SpringBoot源码解析(五):准备应用环境
SpringBoot源码系列文章
SpringBoot源码解析(一):SpringApplication构造方法
SpringBoot源码解析(二):引导上下文DefaultBootstrapContext
SpringBoot源码解析(三):启动开始阶段
SpringBoot源码解析(四):解析应用参数args
SpringBoot源码解析(五):准备应用环境
目录
- 前言
- 一、入口
- 二、环境实例ApplicationServletEnvironment
- 1、PropertyResolver
- 2、Environment
- 3、ConfigurablePropertyResolver
- 4、ConfigurableEnvironment
- 5、ConfigurableWebEnvironment
- 6、AbstractEnvironment
- 7、StandardEnvironment
- 8、StandardServletEnvironment
- 9、ApplicationServletEnvironment
- 三、配置环境
- 1、命令行参数属性源
- 2、配置属性源
- 四、触发的应用监听器
- 1、EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
- 1.1、RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
- 1.2、SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
- 1.3、SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
- 1.4、ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor
- 2、AnsiOutputApplicationListener
- 3、BackgroundPreinitializer
- 4、FileEncodingApplicationListener
- 五、默认属性源
- 六、绑定spring.main配置到SpringApplication对象
- 总结
前言
在前文中,我们深入解析了启动类main函数中args参数被解析为选项参数和非选项参数的过程。接下来,我们将探讨SpringBoot启动时应用环境的准备过程,包括读取配置文件和设置环境变量的步骤。
SpringBoot版本2.7.18SpringApplication的run方法的执行逻辑如下,本文将详细介绍第4小节:准备应用环境
// SpringApplication类方法
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 记录应用启动的开始时间
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
// 1.创建引导上下文,用于管理应用启动时的依赖和资源
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
// 配置无头模式属性,以支持在无图形环境下运行
// 将系统属性 java.awt.headless 设置为 true
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 2.获取Spring应用启动监听器,用于在应用启动的各个阶段执行自定义逻辑
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 启动开始方法(发布开始事件、通知应用监听器ApplicationListener)
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
// 3.解析应用参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 4.准备应用环境,包括读取配置文件和设置环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
// 配置是否忽略 BeanInfo,以加快启动速度
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 5.打印启动Banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 6.创建应用程序上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
// 设置应用启动的上下文,用于监控和管理启动过程
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 7.准备应用上下文,包括加载配置、添加 Bean 等
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 8.刷新上下文,完成 Bean 的加载和依赖注入
refreshContext(context);
// 9.刷新后的一些操作,如事件发布等
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 计算启动应用程序的时间,并记录日志
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
// 10.通知监听器应用启动完成
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
// 11.调用应用程序中的 `CommandLineRunner` 或 `ApplicationRunner`,以便执行自定义的启动逻辑
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 12.处理启动过程中发生的异常,并通知监听器
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 13.计算应用启动完成至准备就绪的时间,并通知监听器
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// 处理准备就绪过程中发生的异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 返回已启动并准备就绪的应用上下文
return context;
}
一、入口
// 4.准备应用环境,包括读取配置文件和设置环境变量
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
- 初始化并配置Spring应用环境
// SpringApplication类方法
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 4.1.获取环境实例 ApplicationServletEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 4.2.配置环境
// 将命令行参数传递给环境配置
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 添加配置属性源到环境中,使其能够解析相关配置属性
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 4.3.通知监听器,环境已准备好
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
