第 31 章 - 源码篇 - Elasticsearch 写入流程深入分析
写入源码分析
接收与处理
请求首先会被 Netty4HttpServerTransport 接收,接着交由 RestController 进行路由分发。
private void tryAllHandlers(final RestRequest request, final RestChannel channel, final ThreadContext threadContext) throws Exception {
// 从 tier 树中,找到该请求路径对应的 RestHandler
Iterator<MethodHandlers> allHandlers = getAllHandlers(request.params(), rawPath);
while (allHandlers.hasNext()) {
final RestHandler handler;
final MethodHandlers handlers = allHandlers.next();
if (handlers == null) {
handler = null;
} else {
handler = handlers.getHandler(requestMethod, restApiVersion);
}
if (handler == null) {
if (handleNoHandlerFound(rawPath, requestMethod, uri, channel)) {
return;
}
} else {
// 找到后,将本次请求转发给该 RestHandler
dispatchRequest(request, channel, handler, threadContext);
return;
}
}
}
那么 ES 如何知道对应的路由应该由谁处理呢?
在 Node 初始化时,会执行 ActionModule#initRestHandlers(...)
public void initRestHandlers(Supplier<DiscoveryNodes> nodesInCluster) {
...
...
// 注册路由
registerHandler.accept(new RestIndexAction());
...
...
}
RestIndexAction 注册的路由如下所示
public List<Route> routes() {
return List.of(
new Route(POST, "/{index}/_doc/{id}"),
new Route(PUT, "/{index}/_doc/{id}"),
Route.builder(POST, "/{index}/{type}/{id}").deprecated(TYPES_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE, RestApiVersion.V_7).build(),
Route.builder(PUT, "/{index}/{type}/{id}").deprecated(TYPES_DEPRECATION_MESSAGE, RestApiVersion.V_7).build()
);
}
每个 RestHandler 在 prepareRequest(final RestRequest request, final NodeClient client) 都会声明与之绑定的 TransportAction,之后所有逻辑会交由 TransportAction 处理。
其绑定的 TransportAction 为 TransportIndexAction。
RestIndexAction#prepareRequest(...)
public RestChannelConsumer prepareRequest(final RestRequest request, final NodeClient client) throws IOException {
...
...
return channel -> client.index(
indexRequest,
new RestStatusToXContentListener<>(channel, r -> r.getLocation(indexRequest.routing()))
);
}
AbstractClient#index(final IndexRequest request, final ActionListener<IndexResponse> listener)
@Override
public void index(final IndexRequest request, final ActionListener<IndexResponse> listener) {
execute(IndexAction.INSTANCE, request, listener);
}
对于写入类型的 TransportAction 在内部又会通过协调节点(接收客户端请求的就是协调节点)先将请求转发给对应主分片所在的节点,主分片节点写入后,主分片节点又会转发给副本分片,副本分片写入后,返回给主分片,主分片再返回给协调节点,最后协调节点返回给客户端。
整体流程如下图所示:
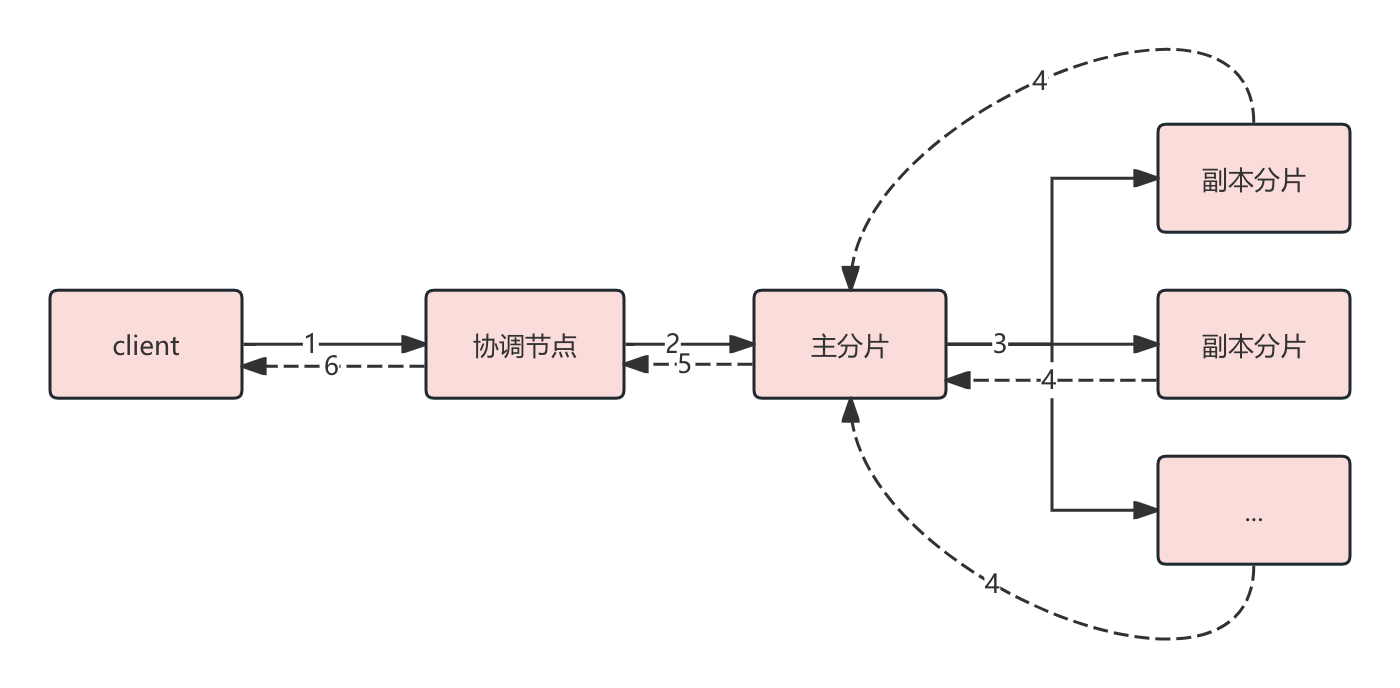
协调节点分发请求
上文 search 读流程有提到,TansportAction 定义了基本流程,每个子类实现 doExecute(...) 方法,自定义执行逻辑,因此我们只需要看 TransportIndexAction#doExecute(...) 即可。
不存在索引则创建
当索引不存在时,则会先创建索引,接着再执行写入操作。如果索引存在,则直接执行写入操作。
TransportBulkAction#doInternalExecute(...)
