Vue3集成ThreeJS实现3D效果,threejs+Vite+Vue3+TypeScript 实战课程【一篇文章精通系列】

Vue3集成ThreeJS实现3D效果,threejs+Vite+Vue3+TypeScript 实战课程【一篇文章精通系列】
- 项目简介
- 一、项目初始化
- 1、添加一些依赖项
- 二、创建3D【基础搭建】
- 1、绘制板子,立方体,球体
- 2、材质和光照
- 3、材质和光照和动画
- 4、性能监控
- 5、交互控制
- 6、响应窗口变化
- 三、基础场景搭建
- 1、创建基础场景【实现添加几何体和删除几何体】
- 2、实现雾化场景
- 3、重写材质
- 4、常见几何体
- 5、修改几何体属性
- 6、相机切换
- 7、相机跟随
- 四、光照
- 1、环境光
- 2、点光源
- 3、聚光灯
- 4、平行光
- 5、半球光
- 五、小车案例
- 1、基础环境搭建
- 2、载入模型,实现轨道控制器
- 3、实现模型颜色材质调整,轮子转动
- 4、源代码下载
项目简介
这是一个使用Vue3,TypeScript,Vite和Three.js的项目。Vue3是一个流行的JavaScript框架,用于构建用户界面。TypeScript是一种静态类型的编程语言,它是JavaScript的超集,可以编译成纯JavaScript。Vite是一个由Evan You开发的新的前端构建工具,能够提供快速的冷启动和即时热更新。
Three.js是一个轻量级的3D库,能够让我们在任何浏览器中创建和显示动画的3D计算机图形。在该项目中,我们将Three.js集成到了Vue3和TypeScript的环境中,使得我们可以在Vue组件中使用Three.js来创建3D图形。
此外,项目中还可能包含一些封装了Three.js的代码,以便于更方便的使用Three.js进行3D开发。
这样的技术组合可以让我们在前端环境中实现复杂的3D可视化效果,为项目增加更丰富的视觉体验。
🔸3D模型下载网站:https://sketchfab.com/feed
🔸3D人物动作绑定:www.mixamo.com
