【机器学习】监督学习-决策树-CART(Classification and Regression Tree,分类与回归树)详尽版
CART(Classification and Regression Trees)法
CART(分类与回归树)是一种决策树算法,由 Breiman 等人在 1984 年提出。它用于构建分类树(Classification Tree)或回归树(Regression Tree),以解决分类和回归问题。
1. CART 方法概述
CART 方法的核心思想是通过递归二分(Binary Recursive Partitioning)将数据集划分成两个子集,最终构建一棵树。其目标是:
- 分类任务(Classification Tree):将数据划分成多个类别,并最大化类别的纯度(如基尼指数最小化)。
- 回归任务(Regression Tree):最小化均方误差(MSE),使得每个叶子节点的预测值与真实值尽可能接近。
2. CART 分类树
(1) 目标
给定数据集:
其中 xix_ixi 是特征向量, 是类别标签。CART 分类树的目标是找到一个分裂方式,使得每个叶子节点尽可能纯(即尽可能属于同一类别)。
(2) 纯度衡量
CART 使用基尼指数(Gini Index)来衡量节点的不纯度:
其中:
是类别 k 在数据集 D 中的概率。
- 基尼指数越小,数据越纯。
如果在某个特征 的某个阈值 s 处分裂数据集 D:
则分裂后的基尼指数为:
目标是找到最小化 的特征
和阈值 s。
(3) 生成分类树
- 计算所有可能分裂点的基尼指数,选择最优分裂点。
- 递归进行分裂,直到满足停止条件(如树的最大深度、样本数等)。
- 叶子节点的类别由该节点中样本的多数决定。
3. CART 回归树
(1) 目标
对于回归问题,CART 采用均方误差(MSE)来衡量误差:
其中 yˉ\bar{y}yˉ 是数据集 D 中所有样本的均值。
如果对数据进行分裂:
则分裂后的均方误差为:
目标是找到使 最小的分裂方式。
(2) 生成回归树
- 计算所有可能分裂点的 MSE,选择最优分裂点。
- 递归分裂,直到满足停止条件(如叶子节点的样本数小于某个阈值)。
- 叶子节点的输出是该节点样本的均值。
4. 剪枝(Pruning)
CART 生成的树容易过拟合,因此需要剪枝。常见的剪枝方法包括:
- 预剪枝(Pre-pruning):在树生长过程中设定阈值,如最大深度、最小样本数等,提前停止生长。
- 后剪枝(Post-pruning):先生成完整的树,再用交叉验证进行剪枝,移除对测试误差贡献不大的节点。
CART 采用代价复杂度剪枝(Cost Complexity Pruning, CCP),定义损失函数:
其中:
- R(T) 是训练误差(如基尼指数或 MSE)。
- ∣T∣ 是树的叶子节点个数。
- α 是正则化参数,控制复杂度。
选择最优 α 使得交叉验证误差最小。
5. CART 与其他决策树的对比
| 方法 | 目标函数 | 分裂标准 | 处理类别型变量 | 剪枝 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ID3 | 信息增益 | 信息增益最大化 | 不支持 | 无剪枝 |
| C4.5 | 信息增益比 | 信息增益比最大化 | 支持 | 预剪枝 |
| CART | Gini指数(分类)/ MSE(回归) | 最小化基尼指数或 MSE | 需要编码 | 后剪枝 |
- ID3 采用信息增益,但偏向于多值特征。
- C4.5 采用信息增益比,可以处理连续变量和缺失值。
- CART 采用基尼指数/MSE,并支持后剪枝,适用于分类和回归。
6. 实例
(1) CART 分类树
假设我们有如下 4 个样本,每个样本有两个特征 和一个类别标签
:
| 样本编号 | 特征 | 特征 | 类别 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.7 | 4.5 | 0 |
| 2 | 3.4 | 1.8 | 1 |
| 3 | 1.3 | 3.7 | 0 |
| 4 | 5.1 | 2.1 | 1 |
目标:构建 CART 分类树,找到最优特征及分裂点。
步骤 1:计算数据集的基尼指数
CART 采用 基尼指数(Gini Index) 作为分类的纯度衡量指标,其计算公式为:
其中:
是类别 k 在数据集中的比例。
- Gini(D) 越小,数据越纯。
我们计算初始数据集的基尼指数:
- 类别 0(Y=0) 的样本:2 个(样本 1, 3)。
- 类别 1(Y=1) 的样本:2 个(样本 2, 4)。
步骤 2:尝试不同的分裂点
CART 采用 二分法,在所有特征的可能切分点中选择使基尼指数最小的那个。
(1) 选取 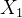 作为分裂特征
作为分裂特征
候选分裂点(取相邻样本的均值):
对每个分裂点计算基尼指数:
① 分裂点 
分裂后:
- 左子集:
→ 样本 {3},类别 {0}
- 右子集:
→ 样本 {1, 2, 4},类别 {0,1,1}
计算基尼指数:
加权基尼指数:
② 分裂点 
分裂后:
- 左子集:
→ 样本 {1, 3},类别 {0, 0}
- 右子集:
→ 样本 {2, 4},类别 {1, 1}
计算基尼指数:
③ 分裂点 
分裂后:
- 左子集:
→ 样本 {1, 2, 3},类别 {0, 1, 0}
- 右子集:
→ 样本 {4},类别 {1}
计算基尼指数:
最优分裂点:,基尼指数最低(0.0)。
步骤 3:递归构建子树
按照 进行分裂,得到:
- 左子树(
):样本 {1, 3},类别全为 0。
- 右子树(
):样本 {2, 4},类别全为 1。
由于子树的类别已纯净,停止分裂。
代码实现
从0开始完整实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import networkx as nx