protected void doInternalExecute(Task task, BulkRequest bulkRequest, String executorName, ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener) {
for (String index : autoCreateIndices) {
// 创建索引
createIndex(index, bulkRequest.timeout(), minNodeVersion, new ActionListener<>() {
@Override
public void onResponse(CreateIndexResponse result) {
// 创建索引成功回调函数,
if (counter.decrementAndGet() == 0) {
// 执行写入操作
threadPool.executor(executorName).execute(new ActionRunnable<>(listener) {
@Override
protected void doRun() {
executeBulk(
task,
bulkRequest,
startTime,
listener,
executorName,
responses,
indicesThatCannotBeCreated
);
}
});
}
}
}
}
}
executeBulk(..) 方法内部会创建 BulkOperation 交由该类做处理
void executeBulk(
Task task,
BulkRequest bulkRequest,
long startTimeNanos,
ActionListener<BulkResponse> listener,
String executorName,
AtomicArray<BulkItemResponse> responses,
Map<String, IndexNotFoundException> indicesThatCannotBeCreated
) {
new BulkOperation(task, bulkRequest, listener, executorName, responses, startTimeNanos, indicesThatCannotBeCreated).run();
}
BulkOperation 继承自 AbstractRunnable。AbstractRunnable 定义了执行的基本流程,子类需要实现 doRun() 方法,因此,只需要关注 BulkOperation#doRun() 方法。
路由计算
BulkOperation#doRun()
protected void doRun() {
// 获取路由计算规则
IndexRouting indexRouting = concreteIndices.routing(concreteIndex);
}
IndexRouting#fromIndexMetadata(...)
public static IndexRouting fromIndexMetadata(IndexMetadata indexMetadata) {
// 索引配置上是否设置 routing_path
if (false == indexMetadata.getRoutingPaths().isEmpty()) {
if (indexMetadata.isRoutingPartitionedIndex()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("routing_partition_size is incompatible with routing_path");
}
return new ExtractFromSource(
indexMetadata.getRoutingNumShards(),
indexMetadata.getRoutingFactor(),
indexMetadata.getIndex().getName(),
indexMetadata.getRoutingPaths()
);
}
// 索引配置上是否设置了分区索引相关参数
if (indexMetadata.isRoutingPartitionedIndex()) {
return new Partitioned(
indexMetadata.getRoutingNumShards(),
indexMetadata.getRoutingFactor(),
indexMetadata.getRoutingPartitionSize()
);
}
// 正常写入
return new Unpartitioned(indexMetadata.getRoutingNumShards(), indexMetadata.getRoutingFactor());
}
上诉 3 个路由算法,底层算法都是类似的,都是基于一致性 hash 计算对应的路由。
hash 计算函数 Murmur3HashFunction#hash(String routing)
我们可以简单将路由算法理解为如下:
- 先计算 hash
- 再根据 hash 计算路由
计算 hash 可以又分为以下几种情况:
- 如果索引配置了 routing_path,则 hash = Murmur3HashFunction#hash(routing_path_value)
- 如果路径上有路由参数,则 hash = Murmur3HashFunction#hash(routing)
- 否则 hash = Murmur3HashFunction#hash(_id)
根据 hash 计算路由的规则如下:
IndexRouting#hashToShardId(...)
