CGAN原理讲解与源码
1.CGAN原理
生成器,输入的是c和z,z是随机噪声,c是条件,对应MNIST数据集,要求规定生成数字是几。
输出是生成的虚假图片。
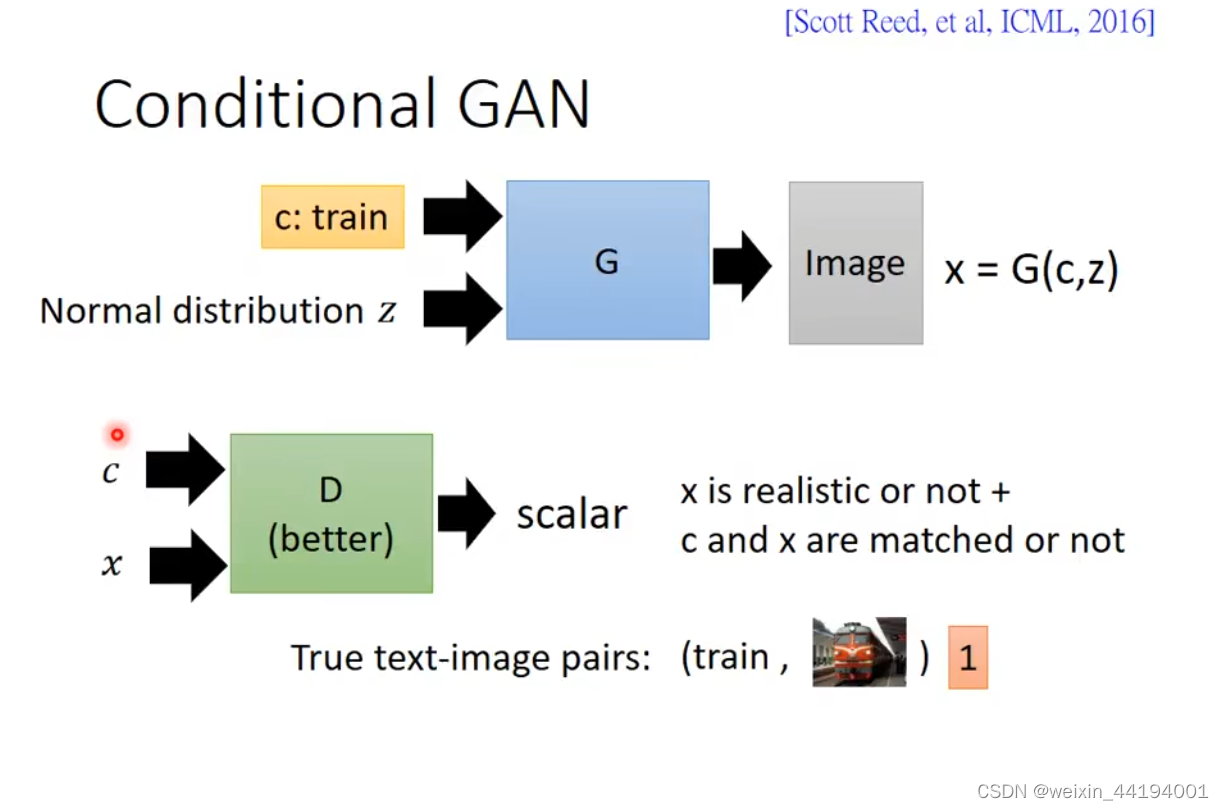
判别器的输入是
1.生成器输出的虚假图片x;
2.对应图片的标签c
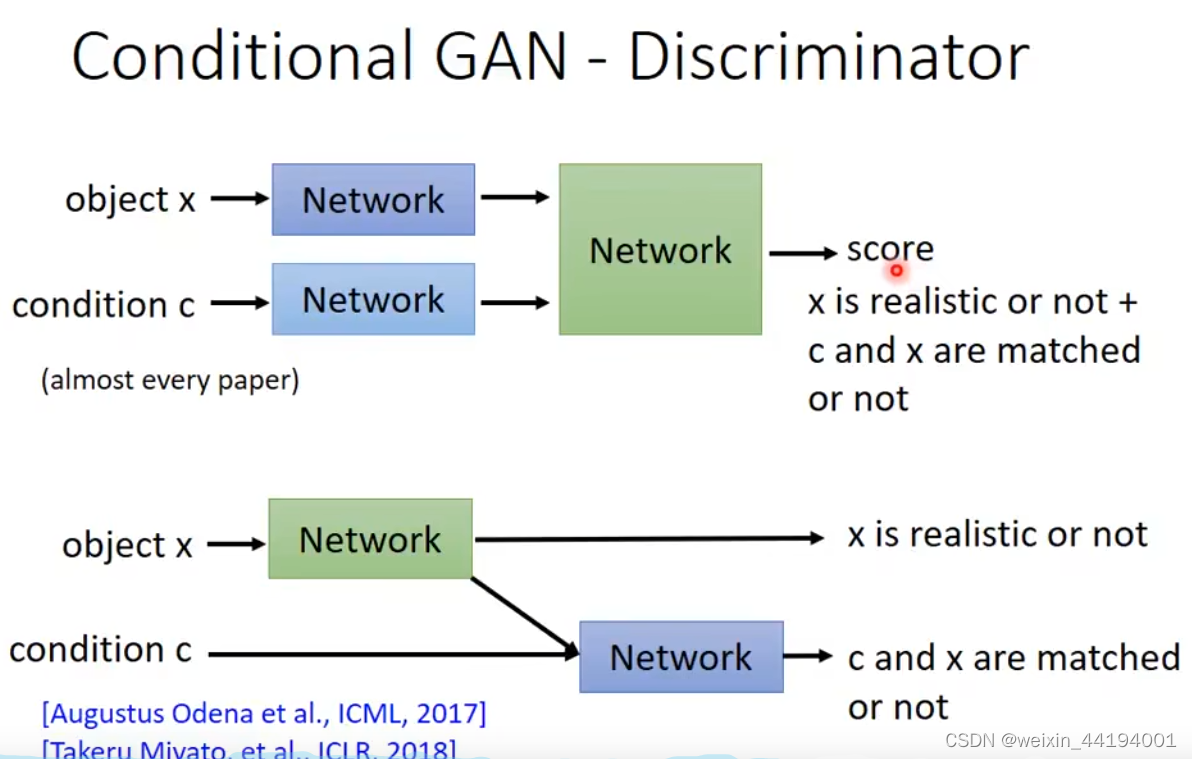
来自真实数据集,且标签是对的,就是1
如果是生成器生成的虚假照片就直接是1,都不需要看是否与标签对应
上面第二张图的意思就是,当图片是来自真实数据集,再来看是否与标签对应
2.CGAN损失函数
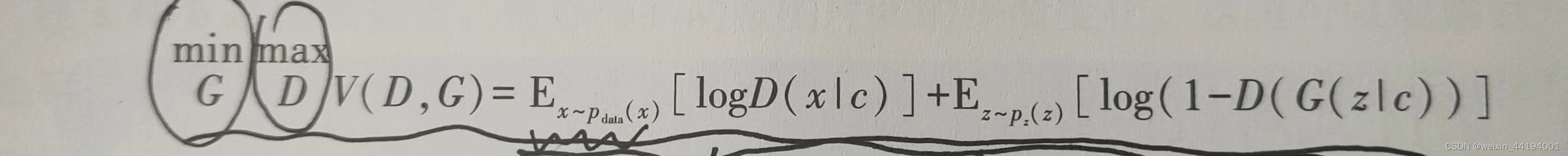
上面这个值,生成器越小越好,即判别器认为真实图片是真实图片的概率越低越好,认为虚假图片是真实图片的概率越高越好
判别器越大越好,即判别器认为真实图片是真实图片的概率越大越好,认为虚假图片是真实图片的概率越小越好
criterion(output, label)
在判别器中,
1)output是预测来自真实数据集的图片和标签是否是真实且符合标签的概率,label是1
2)output是预测虚假图片是否是虚假图片的概率,label是0
在生成器中,
output是判别器预测虚假图片是否是真实图片的概率,label是1
以上三种,都是交叉熵越小越好
3.生成器和判别器的源码
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channel=1, nz=100, nc=10, ngf=64):
super(Generator, self).__init__()
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# 输入维度 110 x 1 x 1
nn.ConvTranspose2d(nz + nc, ngf * 8, 4, 1, 0, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 8),
nn.ReLU(True),
# 特征维度 (ngf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 8, ngf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 4),
nn.ReLU(True),
# 特征维度 (ngf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 4, ngf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf * 2),
nn.ReLU(True),
# 特征维度 (ngf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf * 2, ngf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(ngf),
nn.ReLU(True),
# 特征维度 (ngf) x 32 x 32
nn.ConvTranspose2d(ngf, num_channel, 4, 2, 1, bias=False),
nn.Tanh()
# 特征维度. (num_channel) x 64 x 64
)
self.apply(weights_init)
def forward(self, input_z, onehot_label):
input_ = torch.cat((input_z, onehot_label), dim=1)
n, c = input_.size()
input_ = input_.view(n, c, 1, 1)
return self.main(input_)
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channel=1, nc=10, ndf=64):
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
self.main = nn.Sequential(
# 输入维度 (num_c3
# channel+nc) x 64 x 64 1*64*64的图像和10维的类别 10维类别先转换成10*64*64 然后合并就是11*64*64
# 输入通道 输出通道 卷积核的大小 步长 填充
#原始输入张量:b 11 64 64
nn.Conv2d(num_channel + nc, ndf, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64 32 32
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# 特征维度 (ndf) x 32 x 32
