刷算法题
文章目录
- 1.模拟
- 1.switch case 与 if else 的区别
- 2.格式化输入输出: `scanf("%4d")` 只读取4个长度的int
- 2.排序
- 1.sort(arr,arr+n,comp)
- 2.set
- 3.查找
- 1.结构体数组
- 4.字符串
- 1.string和int的相互转换
- 2.map[key]++
- 3.getline()
- getline(cin,str)一行字符串后,基于空格分割单词
- 4.ASCII码表
- 5.memset()
- 6.getchar() //吃掉回车
- 7.用vector保存多个字符串
- 8.swap()函数
- 9.string之erase()
- 5.数学问题
- 1.求最大公约数 gcd()
- 2.求a^b:pow(a,b)
- 3.求绝对值:abs(i)
- 4.大数问题
- 5.进制转换
- 6.求素数
- 7.完全数
- 6.递归
- 7.动态规划
- 1.输入n,读取n个数
- 2.max()、std::max()
1.模拟
1.xxx定律
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int count = 0;
while(n != 1){
if(n%2 ==0){//n为偶数
n = n/2;
}else{//n为奇数
n = (3*n+1)/2;
}
count++;
}
printf("%d\n",count);
}
return 0;
}
2.学分绩点 (求GPA)
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/a0c09a7e0da04e728810a8aca7226b7b

#include <cstdio>
float getGradeClass(int grade){
float gradeclass;
if( 90<=grade && grade<=100){
gradeclass = 4.0;
}else if(85<=grade && grade<=89){
gradeclass = 3.7;
}else if(82<=grade && grade<=84){
gradeclass = 3.3;
}else if(78<=grade && grade<=81){
gradeclass = 3.0;
}else if(75<=grade && grade<=77){
gradeclass = 2.7;
}else if(72<=grade && grade<=74){
gradeclass = 2.3;
}else if(68<=grade && grade<=71){
gradeclass = 2.0;
}else if(64<=grade && grade<=67){
gradeclass = 1.5;
}else if(60<=grade && grade<=63){
gradeclass = 1.0;
}else{
gradeclass = 0;
}
return gradeclass;
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int credit[10];//学分
int sum_credit = 0;//总学分
int grade[10];//单科成绩
float gradeclass[10];//成绩对应的绩点
float subjectclass[10];//学科绩点 = 成绩对应绩点*学分
float sum_subjectclass = 0;//学科绩点之和
//输入学分
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&credit[i]);
sum_credit += credit[i];
}
//输入成绩
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&grade[i]);
gradeclass[i] = getGradeClass(grade[i]);
subjectclass[i] = gradeclass[i]*credit[i];
sum_subjectclass += subjectclass[i];
}
float GPA = sum_subjectclass/sum_credit;
printf("%0.2f",GPA);
return 0;
}
1.switch case 与 if else 的区别
if else需要从头到尾遍历每个if,但switch会直接找到对应的case。
- 当分支较多时,switch case效率更高
- if else更灵活,应用场景更多
所以,switch case是if else在特定情形下的优化。
学习网址:http://m.biancheng.net/view/171.html
switch的一般形式如下:
switch (表达式)
{
case 常量表达式1: 语句1
case 常量表达式2: 语句2
┇
case 常量表达式n: 语句n
default: 语句n+1
}
举例:
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int val; //variable的缩写, “变量”的意思
printf("请输入您想去的楼层:");
scanf("%d", &val);
switch (val)
{
case 1:
printf("1层开!\n");
break;
case 2:
printf("2层开!\n");
break;
case 3:
printf("3层开!\n");
break;
default:
printf("该层不存在, 请重新输入\n");
}
return 0;
}
3.加减乘除

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/fdc56f9b00b34c70ad36c61ef89e3fc3
解法1:if else
#include <cstdio>
long long int Factorial(int n){
if(n == 0){
return 1;
}else{
return n*Factorial(n-1);
}
}
int main(){
int a,c;
char b;
while(scanf("%d %c",&a,&b) != EOF){
if(b == '+'){
scanf("%d",&c);
printf("%d\n",a+c);
}else if(b == '-'){
scanf("%d",&c);
printf("%d\n",a-c);
}else if(b == '*'){
scanf("%d",&c);
printf("%d\n",a*c);
}else if(b == '!'){
printf("%lld\n",Factorial(a));
}else if(b == '/'){
scanf("%d",&c);
if(c == 0){
printf("error\n");
}else{
printf("%d\n",a/c);
}
}else if(b == '%'){
scanf("%d",&c);
if(c == 0){
printf("error\n");
}else{
printf("%d\n",a%c);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
解法2:switch case
#include <cstdio>
long long int Factorial(int n){
if(n == 0){
return 1;
}else{
return n*Factorial(n-1);
}
}
int main(){
int a,c;
char b;
while(scanf("%d %c",&a,&b) != EOF){
if(b == '!'){
printf("%lld\n",Factorial(a));
}else{
scanf("%d",&c);
switch(b){
case '+':
printf("%d\n",a+c);
break;
case '-':
printf("%d\n",a-c);
break;
case '*':
printf("%d\n",a*c);
break;
case '/':
if(c == 0){
printf("error\n");
}else{
printf("%d\n",a/c);
}
break;
case '%':
if(c == 0){
printf("error\n");
}else{
printf("%d\n",a%c);
}
break;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
4.统计同成绩学生人数
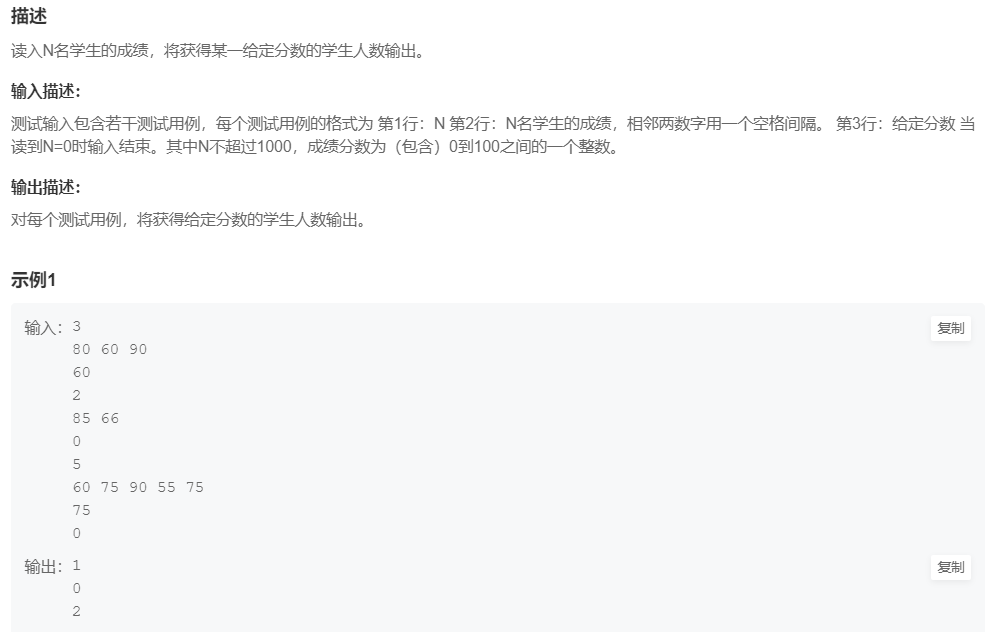
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/987123efea5f43709f31ad79a318ca69
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
int arr[1001];
int target;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
if(n <= 0){
//do nothing
}else{ //n>0
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
scanf("%d",&target);
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if(arr[i] == target){
num++;
}
}
printf("%d\n",num);
}
}
return 0;
}
5.数字之和

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ae759916631f4711a90c4d4d9657f4b0
解法1:非常麻烦地把数字n的每一位保存进数组中
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void sum1(int n){
string str = to_string(n);
int arr[400000];
int len = str.length();
for(int i = len; i >= 0; --i){
arr[i-1] = n%10;
n = n/10;
}
int sum1 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
sum1 += arr[i];
}
printf("%d ",sum1);
}
void sum2(int n){
int sn = n*n;
string str = to_string(sn);
int arr[400000];
int len = str.length();
for(int i = len; i >= 0; --i){
arr[i-1] = sn%10;
sn = sn/10;
}
int sum2 = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
sum2 += arr[i];
}
printf("%d\n",sum2);
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
sum1(n);
sum2(n);
}
return 0;
}
解法2:直接求每位和,不用保存到数组中
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
long long int sn = n*n;
int sum1 = 0,sum2 =0;
while(n){
sum1 += n%10; //根本不需要把每一位存入数组中
n/= 10;
}
printf("%d ",sum1);
while(sn){
sum2 += sn%10;
sn /= 10;
}
printf("%d\n",sum2);
}
return 0;
}
6.计算两个矩阵的乘积