// 4.4.将默认属性源移到环境属性源列表的末尾
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
// spring.main.environment-prefix是SpringBoot用于管理上下文环境的一部分
// 不应该由用户直接修改,如果被用户定义,则抛错
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
// 4.5.绑定spring.main环境配置到SpringApplication对象上
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 如果环境不是自定义的,则进行环境转换,确定必要的环境类型
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
// 再次设置配置属性源,确保配置属性源在第一位
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 返回配置完成的环境对象
return environment;
}
二、环境实例ApplicationServletEnvironment
getOrCreateEnvironment()方法的核心是创建一个 ApplicationServletEnvironment实例,下面将重点研究该类。
先看类图:从上到下逐一分析
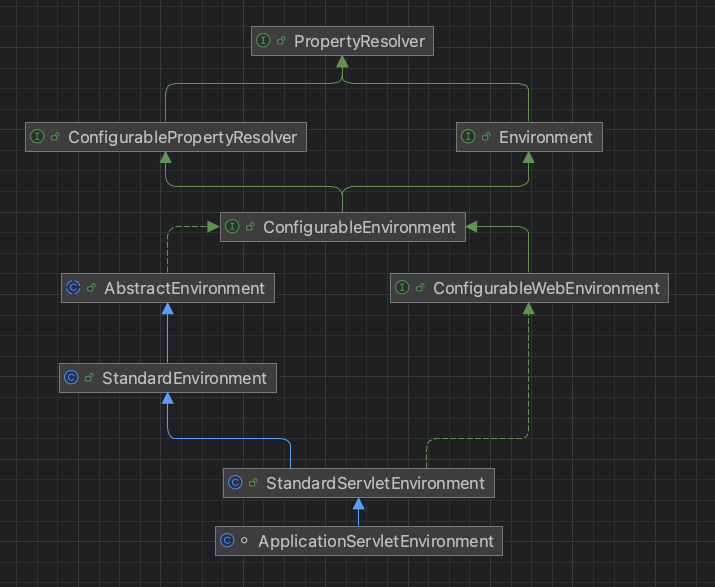
1、PropertyResolver
PropertyResolver是Spring核心框架中的一个接口,提供了解析属性值的统一方法。它支持从多种配置源(如系统属性、环境变量、配置文件等)获取属性值,广泛用于环境配置、占位符解析等场景。
- 属性检查
- 判断某个属性是否存在
- 方法:containsProperty(String key)
- 获取属性值
- 获取指定键的属性值,支持默认值、类型转换等
- 方法:getProperty(String key)、getProperty(String key, String defaultValue)、getProperty(String key, Class targetType) 等
- 必需属性值
- 获取指定键的属性值,若找不到则抛出异常
- 方法:getRequiredProperty(String key)、getRequiredProperty(String key, Class targetType)
- 占位符解析
- 解析字符串中的 ${…} 占位符,替换为对应的属性值
- 方法:resolvePlaceholders(String text)、resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text)
// 用于解析属性值的接口,支持从底层源解析属性
public interface PropertyResolver {
// 判断指定的属性键是否可用,即该键对应的值是否不为null
boolean containsProperty(String key);
// 返回与指定键关联的属性值,如果未找到则返回null
@Nullable
String getProperty(String key);
// 返回与指定键关联的属性值,如果未找到则返回默认值
String getProperty(String key, String defaultValue);
// 返回与指定键关联的属性值,并将其转换为指定的目标类型,如果未找到则返回null
@Nullable
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType);
// 返回与指定键关联的属性值,并将其转换为目标类型,如果未找到则返回默认值
<T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType, T defaultValue);
// 返回与指定键关联的属性值(不能为null)
String getRequiredProperty(String key) throws IllegalStateException;
// 返回与指定键关联的属性值,并将其转换为目标类型(不能为null)
<T> T getRequiredProperty(String key, Class<T> targetType) throws IllegalStateException;
// 解析给定文本中的 ${...} 占位符,并用对应的属性值替换。
// 未解析的占位符会被忽略并原样返回。
String resolvePlaceholders(String text);
// 解析给定文本中的 ${...} 占位符,并用对应的属性值替换
// 未解析的占位符将抛出 IllegalArgumentException 异常
String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException;
}
2、Environment
Environment是Spring框架中的一个核心接口,用于表示应用程序的运行环境。它扩展了PropertyResolver接口,既负责属性解析,也负责Profile管理。在Spring中,它的主要用途是管理配置文件(Profiles)和属性(Properties)。
// 表示当前应用程序运行环境的接口
public interface Environment extends PropertyResolver {
// 返回当前环境中激活的Profiles
String[] getActiveProfiles();
// 返回当前环境中默认激活的 Profiles
String[] getDefaultProfiles();
// 检查给定的 Profile 表达式是否与当前激活的 Profiles 匹配
default boolean matchesProfiles(String... profileExpressions) {
return acceptsProfiles(Profiles.of(profileExpressions));
}
// 检查一个或多个给定的 Profiles 是否被当前环境接受
@Deprecated
boolean acceptsProfiles(String... profiles);
// 检查给定的 Profiles 谓词是否与当前激活的或默认的 Profiles 匹配
boolean acceptsProfiles(Profiles profiles);
}
3、ConfigurablePropertyResolver
ConfigurablePropertyResolver是Spring中PropertyResolver的扩展接口,为属性解析器添加了额外的配置能力,主要用于高级属性管理和占位符解析。它允许自定义属性解析行为,如类型转换服务、占位符格式以及验证必需的属性。
// 用于在将属性值从一种类型转换为另一种类型时使用
public interface ConfigurablePropertyResolver extends PropertyResolver {
// 获取用于属性值类型转换的 ConfigurableConversionService 实例
ConfigurableConversionService getConversionService();
// 设置类型转换服务
void setConversionService(ConfigurableConversionService conversionService);