nn.Conv2d(ndf, ndf * 2, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64*2 16 16
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# 特征维度 (ndf*2) x 16 x 16
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 2, ndf * 4, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64*4 8 8
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# 特征维度 (ndf*4) x 8 x 8
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 4, ndf * 8, 4, 2, 1, bias=False), #b 64*8 4 4
nn.BatchNorm2d(ndf * 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2, inplace=True),
# 特征维度 (ndf*8) x 4 x 4
nn.Conv2d(ndf * 8, 1, 4, 1, 0, bias=False), #b 1 1 1 其实就是一个数值,区间在正无穷到负无穷之间
nn.Sigmoid()
)
self.apply(weights_init)
def forward(self, images, onehot_label):
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
h, w = images.shape[2:]
n, nc = onehot_label.shape[:2]
label = onehot_label.view(n, nc, 1, 1) * torch.ones([n, nc, h, w]).to(device)
input_ = torch.cat([images, label], 1)
return self.main(input_)
4.训练过程
MODEL_G_PATH = "./"
LOG_G_PATH = "Log_G.txt"
LOG_D_PATH = "Log_D.txt"
IMAGE_SIZE = 64
BATCH_SIZE = 128
WORKER = 1
LR = 0.0002
NZ = 100
NUM_CLASS = 10
EPOCH = 10
data_loader = loadMNIST(img_size=IMAGE_SIZE, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE) #原始图片宽高是28*28的,给改变成64*64
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
netG = Generator().to(device)
netD = Discriminator().to(device)
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
real_label = 1.
fake_label = 0.
optimizerD = optim.Adam(netD.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
optimizerG = optim.Adam(netG.parameters(), lr=LR, betas=(0.5, 0.999))
g_writer = LossWriter(save_path=LOG_G_PATH)
d_writer = LossWriter(save_path=LOG_D_PATH)
fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=device)
fix_input_c = (torch.rand(BATCH_SIZE, 1) * NUM_CLASS).type(torch.LongTensor).squeeze().to(device)
fix_input_c = onehot(fix_input_c, NUM_CLASS)
img_list = []
G_losses = []
D_losses = []
iters = 0
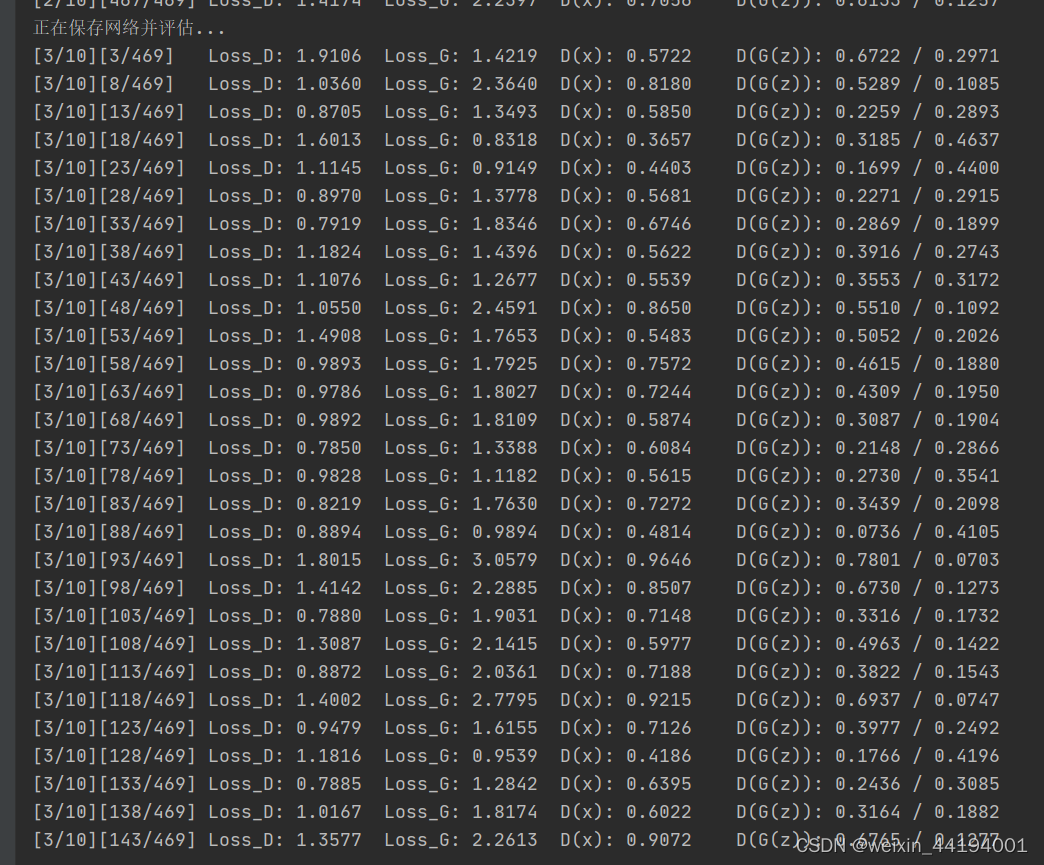
print("开始训练>>>")
for epoch in range(EPOCH):
print("正在保存网络并评估...")
