我们可以在orion的namespace查看OrionX组件:
root@sc-poc-master-1:~# kubectl get pod -n orion
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
orion-container-runtime-hgb5p 1/1 Running 3 63d
orion-container-runtime-qmghq 1/1 Running 1 63d
orion-container-runtime-rhc7s 1/1 Running 1 46d
orion-exporter-fw7vr 1/1 Running 0 2d21h
orion-exporter-j98kj 1/1 Running 0 2d21h
orion-gui-controller-all-in-one-0 1/1 Running 2 87d
orion-plugin-87grh 1/1 Running 6 87d
orion-plugin-kw8dc 1/1 Running 8 87d
orion-plugin-xpvgz 1/1 Running 8 87d
orion-scheduler-5d5bbd5bc9-bb486 2/2 Running 7 87d
orion-server-6gjrh 1/1 Running 1 74d
orion-server-p87qk 1/1 Running 4 87d
orion-server-sdhwt 1/1 Running 1 74d开发机场景:JupyterLab模式
jupyterlab包含了 的所有功能,并升级增加了很多功能。其支持python、R、java等多种编程语言及markdown、letex等写作语言及公式输入,可以集编程与写作于一身,非常适合于代码学习、笔记记录、演示及教学等。jupyter lab相比notebook最大的更新是模块化的界面,可以在同一个窗口以标签的形式同时打开好几个文档,同时插件管理非常强大,使用起来要比jupyter notebook功能丰富许多。jupyternotebook
JupyterLab作为一种基于web的集成开发环境,你可以使用它编写notebook、操作终端、编辑markdown文本、打开交互模式、查看csv文件及图片等功能。
本次场景,我们通过k8s部署jupyterlab来进行基本的机器学习开发,同时我们集成一个开源算法进行实践。
制作镜像
我们使用官方的pytorch镜像或者TensorFlow镜像作为Base镜像来编译一个新的jupyterlab镜像,在使用的时候就有cuda和框架了,省去很多时间。本次我们先以pytorch镜像来进行编译新镜像,新建一个Dockerfile
FROM pytorch/pytorch:1.8.1-cuda10.2-cudnn7-devel
#USER root
RUN sed -i 's/archive.ubuntu.com/mirrors.aliyun.com/g' /etc/apt/sources.list && \
rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/cuda.list && \
rm /etc/apt/sources.list.d/nvidia-ml.list && \
apt update -y && \
apt install -y nodejs npm curl vim wget git && \