// 设置占位符的前缀,默认为 ${
// 示例:若设置为 #{,则占位符形如 #{property}
void setPlaceholderPrefix(String placeholderPrefix);
// 设置占位符的后缀,默认为 }
// 示例:与 setPlaceholderPrefix 配合使用,解析 #{property}
void setPlaceholderSuffix(String placeholderSuffix);
// 设置占位符和默认值之间的分隔符,默认值为 :
// 示例:${property:defaultValue} 表示如果 property 未定义,则返回 defaultValue
void setValueSeparator(@Nullable String valueSeparator);
// 设置是否忽略无法解析的嵌套占位符
// true:保留未解析的占位符(如 ${unresolved})
// false:遇到未解析的占位符时抛出异常
void setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders);
// 设置必须存在的属性
void setRequiredProperties(String... requiredProperties);
// 验证所有必需属性是否存在并解析为非 null
void validateRequiredProperties() throws MissingRequiredPropertiesException;
}
4、ConfigurableEnvironment
ConfigurableEnvironment是Spring框架中的一个核心接口,扩展了Environment和ConfigurablePropertyResolver接口,提供了对Profile和属性源(PropertySources) 的动态管理功能。它主要用于应用启动前的环境配置,允许开发者根据需求自定义属性解析规则和Profile配置。
public interface ConfigurableEnvironment extends Environment, ConfigurablePropertyResolver {
// 设置当前环境的 Active Profiles(激活的配置)
void setActiveProfiles(String... profiles);
// 向当前的 Active Profiles 集合中添加一个 Profile
void addActiveProfile(String profile);
// 设置默认激活的 Profile 集合
void setDefaultProfiles(String... profiles);
// 返回当前环境的属性源集合,允许动态操作属性源
MutablePropertySources getPropertySources();
// 返回JVM的系统属性(System.getProperties())
Map<String, Object> getSystemProperties();
// 返回操作系统的环境变量(System.getenv())
Map<String, Object> getSystemEnvironment();
// 将父环境的 Active Profiles、Default Profiles 和 属性源 合并到当前环境中
void merge(ConfigurableEnvironment parent);
}
5、ConfigurableWebEnvironment
ConfigurableWebEnvironment是Spring框架中ConfigurableEnvironment的特化接口,主要用于基于Servlet环境的Web应用程序。它扩展了 ConfigurableEnvironment,并增加了与Servlet相关的配置功能,确保在ServletContext和ServletConfig可用时,能够尽早初始化与 Servlet 环境相关的属性源。
public interface ConfigurableWebEnvironment extends ConfigurableEnvironment {
// 使用给定的 ServletContext 和(可选的)ServletConfig 初始化属性源。
// 该方法会将占位符性质的属性源替换为实际的 Servlet 上下文或配置属性源。
// 调用时机:Spring Boot 中的内嵌容器(如 Tomcat、Jetty)启动时
void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig);
}
6、AbstractEnvironment
AbstractEnvironment作为Environment实现的基础类,主要提供对配置文件(Profiles) 和属性源(PropertySources)的管理。它支持定义和管理激活配置文件(Active Profiles) 以及 默认配置文件(Default Profiles)。
public abstract class AbstractEnvironment implements ConfigurableEnvironment {
// 激活配置文件集合
private final Set<String> activeProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>();
// 默认配置文件集合 getReservedDefaultProfiles() = 字符串“default”
private final Set<String> defaultProfiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(getReservedDefaultProfiles());
// 属性源集合,上篇文章有介绍,属性源就是一组属性map键值对,这里集合就是多组键值对
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources;
// 属性解析器
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver;
public AbstractEnvironment() {
this(new MutablePropertySources());
}
protected AbstractEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
this.propertySources = propertySources;
this.propertyResolver = createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
// 自定义属性源,对属性源增删改查做操作
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
// 默认无操作,子类可覆盖
}
// 省略其他方法
}
PropertySource表示属性来源的抽象概念,每个属性源(PropertySource)封装了一组键值对(key-value),并可以根据键解析属性值。用于从各种来源(如系统属性、环境变量、配置文件等)加载属性
public abstract class PropertySource<T> {
// 属性源名称,唯一标识
protected final String name;
// 一般是map键值对
protected final T source;
...