class Node:
def __init__(self, feature=None, threshold=None, left=None, right=None, value=None):
self.feature = feature # 选择的特征
self.threshold = threshold # 分裂点
self.left = left # 左子树
self.right = right # 右子树
self.value = value # 叶子节点的类别
class CARTClassifier:
def __init__(self, max_depth=2):
self.max_depth = max_depth
self.root = None
def gini(self, y):
"""计算 Gini 系数"""
classes, counts = np.unique(y, return_counts=True)
p = counts / len(y)
return 1 - np.sum(p ** 2)
def best_split(self, X, y):
"""寻找最佳分裂特征和分裂点"""
m, n = X.shape
best_feature, best_threshold, best_gini = None, None, float('inf')
best_left_idx, best_right_idx = None, None
for feature in range(n):
# 排序 X[:, feature] 以便找到最佳分裂点
sorted_indices = np.argsort(X[:, feature])
sorted_X = X[sorted_indices]
sorted_y = y[sorted_indices]
for i in range(1, m): # 从1开始,避免最左或最右的分裂
if sorted_X[i, feature] == sorted_X[i-1, feature]: # 如果相邻元素相等,跳过
continue
# 计算分裂点
threshold = (sorted_X[i, feature] + sorted_X[i-1, feature]) / 2
left_idx = sorted_X[:, feature] <= threshold
right_idx = sorted_X[:, feature] > threshold
left_gini = self.gini(sorted_y[left_idx])
right_gini = self.gini(sorted_y[right_idx])
gini_score = (len(left_idx) * left_gini + len(right_idx) * right_gini) / m
if gini_score < best_gini:
best_feature, best_threshold, best_gini = feature, threshold, gini_score
best_left_idx, best_right_idx = left_idx, right_idx
return best_feature, best_threshold, best_left_idx, best_right_idx
def build_tree(self, X, y, depth=0):
"""递归构建决策树"""
if len(set(y)) == 1 or depth >= self.max_depth:
return Node(value=max(set(y), key=list(y).count))
feature, threshold, left_idx, right_idx = self.best_split(X, y)
if feature is None:
return Node(value=max(set(y), key=list(y).count))
left_subtree = self.build_tree(X[left_idx], y[left_idx], depth + 1)
right_subtree = self.build_tree(X[right_idx], y[right_idx], depth + 1)
return Node(feature, threshold, left_subtree, right_subtree)
def fit(self, X, y):
"""训练分类树"""
self.root = self.build_tree(X, y)
def predict_one(self, x, node):
"""单样本预测"""
if node.value is not None:
return node.value
if x[node.feature] <= node.threshold:
return self.predict_one(x, node.left)
else:
return self.predict_one(x, node.right)
def predict(self, X):
"""批量预测"""
return np.array([self.predict_one(sample, self.root) for sample in X])
def print_tree(self, node=None, depth=0):
"""文本格式输出决策树"""
if node is None:
node = self.root
if node.value is not None:
print(" " * depth + f"Leaf: Class {node.value}")
return
feature_name = f"X{node.feature + 1}" # 显示为 X1, X2, ...