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ed6552d03e624ba58d16af6d57e1c3e9
解法1:暴力解
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int a11,a12,a13,a21,a22,a23;
int b11,b12,b21,b22,b31,b32;
int c11,c12,c21,c22;
scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d",
&a11,&a12,&a13,&a21,&a22,&a23,
&b11,&b12,&b21,&b22,&b31,&b32);
c11 = a11*b11 + a12*b21 + a13*b31;
c12 = a11*b12 + a12*b22 + a13*b32;
c21 = a21*b11 + a22*b21 + a23*b31;
c22 = a21*b12 + a22*b22 + a23*b32;
printf("%d %d\n%d %d\n",c11,c12,c21,c22);
return 0;
}
解法2:二维数组
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
int x[2][3];
int y[3][2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
scanf("%d", &x[i][j]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 2; j++) {
scanf("%d", &y[i][j]);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
printf("%d %d\n", x[i][0]*y[0][0] + x[i][1]*y[1][0] + x[i][2]*y[2][0],
x[i][0]*y[0][1] + x[i][1]*y[1][1] + x[i][2]*y[2][1]);
}
return 0;
}
7.ZOJ (简单)
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/7557d470617c464f9200d93acf721471
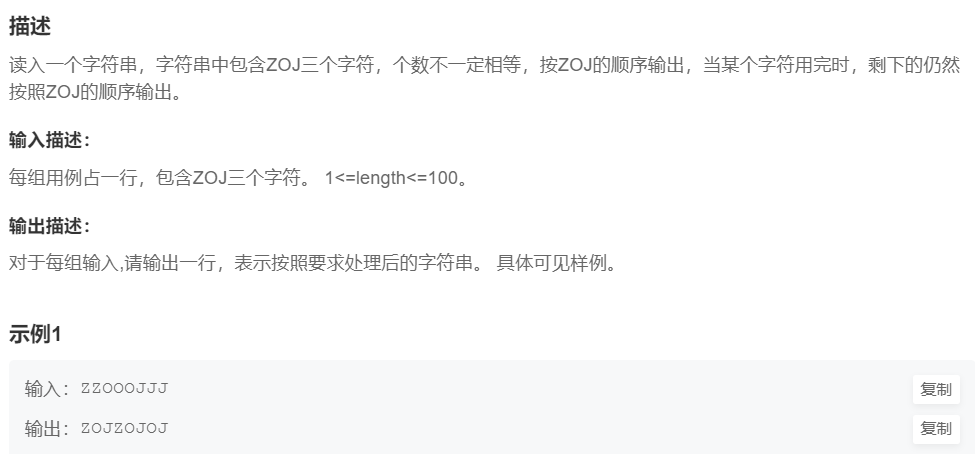
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string ZOJ;
int Z = 0,O = 0,J = 0;
while(cin>>ZOJ){
int len = ZOJ.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
if(ZOJ[i] == 'Z') Z++;
if(ZOJ[i] == 'O') O++;
if(ZOJ[i] == 'J') J++;
}
//按照ZOJ顺序输出
while(Z>0 || O>0 || J>0){
if(Z>0){
cout << "Z";
Z--;
}
if(O>0){
cout << "O";
O--;
}
if(J>0){
cout << "J";
J--;
}
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
8.日期类(中等)
提交网址
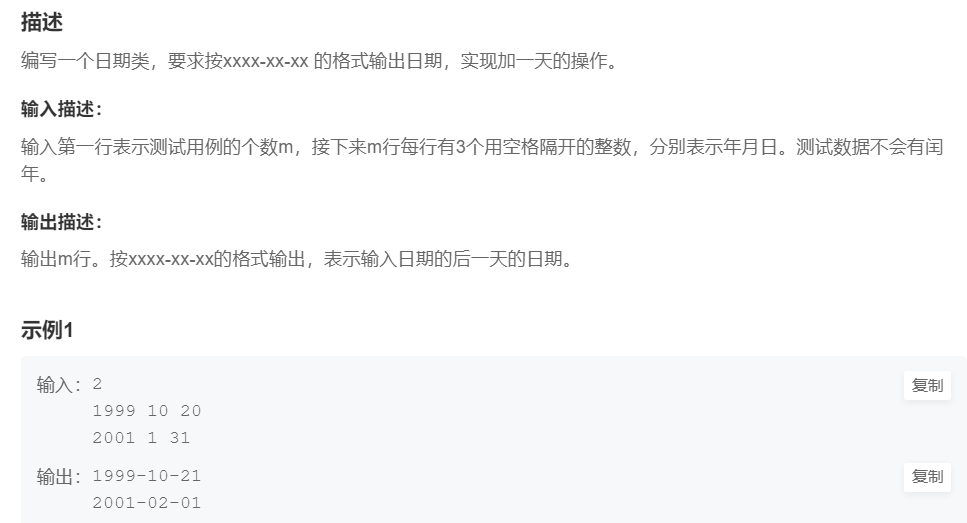
解法1:纯模拟
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
int year,month,day;
scanf("%d %d %d",&year,&month,&day);
if(month == 2){//2月只有28天
if(day == 28){
day = 1;
month++;
}else{ //day < 28
day++;
}
}else if(month==4 || month==6 || month==9 || month==11 ){//4、6、9、11只有30天
if(day == 30){
day = 1;
month++;
}else{ //day < 30
day++;
}
}else{//1、3、5、7、8、10、12月有31天
if(month==12 && day==31){ //12月要跨年
day = 1;
month = 1;
year++;
}else{
if(day == 31){
day = 1;
month++;
}else{ //day < 31
day++;
}
}
}
string smonth,sday;
if(month<10){
smonth = '0'+to_string(month);
}else{
smonth = to_string(month);
}
if(day<10){
sday = '0'+to_string(day);
}else{
sday = to_string(day);
}
printf("%d-%s-%s\n",year,smonth.c_str(),sday.c_str());
}
}
return 0;
}
2.格式化输入输出: scanf("%4d") 只读取4个长度的int
2.排序
1.小白鼠排队
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/27fbaa6c7b2e419bbf4de8ba60cf372b
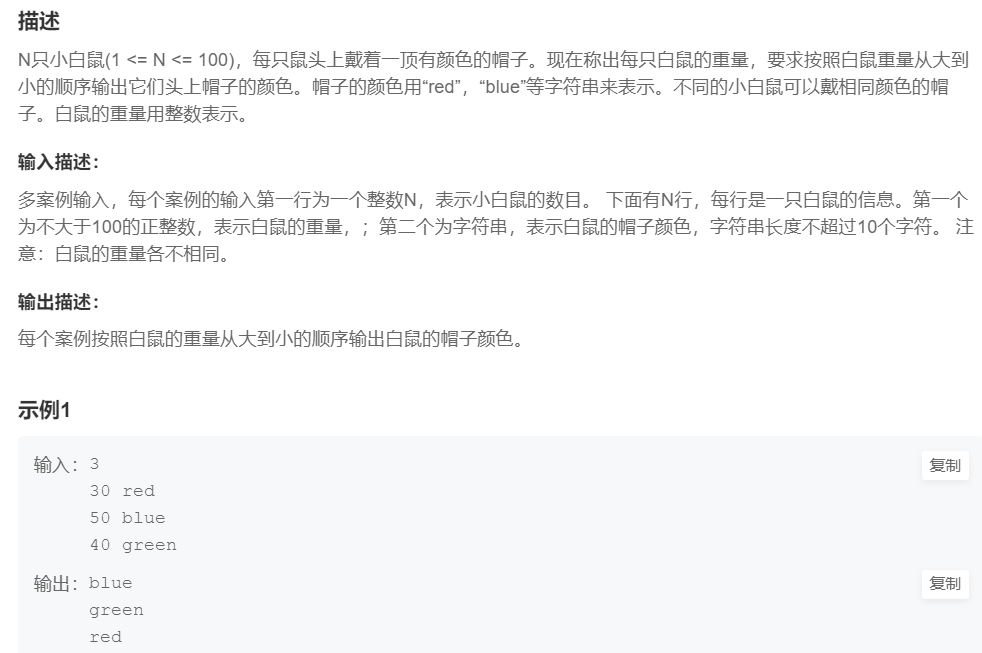
1.sort(arr,arr+n,comp)
解法1:结构体+排序(结构体数组+自定义排序规则)
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Mouse{
int weight;
string color;
};
bool comp(Mouse lhs,Mouse rhs){
return lhs.weight>rhs.weight;
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int weight;
char color1[100];
Mouse arr[100];
for(int i = 0; i < n ;++i){
scanf("%d %s",&weight,color1);
string color = color1;
arr[i].weight = weight;
arr[i].color = color;
}
sort(arr,arr+n,comp);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
printf("%s\n",arr[i].color.c_str());
}
return 0;
}
解法2:map自动排序
#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <string>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
map<int,string,greater<int>> Mouse;
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int weight;
char color[100];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d %s",&weight,color);
string color1 = color;
Mouse.insert(pair<int,string>(weight,color1));
}
map<int,string>::iterator it;
for(it = Mouse.begin();it != Mouse.end();++it){
printf("%s\n",it->second.c_str());
}
return 0;
}
2.set
2.Simple Sorting
题目大义:给一串数字,去重后进行排序

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/139761e0b59a405786898b7f2db9423f
解法:STL之set(自动去重+升序排序)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int a;
set<int> num;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&a);
num.insert(a);
}
set<int>::iterator it;
for(it = num.begin();it != num.end();++it){
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
3.寻找大富翁

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/38131e23663746a992581d45f16e7a86
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool comp(int lhs, int rhs) {
return lhs > rhs; //降序排序
}
int main() {
int n, m;
while (scanf("%d %d", &n, &m) != EOF) {
int arr[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d", &arr[i]);
}
sort(arr, arr + n, comp);
if (n>m) {
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}else{ //n<m
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
printf("%d ",arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
4.成绩排序
提交网址

易错点(bug原因):C字符数组不能直接比较大小,只有C++的string才可以直接比大小。
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Student{
string name;
int age;
int grade;
};
bool comp(Student lhs, Student rhs){
if(lhs.grade < rhs.grade){ //1.按成绩
return true;
}else if(lhs.grade == rhs.grade && lhs.name < rhs.name){ //2.按名字
return true;
}else if(lhs.grade == rhs.grade && lhs.name == rhs.name && lhs.age < rhs.age){//3.按年龄
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
Student stu[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
char cname[101];
scanf("%s %d %d",&cname,&stu[i].age,&stu[i].grade);
stu[i].name = cname;
}
sort(stu,stu+n,comp);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
printf("%s %d %d\n",stu[i].name.c_str(),stu[i].age,stu[i].grade);
}
}
return 0;
}
5.成绩排序(困难,实际中等)
提交网址:http://t.cn/E9gyHM1