save_network(MODEL_G_PATH, netG, epoch)
with torch.no_grad():
fake_imgs = netG(fix_noise, fix_input_c).detach().cpu()
images = recover_image(fake_imgs)
full_image = np.full((5 * 64, 5 * 64, 3), 0, dtype="uint8")
for i in range(25):
row = i // 5
col = i % 5
full_image[row * 64:(row + 1) * 64, col * 64:(col + 1) * 64, :] = images[i]
plt.imshow(full_image)
#plt.show()
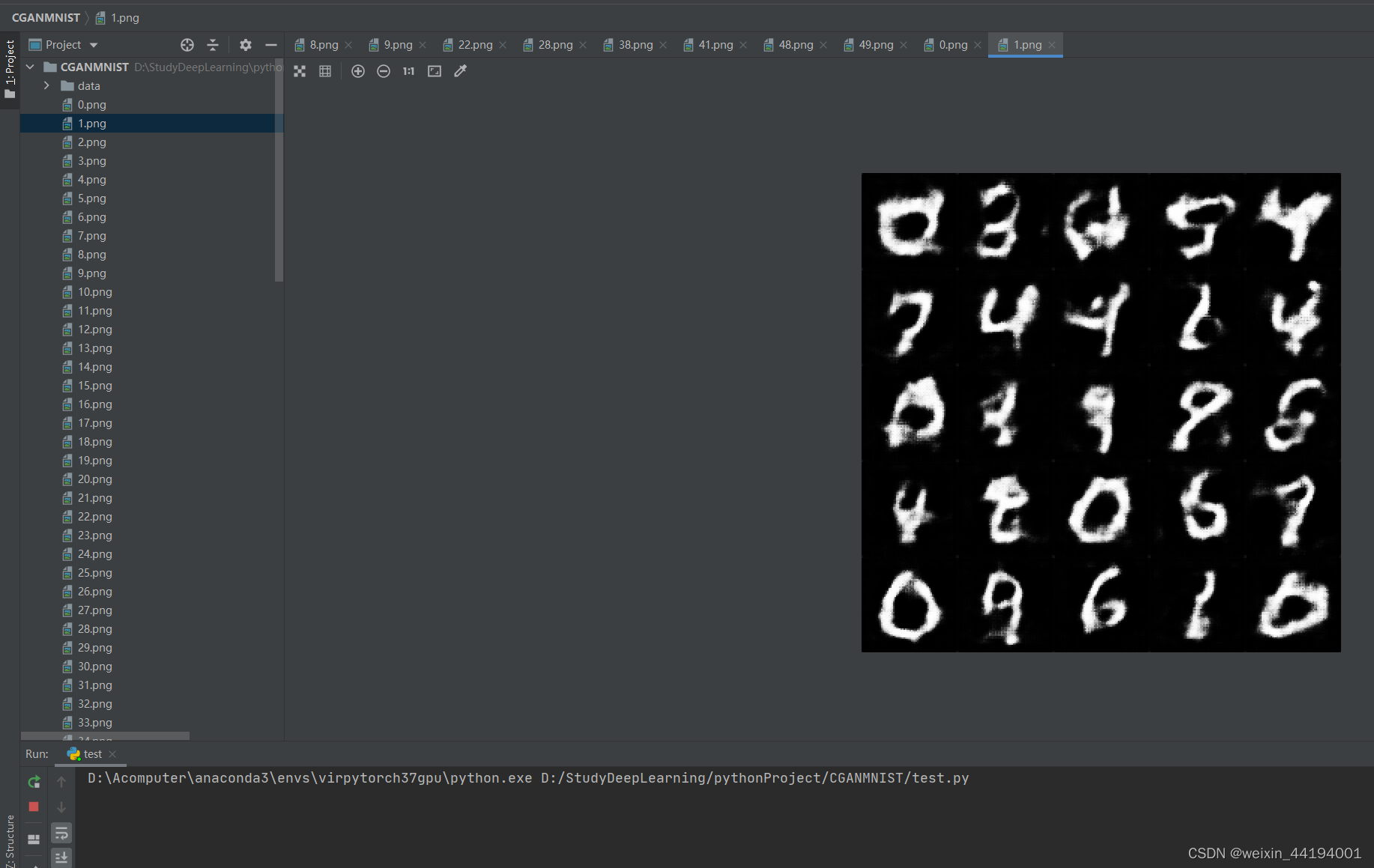
plt.imsave("{}.png".format(epoch), full_image)
for data in data_loader:
#################################################
#判别器交叉熵越小越好
# 1. 更新判别器D: 最大化 log(D(x)) + log(1 - D(G(z)))
# 等同于最小化 - log(D(x)) - log(1 - D(G(z)))
#################################################
netD.zero_grad()
real_imgs, input_c = data #这里的input_c其实就是数据集每一批中的每个图片对应的标签
input_c = input_c.to(device)
input_c = onehot(input_c, NUM_CLASS).to(device)
# 1.1 来自数据集的样本
#这里这一步就是想训练判别器,能够识别出是否真实图片,以及图片与对应的标签是否对应
real_imgs = real_imgs.to(device)
b_size = real_imgs.size(0)
label = torch.full((b_size,), real_label, dtype=torch.float, device=device)