🔸3D角色生产工具:https://readyplayer.me/
🔸模型压缩网站:gltf.report
🔸查找天空背景:google key words: equirectangular sky / skybox background
🔸材质贴图素材:https://www.textures.com
🔸hdr素材库(环境贴图): https://polyhaven.com
🔸二次元风3D角色生产软件VRoid Studio: https://vroid.com/en/studio
🕹Sketchfab公用账号:
Login: lingo3dchina@gmail.com
PW: Lingo3dxoxo
Code:640841
一、项目初始化
npm install -g vite
npm init vite@latest threejs-vite-vue -- --template vue
cd threejs-vite-vue
npm install
npm run dev
项目创建成功
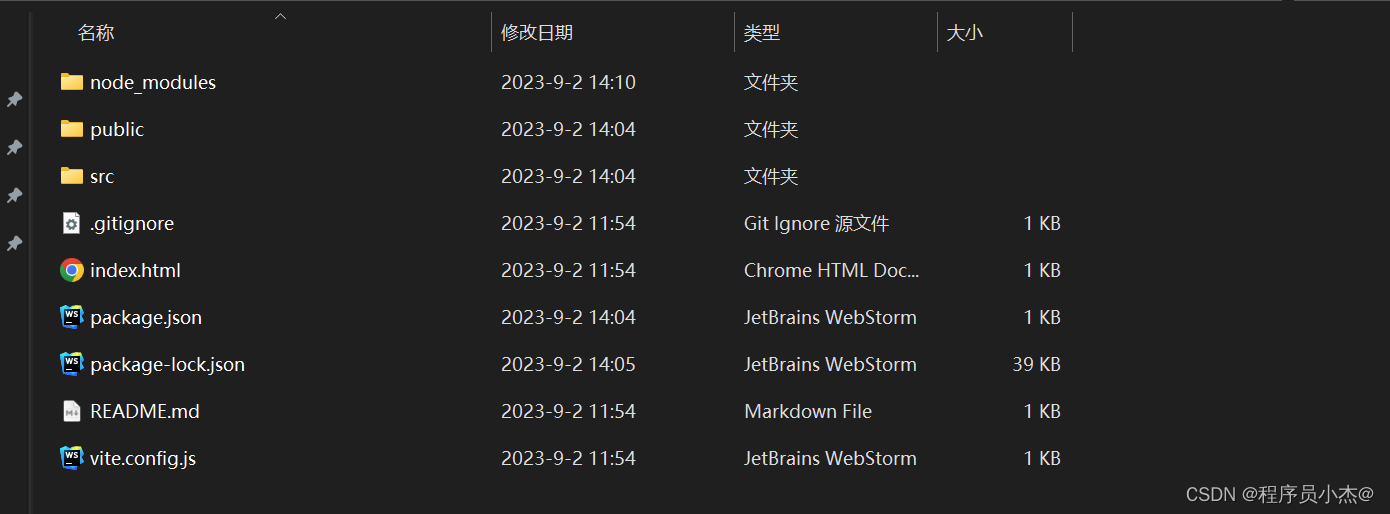 注意threejs的版本
注意threejs的版本
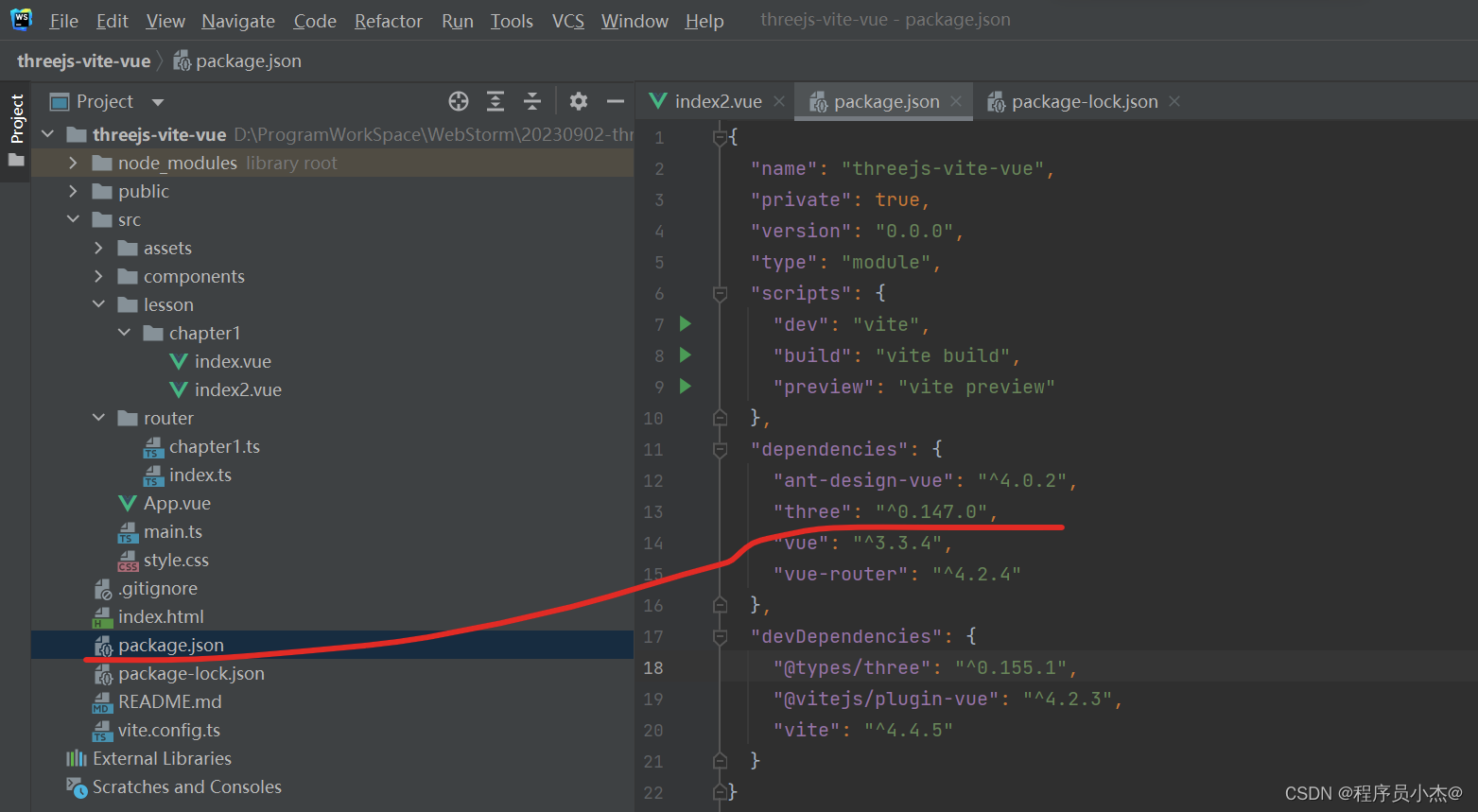
"@types/three": "^0.155.1",
项目创建成功在IDE当中导入项目
1、添加一些依赖项
npm install vue-router
npm install three
npm install @types/three -D
npm install ant-design-vue
 创建一些路由相关
创建一些路由相关
import {createRouter,createWebHistory,RouteRecordRaw} from "vue-router";
const routes: RouteRecordRaw[] = [
]
const router = createRouter({
history:createWebHistory(),
