栈和队列知识点+例题
1.栈
1.1栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素的操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端成为栈顶,另一端成为栈底。遵守后进先出的原则(类似于弹夹)
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/入栈/压栈,入数据在栈顶
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈,出数据也在栈顶
那如何实现栈呢?

经过比较,数组栈是最优解,(链式的扩容会很久才会扩容一下)
由于top的位置意义不同,我们分为两种解决方案

1.2基本操作
1.定义一个栈
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
int *a;
int top;
int capacity;
}
2,初始化一个栈
void STInit(ST*pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a=NULL;
pst->top=0;
pst->capacity=0;
}
3压栈
void STPush(ST* pst, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
ST* newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : capacity * 2;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc((SLDataType)*newcapacity);
if (newcapacity == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
}
}4,弹栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top>0);
pst->top--;
}5 返回栈顶元素
void STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top>0);
return pst->a[pst->top-1];
}6 判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}7 栈的大小
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}8销毁栈
void STDestory(ST*pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a=NULL;
pst->top=pst->capacity=0;
}让我们看几道例题吧
例题1:

思路:栈的顺序是后进先出,有题可知,最后一个是E,所以E先出,故选B
例题2:

我们首先看选项,A选项:1先进,1先出,把2 3 4放进去,把4拿出来,再把3拿出来,最后把2拿出来。同理,我们看C选项,把1 2 3放进去,然后把3拿出来,然后我们会发现,如果想要拿1的话,拿2是必经之路,所以此选项错误
例题3:

思路:
1,先建立一个栈,初始化一个栈,
2,然后我们把所有的左括号放入栈里面,如果不是左括号,即是有括号;
3,其次我们要知道,本题的关键在于数量匹配和顺序匹配。所以我们要考虑一下栈是否为空(右括号的数量大于左括号的数量),然后考虑顺序匹配的问题
4,最后我们看栈是否为空,如果为空,就返回true,然后把栈毁掉
bool isVaild(char* s)
{
ST st;// 定义一个栈
STInit(&st);
while (*s)
{
if (*s == '[' || *s == '{' || *s == '(')
{
STPush(&st, *s);
s++;
}
else
{
if (STEmpty(&st))
{
return false;
}
//栈里面取左括号
char top = STTop(&st);
STPop(&st);
//顺序不匹配
if (*s == ']' && top != '[') || (8s == '}' && top != '{') || (*s == ')' && top == '(')
{
return false;
}
s++;
}
}
//栈为空,返回真,说明数量都匹配
bool ret = STEmpty(&st);
STDestory(&pst);
return ret;
}好啦~栈我们就先讲到这里啦,让我们看一下队列的知识点吧
2,队列
2.1队列的概念和结构

我们可以考虑一个问题
入队之后,出队的时候顺序是唯一一定的吗?
答案是:当然是;
从以上我们可以了解到,栈用数组的方法比较好;而队列用单链表,头删尾插的方式比较好
2.2基本操作
1定义一个队列
typedef int QueueType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
QueueType val;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;为了解决二级指针以及两个指针的问题,我们可以把两个指针放入一个结构体里面,然后进行一级指针的操作即可
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* phead;
QNode* ptail;
int size;
}Queue;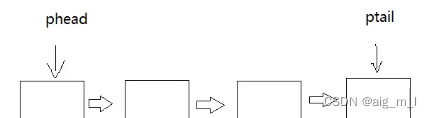
2.初始化一个队列
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->size = 0;
pq->phead = pq->ptail = NULL;
}3.插入到队列
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
return -1;
else
{
newnode->val = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
}
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
return -1;
pq->tail = pq->phead = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
4. 头删
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
QNode* del = pq->phead;
pq->phead = pq->phead->next;
if (pq->phead = NULL)
pq->tail = NULL;
}5找头结点的值
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->phead);
return pq->phead->val;
}6队列是否为空
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->phead=NULL;
}7队列大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}8销毁队列
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->phead;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
cur = next;
}
pq->phead=pq->ptail=NULL;
}让我们看几道关于队列和栈的例题吧
例题1:
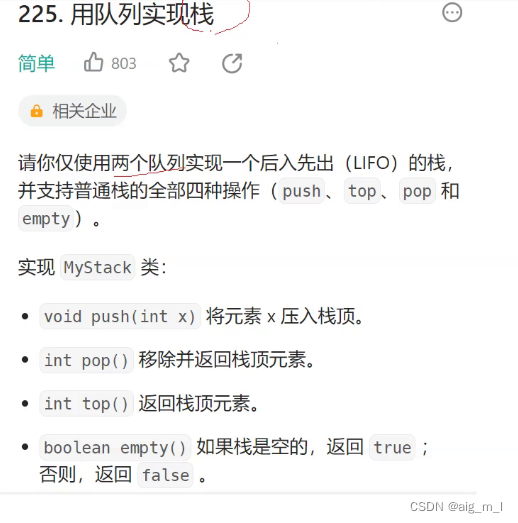
思路:
 代码实现:
代码实现:
typedef struct
{
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
}Stack;
MyStack* CreateStack()
{
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void mystackpush(Mystack* obj, int x)
{
Queue Empty = &obj->q1;
Queue nonEmpty =&obj->q2;
if (!Empty(&obj->q1))
{
Queue Empty = &obj->q2;
Queue nonEmpty = &obj->q1;
}
//开始到数据
while (QueueSize(nonempty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(Empty, QueueFront(nonempty));
QueuePop(nonempty);
}
int top = QueueFront(nonempty);
QueuePop(nonempty);
return top;
}
int mystackTop(Mystack* obj)
{
if (!Empty(&obj->q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool mystackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void mystackFree(Mystack* obj)
{
QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}例题2:
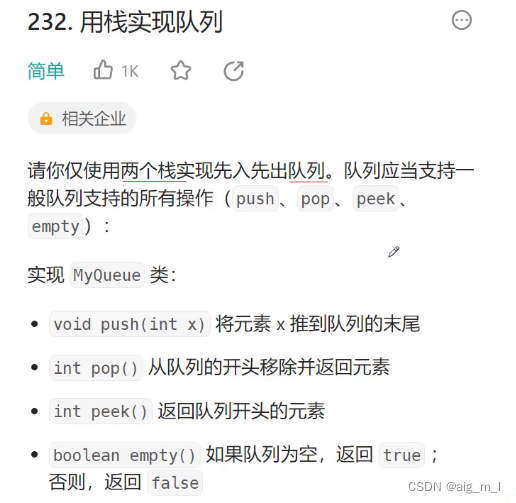
思路:

