【数据结构】树与二叉树(廿五):树搜索指定数据域的结点(算法FindTarget)
文章目录
- 5.3.1 树的存储结构
- 5. 左儿子右兄弟链接结构
- 5.3.2 获取结点的算法
- 1. 获取大儿子、大兄弟结点
- 2. 搜索给定结点的父亲
- 3. 搜索指定数据域的结点
- a. 算法FindTarget
- b. 算法解析
- c. 代码实现
- a. 使用指向指针的指针
- b. 直接返回找到的节点
- 4. 代码整合
5.3.1 树的存储结构
5. 左儿子右兄弟链接结构
【数据结构】树与二叉树(十九):树的存储结构——左儿子右兄弟链接结构(树、森林与二叉树的转化)
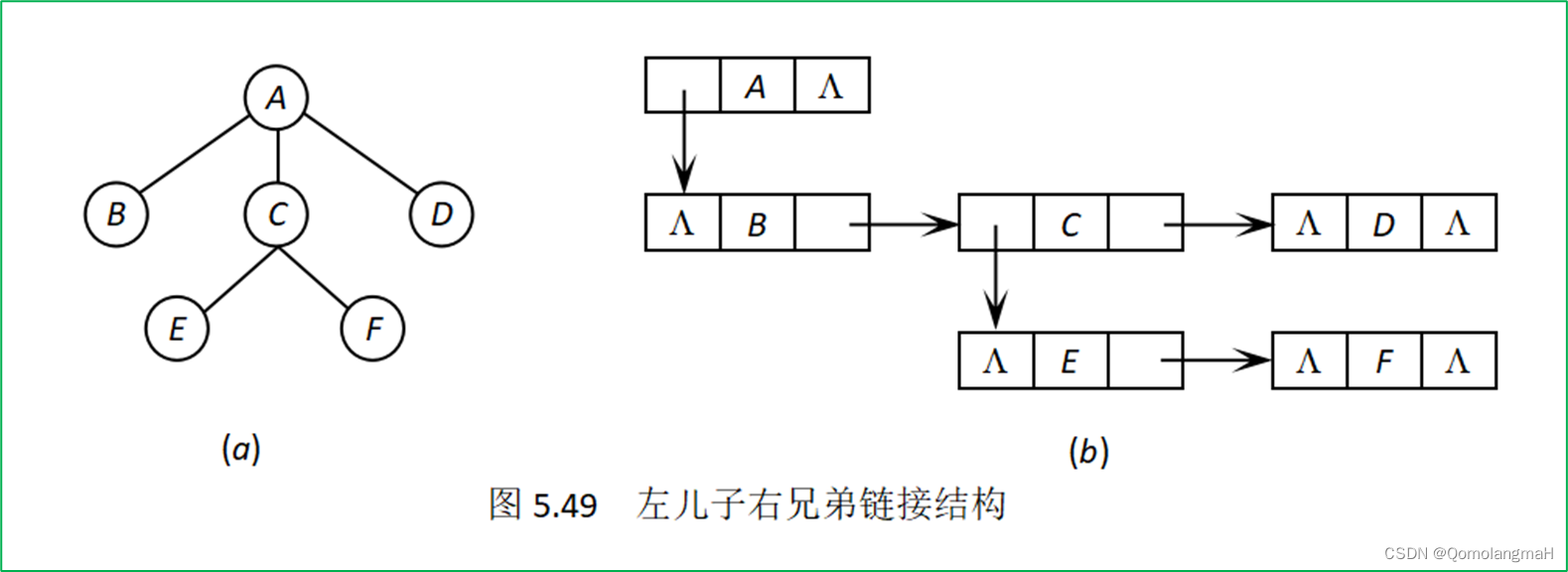
左儿子右兄弟链接结构通过使用每个节点的三个域(FirstChild、Data、NextBrother)来构建一棵树,同时使得树具有二叉树的性质。具体来说,每个节点包含以下信息:
- FirstChild: 存放指向该节点的大儿子(最左边的子节点)的指针。这个指针使得我们可以迅速找到一个节点的第一个子节点。
- Data: 存放节点的数据。
- NextBrother: 存放指向该节点的大兄弟(同一层中右边的兄弟节点)的指针。这个指针使得我们可以在同一层中迅速找到节点的下一个兄弟节点。
通过这样的结构,整棵树可以用左儿子右兄弟链接结构表示成一棵二叉树。这种表示方式有时候被用于一些特殊的树结构,例如二叉树、二叉树的森林等。这种结构的优点之一是它更紧凑地表示树,而不需要额外的指针来表示兄弟关系。
A
/|\
B C D
/ \
E F
A
|
B -- C -- D
|
E -- F
即:
A
/
B
\
C
/ \
E D
\
F
5.3.2 获取结点的算法
1. 获取大儿子、大兄弟结点
【数据结构】树与二叉树(二十):树获取大儿子、大兄弟结点的算法(GFC、GNB)
2. 搜索给定结点的父亲
【数据结构】树与二叉树(廿四):树搜索给定结点的父亲(算法FindFather)
3. 搜索指定数据域的结点
a. 算法FindTarget

b. 算法解析
算法FindTarget在以t为根指针的树中搜索数据成员等于target的节点,类似先根遍历,其时间复杂度为O(n) 。
- 首先,将
result指针设置为空。 - 如果
t为空,直接返回。 - 如果
t的数据成员等于target,表示找到了目标节点,将result指针指向t,然后返回。 - 将指针
p指向t的第一个子节点。 - 进入一个循环,只要
p不为空:- 递归调用
FindTarget函数,传入参数p和target,并将结果存储在result中。 - 如果
result不为空,表示已经找到了目标节点,直接返回。 - 将指针
p更新为p的下一个兄弟节点。
- 递归调用
- 如果循环结束仍然没有找到目标节点,那么
result仍然为空。
c. 代码实现
a. 使用指向指针的指针
TreeNode* FindTarget(TreeNode* t, char target) {
if (t == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
if (t->data == target) {
return t;
}
TreeNode* p = t->firstChild;
while (p != NULL) {
struct TreeNode* resultt = FindTarget(p, target);
if (resultt != NULL) {
return resultt;
}
p = p->nextBrother;
}
}
b. 直接返回找到的节点
void FindTarget(TreeNode* t, char target, TreeNode** result) {
*result = NULL;
if (t == NULL) {
return;
}
if (t->data == target) {
*result = t;
return;
}
TreeNode* p = t->firstChild;
