【并发编程】异步编程CompletableFuture实战
文章目录
- 1.CompletableFuture简介
- 2.CompletableFuture核心API实战
- 3.CompletableFuture嵌套案例实战
- 4.合并两个CompletableFuture案例实战
- 5.多个CompletableFuture任务组合调度实战
1.CompletableFuture简介
在JDK8之前,我们使用的Java多线程变成,主要是 Thread+Runnable 来完成,但是这种方式有个弊端就是没有返回值。如果想要返回值怎么办呢,大多数人就会想到 Callable + Thread 的方式来获取到返回值。

通过上面的类继承关系图可以知道 CompletableFuture 实现了 Future 接口和 CompletionStage 。因此 CompletableFuture是对 Futrue的功能增强包含了Future的功能。从继承的另一个 CompletionStage 的名称来看完成阶段性的接口。
CompletableFuture的核心用途:
- 在项目开发中,由于业务规划逻辑的原因,业务需要从多个不同的地方获取数据,
- 然后汇总处理为最终的结果,再返回给请求的调用方,就是聚合信息处理类的处理逻辑
- 如果常用串行请求,则接口响应时间长;利用CompletableFuture则可以大大提升性能
- 针对多任务,需要进行任务编排调度,也可以使用CompletableFuture进行完成
CompletableFuture类实现了Future和CompletionStage接口,相当于一个Task编排工具
-
Future
- 表示异步计算的结果,它提供了检查计算是否完成的方法,以等待计算的完成
- 计算完成后只能使用 get 方法来获取结果,有cancel、get、isDone、isCancelled等方法
-
CompletionStage
- 是Java8新增接口,用于异步执行中的阶段处理,CompletableFuture是其中的一个实现类
- 对任务处理可以构造一条结果传递链,在结果传递过程中任何一个CompletionStage都可以对结果进行处理
- 包括异常处理、类型转换,可以构造非常简单的传递链也可以构造很复杂的传递链
- 几个CompletionStage可以串联起来,一个完成的阶段可以触发下一阶段的执行
-
当前的Task到底由那个Thread执行,使用的不好可能会有性能问题, 根据
CompletableFuture的方法命名可以掌握- 不带Async的方法,比如thenAccept,表示该方法将继续在当前执行CompletableFuture的方法线程中执行
- 带Async的方法,比如thenAcceptAsync,表示异步,在线程池中执行
- 在没有指定线程池的情况下,使用的是CompletableFuture内部的线程池 ForkJoinPool ,线程数默认是 CPU 的核心数
- 一般不要所有业务共用一个线程池,避免有任务执行一些很慢的 I/O 操作,
- 会导致线程池中所有线程都阻塞在 I/O 操作上,从而造成线程饥饿,影响整个系统的性能
方法API
- CompletableFuture静态方法,执行异步任务的API
//无返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable)
//无返回值,可以自定义线程池
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable, Executor executor)
//有返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier)
//有返回值,可以自定义线程池
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier, Executor executor)
- CompletableFuture对象,获取结果的API
//如果返回值没有返回,一直阻塞
V get()
//设置等待超时的时间
V get(long timeout,Timeout unit);
//有返回值就返回, 线程抛出异常就返回设置的默认值
T getNow(T defaultValue);
- CompletableFuture对象,其他重点API
//方法无返回值,当前任务正常完成以后执行,当前任务的执行结果可以作为下一任务的输入参数
thenAccept
//方法有返回值,当前任务正常完成以后执行,当前任务的执行的结果会作为下一任务的输入参数
thenApply
//对不关心上一步的计算结果,执行下一个操作
thenRun
2.CompletableFuture核心API实战
(1)supplyAsync方法实战,有返回值,默认使用ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
public static void testCompletableFuture1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
return "lixiang";
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}

(2)runAsync方法实战,无返回值
public static void testCompletableFuture2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.runAsync(()->{
System.out.println("runAsync方法执行。。。");
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}

(3)thenApply 组合调度,能拿到上步执行的结果,并且当前执行完有任务返回值的
public static void testCompletableFuture3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("supplyAsync方法执行。。。");
return "lixiang";
}).thenApply((ele)->{
System.out.println("thenApply方法执行。。。,拿到上一步的执行结果:"+ele);
return ele + " is a java工程师";
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}