routes
})
router.beforeEach((to)=>{
document.title = 'three+vite+vue3'+to.meta.title as string
})
export default router
import { createApp } from 'vue'
import './style.css';
import Antd from 'ant-design-vue';
import App from './App.vue';
import router from './router/index';
import 'ant-design-vue/dist/reset.css';
let app = createApp(App)
app.use(router)
app.use(Antd)
app.mount('#app')
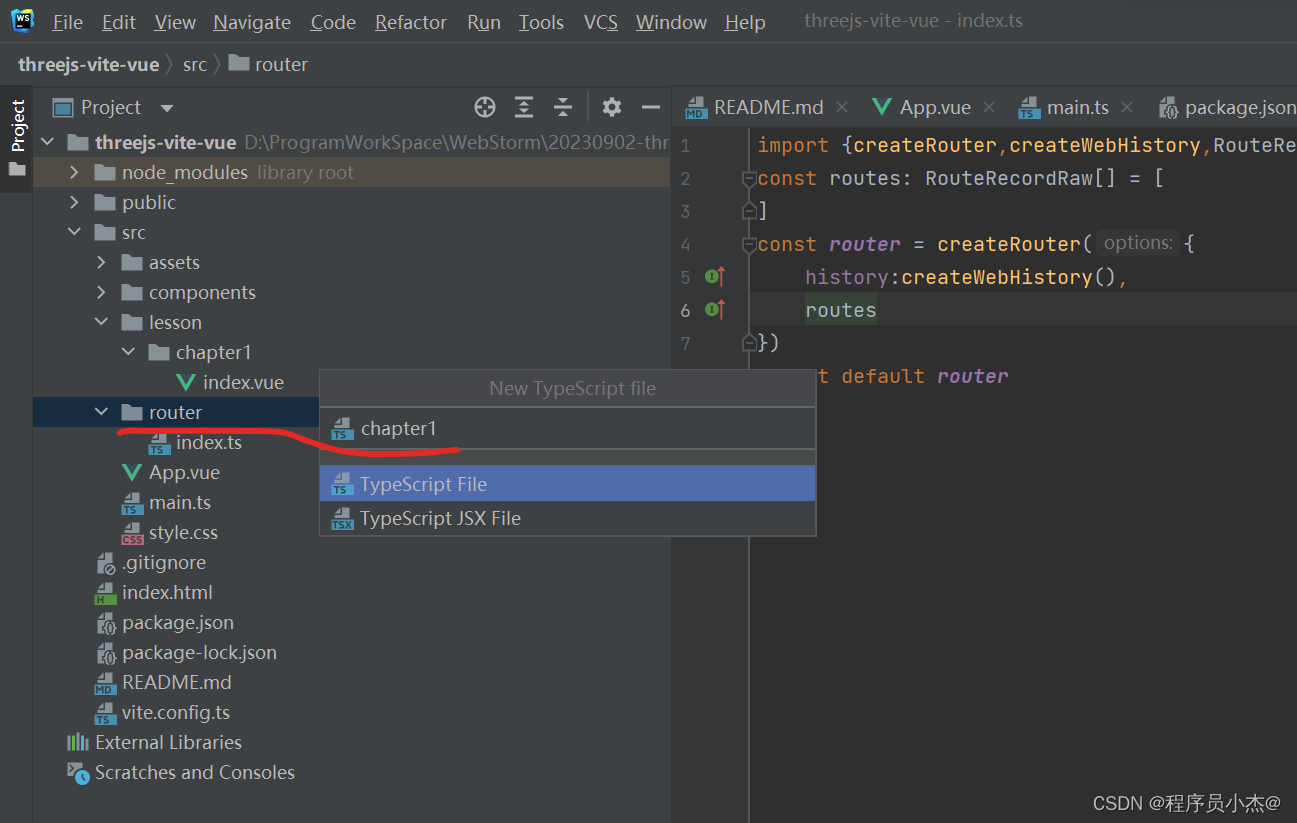