protected final int hashToShardId(int hash) {
return Math.floorMod(hash, routingNumShards) / routingFactor;
}
- routingNumShards
值默认依赖主分片数(number_of_shards),如果创建索引时未指定,默认按因子2拆分,并且最多可拆分为1024个分片。例如原索引主分片数为1,则可拆分为1~1024中的任意数;原索引主分片为5,则支持拆分的分片数为:10、20、40、80、160、320以及最大数640(不能超过1024)。 可通过索引的index.number_of_routing_shards配置,但不建议配置。 - routingFactor
默认为routingNumShards/number_of_shards
简单说,你可以将 number_of_routing_shards 理解为虚拟的分片数、 number_of_shards 则为物理的分片数。其本质就是 一致性 hash。
分发请求至主分片
TransportReplicationAction#doExecute(...)
@Override
protected void doExecute(Task task, Request request, ActionListener<Response> listener) {
assert request.shardId() != null : "request shardId must be set";
runReroutePhase(task, request, listener, true);
}
ReroutePhase#doRun()
protected void doRun() {
if (primary.currentNodeId().equals(state.nodes().getLocalNodeId())) {
// 主分片节点在协调节点上
performLocalAction(state, primary, node, indexMetadata);
} else {
// 主分片节点不在协调节点上
performRemoteAction(state, primary, node);
}
}
主分片写入
接收请求
TransportReplicationAction 构造函数,注册了主分片写入的处理函数
protected TransportReplicationAction(
...
...
) {
transportService.registerRequestHandler(
transportPrimaryAction,
executor,
forceExecutionOnPrimary,
true,
in -> new ConcreteShardRequest<>(requestReader, in),
this::handlePrimaryRequest
);
}
主分片写入
TransportShardBulkAction#dispatchedShardOperationOnPrimary(...)
@Override
protected void dispatchedShardOperationOnPrimary(
BulkShardRequest request,
IndexShard primary,
ActionListener<PrimaryResult<BulkShardRequest, BulkShardResponse>> listener
) {
...
...
// 在主分片上执行
performOnPrimary(request, primary, updateHelper, threadPool::absoluteTimeInMillis, (update, shardId, mappingListener) -> {
...
}), listener, threadPool, executor(primary));
}
异步转发请求至副本分片
转发请求至副本分片,是在主分片写入数据后,才执行的
ReplicationOperation#execute(...)
public void execute() throws Exception {
...
...
// 执行主分片写入
primary.perform(request, ActionListener.wrap(this::handlePrimaryResult, this::finishAsFailed));
}
handlePrimaryResult() 方法是写入主分片后的回调函数
ReplicationOperation#handlePrimaryResult(..)
private void handlePrimaryResult(final PrimaryResultT primaryResult) {
...
// 异步发送同步副本分片请求
performOnReplicas(replicaRequest, globalCheckpoint, maxSeqNoOfUpdatesOrDeletes, replicationGroup, pendingReplicationActions);
...
}
副本分片写入
接收请求
类似的,TransportReplicationAction 构造函数,注册了副本分片写入的处理函数
transportService.registerRequestHandler(
transportReplicaAction,
executor,
true,
true,
in -> new ConcreteReplicaRequest<>(replicaRequestReader, in),
this::handleReplicaRequest
);
数据写入
而后请求交给 AsyncReplicaAction#doRun() 处理
@Override
protected void doRun() throws Exception {
...
...
// 获取写入许可后,会回调至 AsyncReplicaAction#onResponse()
acquireReplicaOperationPermit(
replica,
replicaRequest.getRequest(),
this,
replicaRequest.getPrimaryTerm(),
replicaRequest.getGlobalCheckpoint(),
replicaRequest.getMaxSeqNoOfUpdatesOrDeletes()
);
}
AsyncReplicaAction#onResponse()
@Override
public void onResponse(Releasable releasable) {
...
// 执行写入
shardOperationOnReplica(...);
...
}
调用该函数后,最后代码会走到 TransportShardBulkAction#dispatchedShardOperationOnReplica(...)
@Override
protected void dispatchedShardOperationOnReplica(BulkShardRequest request, IndexShard replica, ActionListener<ReplicaResult> listener) {
ActionListener.completeWith(listener, () -> {
final long startBulkTime = System.nanoTime();
// 执行写入
final Translog.Location location = performOnReplica(request, replica);
replica.getBulkOperationListener().afterBulk(request.totalSizeInBytes(), System.nanoTime() - startBulkTime);
return new WriteReplicaResult<>(request, location, null, replica, logger);
});
}
