Java并发学习总结:原子操作类
本文是学习尚硅谷周阳老师《JUC并发编程》的总结(文末有链接)。
基本类型原子类
- AtomicInteger
- AtomicLong
- AtomicBoolean
AtomicInteger 的方法 getAndIncrement 和 incrementAndGet 的区别:
两个方法都能实现对当前值加 1 , 但返回值不同,getAndIncrement 方法返回加 1 前的旧值,incrementAndGet 方法返回加 1 后的新值。
package juc.cas;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class ShareNumCas {
private AtomicInteger num = new AtomicInteger(0);
public int add() {
return num.getAndIncrement();
}
public int add2() {
return num.incrementAndGet();
}
public int getNum() {
return num.get();
}
}
public class NumPlusDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareNumCas share = new ShareNumCas();
System.out.println("before add num is " + share.getNum());
System.out.println("add return " + share.add());
System.out.println("after add num is " + share.getNum());
}
}
public class NumPlusDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ShareNumCas share = new ShareNumCas();
System.out.println("before add num is " + share.getNum());
System.out.println("add2 return " + share.add2());
System.out.println("after add num is " + share.getNum());
}
}
输出:
before add num is 0
add return 0
after add num is 1
before add num is 0
add2 return 1
after add num is 1
数组类型原子类
- AtomicIntegerArray
- AtomicLongArray
- AtomicReferenceArray
示例代码:
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerArray;
public class AtomicIntegerArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AtomicIntegerArray array = new AtomicIntegerArray(5);
// AtomicIntegerArray array = new AtomicIntegerArray(new int[]{1, 2, 3, 4, 5});
for (int i = 0; i < array.length(); i++) {
System.out.println(array.get(i));
}
System.out.println();
int tmp = array.getAndSet(0, 100);
System.out.println(tmp + " " + array.get(0));
tmp = array.getAndIncrement(0);
System.out.println(tmp + " " + array.get(0));
}
}
输出:
0
0
0
0
0
0 100
100 101
引用类型原子类
- AtomicReference
- AtomicStampedReference
- AtomicMarkableReference
AtomicReference 实现自旋锁
package juc.cas;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReference;
public class SpinLockDemo {
AtomicReference<Thread> atomicReference = new AtomicReference<>();
public void lock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " come in");
while (!atomicReference.compareAndSet(null, thread)) {
}
}
public void unlock() {
Thread thread = Thread.currentThread();
atomicReference.compareAndSet(thread, null);
System.out.println(thread.getName() + " task over, unlock");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpinLockDemo spinLockDemo = new SpinLockDemo();
new Thread(() -> {
spinLockDemo.lock();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
spinLockDemo.unlock();
}, "A").start();
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
new Thread(() -> {
spinLockDemo.lock();
spinLockDemo.unlock();
}, "B").start();
}
}
输出:
A come in
B come in
A task over, unlock
B task over, unlock
AtomicStampedReference VS AtomicMarkableReference
AtomicStampedReference 可以记录对象被修改过几次
AtomicMarkableReference 只能记录对象是否被修改过
AtomicMarkableReference 示例代码:
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicMarkableReference;
public class AtomicMarkableReferenceDemo {
static AtomicMarkableReference<Integer> atomicMarkableReference = new AtomicMarkableReference<>(100, false);
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(() -> {
boolean marked = atomicMarkableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " init marked = " + marked);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
boolean result = atomicMarkableReference.compareAndSet(100, 101, marked, !marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " result = " + result +
", marked = " + atomicMarkableReference.isMarked() + ", value = " + atomicMarkableReference.getReference());
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
boolean marked = atomicMarkableReference.isMarked();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " init marked = " + marked);
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
boolean result = atomicMarkableReference.compareAndSet(100, 102, marked, !marked);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " result = " + result
+ ", marked = " + atomicMarkableReference.isMarked() + ", value = " + atomicMarkableReference.getReference());
}, "t2").start();
}
}
输出:
t2 init marked = false
t1 init marked = false
t1 result = true, marked = true, value = 101
t2 result = false, marked = true, value = 101
对象的属性修改原子类
- AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater
- AtomicLongFieldUpdater
- AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<T,V>
下例中可以将 money 定义为 AtomicInteger,已经有了 AtomicInteger ,AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 有什么使用场景?