import {RouteRecordRaw} from "vue-router";
const chapter1 : RouteRecordRaw[] = [
]
export default chapter1;
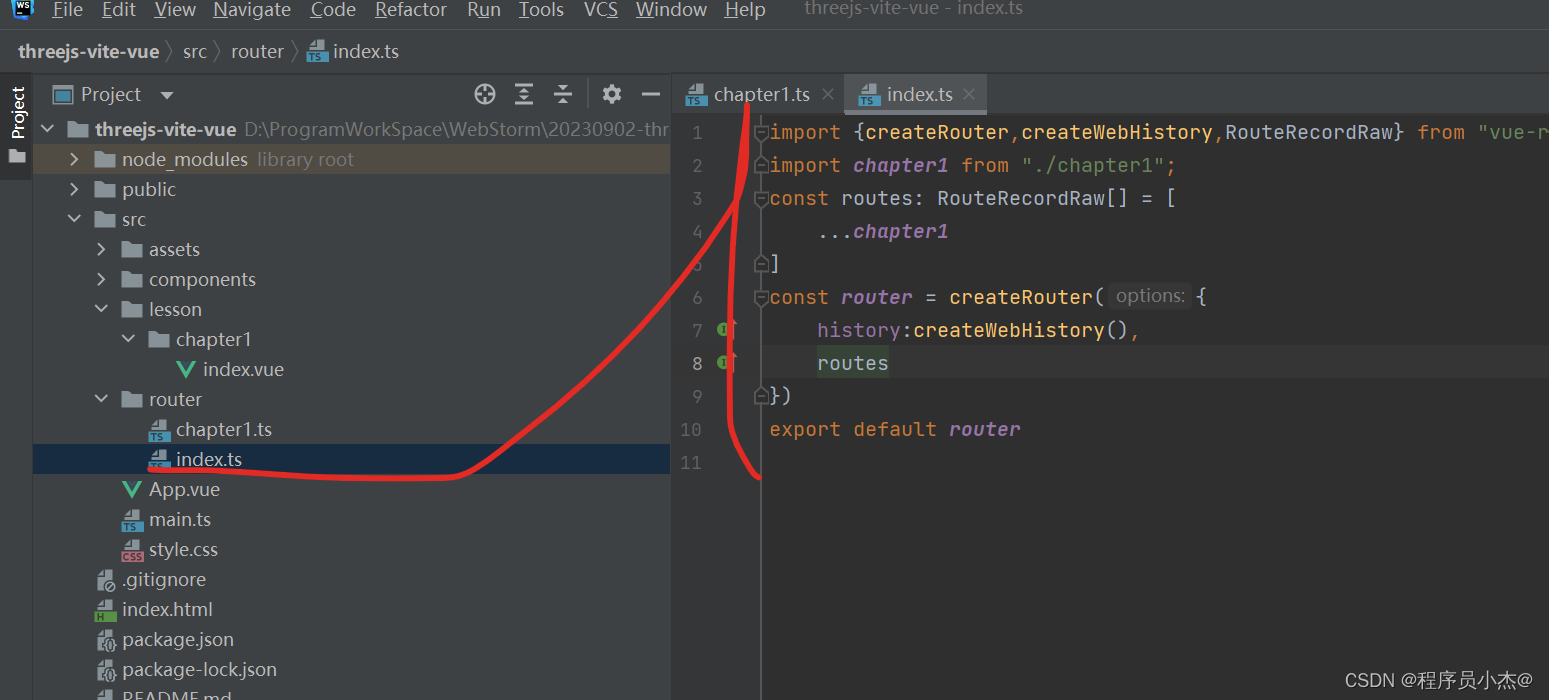
import {createRouter,createWebHistory,RouteRecordRaw} from "vue-router";
import chapter1 from "./chapter1";
const routes: RouteRecordRaw[] = [
...chapter1
]
const router = createRouter({
history:createWebHistory(),
routes
})
export default router
<template>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>