解题思路:结构体里还需要保存 输入的次序 order,以便在成绩相同时按order升序排序
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct Student{
string name;
int grade;
int order; //输入的次序
};
bool comp0(Student lhs,Student rhs){ //按成绩降序
if(lhs.grade > rhs.grade){
return true;
}else if(lhs.grade == rhs.grade){
return lhs.order < rhs.order;
}else{
return false;
}
}
bool comp1(Student lhs,Student rhs){ //按成绩升序
if(lhs.grade < rhs.grade){
return true;
}else if(lhs.grade == rhs.grade){
return lhs.order < rhs.order;
}else{
return false;
}
}
int main(){
int n,rule;
while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&rule) != EOF){
//1.输入
Student stu[n]; //申请长度为n的结构体数组
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
char cname[100];
scanf("%s %d",cname,&stu[i].grade);
stu[i].name = cname; //C字符数组转string
stu[i].order = i; //保存输入的次序,便于在成绩相同时,按order升序排序
}
//2.排序
if(rule == 0){ //降序
sort(stu,stu+n,comp0);
}else{ //rule ==1,升序
sort(stu,stu+n,comp1);
}
//3.输出
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
printf("%s %d\n",stu[i].name.c_str(),stu[i].grade);
}
}
return 0;
}
3.查找
1.找x (数组)
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/069e2130430c41229ab25e47fa0949a6
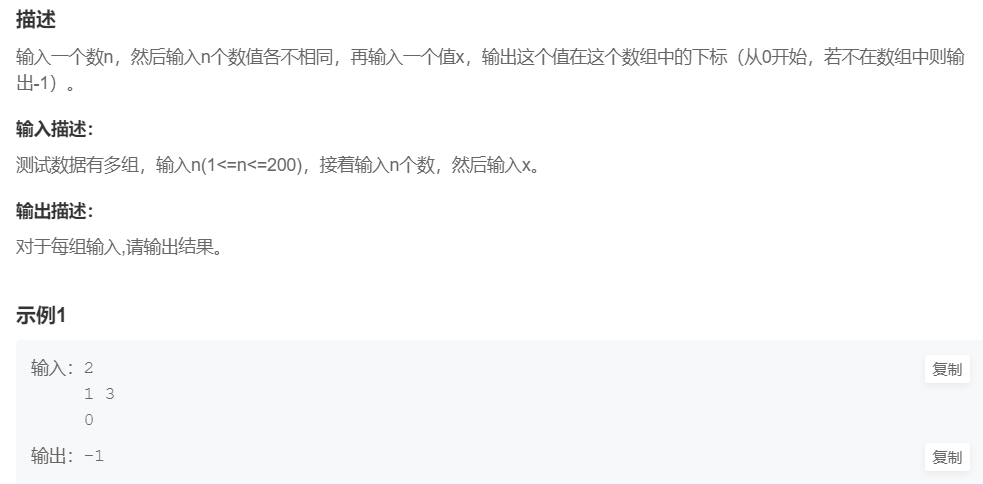
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int arr[300];
for(int i =0;i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
int x;
scanf("%d",&x);
bool flag = false;
for(int i =0; i < n; ++i){
if(arr[i] == x){
printf("%d",i);
flag = true;//找到了
}
}
if(flag == false){//没找到
printf("-1");
}
return 0;
}
2.求最大最小数
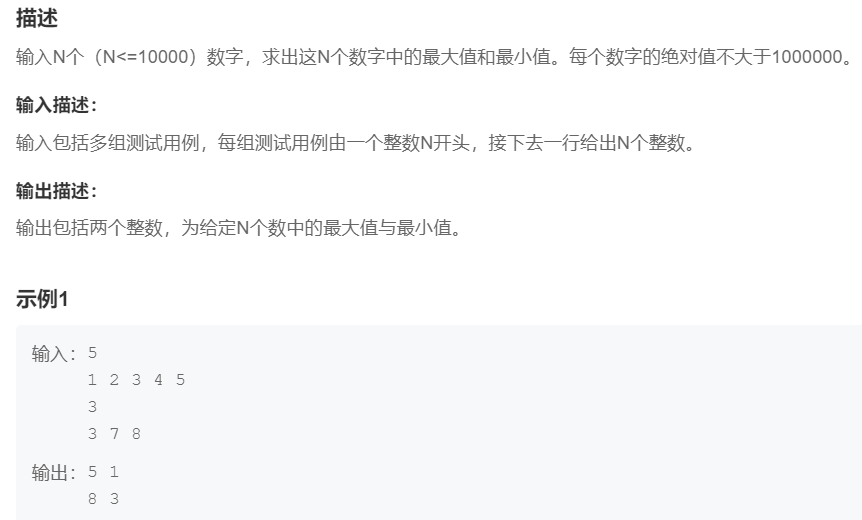
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/82e5ff335eeb486aab359767895cc7b4
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int arr[n];
for(int i =0 ;i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
sort(arr,arr+n);
printf("%d %d\n",arr[n-1],arr[0]);
}
return 0;
}
3.开门人和关门人
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/a4b37b53a44d454ab0834e1517983215
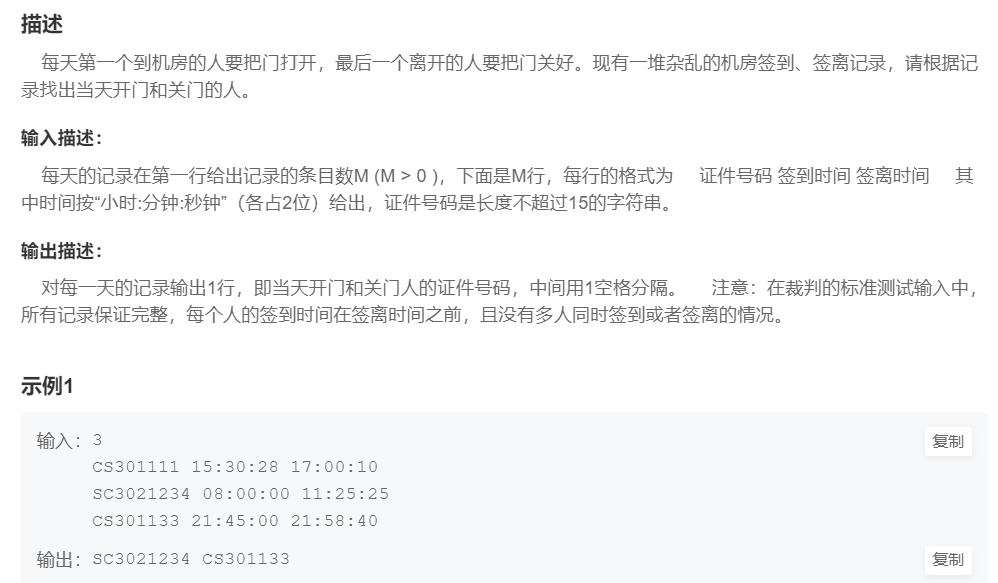
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
string id,signIn,signOut;
string openId,closeId;
string signInTime = "24:00:00",signOutTime = "00:00:00";
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
cin >> id >> signIn >> signOut;
//最早来
if(signIn < signInTime){
signInTime = signIn;
openId = id;
}
//最晚走
if(signOut > signOutTime){
signOutTime = signOut;
closeId = id;
}
}
cout << openId << " " << closeId<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
4.查找 (Easy)
提交网址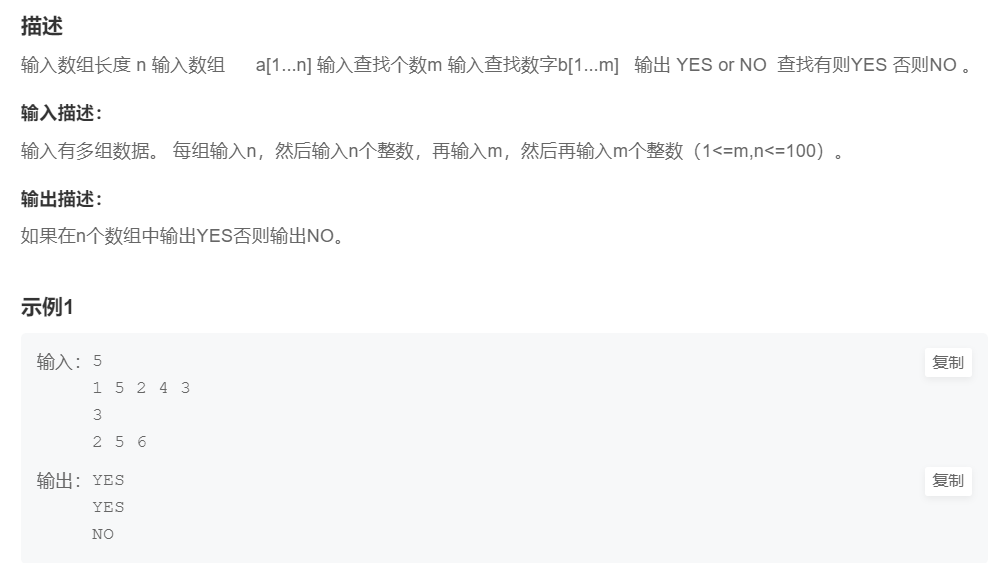
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int arr[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n ; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
int m;
int target;
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
scanf("%d",&target);
//顺序查找
int flag = false;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if(arr[i] == target){
flag = true;
}
}
if(flag){ //找到了
printf("YES\n");
}else{
printf("NO\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
1.结构体数组
struct Student{
int Number;
char Name[100];
char sex[20];
int age;
};
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
Student stu[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d %s %s %d",&stu[i].Number,&stu[i].Name,&stu[i].sex,&stu[i].age);
}
5.学生查询(中等)
提交网址
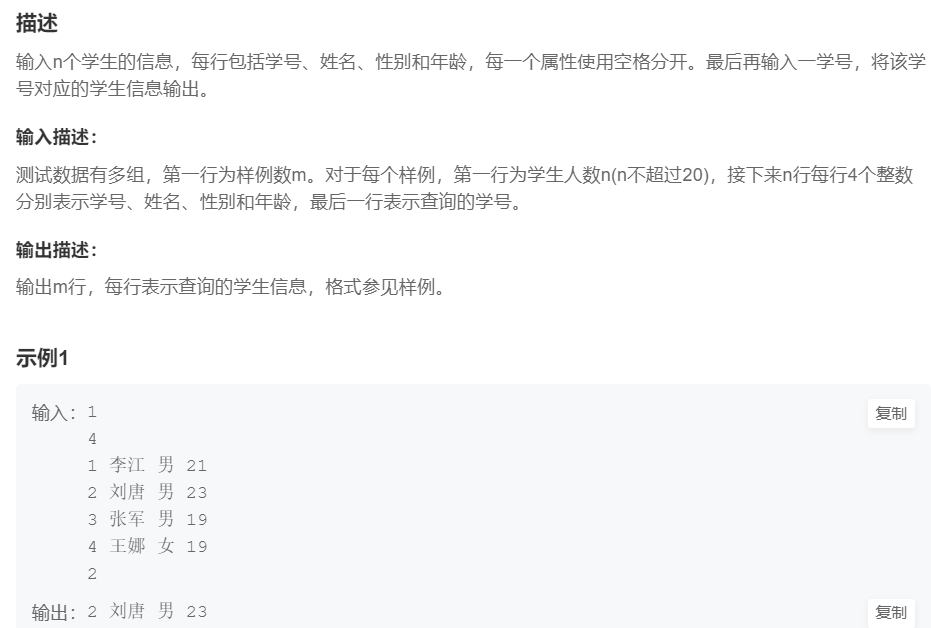
#include <cstdio>
struct Student{
int Number;
char Name[100];
char sex[20];
int age;
};
int main(){
int m;
scanf("%d",&m);
for(int i = 0; i < m; ++i){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
Student stu[n+1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; ++i){
scanf("%d %s %s %d",
&stu[i].Number,&stu[i].Name,&stu[i].sex,&stu[i].age);
}
int id;
scanf("%d",&id);
printf("%d %s %s %d\n",
stu[id].Number,stu[id].Name,stu[id].sex,stu[id].age);
}
return 0;
}
6.找最小数
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ba91786c4759403992896d859e87a6cd
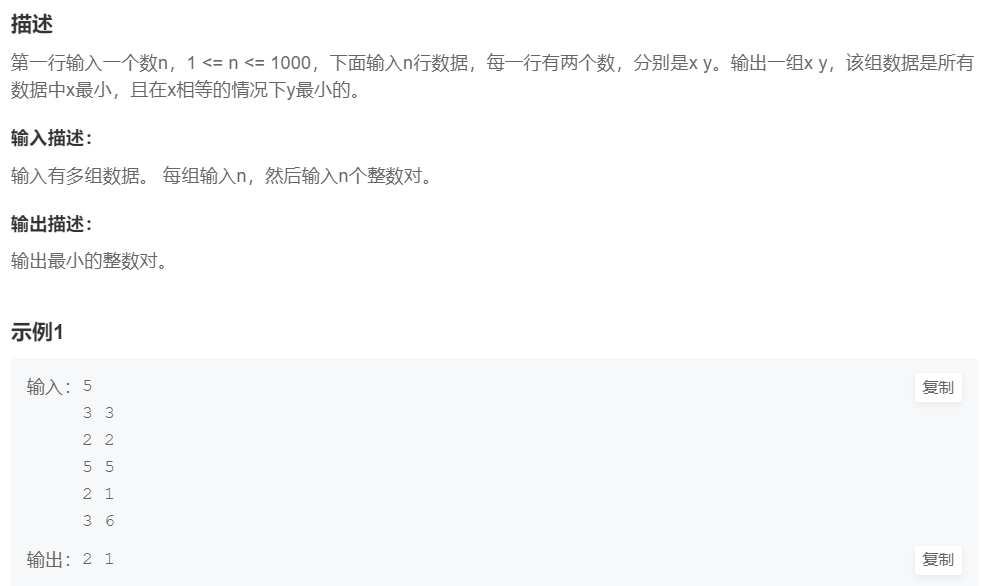
解法1:结构体数组+sort
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct XY{
int x;
int y;
};
bool comp(XY lhs,XY rhs){
if(lhs.x < rhs.x){
return true;
}else if(lhs.x == rhs.x && lhs.y < rhs.y){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
XY arr[2000];//结构体数组
for(int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d %d",&arr[i].x,&arr[i].y);
}
sort(arr,arr+n,comp);//结构体数组排序
printf("%d %d",arr[0].x,arr[0].y);
return 0;
}
4.字符串
1.字符串排序
提交地址
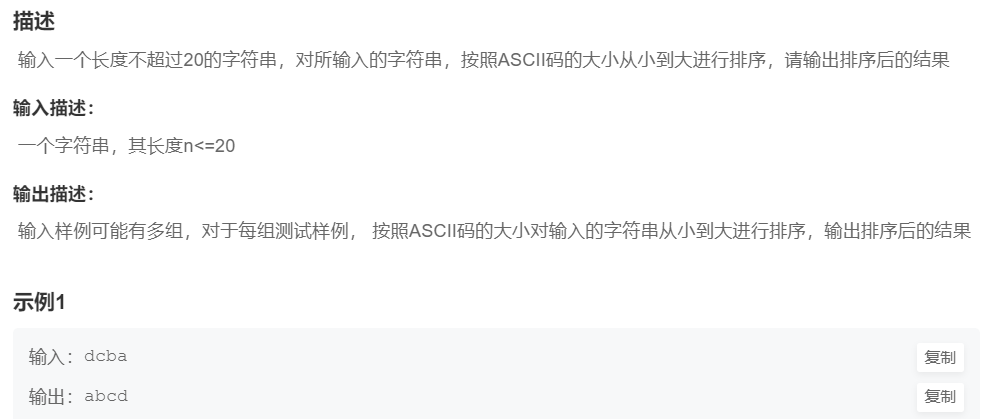
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
while (cin >> str) {
sort(str.begin(),str.end());
cout <<str<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
2.后缀子串排序
提交网址
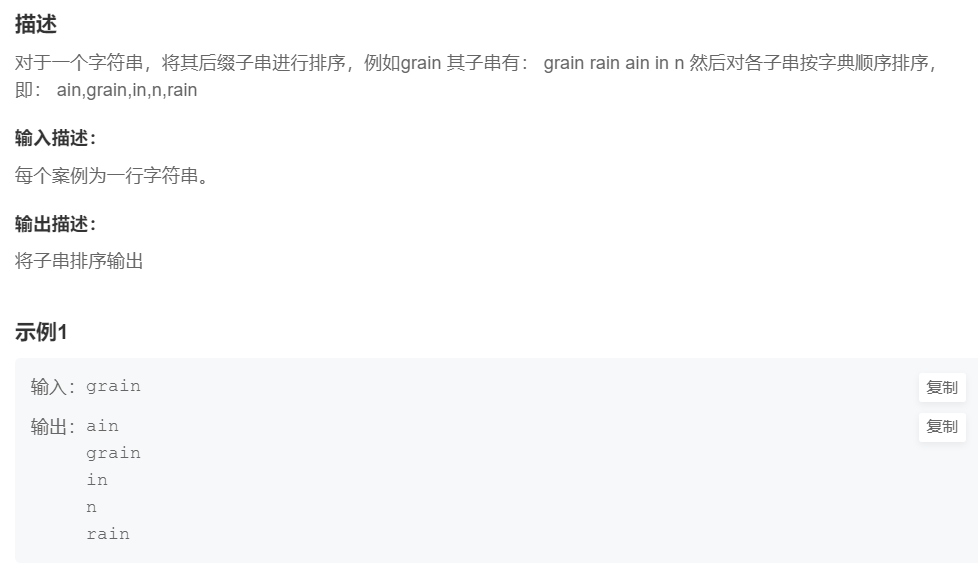
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
cin >> str;
int len = str.length();
string arr[100];
for(int i = 0; i < len ; ++i){
arr[i] = str.substr(i);
}
sort(arr,arr+len);//对整个string数组内排序
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
cout<<arr[i]<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.(字符)数组逆置
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/b4f598480524493aae4686947fbf31dc

