MapReduce分区
目录
- 1. MapReduce分区
- 1.1 哈希分区
- 1.2 自定义分区
- 2. 成绩分组
- 2.1 Map
- 2.2 Partition
- 2.3 Reduce
- 3. 代码和结果
- 3.1 pom.xml中依赖配置
- 3.2 工具类util
- 3.3 GroupScores
- 3.4 结果
- 参考
本文引用的Apache Hadoop源代码基于Apache许可证 2.0,详情请参阅 Apache许可证2.0。
1. MapReduce分区
在默认情况下,MapReduce认为Reduce函数处理的是数据汇总操作,因此其针对的必定是一个Map函数清洗处理后的相对规模较小的数据集,且需要对整个集群中所有Map的中间输出结果进行统一处理,因此只会启动一个Reduce计算节点来处理。
这与某些特殊的应用需求并不相匹配。在某些特定的时刻,开发人员希望启动更多的Reduce并发节点来优化最终结果统计的性能,减小数据处理的延迟,这通过简单的设置代码即可完成;而在更定制化的环境中,开发人员希望符合特定规则的Map中间输出结果交由特定的Reduce节点处理,这就需要使用MapReduce分区,开发人员还可以提供自定义的分区规则。
如果有很多个Reduce任务,每个Map任务就会针对输出进行分区,即为每个Reduce任务建立一个分区。每个分区中有很多键,但每个键对应的键值对记录都在同一分区中。如果不给定自定义的分区规则,则Hadoop使用默认的哈希函数来分区,效率较高。
1.1 哈希分区
下面是Apache Hadoop中默认哈希分区的源代码。在这个分区规则中,选择Reduce节点的计算方法是(key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks。
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.partition;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceAudience;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceStability;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
/** Partition keys by their {@link Object#hashCode()}. */
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public class HashPartitioner<K, V> extends Partitioner<K, V> {
/** Use {@link Object#hashCode()} to partition. */
public int getPartition(K key, V value,
int numReduceTasks) {
return (key.hashCode() & Integer.MAX_VALUE) % numReduceTasks;
}
}
1.2 自定义分区
如果希望实现自定义分区,需要继承Hadoop提供的分区类org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner,下面是该类的声明。继承该分区类的自定义分区类需要实现public abstract int getPartition(KEY key, VALUE value, int numPartitions),该函数的作用是设置Map中间处理结果的分区规则,其中numPartitions是总分区的个数。此外,在自定义分区类时,通过函数返回了多少个分区,那么在MapReduce任务调度代码中需要设置Job.setNumReduceTasks(自定义分区个数)。
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one
* or more contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file
* distributed with this work for additional information
* regarding copyright ownership. The ASF licenses this file
* to you under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the
* "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance
* with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceAudience;
import org.apache.hadoop.classification.InterfaceStability;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configurable;
/**
* Partitions the key space.
*
* <p><code>Partitioner</code> controls the partitioning of the keys of the
* intermediate map-outputs. The key (or a subset of the key) is used to derive
* the partition, typically by a hash function. The total number of partitions
* is the same as the number of reduce tasks for the job. Hence this controls
* which of the <code>m</code> reduce tasks the intermediate key (and hence the
* record) is sent for reduction.</p>
*
* <p>Note: A <code>Partitioner</code> is created only when there are multiple
* reducers.</p>
*
* <p>Note: If you require your Partitioner class to obtain the Job's
* configuration object, implement the {@link Configurable} interface.</p>
*
* @see Reducer
*/
@InterfaceAudience.Public
@InterfaceStability.Stable
public abstract class Partitioner<KEY, VALUE> {
/**
* Get the partition number for a given key (hence record) given the total
* number of partitions i.e. number of reduce-tasks for the job.
*
* <p>Typically a hash function on a all or a subset of the key.</p>
*
* @param key the key to be partioned.
* @param value the entry value.
* @param numPartitions the total number of partitions.
* @return the partition number for the <code>key</code>.
*/
public abstract int getPartition(KEY key, VALUE value, int numPartitions);
}
2. 成绩分组
成绩文本如下,第一列为人名,第二列为成绩。目标是将成绩分为5段,分别为 [ 0 , 20 ) [0, 20) [0,20), [ 20 , 40 ) [20, 40) [20,40), [ 40 , 60 ) [40, 60) [40,60), [ 60 , 80 ) [60, 80) [60,80), [ 80 , 100 ] [80, 100] [80,100]。
1 23
2 78
3 45
4 12
5 67
6 34
7 89
8 56
9 9
10 78
11 21
12 54
13 83
14 10
15 65
16 39
17 92
18 47
19 28
20 72
2.1 Map
假设这个MapReduce作业使用了1个Map,Map的作用是从文本获取<人名,成绩>键值对,同时保证成绩在有效范围内。

2.2 Partition
根据成绩进行分区,其中1的范围是
[
20
,
40
)
[20, 40)
[20,40),3的范围是
[
60
,
80
)
[60, 80)
[60,80),2的范围是
[
40
,
60
)
[40, 60)
[40,60),4的范围是
[
80
,
100
]
[80, 100]
[80,100],0的范围是
[
0
,
20
)
[0, 20)
[0,20)。

