哈希表(Hash Table)
一、哈希表基本概念
1. 核心定义
- 哈希函数:将关键字映射到存储位置的函数
- 哈希冲突:不同关键字映射到相同位置的现象
- 装载因子:α = 元素数量 / 表长度(衡量空间利用率)
2. 重要特性
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|
| 平均时间复杂度 | 查找/插入/删除:O(1) |
| 最坏时间复杂度 | 所有操作退化到O(n) |
| 空间复杂度 | O(n) |
二、哈希函数设计原则
1. 优质哈希函数特征
- 计算简单
- 散列均匀
- 冲突概率低
2. 常见哈希函数类型
| 类型 | 公式 | 适用场景 |
|---|
| 除留余数法 | h(k) = k % p(p为质数) | 整数关键字 |
| 平方取中法 | 取k²中间几位数 | 不知分布的关键字 |
| 折叠法 | 分割相加后取模 | 较长数字关键字 |
三、完整实现示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
typedef int DATATYPE;
typedef struct
{
DATATYPE *head;
int tlen;
} HSTable;
HSTable *HSInit(int len)
{
HSTable *hs = malloc(sizeof(HSTable));
if (NULL == hs)
{
perror("HSInit malloc error");
return NULL;
}
hs->head = malloc(sizeof(HSTable) * len);
if (NULL == hs->head)
{
perror("HSInit malloc2 error");
return NULL;
}
hs->tlen = len;
memset(hs->head, -1, sizeof(HSTable) * len);
return hs;
}
int HSFun(HSTable *hs, DATATYPE *data)
{
return *data % hs->tlen;
}
int HSTableInsert(HSTable *hs, DATATYPE *data)
{
int inx = HSFun(hs, data);
while (hs->head[inx] != -1)
{
printf("data %d confilt pos :%d\n", *data, inx);
inx = (inx + 1) % hs->tlen;
}
memcpy(&hs->head[inx], data, sizeof(DATATYPE));
return 0;
}
int HSTableSearch(HSTable *hs, DATATYPE *data)
{
int inx = HSFun(hs, data);
int oldinx = inx;
while (hs->head[inx] != *data)
{
inx = (inx + 1) % hs->tlen;
if (oldinx == inx)
{
return -1;
}
}
return inx;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
int array[] = {12, 34, 56, 78, 91, 23, 45, 67, 89, 10};
HSTable *hs = HSInit(10);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
HSTableInsert(hs, &array[i]);
}
DATATYPE data = 34;
int idx = HSTableSearch(hs, &data);
if (-1 == idx)
{
printf("can't find\n");
}
else
{
printf("find %d\n", hs->head[idx]);
}
return 0;
}
内核风格链表(klist)
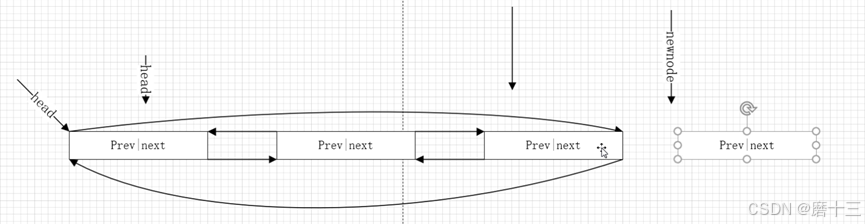
一、链表核心结构
1. 节点定义
typedef struct __klist {
struct __klist *next;
struct __klist *prev;
} KLIST;
2. 数据容器
typedef struct {
int id;
char name[40];
KLIST node; // 嵌入链表节点
} PER;
二、核心操作实现
1. 链表初始化
void klist_init(KLIST* head) {
head->prev = head;
head->next = head;
}
示意图:
head
┌─prev ────┐
│ │
└─next ────┘
2. 通用插入操作
void klist_add(KLIST* newnode, KLIST* prev, KLIST* next) {
newnode->next = next;
newnode->prev = prev;
prev->next = newnode;
next->prev = newnode;
}
// 头部插入
void klist_add_head(KLIST* head, KLIST* newnode) {
klist_add(newnode, head, head->next);
}
// 尾部插入
void klist_add_tail(KLIST* head, KLIST* newnode) {
klist_add(newnode, head->prev, head);
}
三、关键宏解析
1. 容器获取宏
#define offset(type, mem) ((size_t)&((type*)0)->mem)
#define containerof(ptr, type, mem) ({ \
const typeof(((type*)0)->mem)* _mptr = (ptr); \
(type*)((char*)_mptr - offset(type, mem)); })
原理图解:
PER结构体内存布局
+---------------+ +---------------+
| id (4字节) | | name (40字节) |
+---------------+ +---------------+
| node.next | | node.prev |
+---------------+ +---------------+