#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char arr[300];
while(scanf("%s",arr) != EOF){
string str = arr;
int len = str.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
printf("%c",str[len-i-1]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
1.string和int的相互转换
①int转string:to_string(i)
int a;
while(scanf("%d",&a) != EOF){
string str = to_string(a);
printf("%s",str.c_str());
}
②string转int:stoi(str)
#include <string>
int a = stoi(sa);
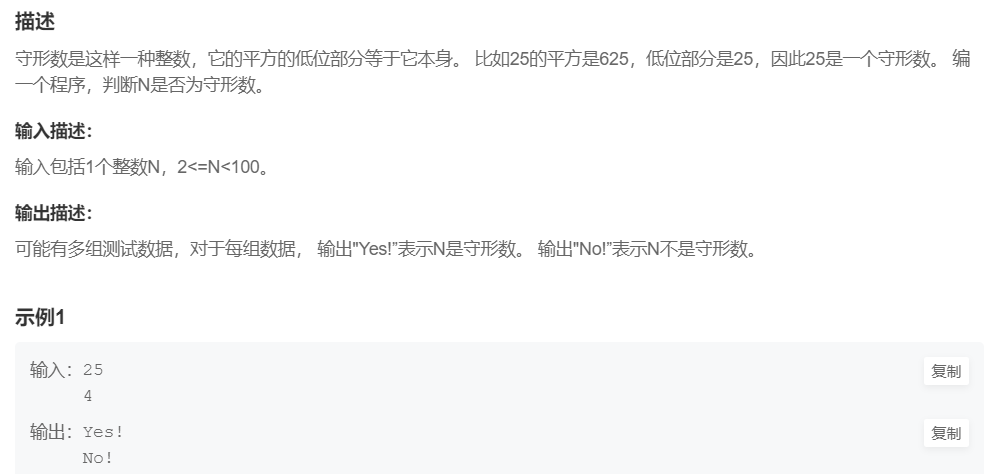
4.守型数
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/99e403f8342b4d0e82f1c1395ba62d7b
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a;
while(scanf("%d",&a) != EOF){
string s = to_string(a);
string str = to_string(a*a);
int len = str.length();
string sub = str.substr(len/2);//无论奇数位偶数位,低位起始位置都是len/2
if(s == sub){
printf("Yes!\n");
}else{
printf("No!\n");
}
}
return 0;
}
5.字符串链接