}
MutablePropertySources用于管理多个属性源(PropertySource)的集合。它提供了一个可变的数据结构,允许开发者动态地添加、删除、替换或调整属性源的顺序。
addFirst(PropertySource<?> propertySource):将属性源添加到集合的首位,优先级最高addLast(PropertySource<?> propertySource):将属性源添加到集合的末尾,优先级最低addBefore(String relativePropertySourceName, PropertySource<?> propertySource):在指定名称的属性源之前插入addAfter(String relativePropertySourceName, PropertySource<?> propertySource):在指定名称的属性源之后插入
public class MutablePropertySources implements PropertySources {
// 属性源集合
private final List<PropertySource<?>> propertySourceList = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
...
}
7、StandardEnvironment
StandardEnvironment提供了对系统属性(System Properties)和环境变量(Environment Variables)的支持,并在默认情况下将这两个属性源添加到 MutablePropertySources中。
AbstractEnvironment构造方法中会调用customizePropertySources方法,也就是创建ApplicationServletEnvironment实例就是添加两个属性源,名称为systemProperties为的JVM系统属性(如 java.version、java.home 等)和名称为systemEnvironment的环境变量(PATH、HOME等操作系统相关变量)。
public class StandardEnvironment extends AbstractEnvironment {
// 系统环境变量属性源的名称
public static final String SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemEnvironment";
// JVM 系统属性源的名称
public static final String SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "systemProperties";
public StandardEnvironment() {
}
protected StandardEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
super(propertySources);
}
// 自定义操作属性源,父类构造中会调用
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
// addLast将属性放到最后,优先级最低,JVM优先级高于环境变量
propertySources.addLast(
// 通过 System.getProperties() 提供的 JVM 系统属性
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
// 通过 System.getenv() 提供的环境变量
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
}
8、StandardServletEnvironment
StandardServletEnvironment是Spring框架中的一个类,继承自StandardEnvironment,用于为基于Servlet的Web应用程序提供专门的Environment实现。它扩展了标准环境(StandardEnvironment)的功能,增加了对Servlet相关属性(如ServletConfig和ServletContext)的支持。
属性优先级:ServletConfig > ServletContext > JNDI > 系统属性 > 环境变量。
在应用上下文启动时,StandardServletEnvironment会将占位符属性(StubPropertySource)替换为实际的ServletConfig和ServletContext属性源。
public class StandardServletEnvironment extends StandardEnvironment implements ConfigurableWebEnvironment {
// ServletContext 初始化参数属性源的名称
public static final String SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletContextInitParams";
// ServletConfig 初始化参数属性源的名称
public static final String SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "servletConfigInitParams";
// JNDI 属性源名称
public static final String JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME = "jndiProperties";
// 防御性地引用 JNDI API,用于 JDK 9+(可选的 java.naming 模块)
private static final boolean jndiPresent = ClassUtils.isPresent(
"javax.naming.InitialContext", StandardServletEnvironment.class.getClassLoader());