#上面的torch.full是生成一维的 b_size这么多的,填充值为1.的张量
# real_label = 1.
# fake_label = 0.
# 使用鉴别器对数据集样本做判断
output = netD(real_imgs, input_c).view(-1) #view() 方法被用来将模型输出的张量进行扁平化操作,即将张量中的所有元素都展开成一个一维向量
# 计算交叉熵损失 -log(D(x))
errD_real = criterion(output, label)
# 对判别器进行梯度回传
errD_real.backward()
D_x = output.mean().item() #对同一批预测结果的交叉熵取平均值
#
# 1.2 生成随机向量 这一步想要训练判别器是否能够识别出是虚假图片
noise = torch.randn(b_size, NZ, device=device)
# 生成随机标签
input_c = (torch.rand(b_size, 1) * NUM_CLASS).type(torch.LongTensor).squeeze().to(device)
input_c = onehot(input_c, NUM_CLASS)
#fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=device)
#fix_input_c = (torch.rand(BATCH_SIZE, 1) * NUM_CLASS).type(torch.LongTensor).squeeze().to(device)
#fix_input_c = onehot(fix_input_c, NUM_CLASS)
# 来自生成器生成的样本
fake = netG(noise, input_c)
label.fill_(fake_label)
# real_label = 1.
# fake_label = 0.
# 使用鉴别器对生成器生成样本做判断
output = netD(fake.detach(), input_c).view(-1) #view() 方法被用来将模型输出的张量进行扁平化操作,即将张量中的所有元素都展开成一个一维向量
# 计算交叉熵损失 -log(1 - D(G(z)))
errD_fake = criterion(output, label)
# 对判别器进行梯度回传
errD_fake.backward()
D_G_z1 = output.mean().item()
# 对判别器计算总梯度,-log(D(x))-log(1 - D(G(z)))
errD = errD_real + errD_fake
# 更新判别器
optimizerD.step()
#################################################
# 2. 更新生成器G: 最小化 log(D(x)) + log(1 - D(G(z))),
# 等同于最小化log(1 - D(G(z))),即最小化-log(D(G(z)))
# 也就等同于最小化-(log(D(G(z)))*1+log(1-D(G(z)))*0)
# 令生成器样本标签值为1,上式就满足了交叉熵的定义
#################################################
netG.zero_grad()
# 对于生成器训练,令生成器生成的样本为真,
label.fill_(real_label)
# real_label = 1.
# fake_label = 0.
output = netD(fake, input_c).view(-1)
# 对生成器计算损失
errG = criterion(output, label)
# 因为这里判别器的角度label真实应该是0,但是站在生成器的角度,label真实应该是1,即生成器希望生成的虚假图片让判别器识别的时候,会误以为1才比较好,即误以为是真实的图片
# 所以生成器交叉熵也是越小越好
# 对生成器进行梯度回传
errG.backward()