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9f27c74ec91e4c7da96ba351dba235fc
解题思路:用string里的 + 完成字符串拼接
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char a[100];
char b[100];
while(scanf("%s %s",a,b) != EOF){
string sa = a;
string sb = b;
string str = sa+sb;
printf("%s\n",str.c_str());
}
return 0;
}
2.map[key]++
map[i]++
①若map中没有为key = i的键,则先insert <key = i,0>,然后value++。最终map中存入<key = i,1>。
②若map中已有key = i,则value++
#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
map<int, int> myMap;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
myMap[i]++;
}
for (auto it = myMap.begin(); it != myMap.end(); it++) {
cout << '<'<< it->first << ',' << it->second <<'>'<< endl;
}
cout<<"第二轮"<<endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
myMap[i]++;
}
for (auto it = myMap.begin(); it != myMap.end(); it++) {
cout << '<'<< it->first << ',' << it->second <<'>'<< endl;
}
return 0;
}
6.子串计算
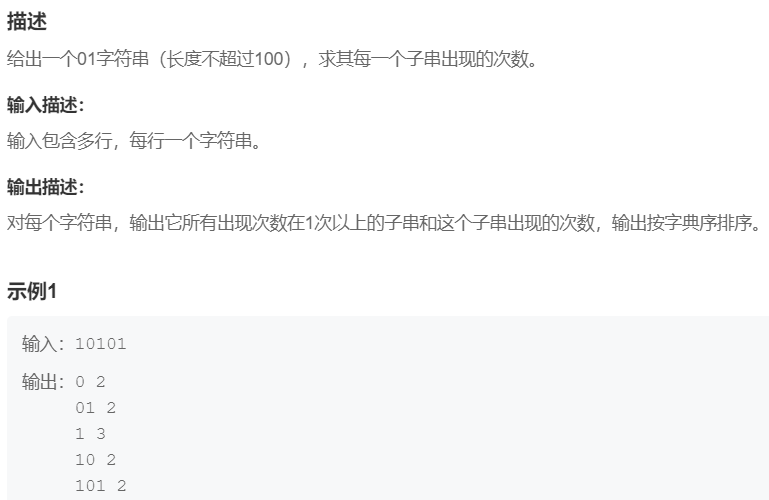
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/bcad754c91a54994be31a239996e7c11
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
int main(){
map<string,int> myMap;
char arr[101];
scanf("%s",arr);
string str = arr;
int len = str.size();
for(int i = 0; i <len; ++i){
for(int j = i; j < len; ++j){//难点
string s = str.substr(i,j-i+1);//难点
myMap[s]++;//重点 map[i]++
}
}
map<string,int>::iterator it;
for(it = myMap.begin();it != myMap.end();++it){
if(it->second > 1){ //输出:出现次数至少2次的子串
printf("%s %d\n",it->first.c_str(),it->second);
}
}
return 0;
}
7.谁是你的潜在朋友
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <map>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n,m; //n个读者,m本书
while(scanf("%d %d",&n,&m) != EOF){
//存入
int book[201]; //i读者喜欢的书号为 book[i]
map<int,int> mymap; //书号->喜欢该书的人数
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&book[i]);
mymap[book[i]]++; //核心
}
//读取
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
if(mymap[book[i]] > 1){
printf("%d\n",(mymap[book[i]])-1);//有几个朋友,不包括自己
}else{
printf("BeiJu\n");
}
}
}
return 0;
}
3.getline()
1.getline()的两种分类
①以换行符 ‘\n’ 结束字符串的读入:getline(cin,str)
②以一个字符来结束字符串的读入:getline(cin ,string str ,char ch)
2.字符串的输入中,getline与cin的区别
①cin遇到空格代表字符串输入结束
②getline遇到换行符代表字符串输入结束
1.①getline(cin,s)
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
cout<<"输入字符串:";
getline(cin,s);
cout<<"输出字符串:";
cout<<s;
return 0;
}
1.②getline(cin,str,'c')
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
cout<<"输入字符串:";
getline(cin,str,'c');
cout<<"输出字符串:";
cout<<str;
return 0;
}
8.密码翻译
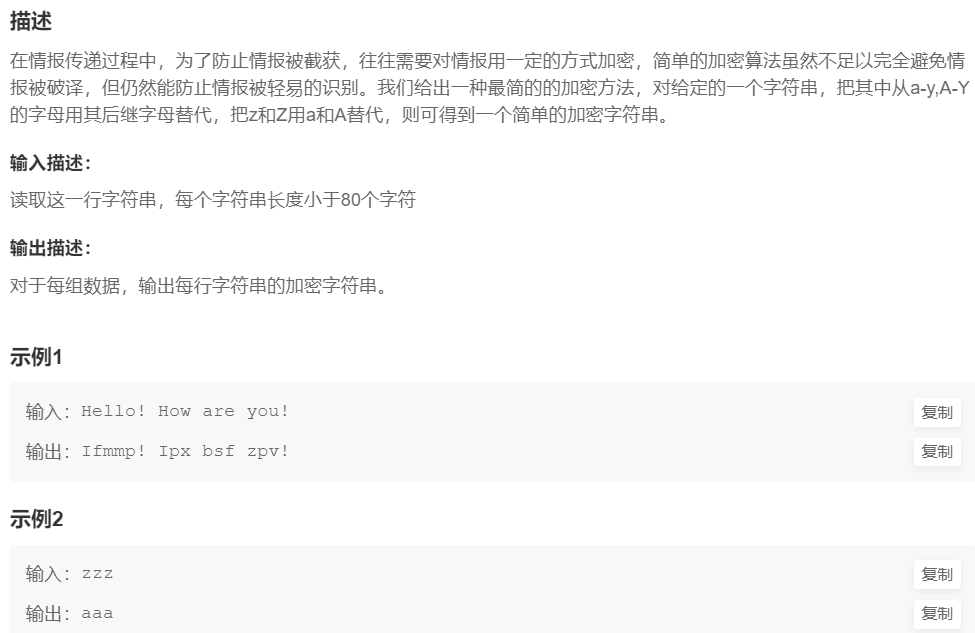
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/136de4a719954361a8e9e41c8c4ad855
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
while(getline(cin,str)){
int len = str.length();
for(int i =0; i < len; ++i)
{ //大写
if('A' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'Z'){
if(str[i] == 'Z'){
str[i] = 'A';
}else{
str[i] = str[i]+1;
}
}
//小写
if('a' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'z'){
if(str[i] == 'z'){
str[i] = 'a';
}else{
str[i] = str[i]+1;
}
}
}
printf("%s\n",str.c_str());
}
return 0;
}
getline(cin,str)一行字符串后,基于空格分割单词
9.单词替换
提交网址
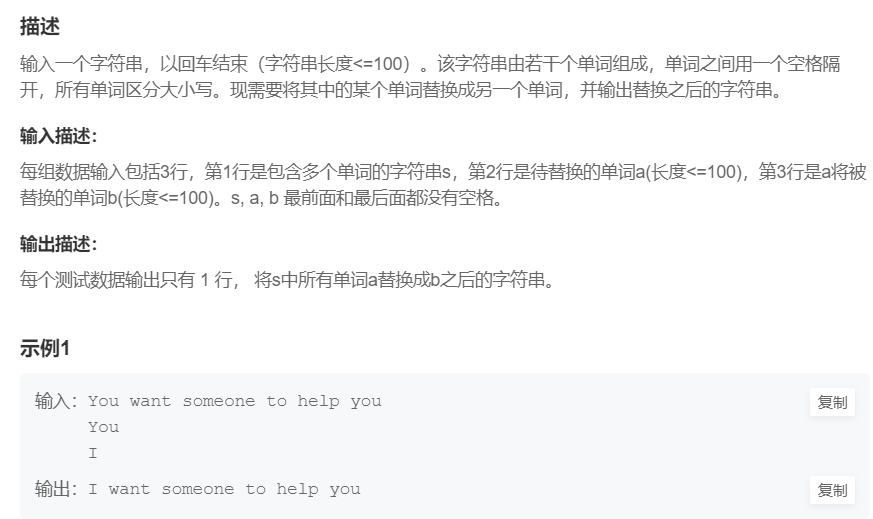
我的解题思路:
①getline读入一整行,遍历s以空格为界,分割单词,存入vector。
②遍历vector[i]进行字符串替换
③遍历输出vector
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(getline(cin,s)){ //1.读入一整行
string a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
vector<string> vec;
//2.分割一整行为一个个的单词,存入vector
string sub = ""; //初始为空
for(int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i){
if(s[i] != ' '){
sub += s[i];
}else{
vec.push_back(sub);
sub.clear();
}
if(i == s.size()-1){ //存入最后一个单词
vec.push_back(sub);
sub.clear();
}
}
//3.替换
for(int i = 0; i < vec.size(); ++i){
if(vec[i] == a){
vec[i] = b;
}
}
//4.遍历输出
vector<string>::iterator it;
for(it = vec.begin();it != vec.end(); ++it){
cout<<*it<<" ";
}
}
return 0;
}
10.首字母大写
提交网址
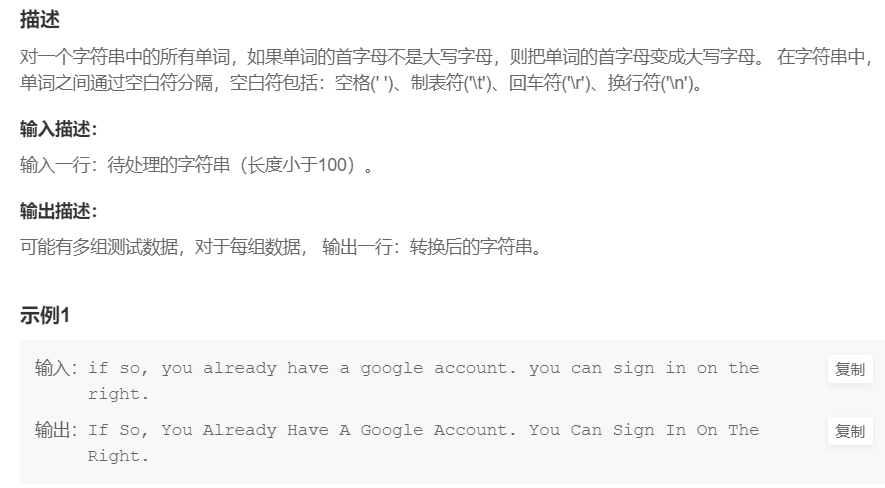
解题思路:用getline(cin,str)读入一行。用空白符分割单词,判断是否为单词的首字母
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
while(getline(cin,str)){
if('a' <= str[0] && str[0] <= 'z') str[0] = str[0]-32;
cout<<str[0];
for(int i = 1; i < str.length(); ++i){
if(str[i]==' ' || str[i]=='\t' || str[i]=='\r' || str[i]=='\n'){
if('a' <= str[i+1] && str[i+1] <= 'z') str[i+1] = str[i+1]-32;
}
cout<<str[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
4.ASCII码表
A:65
Z:90
a:97
z:122
9.简单密码
题目大意:密文→明文(A→V,B→W,C→X,D→Y,E→Z,F→A,G→B)