public StandardServletEnvironment() {
}
protected StandardServletEnvironment(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
super(propertySources);
}
// 自定义属性源集合,添加超类贡献的属性源
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
// 添加 ServletConfig 初始化参数占位符属性源
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONFIG_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
// 添加 ServletContext 初始化参数占位符属性源
propertySources.addLast(new StubPropertySource(SERVLET_CONTEXT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
// 如果 JNDI 可用且默认环境可用,则添加 JNDI 属性源
if (jndiPresent && JndiLocatorDelegate.isDefaultJndiEnvironmentAvailable()) {
propertySources.addLast(new JndiPropertySource(JNDI_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME));
}
// 调用父类的自定义属性源方法
super.customizePropertySources(propertySources);
}
// 初始化属性源,将 Servlet 相关的属性源(如 ServletContext 和 ServletConfig)初始化为真实属性源
@Override
public void initPropertySources(@Nullable ServletContext servletContext, @Nullable ServletConfig servletConfig) {
WebApplicationContextUtils.initServletPropertySources(getPropertySources(), servletContext, servletConfig);
}
}
9、ApplicationServletEnvironment
AbstractEnvironment构造方法中会调用createPropertyResolver方法,也就是创建ApplicationServletEnvironment实例就会创建此自定义属性解析器,重写修改自定义属性解析器为ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertyResolver
class ApplicationServletEnvironment extends StandardServletEnvironment {
// 表示不从任何特定的属性(如 spring.profiles.active)获取活动配置文件
@Override
protected String doGetActiveProfilesProperty() {
return null;
}
// 表示不从任何特定的属性(如 spring.profiles.default)获取默认配置文件
@Override
protected String doGetDefaultProfilesProperty() {
return null;
}
// 自定义属性解析器,
// 默认使用ConfigurationPropertySources的实现,这里重写实现为ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertyResolver
@Override
protected ConfigurablePropertyResolver createPropertyResolver(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
return ConfigurationPropertySources.createPropertyResolver(propertySources);
}
}
三、配置环境
1、命令行参数属性源
// 4.2.配置环境
// 将命令行参数传递给环境配置
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 配置环境方法
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
// 如果需要添加转换服务,用于在应用程序中管理和执行各种类型之间的转换
if (this.addConversionService) {
// 设置转换服务为一个新的 ApplicationConversionService 实例
environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService());
}
// 配置属性源(将命令行参数添加到属性源集合中,放第一位优先级最高)
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 配置活动的配置文件,空实现
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
- 将
命令行参数属性源添加到环境的属性源集合中,且放第一位
/**
* 配置属性源的方法。
* @param environment 可配置的环境对象,用于管理属性源
* @param args 应用程序启动时传入的命令行参数
*/
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
// 获取当前环境中的属性源集合