apt install -y language-pack-zh-hans && \
pip3 install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ jupyterlab && \
pip3 install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple/ jupyterlab-language-pack-zh-CN
RUN pip install pillow && \
pip install cmake && \
pip install dlib && \
pip install face_recognition && \
pip install matplotlib && \
pip install scipy
ENV LANG='zh_CN.utf8'
CMD ["/bin/bash","-c","jupyter lab --ip=0.0.0.0 --no-browser --allow-root --port=8888 --NotebookApp.token='' --NotebookApp.password='' --NotebookApp.allow_origin='*'"]
我们使用了pytorch 1.8.1 cuda 10.2的镜像,然后将ubuntu的软件源改成阿里云的,同时删除nvidia的源,否则会因为网络问题无法安装其他软件。安装jupyterlab和一些基本的科学计算的库,重新build
docker build -t pytorch/pytorch:1.8.1-cuda10.2-cudnn7-devel-jupyterlab .build完之后,我们得到一个新的镜像,接下来我们部署该镜像pytorch/pytorch:1.8.1-cuda10.2-cudnn7-devel-jupyterlab
部署jupyterlab
通过yaml部署,由于该Pod需要对外提供服务,所以我们要暴露8888端口,同时创建svc和ingress提供对外服务地址
jupyterlab的yaml文件如下:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
name: jupyterlab-orion
namespace: orion
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: jupyterlab-orion
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: jupyterlab-orion
spec:
nodeName: sc-poc-worker-2
#hostNetwork: true
schedulerName: orion-scheduler
containers:
- name: jupyterlab-orion
image: pytorch/pytorch:1.8.1-cuda10.2-cudnn7-devel-jupyterlab
ports:
- containerPort: 8888
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
virtaitech.com/gpu: 1
limits:
virtaitech.com/gpu: 1
env:
- name : ORION_GMEM
value : "5000"
- name : ORION_RATIO
value : "50"
- name: ORION_VGPU
value: "1"
- name: ORION_RESERVED
value: "0"
- name: ORION_CROSS_NODE
value: "0"
- name: ORION_TASK_IDLE_TIME
value: "30s"
- name: ORION_EXPORT_CMD
value: "env | grep ORION; orion-smi -j"
- name : ORION_GROUP_ID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.uid
- name: ORION_K8S_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: ORION_K8S_POD_UID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.uid
- name: ORION_K8S_POD_NS
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: jupyterlab-orion
name: jupyterlab-orion
namespace: orion
spec:
ports:
- name: web
port: 8888
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8888
selector:
name: jupyterlab-orion
type: ClusterIP我这边是使用traefik搭建的ingress服务,所以给jupyterlab创建的ingress如下:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: jupyterlab-ingress
annotations:
kubernetes.io/ingress.class: traefik
traefik.ingress.kubernetes.io/router.entrypoints: web
spec:
rules:
- host: jupyterlab.10.10.10.180.nip.io
http:
paths:
- pathType: Prefix
path: /
backend:
service:
name: jupyterlab-orion
port:
number: 8888两个yaml文件部署完后,通过ingress地址可以访问该jupyterlab了

简单测试下pytorch是否可以正常调用vGPU,代码样例:
import torch
from torch import nn
if_cuda = torch.cuda.is_available()
print("if_cuda=",if_cuda)
gpu_count = torch.cuda.device_count()
print("gpu_count=",gpu_count)
torch.cuda.get_device_name(0)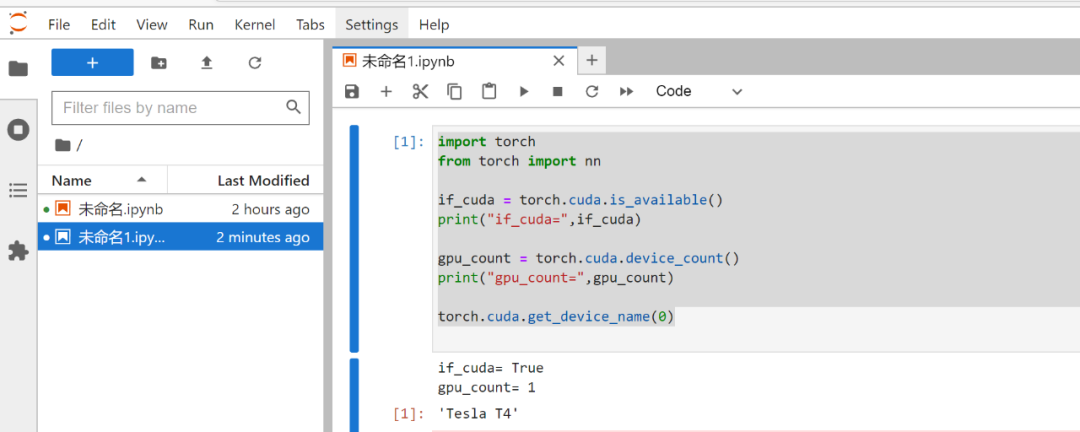