2.3 Reduce
reduce不进行任何操作,直接将分区结果排序后写入5个文件中。

3. 代码和结果
3.1 pom.xml中依赖配置
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-common</artifactId>
<version>3.3.6</version>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-mapreduce-client-core</artifactId>
<version>3.3.6</version>
<type>pom</type>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-mapreduce-client-jobclient</artifactId>
<version>3.3.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.2 工具类util
import java.net.URI;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FSDataInputStream;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileStatus;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IOUtils;
public class util {
public static FileSystem getFileSystem(String uri, Configuration conf) throws Exception {
URI add = new URI(uri);
return FileSystem.get(add, conf);
}
public static void removeALL(String uri, Configuration conf, String path) throws Exception {
FileSystem fs = getFileSystem(uri, conf);
if (fs.exists(new Path(path))) {
boolean isDeleted = fs.delete(new Path(path), true);
System.out.println("Delete Output Folder? " + isDeleted);
}
}
public static void showResult(String uri, Configuration conf, String path) throws Exception {
FileSystem fs = getFileSystem(uri, conf);
String regex = "part-r-";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regex);
if (fs.exists(new Path(path))) {
FileStatus[] files = fs.listStatus(new Path(path));
for (FileStatus file : files) {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(file.getPath().toString());
if (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println(file.getPath() + ":");
FSDataInputStream openStream = fs.open(file.getPath());
IOUtils.copyBytes(openStream, System.out, 1024);
openStream.close();
}
}
}
}
}
3.3 GroupScores
import java.io.IOException;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.IntWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class App {
public static class MyMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String[] splitStr = value.toString().split(" ");
Text keyOut = new Text(splitStr[0]);
int grade = Integer.parseInt(splitStr[1]);
if (grade >= 0 && grade <= 100) {
IntWritable valueOut = new IntWritable(grade);
context.write(keyOut, valueOut);
}
}
}
public static class MyPartitioner extends Partitioner<Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Text key, IntWritable value, int numPartitions) {
if (value.get() >= 80) {
return 0;
} else if (value.get() >= 60) {
return 1;
} else if (value.get() >= 40) {
return 2;
} else if (value.get() >= 20) {
return 3;
} else {
return 4;
}
}
}
public static class MyReducer extends Reducer<Text, IntWritable, Text, IntWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
for (IntWritable value : values) {
context.write(key, value);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
String[] myArgs = {
"file:///home/developer/CodeArtsProjects/mapreduce-partitioner/values.txt",
"hdfs://localhost:9000/user/developer/GroupScores/output"
};
util.removeALL("hdfs://localhost:9000", conf, myArgs[myArgs.length - 1]);
Job job = Job.getInstance(conf, "GroupScores");
job.setMapperClass(MyMapper.class);
job.setPartitionerClass(MyPartitioner.class);
job.setReducerClass(MyReducer.class);
job.setNumReduceTasks(5);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(IntWritable.class);
for (int i = 0; i < myArgs.length - 1; i++) {
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, new Path(myArgs[i]));
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job, new Path(myArgs[myArgs.length - 1]));
int res = job.waitForCompletion(true) ? 0 : 1;
if (res == 0) {
System.out.println("GroupScores结果为:");
util.showResult("hdfs://localhost:9000", conf, myArgs[myArgs.length - 1]);
}
System.exit(res);
}
}
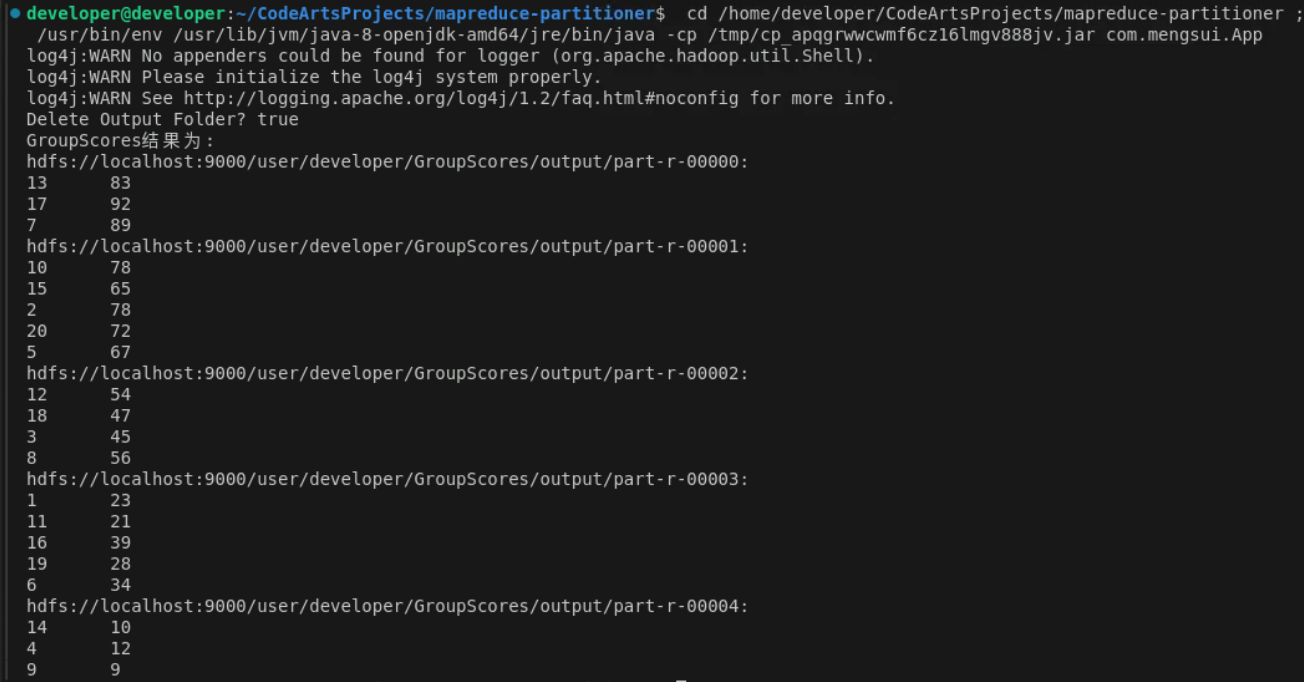
3.4 结果
参考
吴章勇 杨强著 大数据Hadoop3.X分布式处理实战