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ff99c43dd07f4e95a8f2f5448da3772a
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str;
while (getline(cin, str)) {
if (str == "ENDOFINPUT") break;
if (str == "START") { //读取正文
getline(cin, str);
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); ++i){
if('A' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'Z'){ //限定只有大写字母转换
str[i] = (str[i] - 5 - 'A' + 26) % 26 + 'A'; //密文转明
}
}
cout << str << endl;
}
getline(cin, str); //吃掉END
}
return 0;
}
10.反序输出
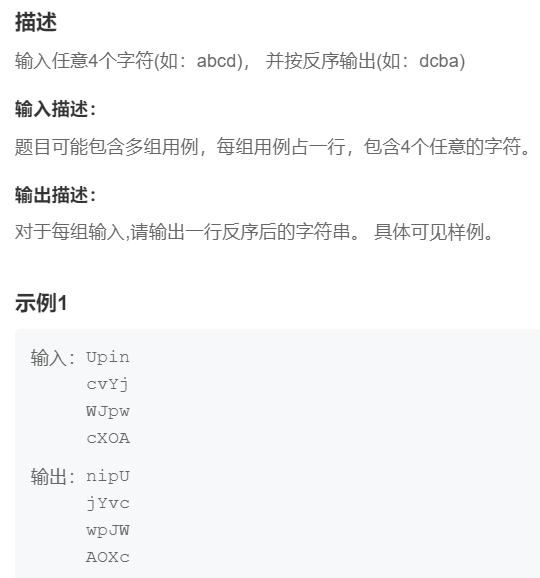
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/171278d170c64d998ab342b3b40171bb
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char arr[5];
char str[5];
while(scanf("%s",arr) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){
str[3-i] = arr[i];
}
printf("%s\n",str);
}
return 0;
}
5.memset()
初始化数组:memset()
int count[26];
memset(count,0,sizeof(count));//初始化为0
头文件:#include <cstring>
11.字母统计 (Easy)
提交网址
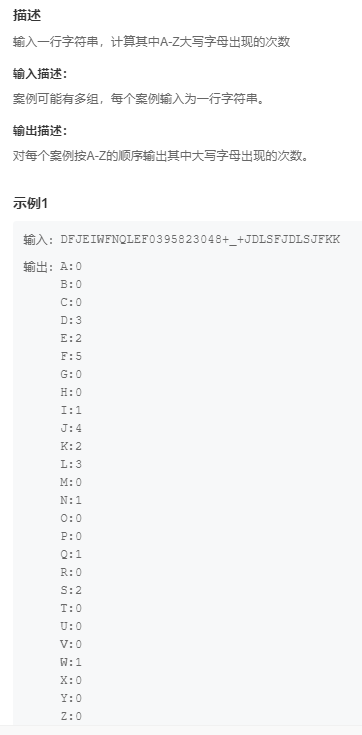
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string str;
while(getline(cin,str)){
int len = str.size();
int count[26];
memset(count,0,sizeof(count));
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
if('A' <= str[i] && str[i] <= 'Z'){
count[str[i]-'A']++; //核心
}
}
for(int i = 0;i < 26; ++i){
printf("%c:%d\n",'A'+i,count[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
6.getchar() //吃掉回车
读行之前如果出现过cin或scanf,一定要把最后一个回车换行给吞掉,不然输入会出错
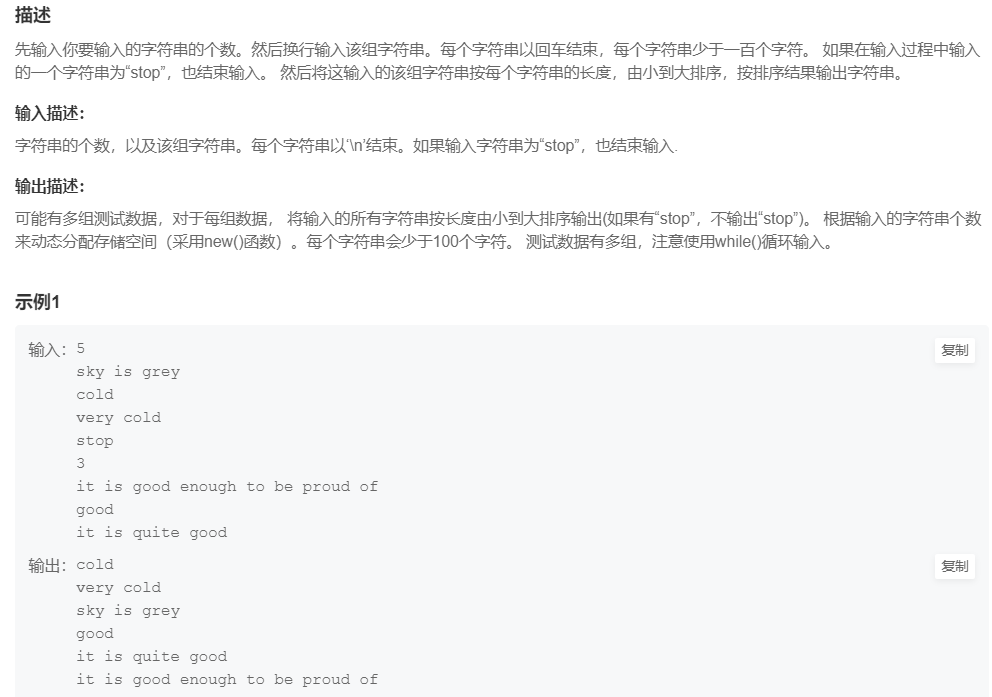
12.字符串排序
提交网址
解题思路:
①用vec保存各字符串(用getchar()吃掉输入时缓存的回车)
②用sort进行排序(自定义comp规则为按照长度排序)
③遍历输出
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream> //getline(cin,str)
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm> //sort()
using namespace std;
bool comp(string &lhs,string &rhs){
return lhs.length()<rhs.length();
}
int main(){
int n;
string str;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
//1.读入
getchar(); //吞回车
vector<string> vec;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
getline(cin,str); //一行行读入
if(str == "stop")
break;
vec.push_back(str);
}
//2.排序
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),comp);
//3.输出
vector<string>::iterator it;
for(it = vec.begin();it != vec.end(); ++it){
printf("%s\n",it->c_str());
}
}
return 0;
}
13.字符串去特定字符
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char s[500],c;
while(scanf("%s",s) != EOF){
getchar(); //吃掉回车。避免scanf读入\n
scanf("%c",&c);
int len = strlen(s);
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
if(s[i] != c){
printf("%c",s[i]);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
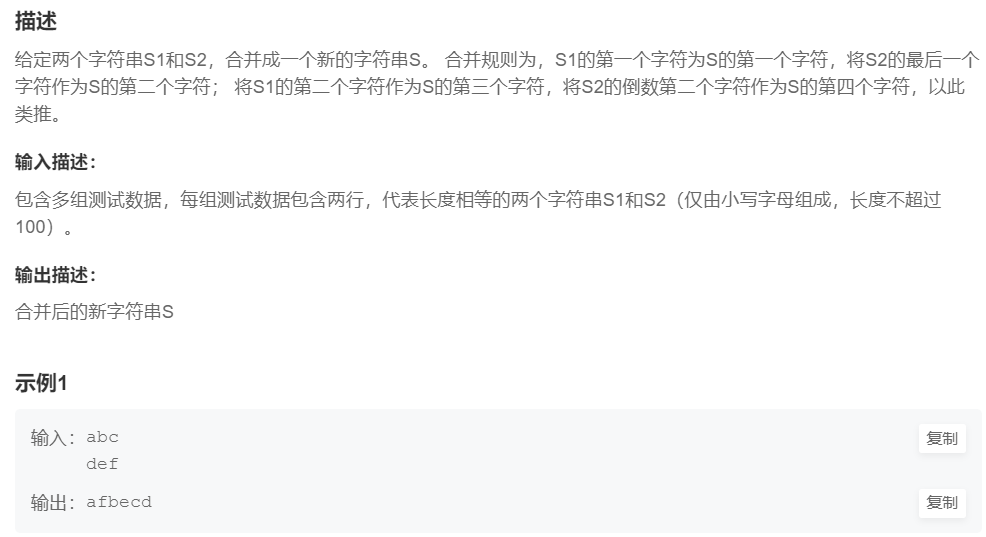
14.合并符串
提交网址
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char s1[101];
char s2[101];
while(scanf("%s %s",s1,s2) != EOF){
string str1 = s1;
string str2 = s2;
int len = str1.length();
for(int i = 0; i < len; ++i){
printf("%c%c",str1[i],str2[len-1-i]);//一个字符一个字符遍历输出
}
}
return 0;
}
7.用vector保存多个字符串
vector<string> vec;
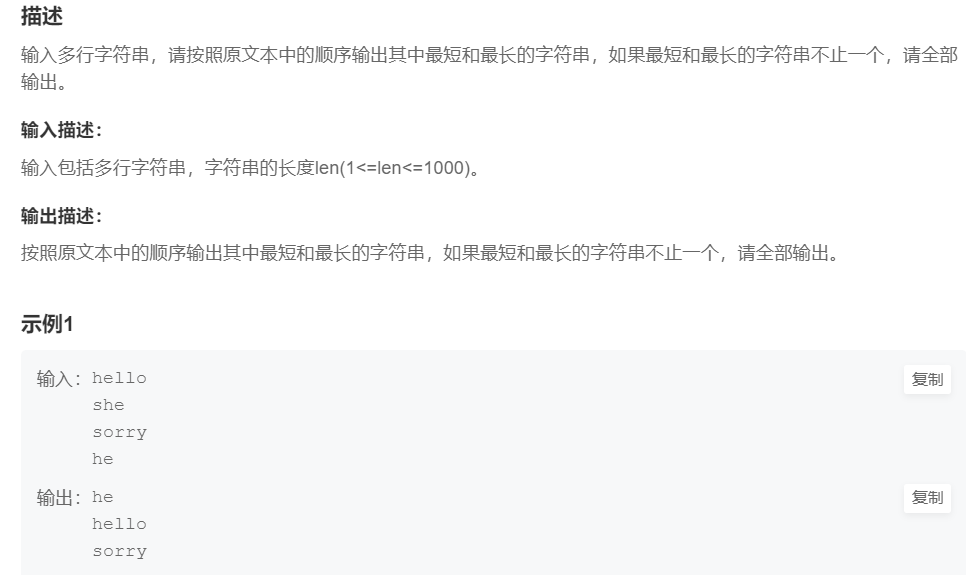
15.最长最短文本
提交网址
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool comp(string lhs,string rhs){
return lhs.length() < rhs.length();
}
int main(){
vector<string> vec;
string str;
while(getline(cin,str)){
vec.push_back(str);
}
sort(vec.begin(),vec.end(),comp);//按字符串长度递增排序
int maxlen = 0,minlen = 1000;
vector<string>::iterator it;
for(it = vec.begin();it != vec.end();++it){
if((*it).length() > maxlen) maxlen = it->length();
if((*it).length() < minlen) minlen = it->length();
}
for(it = vec.begin();it != vec.end();++it){
if(it->length() == minlen || it->length() == maxlen){
cout<<*it<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
16.编排字符串
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m;
while(scanf("%d",&m) != EOF){
string str;
vector<string> vec;
for(int i = 0;i < m; ++i){
cin>>str;
vec.insert(vec.begin(),str); //vector头部插入字符串
for(int j = 0; j < vec.size() && j <4; ++j){
cout<<j+1<<"="<<vec[j]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
8.swap()函数
头文件
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
swap也可以交换字符串
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char ch[2]={'a','b'};
swap(ch[0],ch[1]);
printf("%c %c",ch[0],ch[1]);
return 0;
}
9.string之erase()
17.A+B
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string sa,sb;
while(cin>>sa>>sb){
string::iterator it;
for(it=sa.begin();it!=sa.end();++it){
if(*it == ','){
sa.erase(it);
}
}
for(it=sb.begin();it!=sb.end();++it){
if(*it == ','){
sb.erase(it); //删除逗号
}
}
int a,b;
a = stoi(sa);
b = stoi(sb);
printf("%d\n",a+b);
}
return 0;
}
### 10.大写转小写 (手动实现)
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string tolower(string str){
for(int i = 0; i < str.size(); ++i){
if('A' <= str[i] &&str[i] <= 'Z'){ //大写转小写
str[i] = str[i]+32;
}
}
return str;
}
int main(){
string str = "Ab1";
str = tolower(str);
cout <<str;
return 0;
}
5.数学问题
1.求最大公约数 gcd()
辗转相除法:
int gcd(int a, int b){//欧几里得算法求最大公约数
if(b==0) return a;
else return gcd(b, a%b);
}
三目运算符
表达式1 ? 表达式2 : 表达式3;
若1为真,则执行2;若1为假,则执行3;
1.求最大公约数
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/20216f2c84bc438eb5ef05e382536fd3

解法1:暴力枚举(导致运行时间比别人长):
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int m,n;
while(scanf("%d %d",&m,&n) != EOF){
//x为较小的那个数
int x;
if(m > n){
x = n;
}else{
x = m;
}
for(int i = x; i > 0; i--){
if(m%x == 0 && n%x == 0){
printf("%d\n",x);
break;
}
x--;
}
}
return 0;
}
解法2:gcd()函数
#include <cstdio>
int gcd(int a,int b){
return b ? gcd(b,a%b) : a;
}
int main(){
int a,b;
while(scanf("%d %d",&a,&b) != EOF){
printf("%d",gcd(a,b));
}
return 0;
}
2.最简真分数
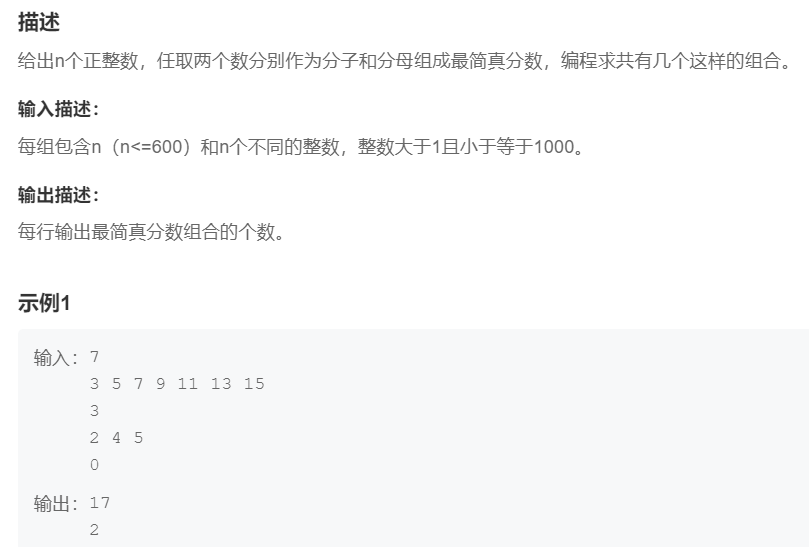
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/1f1db273eeb745c6ac83e91ff14d2ec9
#include <cstdio>
int gcd(int a, int b){ //辗转相除法 求最小公因数
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
if(n == 0) break;
int arr[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
for(int j = i+1; j < n; ++j){
if(arr[j] % arr[i] != 0 ){ //真分数,分母不是分子的倍数
if(gcd(arr[i],arr[j]) == 1){ //也不能有公因子
count++;
}
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",count);
}
return 0;
}
3.百万富翁问题
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/9fe25b6cf93e46dcb09ba67aeef2c4cc