(4)thenAccept 组合调度,能拿到上步执行的结果,当前执行完无任务返回值的
public static void testCompletableFuture4() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<Void> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(()->{
System.out.println("supplyAsync方法执行。。。");
return "lixiang";
}).thenAccept((ele)->{
System.out.println("thenAccept方法执行。。。,拿到上一步的执行结果:"+ele);
});
System.out.println(future.get());
}

3.CompletableFuture嵌套案例实战
-
需求
- 日常的任务中,通常定义的方法都会返回 CompletableFuture 类型,方便后续操作
- 然后将该任务的执行结果Future作为方法入参然后执行指定的方法, 返回一个新的CompletableFuture
- 任务它们之间存在着业务逻辑上的先后顺序
-
thenCompose
- 用来连接两个CompletableFuture,是生成一个新的CompletableFuture,用于组合多个CompletableFuture
- 也可以使用 thenApply() 方法来描述关系,但返回的结果就会发生 CompletableFuture 的嵌套
- CompletableFuture<CompletableFuture< Product >> 这样的情况,需要get两次
(1)编写商品类
@Data
public class Product {
private int id;
private String title;
private String detail;
}
(2)模拟商品service
public class ProductService {
private static final Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
static {
map.put(1,"iphone14");
map.put(2,"iphone 蓝牙耳机");
map.put(3,"Mac Book Pro-详情图内容");
map.put(4,"小香风深蓝色大衣");
map.put(5,"清热解火菊花茶");
map.put(6,"补肝养肾枸杞大枣茶");
map.put(7,"颈椎病康复指南");
}
public String getById(int id){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("ProductService#getById方法运行线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return map.get(id);
}
}
(3)模拟商品详情service
public class ProductDetailService {
private static final Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<>();
static {
map.put(1,"iphone14-详情图内容");
map.put(2,"iphone 蓝牙耳机-详情图内容");
map.put(3,"Mac Book Pro-详情图内容");
map.put(4,"小香风深蓝色大衣-详情图内容");
map.put(5,"清热解火菊花茶-详情图内容");
map.put(6,"补肝养肾枸杞大枣茶-详情图内容");
map.put(7,"颈椎病康复指南-详情图内容");
}
public String getById(int id){
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println("DetailService # getById方法运行线程:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return map.get(id);
}
}
(4)测试方法,正常用thenApply,需要get两次
public static void test1() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService productDetailService = new ProductDetailService();
//第一步异步 ,第二部异步
CompletableFuture<CompletableFuture<Product>> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
Product product = new Product();
String title = productService.getById(1);
product.setId(product.getId());
product.setTitle(title);
return product;
}).thenApply(product -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String detail = productDetailService.getById(1);
product.setDetail(detail);
return product;
}));
//这块 获取 商品信息要get两次
System.out.println("获取商品信息:"+future.get().get());
}
(5)测试方法,用thenCompose,只需要get一次即可
public static void test2() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService productDetailService = new ProductDetailService();
//第一步异步 ,第二部异步
CompletableFuture<Product> compose = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
Product product = new Product();
String title = productService.getById(1);
product.setId(product.getId());
product.setTitle(title);
return product;
}).thenCompose(product -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String detail = productDetailService.getById(1);
product.setDetail(detail);
return product;
}));
//这块 获取 商品信息要get两次
System.out.println("获取商品信息:"+compose.get());
}

4.合并两个CompletableFuture案例实战
-
需求
- 需要请求两个个接口,然后把对应的CompletableFuture进行合并,返回一个新的CompletableFuture
-
thenCombine
- 在两个任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果合并,有返回值。
-
编码实战
public static void test3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService detailService = new ProductDetailService();
int id = 1;
//第1个任务
CompletableFuture<Product> baseProductFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String title = productService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setTitle(title);
product.setId(id);
return product;
});
//第2个任务
CompletableFuture<Product> detailProductFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String detail = detailService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setDetail(detail);
product.setId(id);
return product;
});
CompletableFuture<Product> compose = baseProductFuture.thenCombine(detailProductFuture,
(base, detail) -> {
base.setDetail(detail.getDetail());
return base;
});
System.out.println(compose.get());
}