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater 示例代码:
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater;
class BankAccount {
String bankName = "CCB";
public volatile int money = 0;
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<BankAccount> updater =
AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(BankAccount.class, "money");
public void add(BankAccount bankAccount) {
updater.getAndIncrement(bankAccount);
}
}
public class AtomicIntegerFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
BankAccount bankAccount = new BankAccount();
CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
for (int j = 0; j < 1000; j++) {
bankAccount.add(bankAccount);
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}).start();
}
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("after add money is " + bankAccount.money);
}
}
输出:
after add money is 10000
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<T,V> 示例代码:
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater;
class MyVar {
public volatile Boolean isInit = Boolean.FALSE;
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater<MyVar, Boolean> updater =
AtomicReferenceFieldUpdater.newUpdater(MyVar.class, Boolean.class, "isInit");
public void init(MyVar myVar) {
if(updater.compareAndSet(myVar, Boolean.FALSE, Boolean.TRUE)) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " start init");
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " init success");
} else {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " other thread is initing...");
}
}
}
public class AtomicReferenceFieldUpdaterDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyVar myVar = new MyVar();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(() -> myVar.init(myVar), "t" + i).start();
}
}
}
输出:
t3 other thread is initing...
t1 other thread is initing...
t4 other thread is initing...
t2 other thread is initing...
t0 start init
t0 init success
原子操作增强类
- LongAdder
- LongAccumulator
- DoubleAdder
- DoubleAccumulator

LongAdder VS LongAccumulator
- LongAdder 的初始值只能为 0
- LongAdder 只能进行加减操作
- LongAccumulator 没有上面两个限制,更灵活
LongAdder#sum() 不会加锁,不会影响对数的操作。
LongAdder 简单示例:
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
public class LongAdderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
longAdder.increment();
System.out.println(longAdder.sum());
}
}
输出:
5
LongAccumulator 简单示例:
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAccumulator;
public class LongAccumulatorDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y) -> x + y, 0);
// 可以使用方法引用简写
// LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator(Long::sum, 0);
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
System.out.println(longAccumulator.get());
longAccumulator.accumulate(2);
System.out.println(longAccumulator.get());
}
}
输出:
1
3
各种计数性能比较
package juc.atomic;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAccumulator;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.LongAdder;
class ClickNum {
int number = 0;
public synchronized void add() {
number++;
}
AtomicLong atomicLong = new AtomicLong(0);
public void addAtomic() {
atomicLong.getAndIncrement();
}
LongAdder longAdder = new LongAdder();
public void addLongAdder() {
longAdder.increment();
}
LongAccumulator longAccumulator = new LongAccumulator((x, y) -> x + y, 0);
public void addLongAccumulator() {
longAccumulator.accumulate(1);
}
}
public class CountPerfTester {
private static final int THREADS_COUNT = 50;
private static final int TEN_THOUSANDS = 10000;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ClickNum clickNum = new ClickNum();
long start = 0L;
long end = 0L;
CountDownLatch countDownLatch1 = new CountDownLatch(THREADS_COUNT);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch2 = new CountDownLatch(THREADS_COUNT);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch3 = new CountDownLatch(THREADS_COUNT);
CountDownLatch countDownLatch4 = new CountDownLatch(THREADS_COUNT);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < THREADS_COUNT; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * TEN_THOUSANDS; j++) {
clickNum.add();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch1.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
countDownLatch1.await();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("synchronized add cost time : " + (end - start) + " ms, " + "result is " + clickNum.number);
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < THREADS_COUNT; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * TEN_THOUSANDS; j++) {
clickNum.addAtomic();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch2.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
countDownLatch2.await();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("addAtomic cost time : " + (end - start) + " ms, " + "result is " + clickNum.atomicLong.get());
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < THREADS_COUNT; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * TEN_THOUSANDS; j++) {
clickNum.addLongAdder();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch3.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