D_G_z2 = output.mean().item()
# 更新生成器
optimizerG.step()
# 输出损失状态
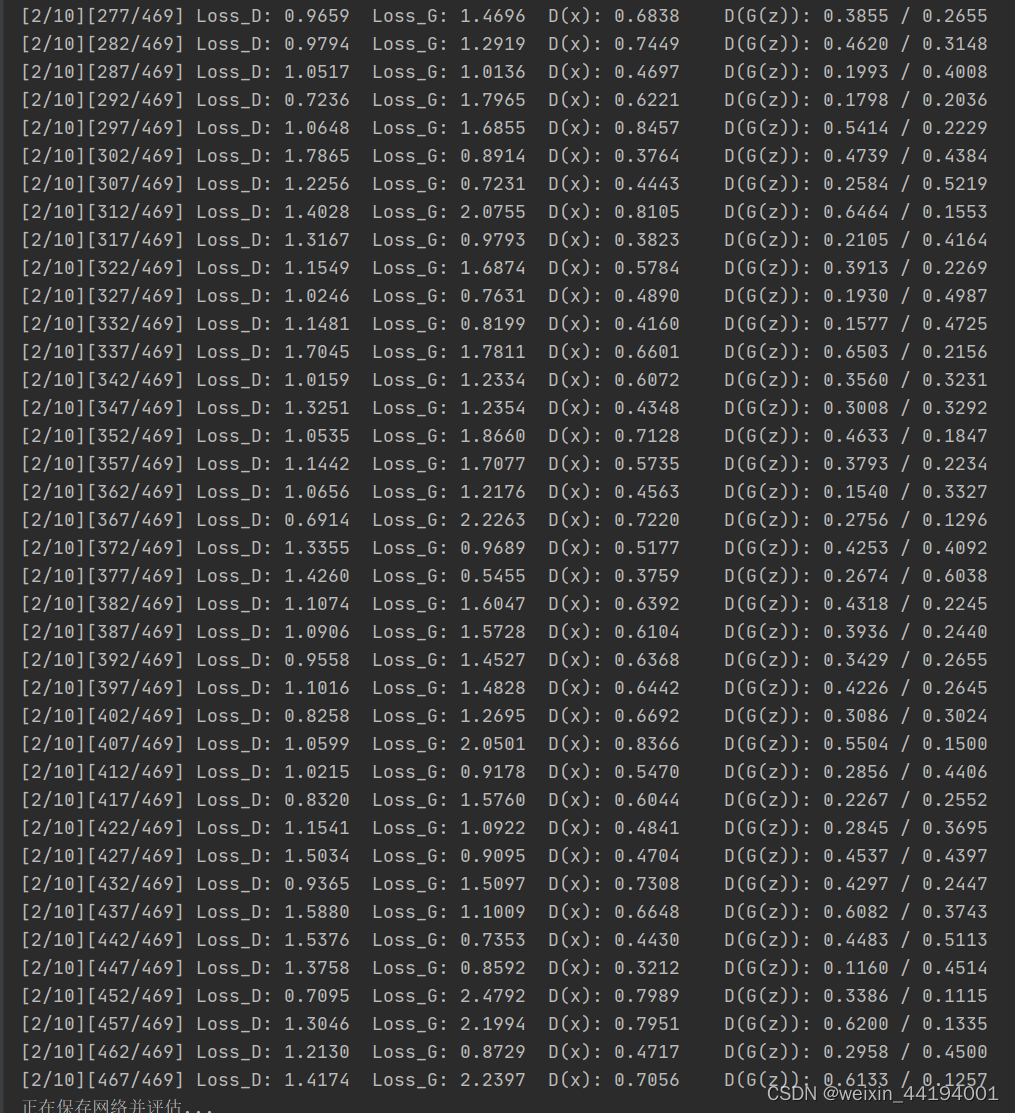
if iters % 5 == 0:
print('[%d/%d][%d/%d]\tLoss_D: %.4f\tLoss_G: %.4f\tD(x): %.4f\tD(G(z)): %.4f / %.4f'
% (epoch, EPOCH, iters % len(data_loader), len(data_loader),
errD.item(), errG.item(), D_x, D_G_z1, D_G_z2))
d_writer.add(loss=errD.item(), i=iters)
g_writer.add(loss=errG.item(), i=iters)
# 保存损失记录
G_losses.append(errG.item())
D_losses.append(errD.item())
iters += 1
5.关于交叉熵
熵代表确定性,熵越小越好,说明确定性越好
在这里,因为参照的是真实标签,它的熵是0
而交叉熵-熵=相对熵
故相对熵在预测情况相对真实情况的时候,相对熵=交叉熵,相对熵越小,说明预测情况越接近真实情况;
同理,交叉熵越小,说明预测情况越接近真实情况。
在二分类0,1任务中,经过卷积、正则化、激活函数ReLU等操作之后,假如生成了一个(B,1,1,1)的张量,每个值在(无穷小,无穷大)之间,经过sigmoid函数,会变成一个(B,1,1,1)的张量,数值h在(0,1)之间,如果这个h>0.5说明模型预测的是1,如果h<0.5说明模型预测的是0,但是这是模型预测的标签值y*,而还有个真实标签值y。假如现在h=0.6,那么说明模型预测的标签y*是1,真实标签却是0,
交叉熵= -y(lgh) -(1-y)(lg(1-h))
即当y=1时,交叉熵是-lgh 这个情况下,h越大越好