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 如果存在默认属性(defaultProperties),将其添加或合并到属性源中
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.defaultProperties)) {
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.addOrMerge(this.defaultProperties, sources);
}
// 如果启用了命令行属性解析,并且命令行参数非空
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
// 获取命令行属性源的默认名称 “commandLineArgs”
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
// 如果当前属性源集合中已经包含命令行属性源,这里第一次进来不包含
if (sources.contains(name)) {
// 获取已存在的命令行属性源
PropertySource<?> source = sources.get(name);
// 创建一个组合属性源,用于合并新的和已有的命令行属性
CompositePropertySource composite = new CompositePropertySource(name);
// 将新的命令行参数解析为属性源并添加到组合属性源中
composite.addPropertySource(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource("springApplicationCommandLineArgs", args));
// 添加已有的命令行属性源到组合属性源中
composite.addPropertySource(source);
// 替换旧的命令行属性源为新的组合属性源
sources.replace(name, composite);
} else {
// 如果属性源集合中不存在命令行属性源,则直接将解析的命令行属性源添加到最前面
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
2、配置属性源
ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource这个类的作用是将 Spring 配置属性源(如 .properties 文件、.yml 文件、环境变量等)转换为一个统一的PropertySource,并将这些属性源集成到Spring的Environment中。具体解析内容后面单独讲
将名称为configurationProperties,对象为SpringConfigurationPropertySources的属性源添加到环境的属性源集合中,且放第一位,优先级最高。
// 4.2.配置环境
// 添加配置属性源到环境中,使其能够解析相关配置属性
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
public static void attach(Environment environment) {
// 确保传入的 environment 是 ConfigurableEnvironment 类型
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableEnvironment.class, environment);
// 获取当前环境的属性源集合
MutablePropertySources sources = ((ConfigurableEnvironment) environment).getPropertySources();
// 检查是否已经附加了名为“configurationProperties”的属性源
PropertySource<?> attached = getAttached(sources);
// 如果尚未附加,或者附加的属性源未正确使用当前属性源集合
if (attached == null || !isUsingSources(attached, sources)) {
// 创建一个新的 ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource,
// 它包装了当前的属性源集合
attached = new ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource(
ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME,
new SpringConfigurationPropertySources(sources)
);
}
// 移除已有的同名属性源(如果存在)
sources.remove(ATTACHED_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
// 将新的属性源添加到属性源集合的最前面,确保其具有最高优先级
sources.addFirst(attached);
}
四、触发的应用监听器
// 4.3.通知监听器,环境已准备好
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
在之前文章SpringBoot源码解析(三):启动开始阶段已经介绍过,广播器将特定的事件(之前的应用启动事件,现在这里就是准备环境事件)推给合适的监听器(匹配监听器的事件类型,这里就是匹配准备环境事件的监听器)。下面我们自己所有匹配到监听器的具体内容。
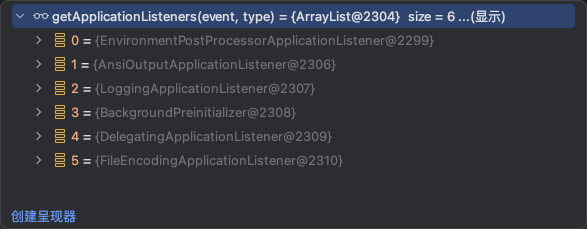
1、EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener
EnvironmentPostProcessorApplicationListener的作用是监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,加载并执行所有EnvironmentPostProcessor实现类,用于在SpringBoot应用启动过程中对环境配置 (Environment) 进行动态调整和扩展,例如加载额外的配置源、设置属性或修改激活的 profiles,确保在应用上下文初始化之前完成环境的定制化操作。
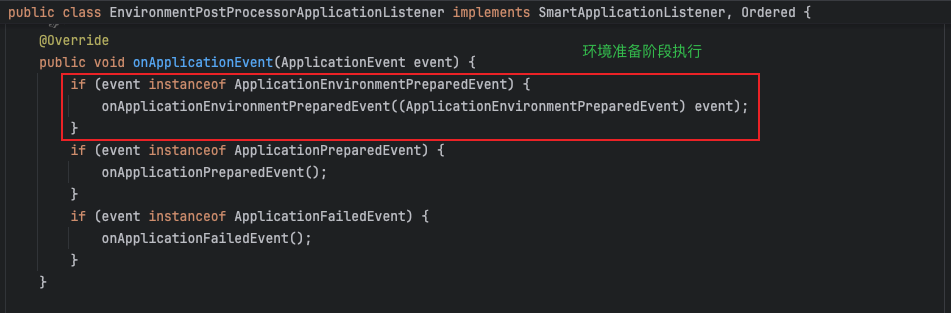
- 环境后置处理器
EnvironmentPostProcessor的实现类也是从META-INF/spring.factories文件中加载
// 当应用环境准备事件触发时执行的方法
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
// 获取应用的环境配置
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = event.getEnvironment();
// 获取 Spring 应用对象
SpringApplication application = event.getSpringApplication();
// 遍历所有的 EnvironmentPostProcessor(环境后置处理器)
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : getEnvironmentPostProcessors(application.getResourceLoader(),
event.getBootstrapContext())) {
// 调用每个后置处理器的 postProcessEnvironment 方法,处理环境配置
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(environment, application);
}
}
// 环境后置处理器接口
@FunctionalInterface
public interface EnvironmentPostProcessor {
void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application);
}
- 下面看下加载到的所有环境后置处理器
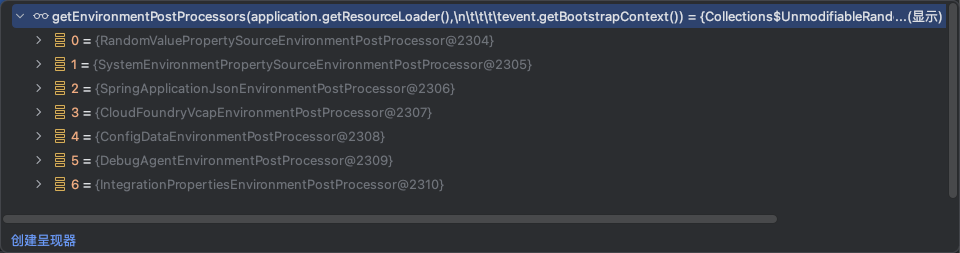
1.1、RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
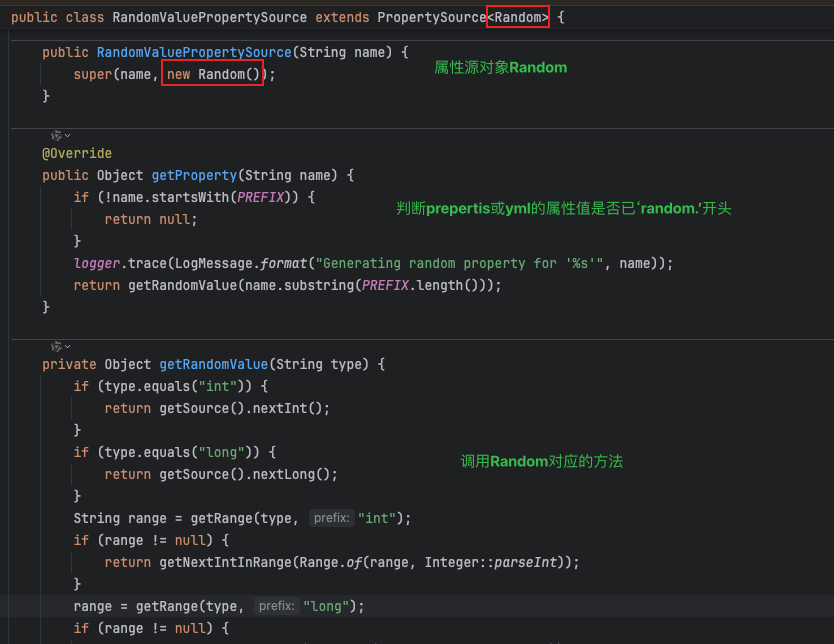
RandomValuePropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor是SpringBoot提供的一个内置类,用于在Spring应用程序启动时向环境中添加一个RandomValuePropertySource。
它通过 RandomValuePropertySource 提供生成随机值的功能(如随机字符串、整数或 UUID),供配置文件中使用。
- 生成随机值:
- 支持
random.int、random.long、random.uuid、random.value等 - 允许在配置文件中动态生成随机值,常用于密钥、端口号等需要唯一性或随机性的场景
- 支持
- 在配置文件中用法
# 动态生成一个 UUID my.secret.key=${random.uuid} # 一个介于 1024 和 65535 之间的随机整数 my.random.port=${random.int[1024,65535]}
RandomValuePropertySource原理很简单,就是讲属性源对象设置为new Random()
1.2、SystemEnvironmentPropertySourceEnvironmentPostProcessor
在上面环境实例ApplicationServletEnvironment实例化阶段,就添加了环境变量属性源SystemEnvironmentPropertySource,这里把它替换成OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource,主要目的是增强对配置属性来源的追踪能力,从而提升可维护性和调试性。
举例:
logging.level.org.springframework.core.env=DEBUG
2024-11-24 12:34:56.123 DEBUG o.s.b.c.c.ConfigFileApplicationListener - Loaded property source 'applicationConfig: [classpath:/application.properties]'
2024-11-24 12:34:56.124 DEBUG o.s.b.c.c.ConfigFileApplicationListener - Loaded property source 'applicationConfig: [classpath:/application.yml]'
2024-11-24 12:34:56.125 DEBUG o.s.b.e.e.PropertySourcesPropertyResolver - Found key 'my.app.port' in 'systemEnvironment' with value '8080'
1.3、SpringApplicationJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
作用是将环境变量SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON的JSON格式内容解析为配置属性。
举例:
export SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON='{"server.port":8081,"spring.datasource.url":"jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb"}'
java -jar my-app.jar
