leetcode:用栈实现队列(先进先出)
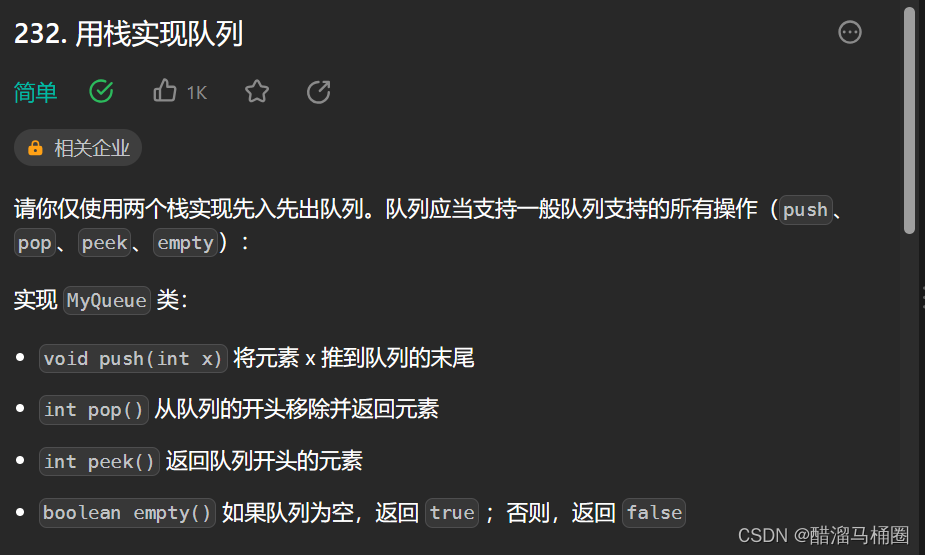
题目描述
题目链接:232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)
题目分析
我们先把之前写的数组栈的实现代码搬过来
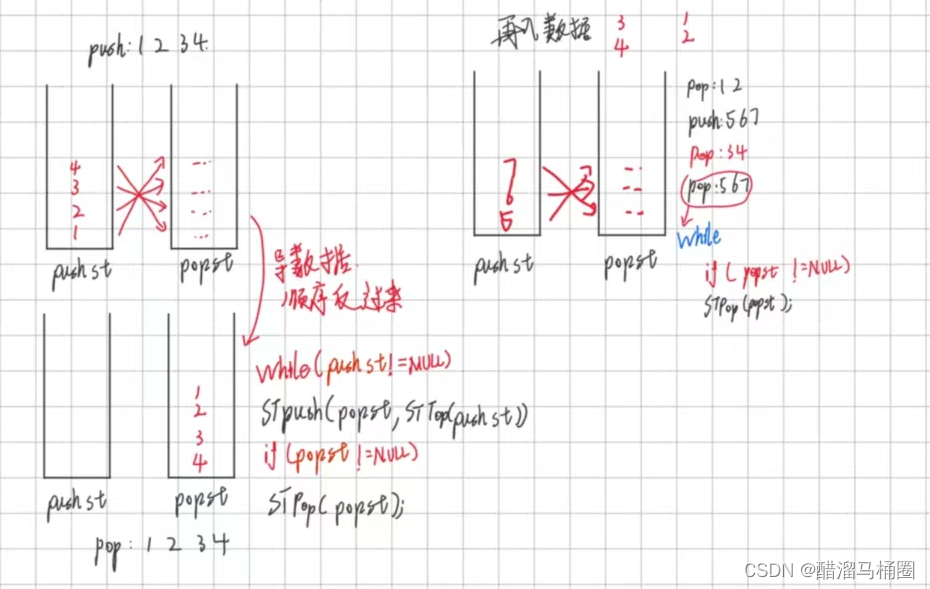
用栈实现队列最主要的是实现队列先进先出的特点,而栈的特点是后进先出,那么我们可以用两个栈来实现:
- 一个pushst用来入队列
- 一个popst用来出队列
 具体的接口有下面几个:
具体的接口有下面几个:
初始化
malloc一块空间来存两个栈,同时初始化这两个栈


入队列
入数据都入到pushst

出队列
出数据前先需要导数据:当popst为空且pushst不为空的时候,pushst的top数据依次push到popst中,然后返回pop的top数据,然后pop掉top数据;如果pop不为空,则直接返回poptop并pop

返回队头数据

判空
两个栈同时为空则为空

销毁
销毁还是依次销毁

代码示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;//标识栈顶位置
int capacity;
}ST;
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst);
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst);
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst);
//返回栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
//栈的元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst);
//初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->top = 0;
}
//销毁
void STDestroy(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = pst->capacity = 0;
}
//入栈
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType * )realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
pst->top++;
}
//出栈
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
pst->top--;
}
//返回栈顶元素
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top > 0);
return pst -> a[pst->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
/*if (pst->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}*/
return pst->top == 0;
}
//栈的元素个数
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
typedef struct {
ST pushst;
ST popst;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj=(MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
STInit(&(obj->pushst));
STInit(&(obj->popst));
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
STPush(&(obj->pushst),x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
int front=myQueuePeek(obj);
STPop(&(obj->popst));
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
if(STEmpty(&(obj->popst)))
{
while(!STEmpty(&(obj->pushst)))
{
STPush(&(obj->popst),STTop(&(obj->pushst)));
STPop(&(obj->pushst));
}
}
return STTop(&(obj->popst));
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
return STEmpty(&(obj->pushst))&&STEmpty(&(obj->popst));
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
STDestroy(&(obj->pushst));
STDestroy(&(obj->popst));
free(obj);
}
/**
* Your MyQueue struct will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue* obj = myQueueCreate();
* myQueuePush(obj, x);
* int param_2 = myQueuePop(obj);
* int param_3 = myQueuePeek(obj);
* bool param_4 = myQueueEmpty(obj);
* myQueueFree(obj);
*/