print(" " * depth + f"|--- {feature_name} <= {node.threshold:.3f}")
self.print_tree(node.left, depth + 1)
self.print_tree(node.right, depth + 1)
def plot_tree(self):
"""可视化决策树"""
graph = nx.DiGraph()
pos = {}
def traverse(node, depth=0, x=0, parent=None):
if node is None:
return
node_id = id(node)
pos[node_id] = (x, -depth)
label = f"X[{node.feature}] <= {node.threshold:.2f}" if node.value is None else f"Class {node.value}"
graph.add_node(node_id, label=label)
if parent is not None:
graph.add_edge(parent, node_id)
traverse(node.left, depth + 1, x - 2 ** (-depth), node_id)
traverse(node.right, depth + 1, x + 2 ** (-depth), node_id)
traverse(self.root)
labels = nx.get_node_attributes(graph, 'label')
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
nx.draw(graph, pos, with_labels=True, labels=labels, node_size=2000, node_color="lightblue", font_size=10)
plt.title("CART 分类树可视化")
plt.show()
# 数据集
X = np.array([[2.7, 4.5], [3.4, 1.8], [1.3, 3.7], [5.1, 2.1]])
y = np.array([0, 1, 0, 1]) # 分类标签
# 训练分类树
tree = CARTClassifier(max_depth=2)
tree.fit(X, y)
# 预测
y_pred = tree.predict(X)
print("预测结果:", y_pred)
# 输出树结构
tree.print_tree()
# 设置支持中文的字体
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 使用黑体
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# 画出分类树
tree.plot_tree()
运行效果
预测结果: [0 1 0 1]
|--- X1 <= 3.050
|--- X1 <= 3.050
Leaf: Class 0
Leaf: Class 1
|--- X1 <= 3.200
Leaf: Class 0
Leaf: Class 1
sklearn实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, plot_tree, export_text
# 数据集
X = np.array([[2.7, 4.5], [3.4, 1.8], [1.3, 3.7], [5.1, 2.1]])
y = np.array([0, 1, 0, 1]) # 分类标签
# 训练 sklearn 的分类树
sklearn_tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="gini", max_depth=2)
sklearn_tree.fit(X, y)
# 预测
y_pred_sklearn = sklearn_tree.predict(X)
print("sklearn 预测结果:", y_pred_sklearn)
# 文本格式输出
print(export_text(sklearn_tree, feature_names=["X1", "X2"]))
# 设置支持中文的字体
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 使用黑体
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# 画出分类树
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plot_tree(sklearn_tree, feature_names=["X1", "X2"], class_names=["0", "1"], filled=True)
plt.title("sklearn 决策树")
plt.show()
运行效果
sklearn 预测结果: [0 1 0 1]
|--- X1 <= 3.05
| |--- class: 0
|--- X1 > 3.05
| |--- class: 1 
总结
- 计算整个数据集的基尼指数(初始为 0.5)。
- 依次尝试所有可能的分裂点,计算基尼指数,选择使基尼指数最小的
作为最优分裂点。
- 递归构建子树:
- 若子集数据的类别已经纯净,则停止分裂。
- 否则继续递归分裂,直到满足终止条件。
最终得到最优的二分决策树,能够对新的数据进行分类。
(2) CART 回归树
假设我们有如下 5 个样本,每个样本有一个特征 X 和对应的目标值 Y:
| 样本编号 | 特征 X | 目标值 Y |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| 2 | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| 3 | 3.0 | 4.0 |
| 4 | 4.0 | 4.5 |
| 5 | 5.0 | 5.0 |
目标:构建 CART 回归树,找到最优的分裂点,使得均方误差(MSE)最小。
步骤 1:计算数据集的总方差
回归树使用 均方误差(Mean Squared Error, MSE) 作为分裂标准:
其中:
是数据集的平均目标值。
计算整个数据集的均值:
计算整体均方误差:
步骤 2:尝试不同的分裂点
CART 采用 二分法,在所有可能的分裂点中选择使得 MSE 最小的点。
(1) 选取 X 作为分裂特征
候选分裂点(取相邻样本的均值):
对每个分裂点计算 MSE。
① 分裂点 X=1.5
分裂后:
- 左子集:X ≤ 1.5 → 样本 {1},Y={2.0}Y = \{2.0\}Y={2.0}。