当y=0时,交叉熵是-(lg(1-h)) 这个情况下,h越小越好
6.训练过程运行结果
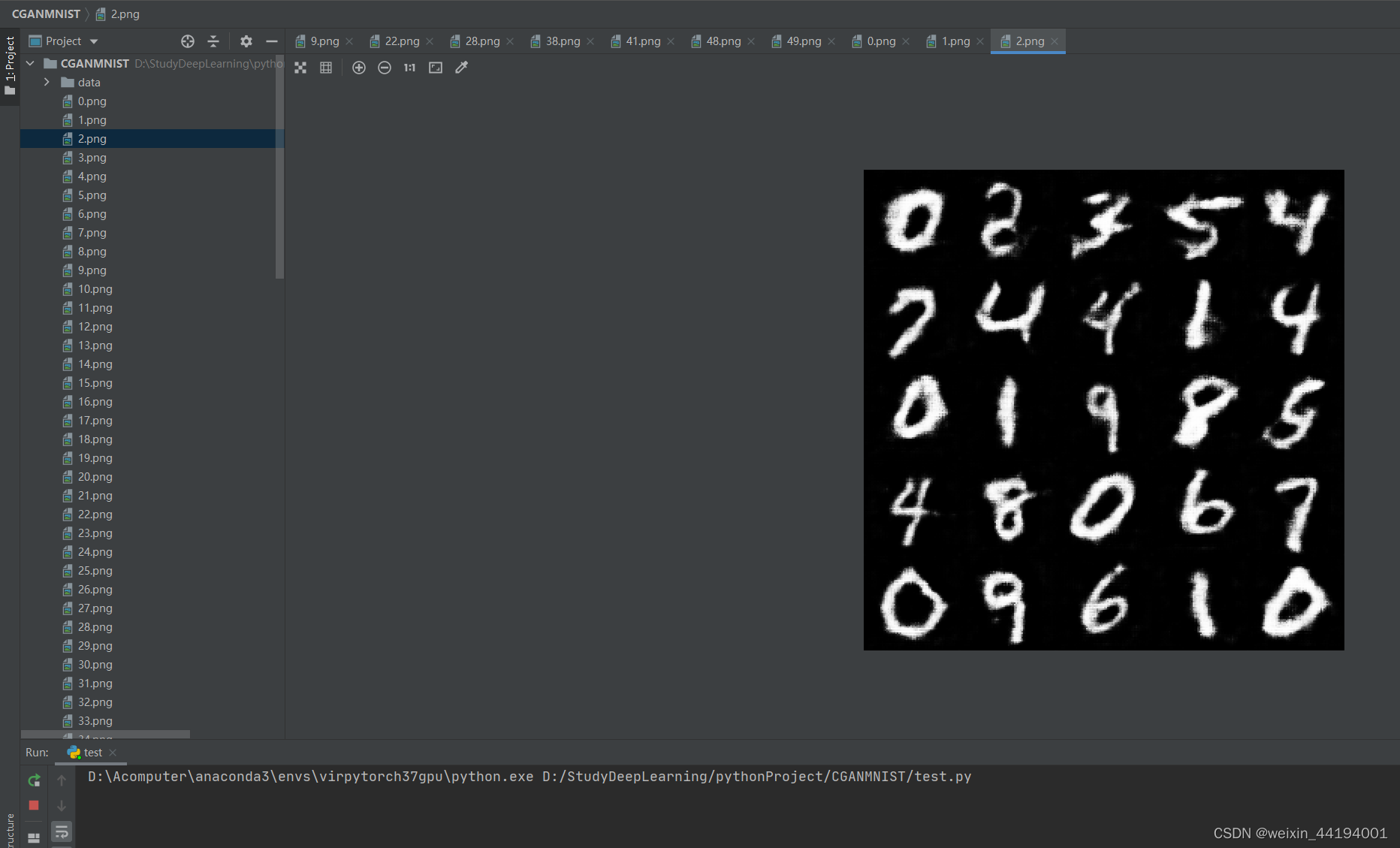
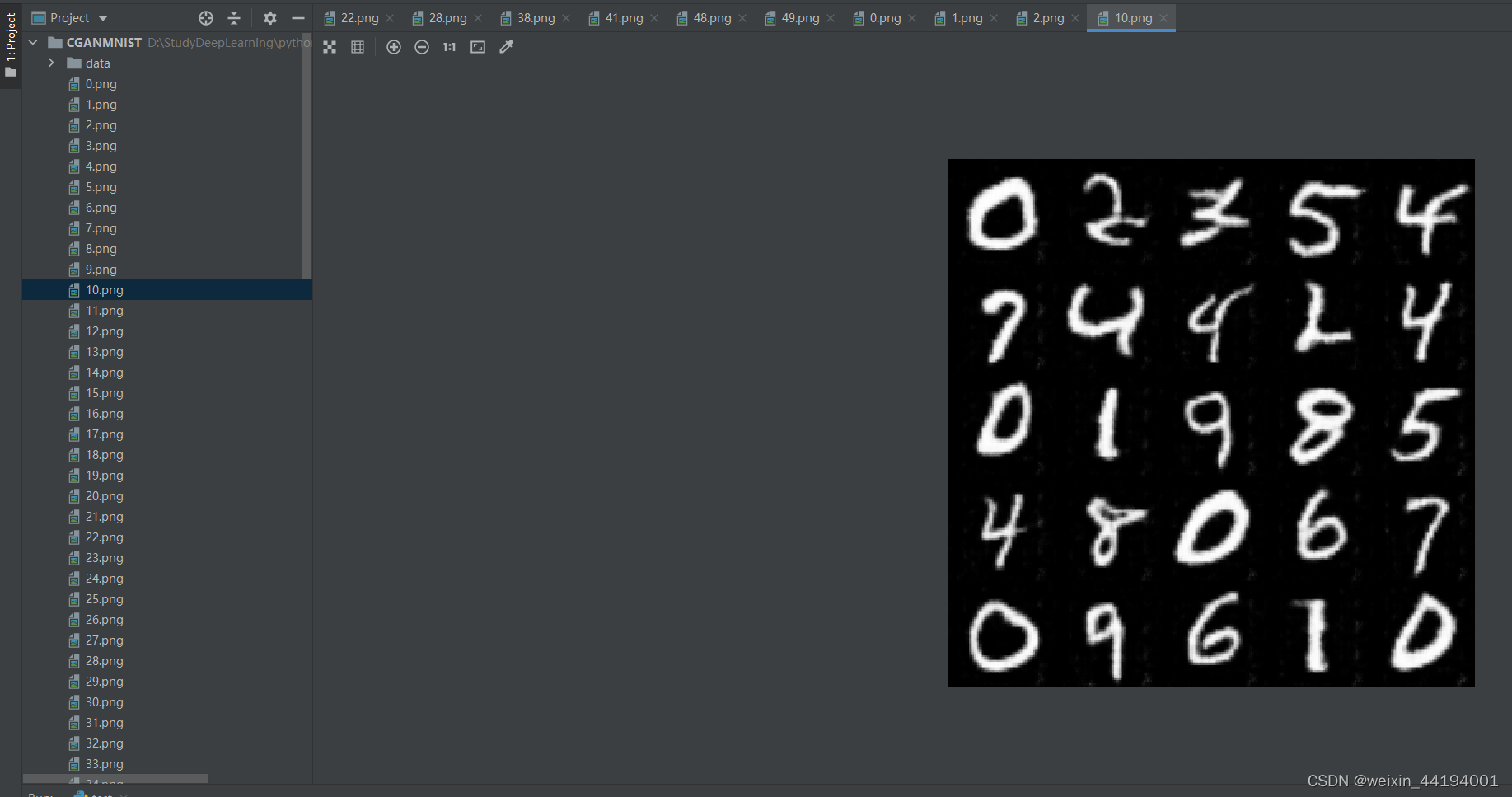
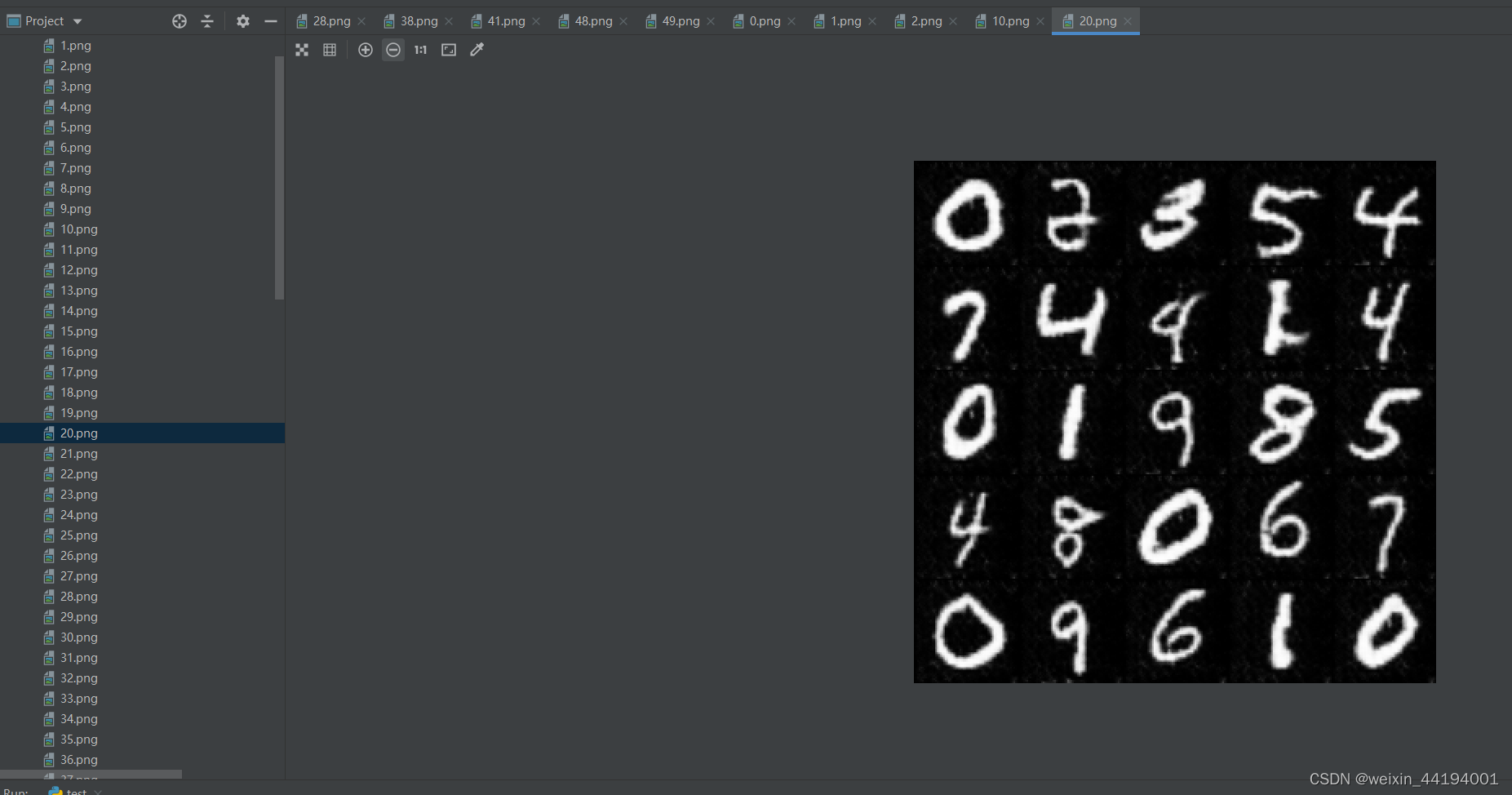
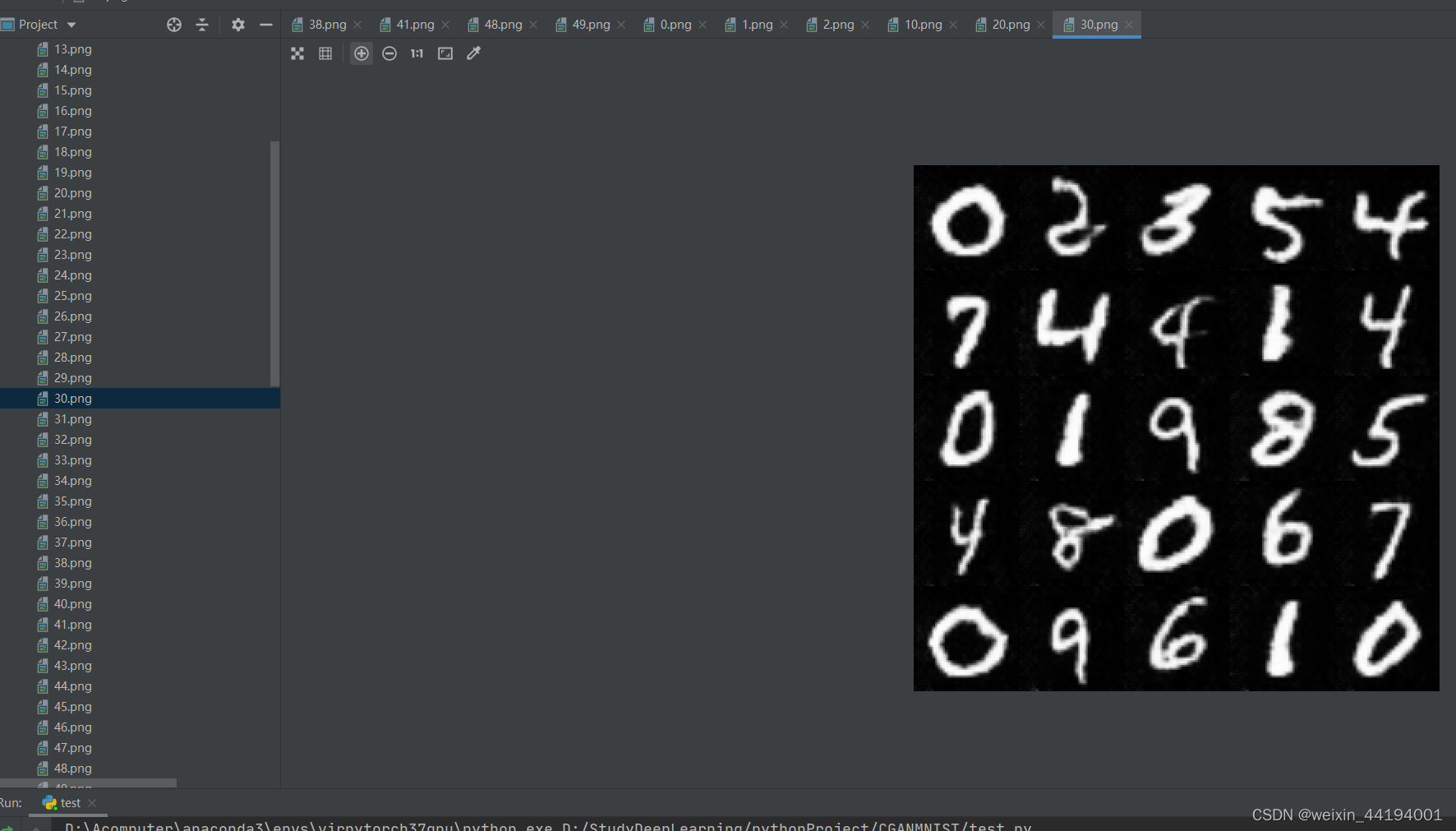
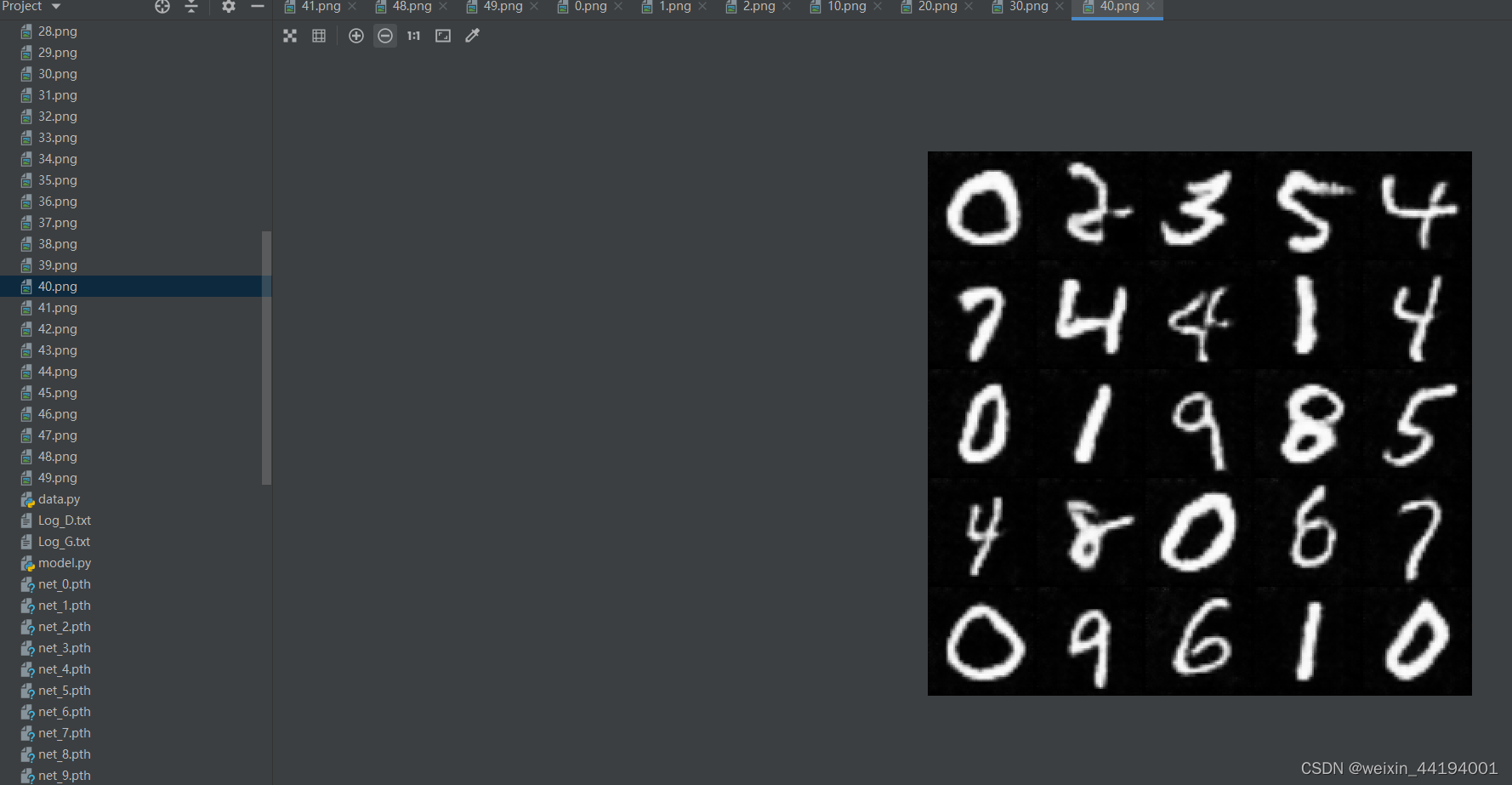
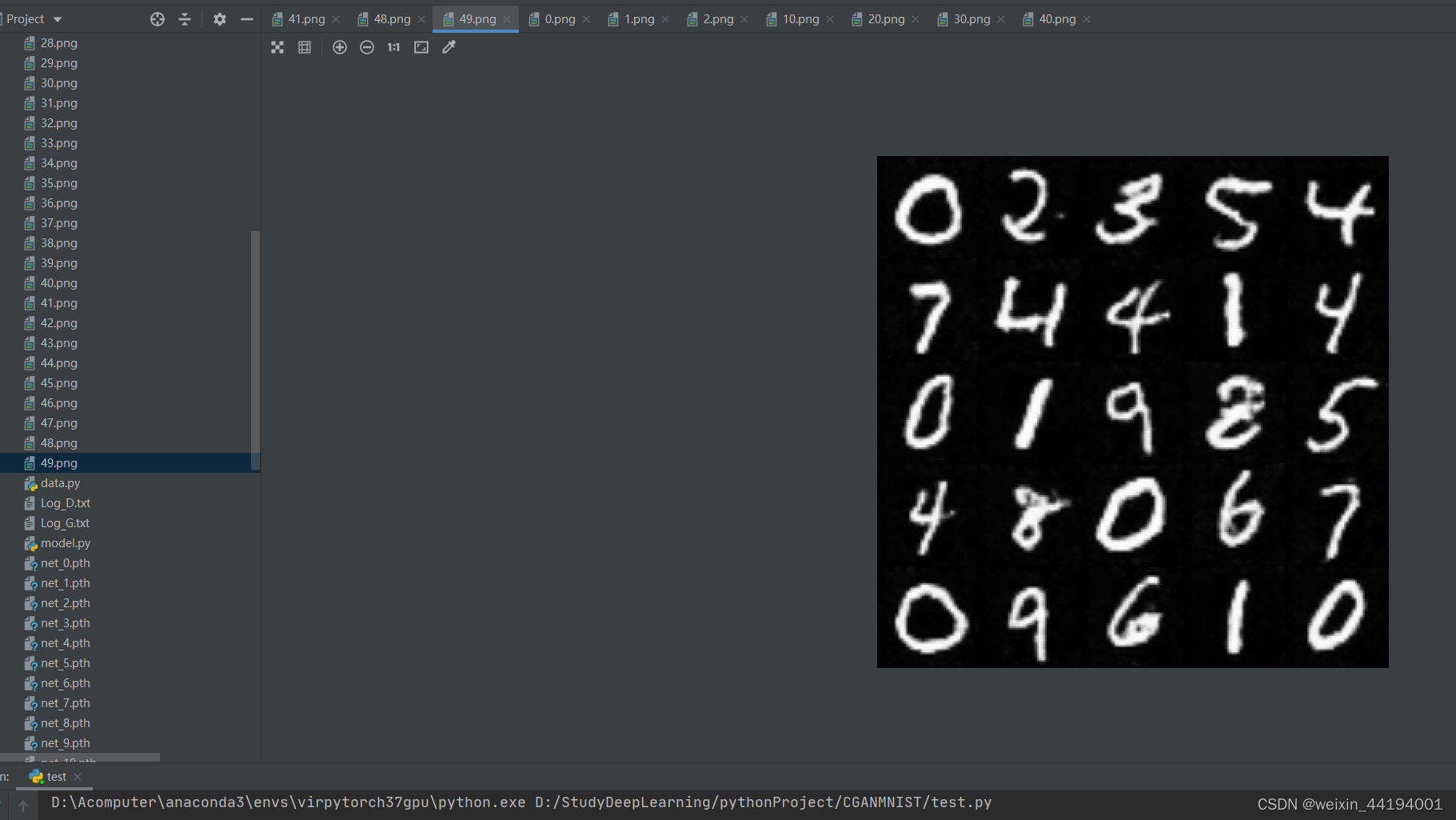
7.测试结果
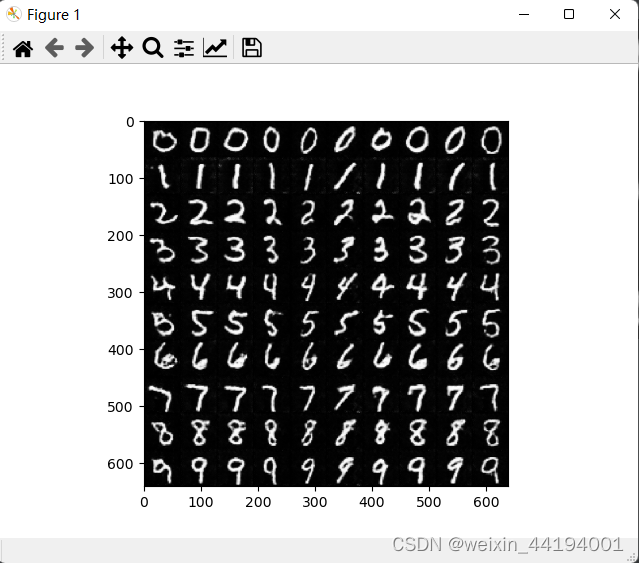
测试代码
NZ = 100
NUM_CLASS = 10
BATCH_SIZE = 10
DEVICE = "cpu"
# fix_input_c = (torch.rand(BATCH_SIZE, 1) * NUM_CLASS).type(torch.LongTensor).squeeze().to(DEVICE)
netG = Generator()
netG = restore_network("./", "49", netG)
fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=DEVICE)
fix_input_c = torch.tensor([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0])
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
fix_input_c = onehot(fix_input_c, NUM_CLASS)
fix_input_c = fix_input_c.to(device)
fix_noise = fix_noise.to(device)
netG = netG.to(device)
#fake_imgs = netG(fix_noise, fix_input_c).detach().cpu()
# images = recover_image(fake_imgs)
# full_image = np.full((1 * 64, 10 * 64, 3), 0, dtype="uint8")
# for i in range(10):
# row = i // 10
# col = i % 10
# full_image[row * 64:(row + 1) * 64, col * 64:(col + 1) * 64, :] = images[i]
#fix_noise = torch.randn(BATCH_SIZE, NZ, device=DEVICE)
full_image = np.full((10 * 64, 10 * 64, 3), 0, dtype="uint8")
for num in range(10):
input_c = torch.tensor(np.ones(10, dtype="int64") * num)
input_c = onehot(input_c, NUM_CLASS)
fix_noise = fix_noise.to(device)
input_c = input_c.to(device)
fake_imgs = netG(fix_noise, input_c).detach().cpu()
images = recover_image(fake_imgs)
for i in range(10):
row = num
col = i % 10
full_image[row * 64:(row + 1) * 64, col * 64:(col + 1) * 64, :] = images[i]
plt.imshow(full_image)
plt.show()
plt.imsave("hah.png", full_image)