- 优先级通常高于文件配置(如 application.properties 或 application.yml)
- 在容器化部署(如 Kubernetes、Docker)中,环境变量是常见的配置传递方式
关键代码片段:
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplication application) {
String json = environment.getProperty("SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON");
if (StringUtils.hasText(json)) {
try {
Map<String, Object> map = parseJson(json);
PropertySource<?> propertySource = new MapPropertySource("spring.application.json", map);
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(propertySource);
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON: " + json, ex);
}
}
}
1.4、ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor
ConfigDataEnvironmentPostProcessor是SpringBoot2.4引入的一部分,作为Spring配置加载机制的新实现的核心组件。它取代了早期的ConfigFileApplicationListener,专注于从多种来源(如 application.properties、application.yml、环境变量等)加载配置数据。具体解析内容后面单独讲
2、AnsiOutputApplicationListener
AnsiOutputApplicationListener是SpringBoot提供的一个监听器,用于在应用启动时配置ANSI控制台输出(彩色日志或彩色信息) 的行为。它可以根据环境配置决定是否启用ANSI颜色支持,并设置相关属性。
3、BackgroundPreinitializer
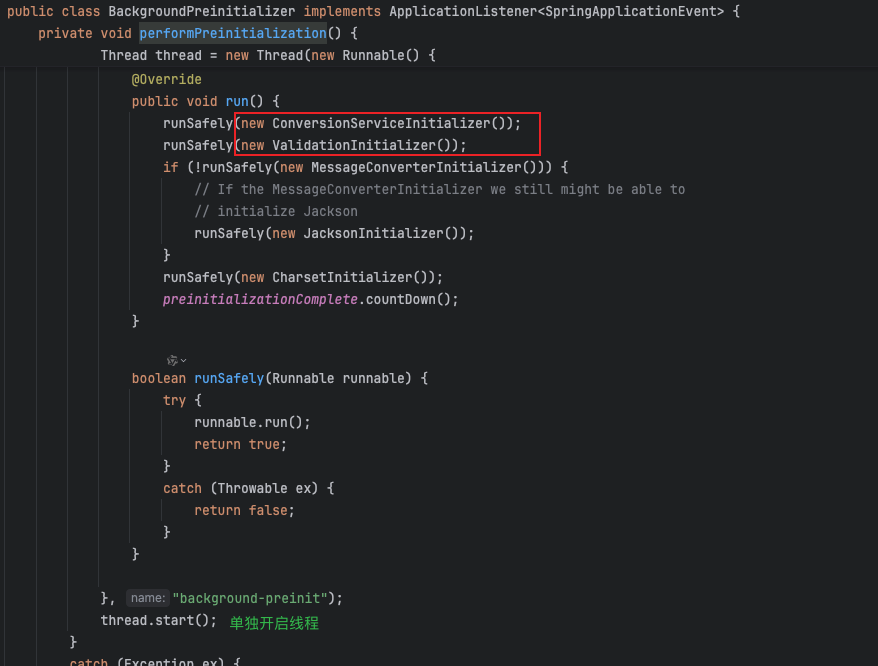
BackgroundPreinitializer是SpringBoot内置的一个类,用于在后台线程中异步加载某些耗时的初始化操作,从而减少应用主线程的阻塞时间,提高应用启动性能。
主线程可以专注于初始化Spring上下文,而耗时的操作(如 JUL日志桥接、默认的Validator实例化等)在后台进行,从而加快应用的总体启动速度。
4、FileEncodingApplicationListener
FileEncodingApplicationListener是SpringBoot的一个监听器,用于检测和验证 JVM 的文件编码(file.encoding)属性,确保其值符合应用程序的要求。如果文件编码未设置为期望的值,可能会引发警告或异常。
五、默认属性源
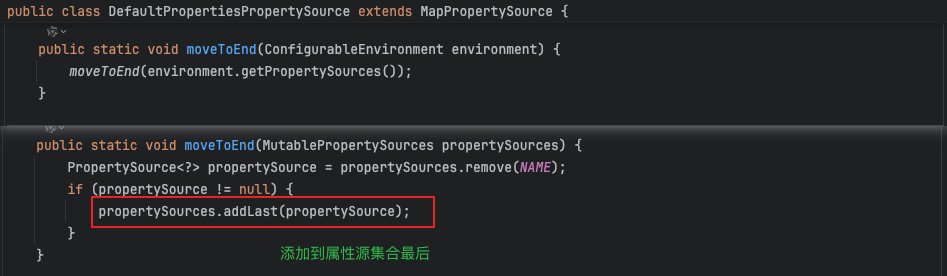
将DefaultProperties(默认属性源)移动到Spring环境(Environment)中属性源的最后面。这通常用于确保用户配置的属性(如文件配置、环境变量、命令行参数等)优先于默认属性,从而允许用户覆盖默认配置。
// 4.4.将默认属性源移到环境属性源列表的末尾
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
- SpringBoot默认情况下
没有添加默认属性源,用户可以自定义设置默认值
@Configuration
public class DefaultPropertyConfig {
@Bean
public PropertySource<?> defaultPropertySource() {
return new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", Map.of(
"server.port", "8080"
));
}
}
六、绑定spring.main配置到SpringApplication对象
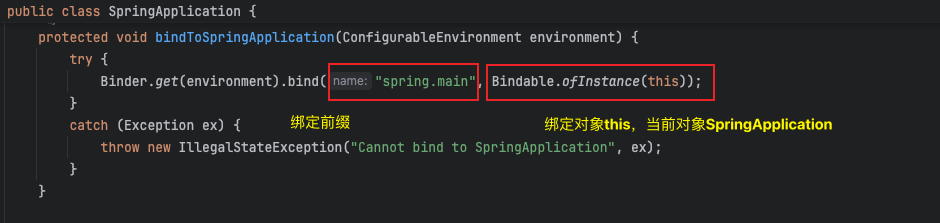
// 4.5.绑定spring.main环境配置到SpringApplication对象上
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
它的作用是从ConfigurableEnvironment中提取所有与spring.main前缀相关的配置,并将这些配置值赋值给SpringApplication类中的相应字段。
绑定的属性
| 属性名 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
spring.main.banner-mode | console | 启动横幅的显示模式,默认输出到控制台 |
spring.main.lazy-initialization | false | 是否启用懒加载模式 |
spring.main.log-startup-info | true | 是否输出启动日志信息 |
spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding | 环境决定(true 或 false) | 是否允许覆盖 Bean 定义 |
spring.main.web-application-type | 自动检测 | 应用类型:none、servlet 或 reactive |
spring.main.register-shutdown-hook | true | 是否注册 JVM 的关闭钩子(用于资源清理) |
总结
本文深入探讨了SpringBoot启动过程中应用环境的准备阶段,包括从配置文件、命令行参数、系统属性等多种配置源加载属性,以及对环境对象进行调整和绑定。通过SpringBoot的灵活机制,开发者可以轻松扩展和调整应用环境,从而满足各种复杂的场景需求。