通过pytorch的api我们可以直接拿到GPU的信息,跟物理卡是一致的,物理卡是T4,vGPU同样是T4,此时vGPU是分配了一块卡,所以显示的数量也是一样的,根据pytorch拿到的信息我们可以发现对于上层的框架而言调用vGPU资源跟调用物理GPU资源是一样的,不会有什么改变,那对于上层的应用来说也是透明的使用vGPU资源。
跑一个demo
我们在jupyterlab中跑一个pytorch线性回归代码测试下pytorch调用vGPU是否正常使用。我们之前启动pod的时候申请了50%的算力和5G的显存
代码如下:
import time
import torch
from torch import nn
# 准备数据
n = 1000000 #样本数量
X = 10*torch.rand([n,2])-5.0 #torch.rand是均匀分布
w0 = torch.tensor([[2.0,-3.0]])
b0 = torch.tensor([[10.0]])
Y = X@w0.t() + b0 + torch.normal( 0.0,2.0,size = [n,1]) # @表示矩阵乘法,增加正态扰动
# 移动到GPU上
print("torch.cuda.is_available() = ",torch.cuda.is_available())
X = X.cuda()
Y = Y.cuda()
print("X.device:",X.device)
print("Y.device:",Y.device)
# 定义模型
class LinearRegression(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.w = nn.Parameter(torch.randn_like(w0))
self.b = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros_like(b0))
#正向传播
def forward(self,x):
return x@self.w.t() + self.b
linear = LinearRegression()
# 移动模型到GPU上
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
linear.to(device)
#查看模型是否已经移动到GPU上
print("if on cuda:",next(linear.parameters()).is_cuda)
# 训练模型
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(linear.parameters(),lr = 0.1)
loss_func = nn.MSELoss()
def train(epoches):
tic = time.time()
for epoch in range(epoches):
optimizer.zero_grad()
Y_pred = linear(X)
loss = loss_func(Y_pred,Y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if epoch%50==0:
print({"epoch":epoch,"loss":loss.item()})
toc = time.time()
print("time used:",toc-tic)
train(5000)运行结果如下:
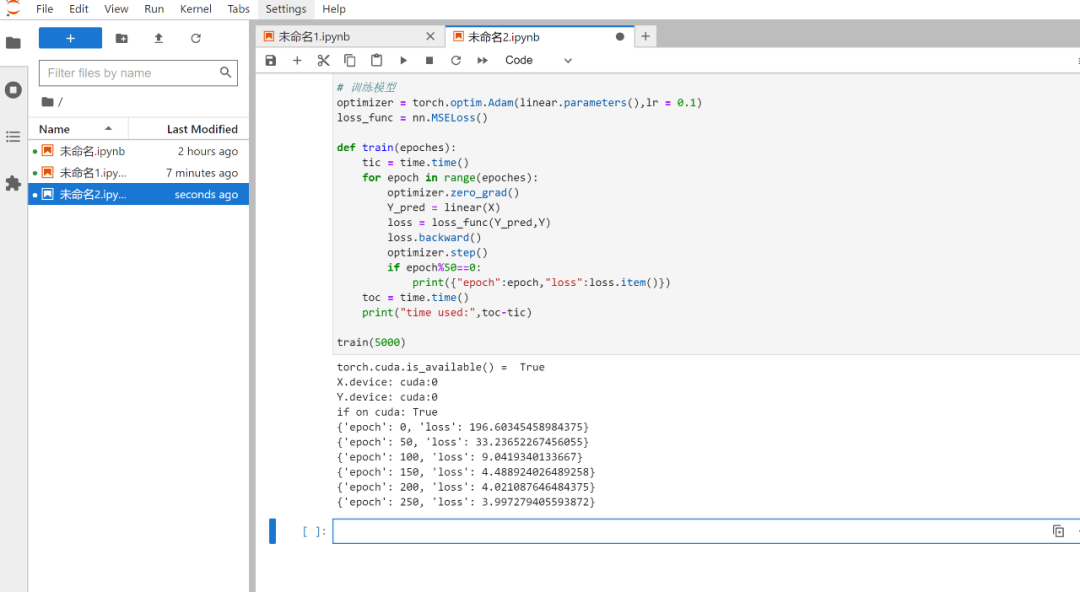
OrionX 申请资源情况如下
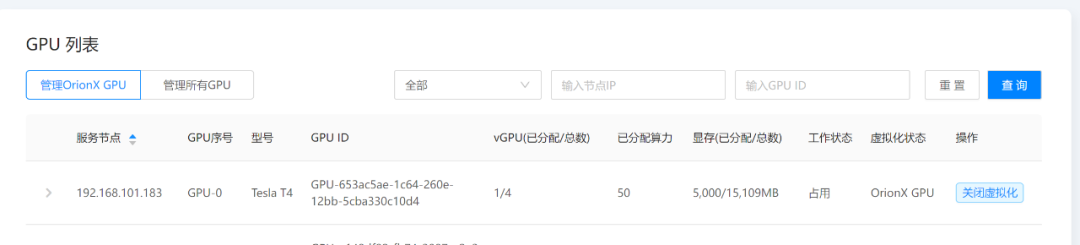
综上,我们在jupyterlab中通过pytorch调用vGPU能正常使用。
项目实践
我们基于一个开源项目在jupyterlab进行实际的开发体验,它可以将视频、人物、风景动漫化,我们本次使用的是pytorch版本的实现,项目地址为:animegan2-pytorchhttps://github.com/bryandlee/animegan2-pytorch
为了方便使用我们需要做一些准备工作,1、准备一个nfs server用来持久化 2、将该项目clone下来存入nfs中去,我在nfs server建了一个目录,然后把该项目拷贝进去;3、下载一个人脸关键点模型,后续可以直接使用该模型,当然你也可以训练自己的人脸关键点检测模型,该模型下载地址/mnt/nfs_share/animegan2-pytorchshape_predictor_68_face_landmarks.dat
https://github.com/davisking/dlib-models,将下载的模型同样拷贝到目录下面。接下来我们就将这个目录挂载给jupyterlab的pod里面,具体的挂载参考YAML文件如下:/mnt/nfs_share/animegan2-pytorch
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
name: jupyterlab-orion
namespace: orion
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
name: jupyterlab-orion
template:
metadata:
labels:
name: jupyterlab-orion
spec:
nodeName: sc-poc-worker-2
#hostNetwork: true
schedulerName: orion-scheduler
volumes:
- name: animegan2-data
nfs:
server: 10.10.10.180
path: /mnt/nfs_share/animegan2-pytorch
containers:
- name: jupyterlab-orion
image: pytorch/pytorch:1.8.1-cuda10.2-cudnn7-devel-jupyterlab
volumeMounts:
- name: animegan2-data
mountPath: /workspace/animegan2-pytorch
ports:
- containerPort: 8888
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
resources:
requests:
virtaitech.com/gpu: 1
limits:
virtaitech.com/gpu: 1
env:
- name : ORION_GMEM
value : "5000"
- name : ORION_RATIO
value : "50"
- name: ORION_VGPU
value: "1"
- name: ORION_RESERVED
value: "0"
- name: ORION_CROSS_NODE