while (p != NULL) {
FindTarget(p, target, result);
if (*result != NULL) {
return;
}
p = p->nextBrother;
}
}
两种实现方式在逻辑上是等价的,主要的区别在于结果的返回方式和对指针的处理。
4. 代码整合
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 定义树节点
typedef struct TreeNode {
char data;
struct TreeNode* firstChild;
struct TreeNode* nextBrother;
} TreeNode;
// 创建树节点
TreeNode* createNode(char data) {
TreeNode* newNode = (TreeNode*)malloc(sizeof(TreeNode));
if (newNode != NULL) {
newNode->data = data;
newNode->firstChild = NULL;
newNode->nextBrother = NULL;
}
return newNode;
}
// 释放树节点及其子树
void freeTree(TreeNode* root) {
if (root != NULL) {
freeTree(root->firstChild);
freeTree(root->nextBrother);
free(root);
}
}
// 算法GFC:获取大儿子结点
TreeNode* getFirstChild(TreeNode* p) {
if (p != NULL && p->firstChild != NULL) {
return p->firstChild;
}
return NULL;
}
// 算法GNB:获取下一个兄弟结点
TreeNode* getNextBrother(TreeNode* p) {
if (p != NULL && p->nextBrother != NULL) {
return p->nextBrother;
}
return NULL;
}
// 队列结构
typedef struct QueueNode {
TreeNode* treeNode;
struct QueueNode* next;
} QueueNode;
typedef struct {
QueueNode* front;
QueueNode* rear;
} Queue;
// 初始化队列
void initQueue(Queue* q) {
q->front = NULL;
q->rear = NULL;
}
// 入队列
void enqueue(Queue* q, TreeNode* treeNode) {
QueueNode* newNode = (QueueNode*)malloc(sizeof(QueueNode));
newNode->treeNode = treeNode;
newNode->next = NULL;
if (q->rear == NULL) {
q->front = newNode;
q->rear = newNode;
} else {
q->rear->next = newNode;
q->rear = newNode;
}
}
// 出队列
TreeNode* dequeue(Queue* q) {
if (q->front == NULL) {
return NULL; // 队列为空
}
TreeNode* treeNode = q->front->treeNode;
QueueNode* temp = q->front;
q->front = q->front->next;
free(temp);
if (q->front == NULL) {
q->rear = NULL; // 队列为空
}
return treeNode;
}
// 层次遍历的算法
void LevelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
