哈希表——闭散列表
该哈希表实现是闭散列实现法。
闭散列表:
闭散列:也叫开放定址法,当发生哈希冲突时,如果哈希表未被装满,说明在哈希表中必然还有空位置,那么可以把key存放到冲突位置中的“下一个” 空位置中去。
那如何寻找下一个空位置呢?
线性探测:
线性探测:从发生冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
注意:除了线性探测,你还可以进行二次探测等,看个人实现策略。
如何插入
通过哈希函数获取待插入元素在哈希表中的位置
如果该位置中没有元素则直接插入新元素,如果该位置中有元素发生哈希冲突,
使用线性探测找到下一个空位置,插入新元素
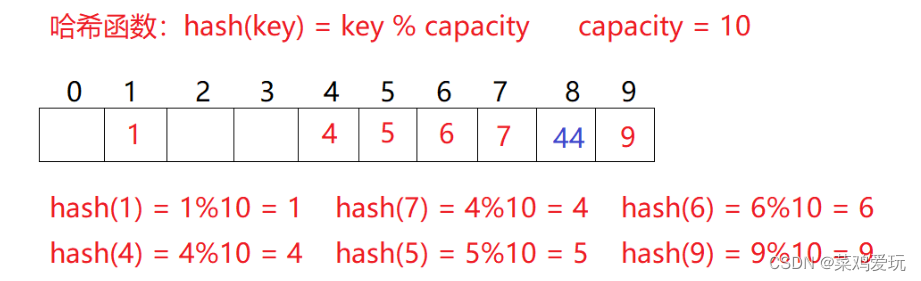
比如2.1中的场景,现在需要插入元素44,先通过哈希函数计算哈希地址,hashAddr为4,
因此44理论上应该插在该位置,但是该位置已经放了值为4的元素,即发生哈希冲突。
如何删除
采用闭散列处理哈希冲突时,不能随便物理删除哈希表中已有的元素,若直接删除元素会影响其他元素的搜索。比如删除元素4,如果直接删除掉,44查找起来可能会受影响。因此线性探测采用标记的伪删除法来删除一个元素。
// 哈希表每个空间给个标记
// EMPTY此位置空, EXIST此位置已经有元素, DELETE元素已经删除
enum State{EMPTY, EXIST, DELETE};线性探测实现插入:
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
// 负载因子0.7就扩容
if (_n*10 / _tables.size() == 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V, Hash> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
// 遍历旧表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i]._s == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(_tables[i]._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hf;
// 线性探测
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._s = EXIST;
++_n;
return true;
}
什么是负载因子?
负载因子是关键词key的存储个数与哈希表内存大小之比,一般取0.75左右,这样做是为了提高存储效率,(只有百分之75的内存可以用,剩余的百分之25,是不存储的)减少哈希冲突。
如何扩展内存?
定义一个新的对象,开好想要的内存,将旧表的数据重新查到新的哈希表中,旧表的数据分布与新表的数据分布不一样,将旧表数据插入完之后,再将新表的哈希表数据与旧表的数据进行交换。
哈希表的查找:
HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST
&& _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return NULL;
}数据有三种状态:存在,删除,为空。
存在和删除的状态下如果没有找到要查找的数据就要向后继续查找,因为插入时进行的是线性插入,只有为空和删除的位置才进行插入,所以有可能想要的数据会出现在,删除状态的后面。
注意:如果是二次探测就进行二次查找
哈希表的删除:
// 伪删除法
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_s = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}将要删除的数据状态进行标记就行了,如果标记为空,就会影响查找函数的进行,就可能会出现查找错误的情况。
完整代码及其测试代码:
#include<vector>
template<class K>
struct HashFunc
{
size_t operator()(const K& key)
{
return (size_t)key;
}
};
template<>
struct HashFunc<string>
{
size_t operator()(const string& key)
{
// BKDR
size_t hash = 0;
for (auto e : key)
{
hash *= 31;
hash += e;
}
//cout << key << ":" << hash << endl;
return hash;
}
};
namespace open_address
{
enum Status
{
EMPTY,
EXIST,
DELETE
};
template<class K, class V>
struct HashData
{
pair<K, V> _kv;
Status _s; //状态
};
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>
class HashTable
{
public:
HashTable()
{
_tables.resize(10);
}
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{
if (Find(kv.first))
return false;
// 负载因子0.7就扩容
if (_n*10 / _tables.size() == 7)
{
size_t newSize = _tables.size() * 2;
HashTable<K, V, Hash> newHT;
newHT._tables.resize(newSize);
// 遍历旧表
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i]._s == EXIST)
{
newHT.Insert(_tables[i]._kv);
}
}
_tables.swap(newHT._tables);
}
Hash hf;
// 线性探测
size_t hashi = hf(kv.first) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST)
{
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
_tables[hashi]._kv = kv;
_tables[hashi]._s = EXIST;
++_n;
return true;
}
HashData<K, V>* Find(const K& key)
{
Hash hf;
size_t hashi = hf(key) % _tables.size();
while (_tables[hashi]._s != EMPTY)
{
if (_tables[hashi]._s == EXIST
&& _tables[hashi]._kv.first == key)
{
return &_tables[hashi];
}
hashi++;
hashi %= _tables.size();
}
return NULL;
}
// 伪删除法
bool Erase(const K& key)
{
HashData<K, V>* ret = Find(key);
if (ret)
{
ret->_s = DELETE;
--_n;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void Print()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++)
{
if (_tables[i]._s == EXIST)
{
//printf("[%d]->%d\n", i, _tables[i]._kv.first);
cout << "[" << i << "]->" << _tables[i]._kv.first <<":" << _tables[i]._kv.second<< endl;
}
else if (_tables[i]._s == EMPTY)
{
printf("[%d]->\n", i);
}
else
{
printf("[%d]->D\n", i);
}
}
cout << endl;
}
private:
vector<HashData<K, V>> _tables;
size_t _n = 0; // 存储的关键字的个数
};
void TestHT1()
{
HashTable<int, int> ht;
int a[] = { 4,14,24,34,5,7,1 };
for (auto e : a)
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, e));
}
ht.Insert(make_pair(3, 3));
ht.Insert(make_pair(3, 3));
ht.Insert(make_pair(-3, -3));
ht.Print();
ht.Erase(3);
ht.Print();
if (ht.Find(3))
{
cout << "3存在" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "3不存在" << endl;
}
ht.Insert(make_pair(3, 3));
ht.Insert(make_pair(23, 3));
ht.Print();
}
void TestHT2()
{
string arr[] = { "香蕉", "甜瓜","苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };
//HashTable<string, int, HashFuncString> ht;
HashTable<string, int> ht;
for (auto& e : arr)
{
//auto ret = ht.Find(e);
HashData<string, int>* ret = ht.Find(e);
if (ret)
{
ret->_kv.second++;
}
else
{
ht.Insert(make_pair(e, 1));
}
}
ht.Print();
ht.Insert(make_pair("apple", 1));
ht.Insert(make_pair("sort", 1));
ht.Insert(make_pair("abc", 1));
ht.Insert(make_pair("acb", 1));
ht.Insert(make_pair("aad", 1));
ht.Print();
}
}