- 右子集:X > 1.5 → 样本 {2, 3, 4, 5},Y={2.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0}。
计算左子集 MSE:
(只有一个样本)
计算右子集的均值:
计算右子集 MSE:
加权 MSE:
② 分裂点 X=2.5
分裂后:
- 左子集:X ≤ 2.5 → 样本 {1, 2},Y={2.0, 2.5}。
- 右子集:X > 2.5 → 样本 {3, 4, 5},Y={4.0, 4.5, 5.0}。
计算左子集均值:
计算左子集 MSE:
计算右子集均值:
计算右子集 MSE:
加权 MSE:
步骤 3:选择最优分裂点
- X = 1.5 时
。
- X = 2.5 时
(最小)。
- 其他分裂点的 MSE 更大。
最优分裂点:X = 2.5。
步骤 4:递归构建子树
按照 X = 2.5 进行分裂,得到:
- 左子树(X ≤ 2.5):均值为 2.25。
- 右子树(X > 2.5):均值为 4.5。
由于误差已足够小,停止分裂。
最终的回归树
如果输入新的 X 值:
- 若 X ≤ 2.5,则预测值为 2.25。
- 若 X > 2.5,则预测值为 4.5。
代码实现
从0开始完整实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
# 定义节点类
class Node:
"""回归树节点"""
def __init__(self, feature=None, threshold=None, left=None, right=None, value=None):
self.feature = feature # 分裂的特征索引(这里只有 1 个特征,固定为 0)
self.threshold = threshold # 分裂阈值
self.left = left # 左子树
self.right = right # 右子树
self.value = value # 叶子节点的预测值
# 定义 CART 回归树
class CARTRegressionTree:
def __init__(self, min_samples_split=2, max_depth=None):
self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split # 最小分裂样本数
self.max_depth = max_depth # 最大树深
self.root = None # 树的根节点
def fit(self, X, y):
"""训练回归树"""
self.root = self._build_tree(X, y, depth=0)
def _build_tree(self, X, y, depth):
num_samples = X.shape[0]
# 如果当前节点所有样本的目标值都相同,则无需继续分裂
if len(np.unique(y)) == 1:
return Node(value=y[0])
# 叶子节点的预测值为当前节点样本目标值的均值
leaf_value = np.mean(y)
# 如果样本数不足或已达到最大深度,返回叶子节点
if num_samples < self.min_samples_split or (self.max_depth is not None and depth >= self.max_depth):
return Node(value=leaf_value)
# 寻找最佳分裂:返回最佳特征、最佳分裂点以及左右分割的索引
best_feature, best_threshold, best_mse, best_left_idx, best_right_idx = self._find_best_split(X, y)
# 若没有找到有效的分裂(通常不会发生),返回叶子节点
if best_feature is None:
return Node(value=leaf_value)
# 递归构建左右子树
left_subtree = self._build_tree(X[best_left_idx], y[best_left_idx], depth + 1)
right_subtree = self._build_tree(X[best_right_idx], y[best_right_idx], depth + 1)
return Node(feature=best_feature, threshold=best_threshold, left=left_subtree, right=right_subtree)
def _find_best_split(self, X, y):
"""遍历所有候选分裂点,找到最优分裂"""
best_mse = float("inf")
best_feature, best_threshold = None, None
best_left_idx, best_right_idx = None, None
n_features = X.shape[1]
# 对每个特征(这里只有 1 个特征)
for feature in range(n_features):
# 取该特征上的所有唯一值并排序
unique_vals = np.sort(np.unique(X[:, feature]))
# 如果唯一值个数不足 2,则无法分裂
if unique_vals.shape[0] < 2:
continue
# 候选分裂点:相邻唯一值的中点
candidate_thresholds = (unique_vals[:-1] + unique_vals[1:]) / 2.0
for threshold in candidate_thresholds:
left_idx = X[:, feature] <= threshold
right_idx = X[:, feature] > threshold
# 如果任一侧为空,则跳过
if np.sum(left_idx) == 0 or np.sum(right_idx) == 0:
continue
mse = self._calculate_weighted_mse(y[left_idx], y[right_idx])
if mse < best_mse:
best_mse = mse
best_feature = feature
best_threshold = threshold
best_left_idx = left_idx
best_right_idx = right_idx
return best_feature, best_threshold, best_mse, best_left_idx, best_right_idx
def _calculate_weighted_mse(self, y_left, y_right):