2. 安全遍历宏
#define klist_for_each(p, n, head, mem) \
for(p = containerof((head)->next, typeof(*p), mem), \
n = containerof(p->mem.next, typeof(*p), mem); \
&p->mem != (head); \
p = n, n = containerof(n->mem.next, typeof(*n), mem))
四、应用层接口
1. 添加人员信息
int add_per(int id, char* name, KLIST* head) {
PER* per = malloc(sizeof(PER));
if (!per) return 1;
per->id = id;
strcpy(per->name, name);
klist_add_tail(head, &per->node);
return 0;
}
2. 显示所有人员
int show_per(KLIST* head) {
PER *p, *n;
klist_for_each(p, n, head, node) {
printf("ID: %-5d Name: %s\n", p->id, p->name);
}
return 0;
}
3. 删除指定人员
int del_per(KLIST* head, int id) {
PER *p, *n;
klist_for_each(p, n, head, node) {
if (p->id == id) {
klist_del(p->node.prev, p->node.next);
free(p);
break; // 删除后立即退出
}
}
return 0;
}
五、性能对比
| 操作 | 时间复杂度 | 特点 |
|---|
| 插入头部 | O(1) | 直接修改头节点指针 |
| 插入尾部 | O(1) | 通过tail指针直接访问 |
| 随机访问 | O(n) | 需要遍历链表 |
| 删除节点 | O(1) | 已知节点位置时直接操作指针 |
六、containerOf 与 offsetof 宏补充
一、核心概念解析
1. offsetof 宏
#include <stddef.h>
#define offsetof(type, member) ((size_t)&(((type *)0)->member))
- 功能:计算结构体成员相对于结构体首地址的字节偏移量
- 原理:
通过将结构体指针强制类型转换为 0 地址指针,获取成员的"虚拟地址",其数值即为偏移量
2. containerOf 宏
#define containerOf(ptr, type, member) \
((type *)((char *)(ptr) - offsetof(type, member)))
- 功能:通过成员指针反推外层结构体指针
- 原理:
成员指针地址减去该成员的偏移量,得到结构体起始地址
二、内存布局图示
1. 结构体内存模型
+-------------------+ <-- 结构体起始地址
| member1 (4字节) |
+-------------------+
| member2 (1字节) |
+-------------------+
| member3 (8字节) |
+-------------------+
2. containerOf 工作流程
假设:
- 结构体类型为 MyStruct
- 成员指针 ptr 指向 member3
- member3 偏移量为 5 字节
ptr 地址:0x1005
结构体地址 = 0x1005 - 5 = 0x1000
三、完整代码示例
1. 数据结构定义
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stddef.h>
typedef struct list_head {
struct list_head *prev, *next;
} LIST_HEAD;
typedef struct task_struct {
int pid;
char state;
LIST_HEAD tasks; // 嵌入链表节点
} PROCESS;
2. 宏实现
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof(((type *)0)->member) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)((char *)__mptr - offsetof(type, member)); })
#define list_entry(ptr) container_of(ptr, PROCESS, tasks)
3. 使用示例
void process_task(LIST_HEAD *task_node) {
// 通过链表节点获取进程结构体
PROCESS *proc = list_entry(task_node);
printf("PID: %d, State: %c\n", proc->pid, proc->state);
}
int main() {
PROCESS p = {.pid = 1001, .state = 'R'};
process_task(&p.tasks); // 输出:PID: 1001, State: R
return 0;
}
四、关键特性对比
| 特性 | offsetof | containerOf |
|---|
| 输入参数 | 结构体类型 + 成员名 | 成员指针 + 结构体类型 + 成员名 |
| 输出结果 | 字节偏移量(size_t) | 外层结构体指针 |
| 计算时机 | 编译时 | 运行时 |
| 标准支持 | C89 标准 | GNU 扩展 |
五、应用场景分析
1. Linux 内核链表
// 内核源码示例(linux/list.h)
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
2. 设备驱动开发
typedef struct usb_device {
int vendor_id;
struct list_head device_list; // 设备链表节点
} USB_DEV;
void scan_devices(struct list_head *dev_node) {
USB_DEV *dev = container_of(dev_node, USB_DEV, device_list);
// 访问设备详细信息
}

