创建一个带有背景图层和前景图层的渲染窗口
开发环境:
- Windows 11 家庭中文版
- Microsoft Visual Studio Community 2019
- VTK-9.3.0.rc0
- vtk-example
demo解决问题: 创建一个带有背景图层和前景图层的渲染窗口,知识点:1. 画布转image;2. 渲染图层设置;3. 相机位置、焦点、距离等属性设置
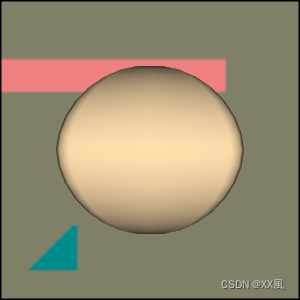
-
构造imageData对象:程序检查是否提供了输入图像文件名。如果提供了,则使用VTK库中的vtkImageReader2类来读取图像数据,并将其存储在imageData对象中。如果没有提供,则创建一个带有三种颜色的矩形图像。程序使用vtkImageCanvasSource2D类来创建一个画布,并使用其FillBox、FillTriangle和FillTube方法在画布上绘制三种颜色的形状。然后,使用canvasSource->GetOutput()方法获取画布上的图像数据,并将其存储在imageData对象中。
-
创建了一个vtkImageActor对象imageActor,并将其设置为显示imageData中的图像数据。然后,程序创建了一个vtkRenderer对象backgroundRenderer,并将其设置为显示imageActor中的图像数据。程序还创建了一个vtkSuperquadricSource对象superquadricSource,并使用其SetPhiRoundness和SetThetaRoundness方法设置超椭球体的形状。然后,程序创建了vtkPolyDataMapper和vtkActor对象来显示超椭球体,并使用colors->GetColor3d方法设置超椭球体的颜色。
-
程序创建了一个vtkRenderer对象sceneRenderer,并将其设置为显示超椭球体。然后,程序创建了一个vtkRenderWindow对象renderWindow,并将其设置为显示backgroundRenderer和sceneRenderer中的内容。程序还使用renderWindow->SetWindowName方法设置窗口名称。
-
创建了一个vtkRenderWindowInteractor对象renderWindowInteractor,并使用renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow方法将其与renderWindow关联。然后,程序将超椭球体添加到sceneRenderer中,将imageActor添加到backgroundRenderer中。
-
程序调用renderWindow->Render方法以确定背景相机的位置。程序使用imageData->GetOrigin、imageData->GetSpacing和imageData->GetExtent方法获取图像数据的原点、间距和范围等信息。然后,程序设置相机的位置、焦点和平行比例等参数以使背景相机填充渲染器中的图像。
prj name: BackgroundImage
#include <vtkActor.h>
#include <vtkCamera.h>
#include <vtkImageActor.h>
#include <vtkImageCanvasSource2D.h>
#include <vtkImageData.h>
#include <vtkImageReader2.h>
#include <vtkImageReader2Factory.h>
#include <vtkNamedColors.h>
#include <vtkNew.h>
#include <vtkPolyDataMapper.h>
#include <vtkProperty.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindow.h>
#include <vtkRenderWindowInteractor.h>
#include <vtkRenderer.h>
#include <vtkSmartPointer.h>
#include <vtkSuperquadricSource.h>
#include <array>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
vtkNew<vtkNamedColors> colors;
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageData> imageData;
// Verify input arguments.
if (argc > 1)
{
// Read the image
vtkNew<vtkImageReader2Factory> readerFactory;
vtkSmartPointer<vtkImageReader2> imageReader;
imageReader.TakeReference(readerFactory->CreateImageReader2(argv[1]));
imageReader->SetFileName(argv[1]);
imageReader->Update();
imageData = imageReader->GetOutput();
}
else
{
std::array<double, 3> drawColor1{0, 0, 0};
std::array<double, 3> drawColor2{0, 0, 0};
std::array<double, 3> drawColor3{0, 0, 0};
auto color1 = colors->GetColor3ub("warm_grey").GetData();
auto color2 = colors->GetColor3ub("DarkCyan").GetData();
auto color3 = colors->GetColor3ub("LightCoral").GetData();
for (auto i = 0; i < 3; ++i)
{
drawColor1[i] = color1[i];
drawColor2[i] = color2[i];
drawColor3[i] = color3[i];
}
vtkNew<vtkImageCanvasSource2D> canvasSource;
canvasSource->SetExtent(0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 0);
canvasSource->SetScalarTypeToUnsignedChar();
canvasSource->SetNumberOfScalarComponents(3);
canvasSource->SetDrawColor(drawColor1.data());
canvasSource->FillBox(0, 100, 0, 100);
canvasSource->SetDrawColor(drawColor2.data());
canvasSource->FillTriangle(10, 10, 25, 10, 25, 25);
canvasSource->SetDrawColor(drawColor3.data());
canvasSource->FillTube(75, 75, 0, 75, 5.0);
canvasSource->Update();
imageData = canvasSource->GetOutput();
}
// Create an image actor to display the image.
vtkNew<vtkImageActor> imageActor;
imageActor->SetInputData(imageData);
// Create a renderer to display the image in the background.
vtkNew<vtkRenderer> backgroundRenderer;
// Create a superquadric.
vtkNew<vtkSuperquadricSource> superquadricSource;
superquadricSource->SetPhiRoundness(1.1);
superquadricSource->SetThetaRoundness(.2);
// Create a mapper and actor.
vtkNew<vtkPolyDataMapper> superquadricMapper;
superquadricMapper->SetInputConnection(superquadricSource->GetOutputPort());
vtkNew<vtkActor> superquadricActor;
superquadricActor->SetMapper(superquadricMapper);
superquadricActor->GetProperty()->SetColor(
colors->GetColor3d("NavajoWhite").GetData());
vtkNew<vtkRenderer> sceneRenderer;
vtkNew<vtkRenderWindow> renderWindow;
// Set up the render window and renderers such that there is
// a background layer and a foreground layer.
backgroundRenderer->SetLayer(0);
backgroundRenderer->InteractiveOff();
sceneRenderer->SetLayer(1);
renderWindow->SetNumberOfLayers(2);
renderWindow->AddRenderer(backgroundRenderer);
renderWindow->AddRenderer(sceneRenderer);
renderWindow->SetWindowName("BackgroundImage");
vtkNew<vtkRenderWindowInteractor> renderWindowInteractor;
renderWindowInteractor->SetRenderWindow(renderWindow);
// Add actors to the renderers
sceneRenderer->AddActor(superquadricActor);
backgroundRenderer->AddActor(imageActor);
// Render once to figure out where the background camera will be.
renderWindow->Render();
// Set up the background camera to fill the renderer with the image.
double origin[3];
double spacing[3];
int extent[6];
imageData->GetOrigin(origin);
imageData->GetSpacing(spacing);
imageData->GetExtent(extent);
vtkCamera* camera = backgroundRenderer->GetActiveCamera();
camera->ParallelProjectionOn();
double xc = origin[0] + 0.5 * (extent[0] + extent[1]) * spacing[0];
double yc = origin[1] + 0.5 * (extent[2] + extent[3]) * spacing[1];
// double xd = (extent[1] - extent[0] + 1)*spacing[0];
double yd = (extent[3] - extent[2] + 1) * spacing[1];
double d = camera->GetDistance();
camera->SetParallelScale(0.5 * yd);
camera->SetFocalPoint(xc, yc, 0.0);
camera->SetPosition(xc, yc, d);
// Render again to set the correct view.
renderWindow->Render();
// Interact with the window.
renderWindowInteractor->Start();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