value: "0"
- name: ORION_TASK_IDLE_TIME
value: "30s"
- name: ORION_EXPORT_CMD
value: "env | grep ORION; orion-smi -j"
- name : ORION_GROUP_ID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.uid
- name: ORION_K8S_POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: ORION_K8S_POD_UID
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.uid
- name: ORION_K8S_POD_NS
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: jupyterlab-orion
name: jupyterlab-orion
namespace: orion
spec:
ports:
- name: web
port: 8888
protocol: TCP
targetPort: 8888
selector:
name: jupyterlab-orion
type: ClusterIP我们把该nfs上的目录直接挂载在jupyterlab的目录下面,启动之后我们通过ingress方式登录该jupyterlab就可以看到挂载的项目了/workspace/animegan2-pytorch
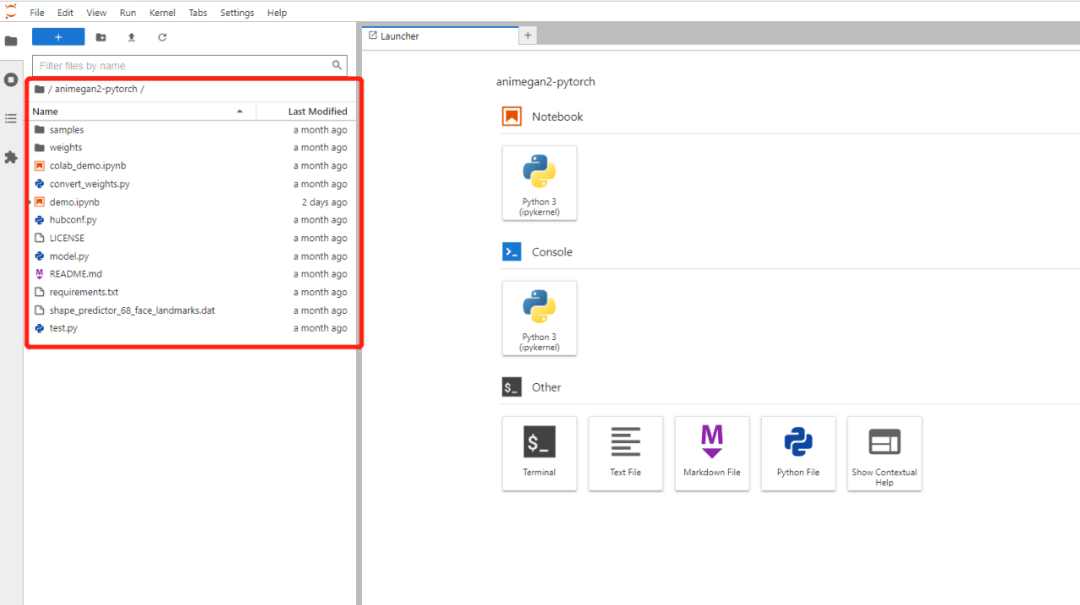
双击我们就可以运行该项目了,但是实际上在运行的时候他会在用户的根目录寻找一些文件,如果没有的话会自动下载,这些文件实际上就是项目里面的文件,由于github很不稳定,所以我们可以手动的在终端里面把这些文件复制到相关目录,需要复制两个目录,1、复制整个目录到;2、复制目录下的目录到 ,这样我们就可以在jupyterlab直接运行该demo了,我们可以通过点击来运行demo.ipynbanimegan2-pytorchanimegan2-pytorch/root/.cache/torch/hub/bryandlee_animegan2-pytorch_mainanimegan2-pytorchweights/root/.cache/torch/hub/checkpointsrun all cells
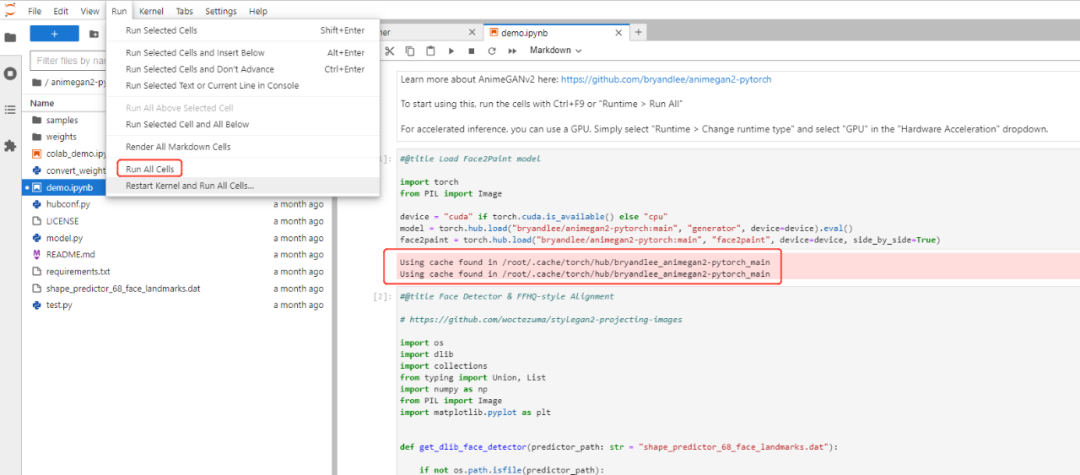
运行的时候我们就可以看到他会调用我们复制的这些目录文件了。
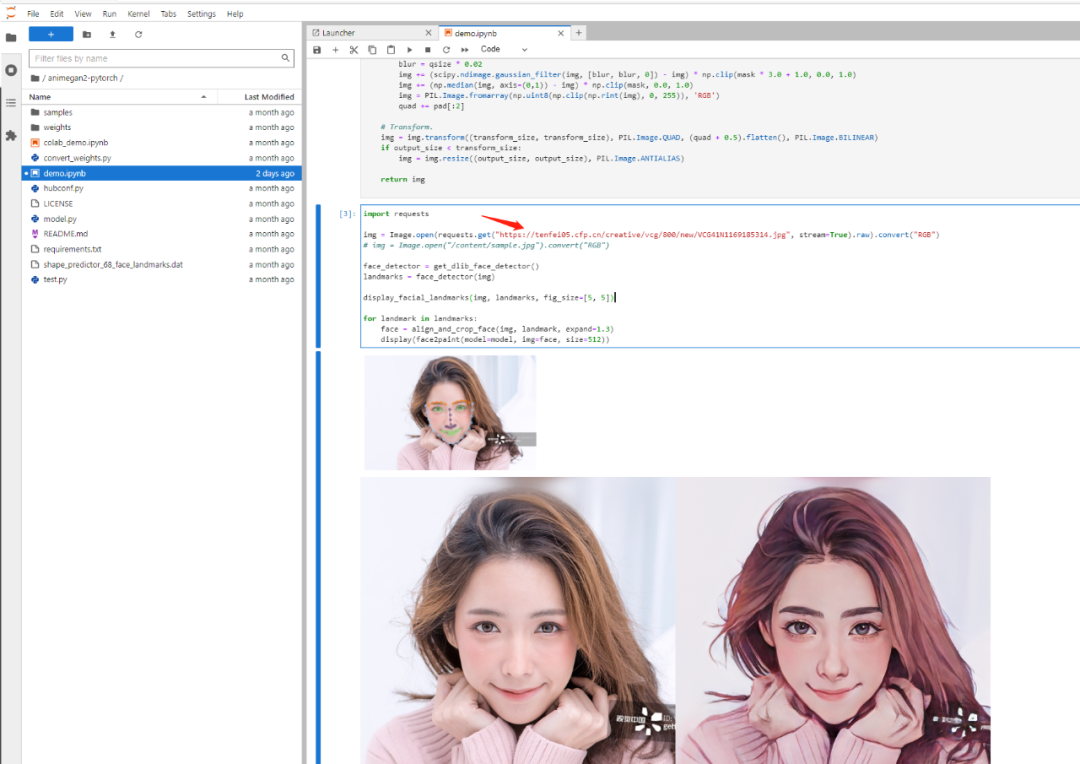
该demo自带了马斯克的人像来进行动漫化,我们也可以找一些图片链接进行替换来运行该demo
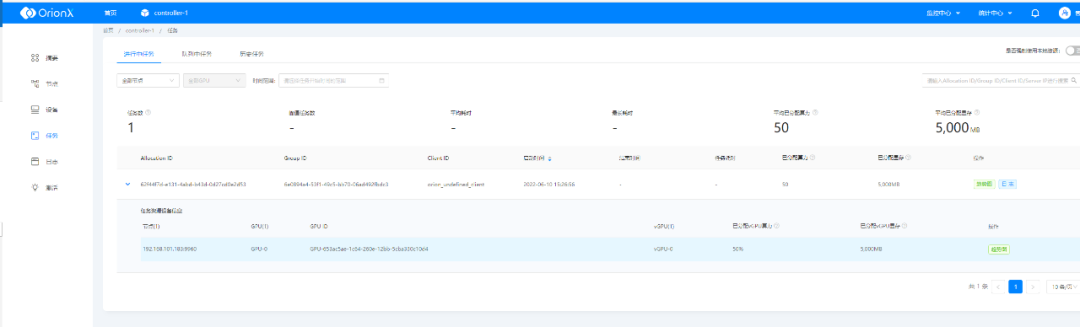
运行的时候我们通过OrionX GUI可以查看运行的任务和使用的资源
以上就是OrionX vGPU在Jupyter模式下的开发机场景的最佳实践,OrionX AI算力资源池化解决方案针对GPU管理粗放给出了相应的解决思路,旨在为用户提高GPU利用率、提供灵活调度平台、统一管理算力资源,实现弹性扩展,按需使用。我们将在以后的文章中继续分享OrionX vGPU基于CodeServer模式下的开发实践,欢迎留言探讨!