代码实现:

typedef struct
{
int* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
typedef struct
{
ST pushst;
ST popst;
}MyQueue;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = 0;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//压栈
void STPush(ST* pst, SLDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
ST* newcapacity = (SLDataType*)malloc(sizeof(SLDataType);
SLDataType* tmp = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : newcapacity * 2;
if (newcapacity == 0)
{
return -1;
}
else
{
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
}
}
//返回栈顶元素
void STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst->a[pst->top - 1];
}
//弹栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
//判断是否为空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&obj->pushst);
STInit(&obj->popst);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
STPush(&obj->pushst, x);
}
返回队列开头的元素(不删除)
void myQueuepeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
if (!STEmpty(&obj->popst))
{
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
else
{
while (!STEmpty(&obj->pushst))
{
STPush(&obj->popst, STTop(&obj->pushst);
STPop(&obj->pushst);
}
return STTop(&obj->popst);
}
}
//从队列开头移除并返回元素
void myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
int front = myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&obj->popst);
return front;
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
return STEmpty(&obj->pushst) && (&obj->popst);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
STDestory(&obj->popst);
STDestory(&obj->pushst);
free(obj);
}
接下来我们看一下循环队列吧
1.判断循环队列是否为空:front==back(front指向对头,back指向队尾的下一个)

如何判断队列是否为满
1.前提:front==back(当size=0时,为空,size!=0则为满)
2,再增加一个地方)
即
数组实现(back+1)%(k+1)==front则为满,其中,k+1指的是开辟空间的个数,k指的是有效数据数 数组实现&(k+1)是为了防止溢出
链表实现,即把上面式子去掉 %(k+1)
链表实现:
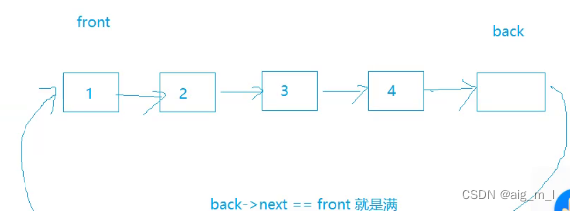
数组实现:
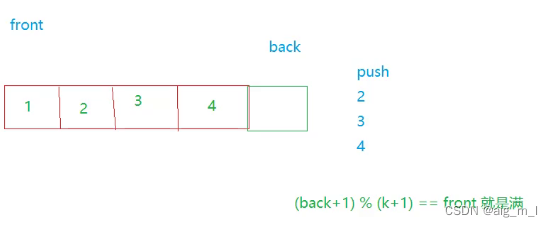
单链表缺陷以及找尾的办法:
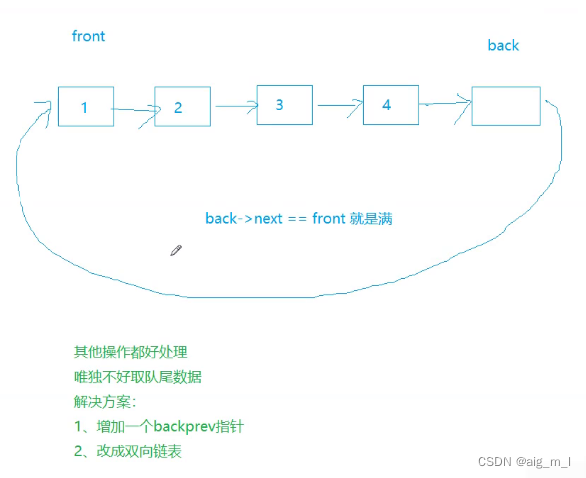
如何计算循环中元素的个数

typedef struct {
int* a;
int front;
int back;
int k;
}MyCircularQueue;
//初始化
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k) {
MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * (k + 1));
obj->front = 0;
obj->back = 0;
obj->k = 0;
return obj;
}
//是否为空
bool myCircularQueueEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return obj->front = obj - back;
}
//是否为满
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return (obj->front) % (obj->k + 1) == obj->front;
}
//插入
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
obj->a[obj->back] = value;
obj->back++;
obj->back % (obj->k + 1) = obj->back;
return true;
}
//删除
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
++obj->front;
obj->front % (obj->k + 1) = obj->front;
return true;
}
//返回队头
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
return obj->a[obj->front];
}
//返回队尾
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if (myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
{
return false;
}
return obj->a[obj->back - 1];
}
//清空
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}好啦~关于栈和队列的知识点就这些啦~谢谢大家观看~