countDownLatch3.await();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("addLongAdder cost time : " + (end - start) + " ms, " + "result is " + clickNum.longAdder.sum());
start = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < THREADS_COUNT; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
try {
for (int j = 1; j <= 100 * TEN_THOUSANDS; j++) {
clickNum.addLongAccumulator();
}
} finally {
countDownLatch4.countDown();
}
}).start();
}
countDownLatch4.await();
end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("addLongAccumulator cost time : " + (end - start) + " ms, " + "result is " + clickNum.longAccumulator.get());
}
}
输出:
synchronized add cost time : 1352 ms, result is 50000000
addAtomic cost time : 844 ms, result is 50000000
addLongAdder cost time : 97 ms, result is 50000000
addLongAccumulator cost time : 74 ms, result is 50000000
可以看出:
LongAdder 和 LongAccumulator 的时间是 synchronized 和 AtomicLong 的十分之一左右。
LongAdder 高性能原理说明
LongAdder 的基本思路是分散热点,将 value 值分散到一个 Cell 数组中,不同的线程会命中到不同的数组元素中,各个线程只对自己数组元素的 value 进行 CAS 操作,冲突概率会小很多,sum() 方法会对 base 和所有 Cell 数组的值累加作为返回值。
某个线程分配到哪个 Cell 的方法是:对线程 id 进行 hash 求值,再根据 hash 值映射到 Cell 数组的某个下标。
Cell 数组元素是 2 的 n 次方,最大是 CPU 的核数。
LongAdder 源码分析
add(1L)
- 最初无竞争时只更新 base
- 如果更新 base 失败时,首次新增一个 Cell 数组
- 当多个线程对同一个 Cell 竞争激烈时,可能就会对 Cell 数组扩容
public void add(long x) {
Cell[] cs; long b, v; int m; Cell c;
if ((cs = cells) != null || !casBase(b = base, b + x)) {
int index = getProbe();
boolean uncontended = true;
if (cs == null || (m = cs.length - 1) < 0 ||
(c = cs[index & m]) == null ||
!(uncontended = c.cas(v = c.value, v + x)))
longAccumulate(x, null, uncontended, index);
}
}

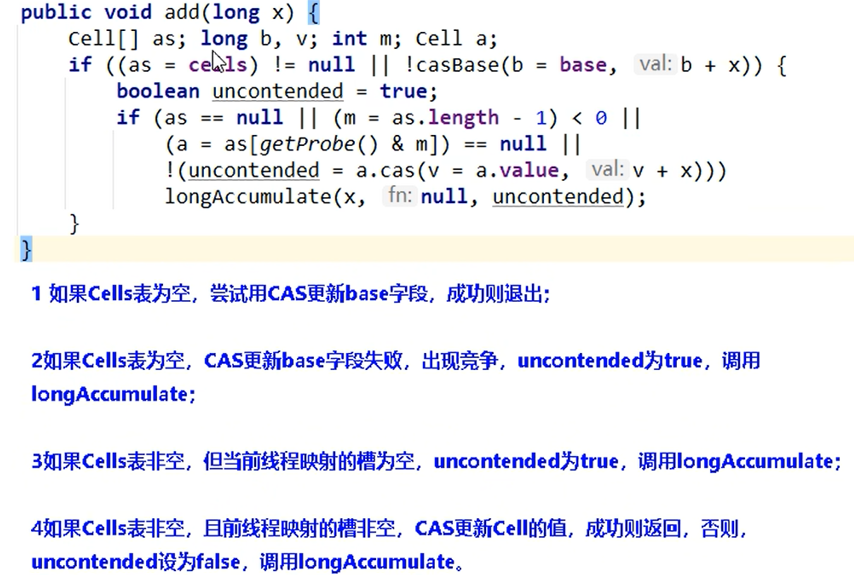
判断代码中有赋值,也有方法调用,简化了代码。
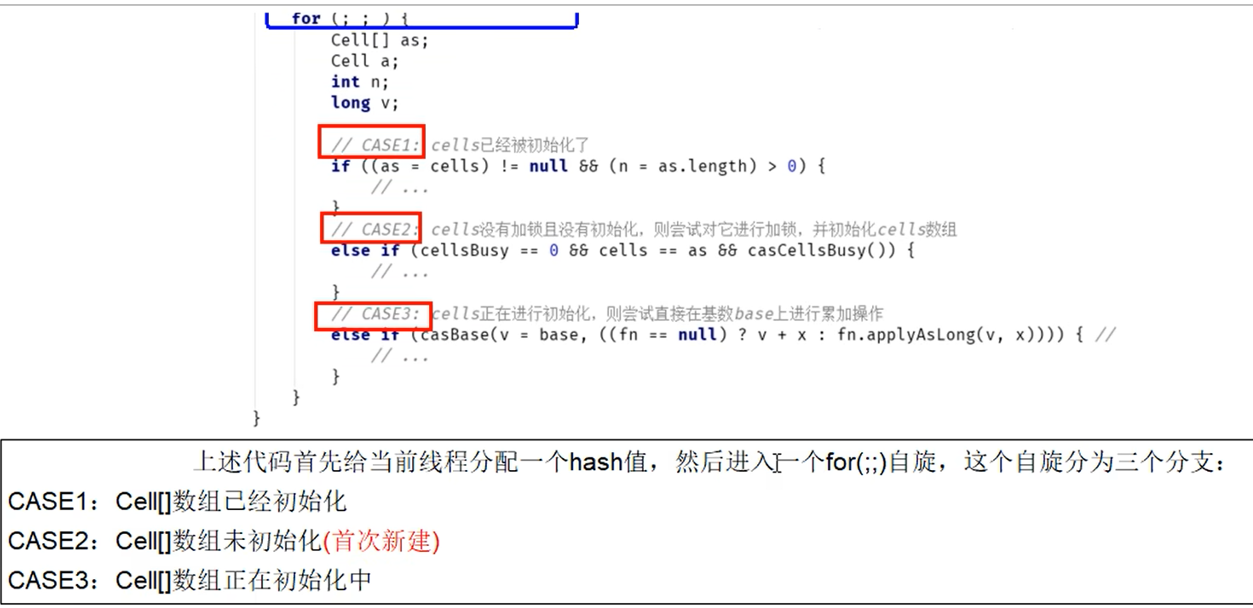
longAccumulator
分为 3 种情况:
-
Cell 数组已经初始化
这种情况下主要进行对某个 Cell 元素的初始化赋值,在某个 Cell 元素上重试 CAS,对 Cell 数组扩容 -
Cell 数组未初始化
这种情况下首次创建 Cell 数组,包含 2 个元素 -
Cell 数组正在初始化,则尝试在 base 上重试 CAS 操作
sum
/**
* Returns the current sum. The returned value is <em>NOT</em> an
* atomic snapshot; invocation in the absence of concurrent
* updates returns an accurate result, but concurrent updates that
* occur while the sum is being calculated might not be
* incorporated.
*
* @return the sum
*/
public long sum() {
Cell[] cs = cells;
long sum = base;
if (cs != null) {
for (Cell c : cs)
if (c != null)
sum += c.value;
}
return sum;
}
sum 会将所有 Cell 数组中的 value 和 base 累加作为返回值,sum 执行时并没有限制对 base 和 Cells 的值更新,所以返回值可能会损失一些精度。LongAdder 不是强一致性的,是最终一致性的。
参考
- 尚硅谷JUC并发编程 (https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1ar4y1x727?spm_id_from=333.788.videopod.episodes&vd_source=9266b9af652d5902d068c94b9d60116f&p=80)
