多态语法详解
多态语法详解
- 一:概念
- 1:多态实现条件
- 二:重写:
- 三:向上转型和向下转型
- 1:向上转型:
- 1:直接赋值:
- 2:方法传参
- 3:返回值
- 2:向下转型
一:概念
1:同一个引用,调用了同一个方法,因为引用的对象不一样,所表现出来的行为也不一样。
1:多态实现条件
1:必须在继承体系下;
2:子类必须对父类中的方法进行重写;
3:通过父类引用调用重写的方法;
二:重写:
重写也称覆盖。重写是子类对父类非静态,非private,非final修饰,非构造方法等的实现过程进行重新编写。
重写规则
1:方法名,参数列表(参数类型,个数,顺序),返回类型都要相同,(返回类型可以构成父子类关系)。
2:子类重写父类同名的方法时,子类方法的访问权限要大于父类的。
3:当在父类的构造方法中,调用了子类和父类同名的方法时,此时会调用子类的方法。
提醒: 不要在构造方法中调用重写的方法。
class Person{
public String name;
public int age;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
fun();
}
public void fun(){
System.out.println("父类的fun()方法");
}
}
class Student extends Person{
public Student(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
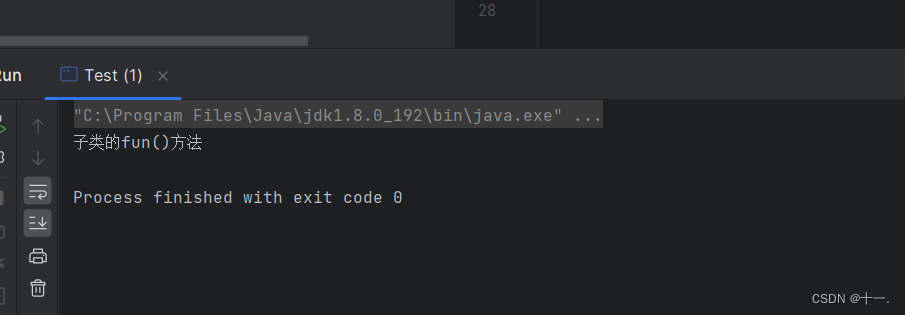
public void fun(){
System.out.println("子类的fun()方法");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student=new Student("张三",20);
}
}
 4:父类方法被static ,final,private修饰不能重写
4:父类方法被static ,final,private修饰不能重写
三:向上转型和向下转型
1:向上转型:
子类对象给到了父类对象,也可以理解为:父类引用引用的是子类对象,通过父类的引用去调用父类和子类同名的方法,不过调用的是子类的方法。(也叫作动态绑定)
1:直接赋值:
class Animal{
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(this.age+"在吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃狗粮");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
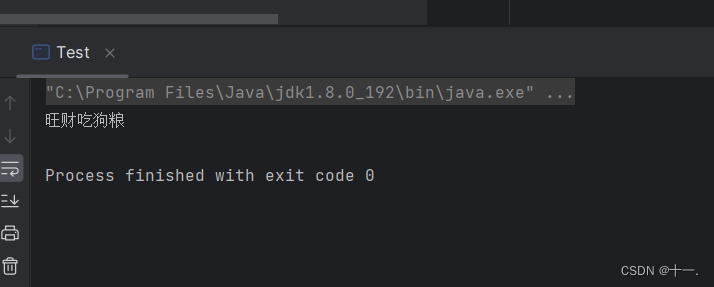
Animal animal=new Dog("旺财",3);//父类引用引用了子类对象
animal.eat();//通过父类引用访问了和父类同名的子类方法,
}
}
2:方法传参
class Animal{
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(this.age+"在吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃狗粮");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃猫粮");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void fun(Animal animal){
animal.eat();//同一个引用,引用了同一个方法,因为引用的对象不一样,所表现出来的行为不一样,我们把这种思想叫做多态
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
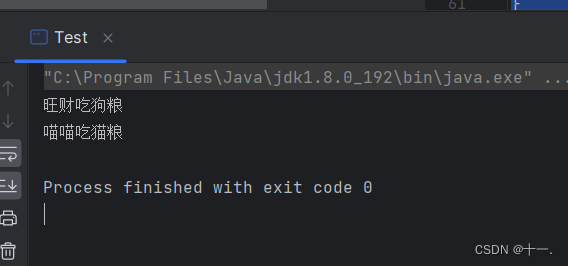
Dog dog=new Dog("旺财",3);
fun(dog);
fun(new Cat("喵喵",2));
}
}
3:返回值
作返回值,返回任意子类对象
class Animal{
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(this.age+"在吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃狗粮");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃猫粮");
}
}
public class Test {
public static Animal fun(){
return new Dog("旺财",3);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal=fun();
animal.eat();
}
}
2:向下转型
将一个子类对象经过向上转型后当成父类方法使用,再也无法调用子类特有的方法,
class Animal{
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(this.age+"在吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃狗粮");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃猫粮");
}
public void barks(){
System.out.println(this.getName()+"摇尾巴");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal =new Dog("旺财",3);
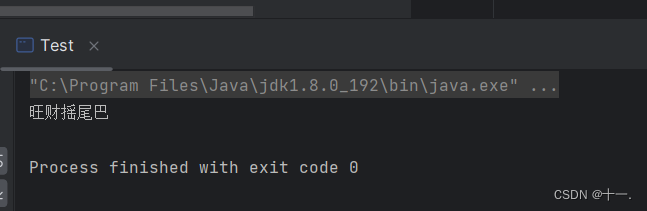
animal.barks();
}
}
但有时需要调用子类特有的方法,此时:将父类引用在还原为子类对象,也就是向下转型。
class Animal{
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(this.age+"在吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
public void barks(){
System.out.println(this.getName()+"摇尾巴");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃狗粮");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃猫粮");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog=new Dog("旺财" ,2);
Animal animal =dog;
dog=**(Dog)** animal;
dog.barks();
}
}
 向下转型用的比较少,而且不完全,万一转换失败,运行时就会抛出异常,Java中为了提高向下转型的安全性,引入了instance,如果表达式为true,则可以安全转换。
向下转型用的比较少,而且不完全,万一转换失败,运行时就会抛出异常,Java中为了提高向下转型的安全性,引入了instance,如果表达式为true,则可以安全转换。
class Animal{
private String name;
private int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println(this.age+"在吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
public Dog(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
public void barks(){
System.out.println(this.getName()+"摇尾巴");
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃狗粮");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public Cat(String name, int age) {
super(name, age);
}
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"吃猫粮");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Dog("旺财", 3);
if (animal instanceof Dog) {
Dog dog = (Dog) animal;
((Dog) animal).barks();
}
}
}