4.数字求和
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/e8cee01f2d834fa9ba3479fafe492b65
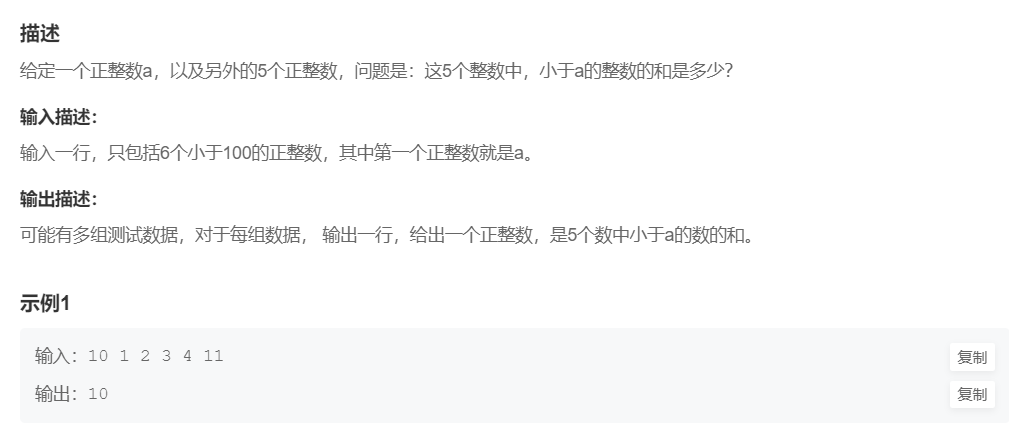
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int a;
int arr[5];
while(scanf("%d",&a) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < 5; ++i){
if(arr[i] < a){
sum += arr[i];
}
}
printf("%d",sum);
}
return 0;
}
5.n的阶乘(简单)
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/97be22ee50b14cccad2787998ca628c8
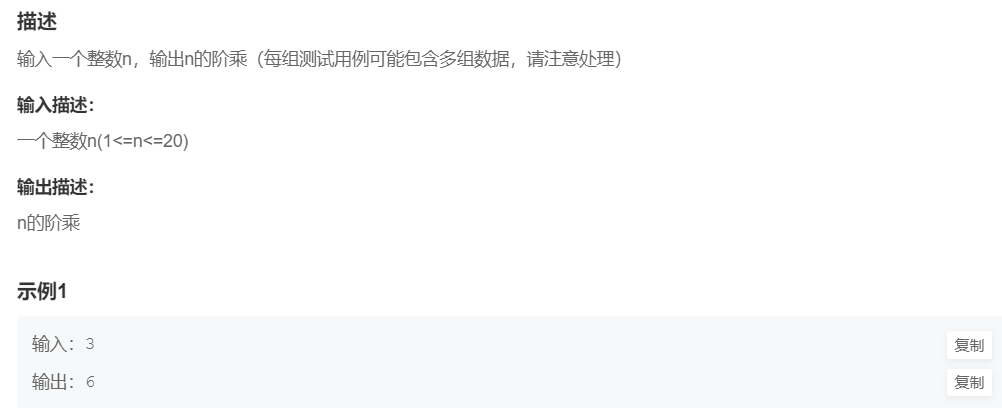
#include <cstdio>
long long int Factorial(int n){
if(n == 0){
return 1;
}else{
return n*Factorial(n-1);
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
printf("%lld",Factorial(n));
}
return 0;
}
6.阶乘(中等)
提交网址

解法1:我的朴素实现(46行)
#include <cstdio>
long long int Factorial(int n){
if(n == 0 || n == 1){
return n;
}else{
return n*Factorial(n-1);
}
}
long long int sy1(int m){
int y1 = 0;
while(m > 0){
y1 += Factorial(m);
m = m-2;
}
return y1;
}
long long int sy2(int p){
int y2 = 0;
while(p > 0){
y2 += Factorial(p);
p = p-2;
}
return y2;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
//判断n是奇数还是偶数
int m,p,y1,y2;
if(n%2 ==0){ //偶数
m = n-1;
p = n;
}else{ //奇数
m = n;
p = n-1;
}
y1 = sy1(m);
y2 = sy2(p);
printf("%lld %lld",y1,y2);
}
return 0;
}
解法2:大佬的简介实现(15行)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n ,ans1, ans2, i, j;
while (cin >> n) {
ans1 = ans2 = 0, j = 1;
for (i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
j *= i; // j = i!
if(i % 2) ans1 += j; //奇数的阶乘之和
else ans2 += j; //偶数的阶乘之和
}
cout << ans1 << " " << ans2 << endl;
}
}
7.特殊乘法
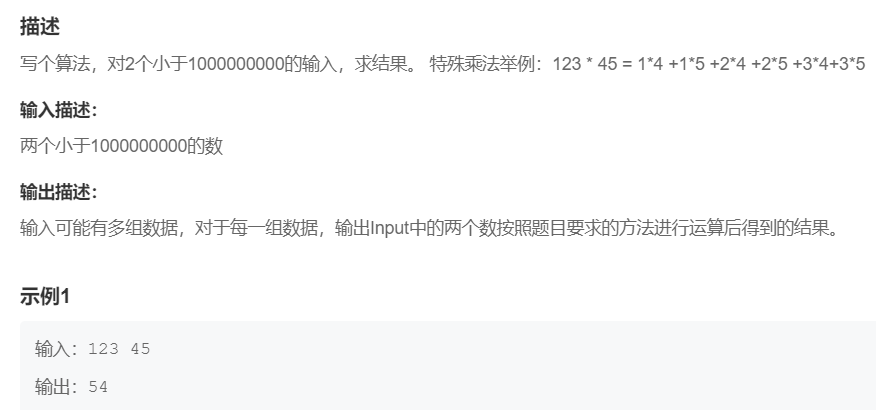
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/a5edebf0622045468436c74c3a34240f
解题思想:实际上是求各位数之和,再相乘。只需要构造一个能求各位之和的函数即可。可参考求逆序数的Reverse函数求法。
#include <cstdio>
int Add(int n){ //各位数之和
int sum = 0;
while(n != 0){
int remain = n%10;
sum += remain;
n /= 10;
}
return sum;
}
int main(){
int a,b;
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b) != EOF){
printf("%d\n",Add(a)*Add(b));
}
return 0;
}
8.三角形的边
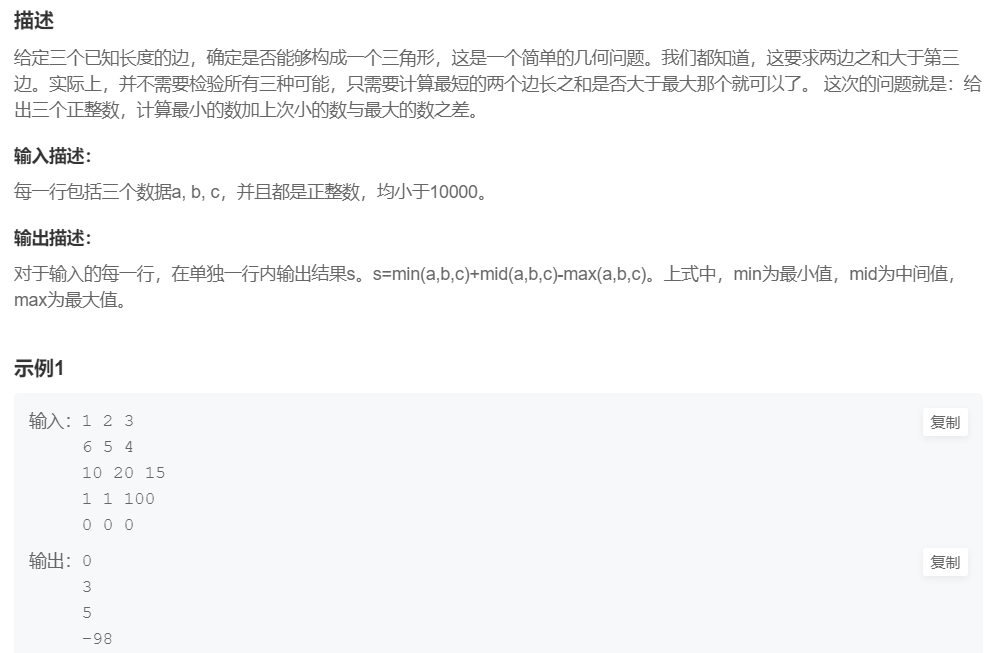
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/05dbd1cd43b24dbbae567b3e816d4e97
#include <cstdio>
int main() {
int a, b, c;
int min, mid, max;
while (scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c) != EOF) {
if (a == 0 && b == 0 && c == 0) {
//do nothing
}else {
if (a >= b && a >= c && b >= c) {
max = a;
mid = b;
min = c;
} else if (a >= b && a >= c && b <= c) {
max = a;
mid = c;
min = b;
} else if (b >= a && b >= c && a >= c) {
max = b;
mid = a;
min = c;
} else if (b >= a && b >= c && a <= c) {
max = b;
mid = c;
min = a;
} else if (c >= a && c >= b && a >= b) {
max = c;
mid = a;
min = b;
} else if (c >= a && c >= b && a >= b) {
max = c;
mid = a;
min = b;
} else if (c >= a && c >= b && a <= b) {
max = c;
mid = b;
min = a;
}
printf("%d\n", min + mid - max);
}
}
return 0;
}
9.求平均年龄