- thenAccepetBoth
- 在两个任务都执行完成后,把两个任务的结果合并,有返回值。
- 编码实战
public static void test3() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ProductService productService = new ProductService();
ProductDetailService detailService = new ProductDetailService();
int id = 1;
//第1个任务
CompletableFuture<Product> baseProductFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String title = productService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setTitle(title);
product.setId(id);
return product;
});
//第2个任务
CompletableFuture<Product> detailProductFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
String detail = detailService.getById(id);
Product product = new Product();
product.setDetail(detail);
product.setId(id);
return product;
});
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptBoth = baseProductFuture.thenAcceptBoth(detailProductFuture, (base, detail) -> {
base.setDetail(detail.getDetail());
System.out.println(base);
});
System.out.println(acceptBoth.get());
}

5.多个CompletableFuture任务组合调度实战
背景
- 前面学习处理两个 Future 的关系,如果超过两个Future,如何处理他们的一些聚合关系呢
- 方法 allOf 和 anyOf
- 两个函数都是静态函数,参数是变长的 CompletableFuture 的集合,前者是「与」,后者是「或」
- allOf
- 返回值是 CompletableFuture< Void >类型
- 因为allOf没有返回值,所以通过thenApply,获取每个 CompletableFuture 的执行结果
- anyOf
- 只要有任意一个 CompletableFuture 结束,就可以做接下来的事情,不像 allOf 要等待所有的 CompletableFuture 结束
- 每个 CompletableFuture 的返回值类型都可能不同,无法判断是什么类型
- 所以 anyOf 的返回值是 CompletableFuture< Object >类型
(1)allOf编码实战
public static void testAllOf() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1执行完成");
return "future1执行完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2执行完成");
return "future2执行完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future3执行完成");
return "future3执行完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Void> all = CompletableFuture.allOf(future1, future2, future3);
//阻塞,直到所有任务结束。
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞");
//调用join方法等待全部任务完成
all.join();
if (all.isDone()) {
//一个需要耗时2秒,一个需要耗时3秒,只有当最长的耗时3秒的完成后,才会结束。
System.out.println("全部任务执行完成");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞结束");
}

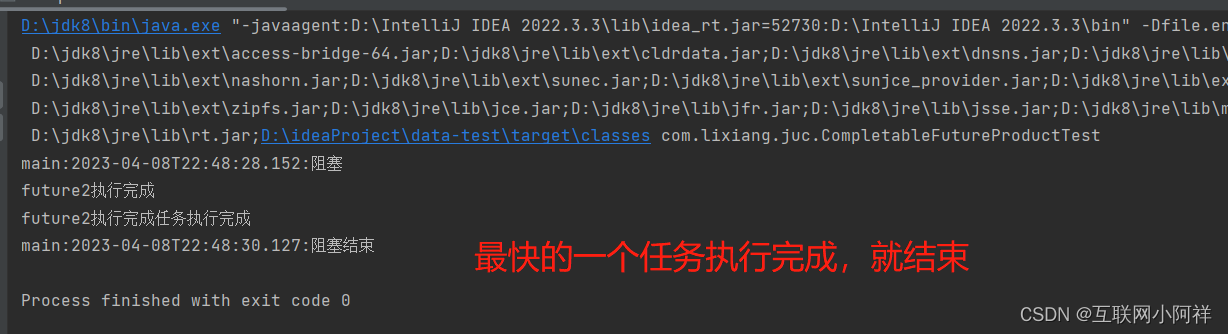
(2)anyOf编码实战
public static void testAnyOf() throws Exception {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future1执行完成");
return "future1执行完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future2执行完成");
return "future2执行完成";
});
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("future3执行完成");
return "future3执行完成";
});
CompletableFuture<Object> any = CompletableFuture.anyOf(future1, future2, future3);
//阻塞,最快任务执行完成 任务结束。
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞");
//调用join方法等待最快的一个任务执行
any.join();
if (any.isDone()) {
//一个需要耗时2秒,一个需要耗时3秒,一个耗时5秒 当最短的完成则会结束
System.out.println(any.get()+"任务执行完成");
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + ":" + LocalDateTime.now() + ":阻塞结束");
}