if (root == NULL) {
return;
}
Queue queue;
initQueue(&queue);
enqueue(&queue, root);
while (queue.front != NULL) {
TreeNode* p = dequeue(&queue);
while (p != NULL) {
// 访问当前结点
printf("%c ", p->data);
// 将大儿子结点入队列
if (getFirstChild(p) != NULL) {
enqueue(&queue, getFirstChild(p));
}
// 移动到下一个兄弟结点
p = getNextBrother(p);
}
}
}
// 算法 FindTarget
void FindTarget(TreeNode* t, char target, TreeNode** result) {
*result = NULL;
if (t == NULL) {
return;
}
if (t->data == target) {
*result = t;
return;
}
TreeNode* p = t->firstChild;
while (p != NULL) {
FindTarget(p, target, result);
if (*result != NULL) {
return;
}
p = p->nextBrother;
}
}
// TreeNode* FindTarget(TreeNode* t, char target) {
// if (t == NULL) {
// return NULL;
// }
//
// if (t->data == target) {
// return t;
// }
//
// TreeNode* p = t->firstChild;
//
// while (p != NULL) {
// struct TreeNode* resultt = FindTarget(p, target);
//
// if (resultt != NULL) {
// return resultt;
// }
//
// p = p->nextBrother;
// }
// }
int main() {
// 构建左儿子右兄弟链接结构的树
TreeNode* A = createNode('A');
TreeNode* B = createNode('B');
TreeNode* C = createNode('C');
TreeNode* D = createNode('D');
TreeNode* E = createNode('E');
TreeNode* F = createNode('F');
A->firstChild = B;
B->nextBrother = C;
C->nextBrother = D;
C->firstChild = E;
E->nextBrother = F;
// 要查找的目标值
char targetValue = 'C';
// 使用算法 FindTarget 查找结点
// TreeNode* result = FindTarget(A, targetValue);
TreeNode* result = NULL;
FindTarget(A, targetValue, &result);
// 输出结果
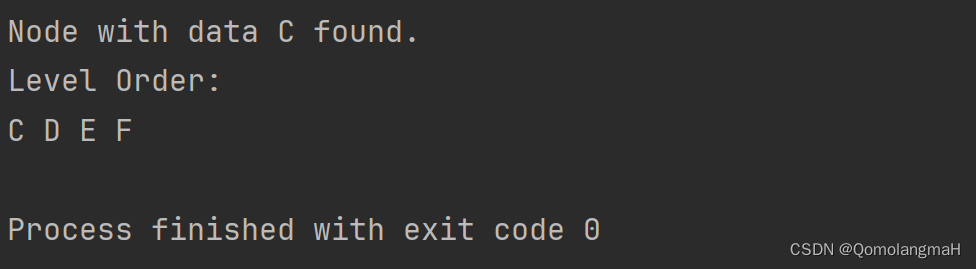
if (result != NULL) {
printf("Node with data %c found.\n", targetValue);
} else {
printf("Node with data %c not found.\n", targetValue);
}
// 层次遍历
printf("Level Order: \n");
LevelOrder(result);
printf("\n");
// 释放树节点
freeTree(A);
return 0;
}