提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/ca319fdb02714994850cc631d76f5547
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int age;
float sum = 0;
for(int i =0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&age);
sum += age;
}
float num = sum/n;
printf("%0.2f",num);
}
return 0;
}
11.鸡兔同笼
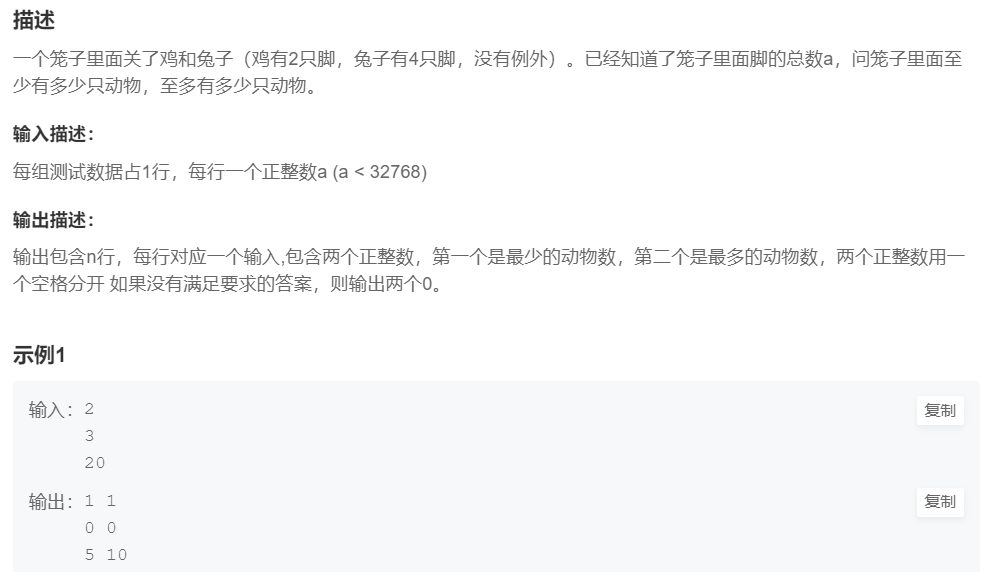
提交网址:https://www.nowcoder.com/practice/fda725b4d9a14010bb145272cababef1
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
if(n == 2){ //n为2
printf("1 1\n");
}else if(n%2 != 0){ //n为奇数
printf("0 0\n");
}else if(n %4 == 0){ //n为4的倍数
printf("%d %d\n",n/4,n/2);
}else{
printf("%d %d\n",n/4+1,n/2);
}
}
return 0;
}
12.求最大值(中等)
提交网址
解法1:用中的max({a,b,c})函数求多个数中的最大值
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6,a7,a8,a9,a10;
int maximum;
while(scanf("%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d%d",&a1,&a2,&a3,&a4,&a5,&a6,&a7,&a8,&a9,&a10) != EOF){
maximum = max({a1,a2,a3,a4,a5,a6,a7,a8,a9,a10});
printf("max=%d",maximum);
}
return 0;
}
解法2:数组保存,遍历一遍求最大值
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int arr[10];
int maximum = n; //输入的第一个数为n,默认为当前最大值
for(int i = 1; i < 10; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
if(arr[i] > maximum){
maximum = arr[i]; //若出现更大的,则代替maximum
}
}
printf("max=%d",maximum);
}
return 0;
}
2.求a^b:pow(a,b)
#include <cmath>
pow(a,b);
3.求绝对值:abs(i)
#include <cmath>
abs(i);
4.大数问题
1.阶乘问题
int 最多可计算12!
long long int 最多可计算20!
n超过20就是大数运算了,需要借助数组
例题1:大整数排序
提交网址
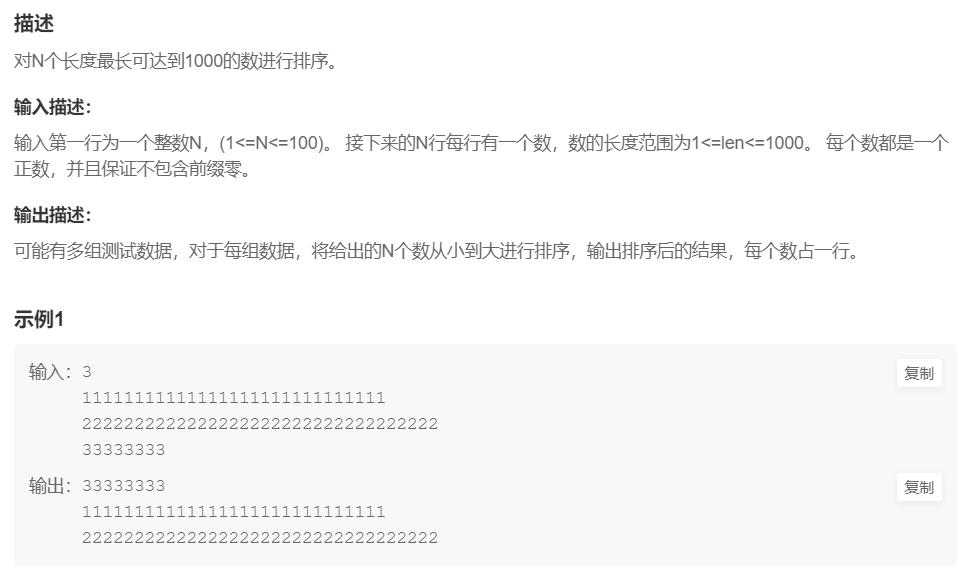
解题思路:用string数组来保存大整数(多个字符串),编写sort的排序规则comp:①先比长度 ②长度相同比大小(string可以直接比大小,从最高位用ASCII码比)
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
bool comp(string lhs, string rhs){
if(lhs.size() < rhs.size()){
return true;
}else if(lhs.size() == rhs.size() && lhs < rhs){
return true;
}
else{
return false;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
string str[101]; //使用string数组来保存多个字符串
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
cin>>str[i];
}
sort(str,str+n,comp);
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
cout<<str[i]<<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
5.进制转换
例题1:又一版A+B【10进制转m进制】
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m;
long long int a,b;
while(scanf("%d %lld %lld",&m,&a,&b) != EOF){
if(m == 0) break;
if(a== 0 && b ==0) printf("0\n");
long long int res10 = a + b;
vector<int> vec;
//10进制转m进制
long long int remain = 0,res_m = 0;
while(res10 > 0){
remain = res10 % m;
res10 /= m;
vec.push_back(remain);
}
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(it = vec.end()-1;it != vec.begin()-1;--it){
printf("%lld",*it);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
6.求素数
#include <cstdio>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
//1.求[2,n]的所有素数
vector<int> prime;
for(int i = 2; i < n; ++i){
int factor = 0; //因子个数
for(int j = 1; j <= i; ++j){
if(i%j==0){
factor++;
}
}
if(factor <= 2){
prime.push_back(i);//i是素数
}
}
//2.遍历输出
vector<int>::iterator it;
for(it=prime.begin();it!=prime.end();++it){
printf("%d ",*it);
}
}
return 0;
}
7.完全数
6、28、496、8128、33550336、8589869056 …
例题1:Problem A
提交网址

解题思路:打表
完全数在数轴上的分布是很稀疏的,对于这种解极少但范围极大的,不要暴力循环,要用打表。
10000以内的完全数只有4个:6、28、496、8128
#include <cstdio>
int main(){
int a,b;
while(scanf("%d %d",&a,&b) != EOF){
int perfectNumber[4] = {6,28,496,8128}; //10^5内的完全数只有4个
for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){
if(a <= perfectNumber[i] && perfectNumber[i] <= b){
printf("%d\n",perfectNumber[i]);
}
}
}
}
6.递归
7.动态规划
1.输入n,读取n个数
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
int arr[n];
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
}
2.max()、std::max()
1.比较两个数大小 max(a,b);
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
max(a,b);
2.比较n个数大小 std::max({});
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a=1,b=2,c=3;
int max = std::max({a,b,c});
printf("%d",max);
return 0;
}
1.最大序列和
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
using namespace std;
long long int arr[1000001];//堆上,全局数组
long long int dp[1000001];
long long MaxSubsequence(int n){
long long maximum = -INT_MAX;//负无穷
for(int i =0; i < n; ++i){
if(i ==0){
dp[i] = arr[i];
}else{
dp[i] = max(arr[i],arr[i]+dp[i-1]);//核心
}
maximum = max(maximum,dp[i]);//不断更新最大的连续子序列和
}
return maximum;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%lld",&arr[i]);
}
printf("%lld\n",MaxSubsequence(n));
}
return 0;
}
2.最大上升子序列和
例题1
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int arr[10001];
int dp[10001];//当前最大递增子序列和
int main(){
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&arr[i]);
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
dp[i] = arr[i];
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j){
if(arr[j] < arr[i]){
dp[i] = max(dp[i],dp[j]+arr[i]);//核心
}
}
answer = max(answer,dp[i]);
}
printf("%d\n",answer);
}
return 0;
}
例题2:拦截导弹
提交网址
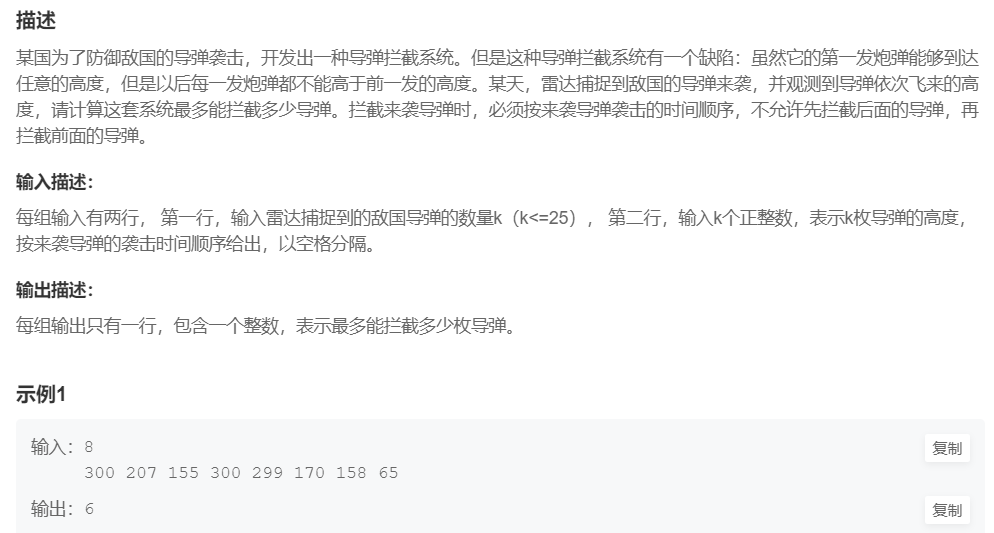
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream> //max()
using namespace std;
int main(){
int height[26]; //导弹高度
int dp[26]; //能拦截的导弹数目
int n;
while(scanf("%d",&n) != EOF){
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
scanf("%d",&height[i]);
}
int answer = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; ++i){
dp[i] = 1; //初始化为1,最少能拦截第一枚(若是递增就只能拦截一枚)
for(int j = 0; j < i; ++j){
if(height[j] >= height[i]){
dp[i] = max(dp[i],dp[j] + 1);
}
}
answer = max(answer,dp[i]);
}
printf("%d\n",answer);
}
return 0;
}
3.最长公共子序列
例题1
提交网址
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int dp[1001][1001];
int main(){
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
char s1[n];
char s2[m];
scanf("%s%s",s1,s2);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i){ //前多少个,0~n 共n+1个
for(int j = 0; j <= m; ++j){ //前多少个,0~m 共m+1个
if(i==0 || j==0){
dp[i][j] = 0;
continue;
}
//核心4句
if(s1[i-1] == s2[j-1]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}else{ //if(s1[i-1] != s2[j-1])
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[n][m]);
return 0;
}
例题2:Coincidence
提交网址

#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
char s1[101];
char s2[101];
int dp[101][101]; //存s1[i]和s2[j]结尾的的公共子序列的长度
while(scanf("%s %s",s1+1,s2+1) != EOF){ //从下标为1开始存
int n = strlen(s1+1); //C字符数组长度用strlen()
int m = strlen(s2+1);
for(int i = 0; i <= n; ++i){
for(int j = 0;j <= m; ++j){
if(i==0 || j==0){
dp[i][j] = 0;
continue;
}
if(s1[i] == s2[j]){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + 1;
}else{
dp[i][j] = max(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1]);
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",dp[n][m]);
}
return 0;
}