"""计算左右子集的加权均方误差(这里用 SSE 再除以样本总数)"""
def sse(y):
mean_y = np.mean(y)
return np.sum((y - mean_y) ** 2)
left_sse = sse(y_left)
right_sse = sse(y_right)
total = len(y_left) + len(y_right)
return (left_sse + right_sse) / total
def predict(self, X):
"""预测多个样本"""
return np.array([self._predict_single(x) for x in X])
def _predict_single(self, x):
"""单个样本预测"""
node = self.root
while node.value is None:
if x[node.feature] <= node.threshold:
node = node.left
else:
node = node.right
return node.value
def print_tree(self, node=None, depth=0):
"""以文本格式打印树结构"""
if node is None:
node = self.root
if node.value is not None:
print(" " * depth + f"Leaf: {node.value:.2f}")
return
print(" " * depth + f"X[{node.feature}] <= {node.threshold:.2f}")
self.print_tree(node.left, depth + 1)
self.print_tree(node.right, depth + 1)
# ----------------------------
# 测试代码
# 数据集
X = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]])
y = np.array([2.0, 2.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0])
# 训练从零实现的 CART 回归树(最大深度设为2)
tree = CARTRegressionTree(max_depth=2)
tree.fit(X, y)
# 打印树结构,输出应为:
# X[0] <= 2.50
# X[0] <= 1.50
# Leaf: 2.00
# Leaf: 2.50
# X[0] <= 3.50
# Leaf: 4.00
# Leaf: 4.75
tree.print_tree()
# 生成预测数据
X_test = np.linspace(0, 6, 10).reshape(-1, 1)
y_pred = tree.predict(X_test)
# 可视化
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
plt.scatter(X, y, color="red", label="训练数据")
plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color="blue", label="CART 预测", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.title("手写 CART 回归树")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
运行效果
X[0] <= 2.50
X[0] <= 1.50
Leaf: 2.00
Leaf: 2.50
X[0] <= 3.50
Leaf: 4.00
Leaf: 4.75 
sklearn实现
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor, export_text
# 1. 构造数据集
X = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]).reshape(-1, 1)
y = np.array([2.0, 2.5, 4.0, 4.5, 5.0])
# 2. 训练回归树模型
reg_tree = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=2) # 限制树深度,避免过拟合
reg_tree.fit(X, y)
# 3. 生成预测数据
X_test = np.linspace(0, 6, 100).reshape(-1, 1) # 测试数据(0到6之间均匀取100个点)
y_pred = reg_tree.predict(X_test)
# 设置支持中文的字体
matplotlib.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 使用黑体
matplotlib.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 解决负号显示问题
# 4. 可视化结果
print(export_text(reg_tree, feature_names=["X"]))
plt.scatter(X, y, color="red", label="训练数据")
plt.plot(X_test, y_pred, color="blue", label="回归树预测", linewidth=2)
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.title("CART 回归树示例")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
运行效果
|--- X <= 2.50
| |--- X <= 1.50
| | |--- value: [2.00]
| |--- X > 1.50
| | |--- value: [2.50]
|--- X > 2.50
| |--- X <= 3.50
| | |--- value: [4.00]
| |--- X > 3.50
| | |--- value: [4.75]
总结
- 计算整个数据集的均方误差。
- 依次尝试所有可能的分裂点,计算 MSE,选择 MSE 最小的分裂点(X = 2.5)。
- 递归构建子树,直到误差足够小。
7. 总结
- CART 是一个用于构建分类树和回归树的决策树算法。
- 采用 基尼指数(分类) 和 MSE(回归) 作为分裂标准。
- 采用 二分法 进行划分,保证树的可解释性。
- 通过 剪枝 避免过拟合,提高泛化能力。
- 相比 ID3 和 C4.5,CART 更适用于数值型数据和回归问题。