<script setup>
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
<template>
<div>
第一个场景
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "index"
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
二、创建3D【基础搭建】
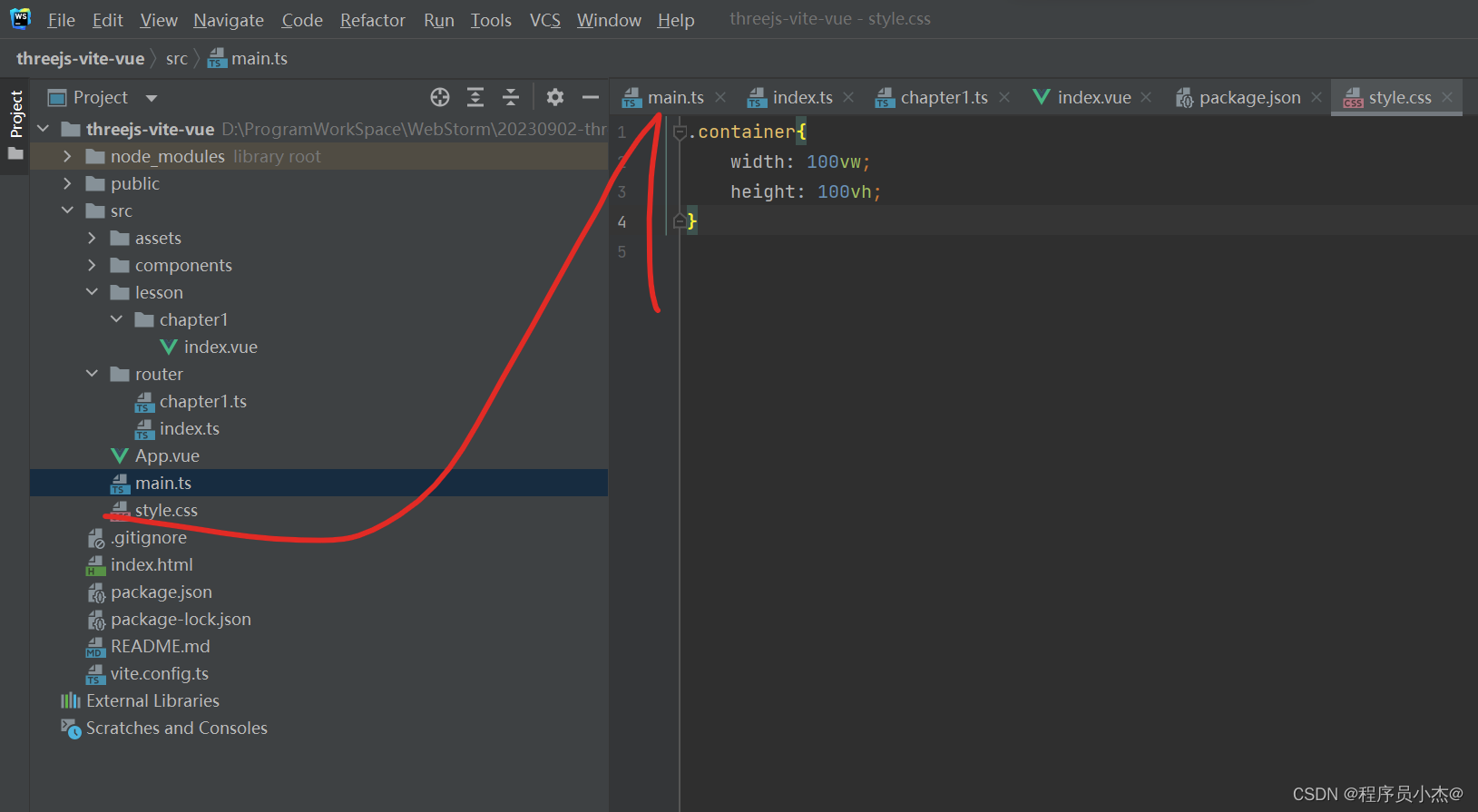
.container{
width: 100vw;
height: 100vh;
}
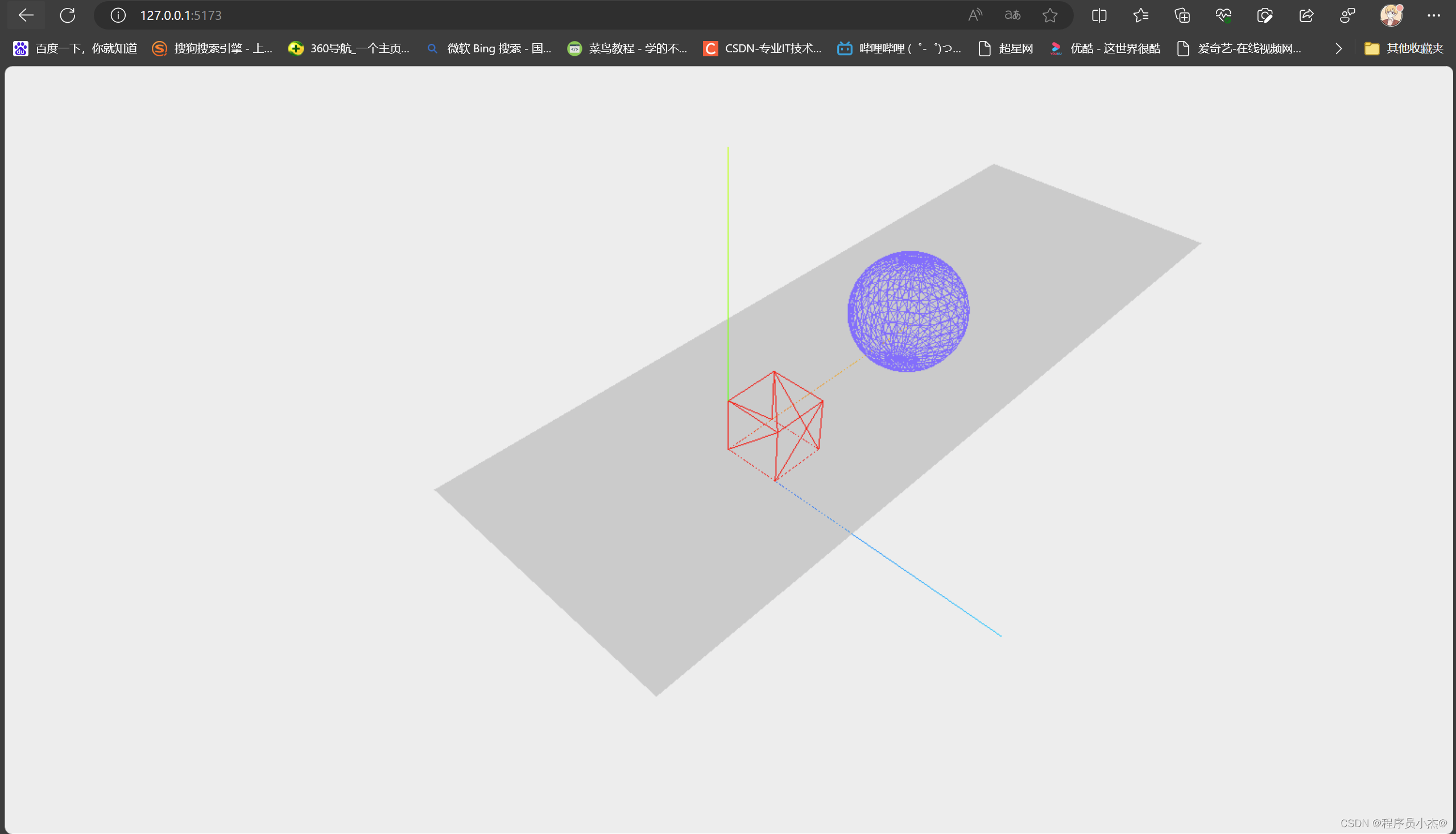
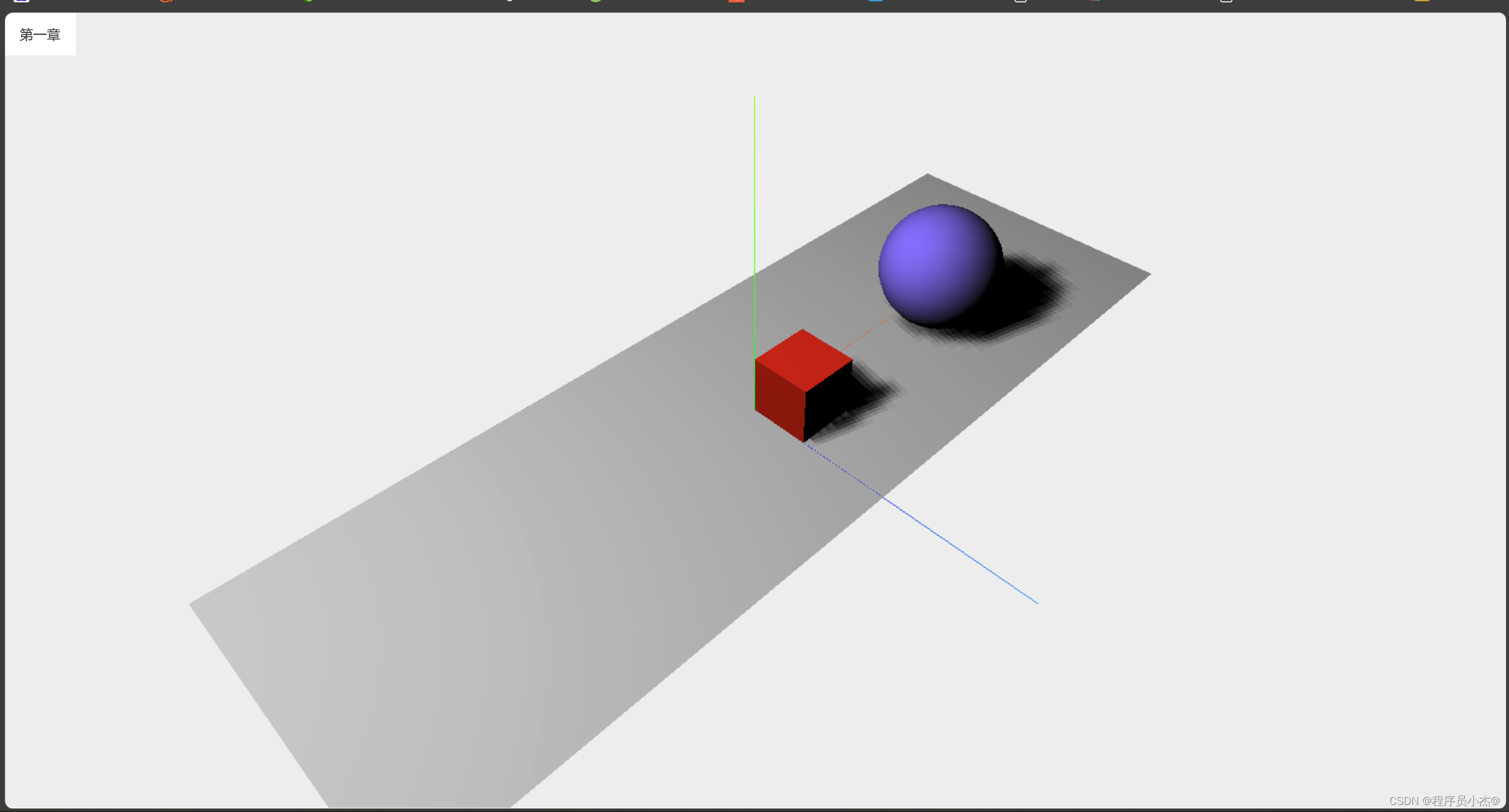
1、绘制板子,立方体,球体
Three.js来绘制一个简单的3D场景,包括一个平面(板子)、一个立方体和一个球体
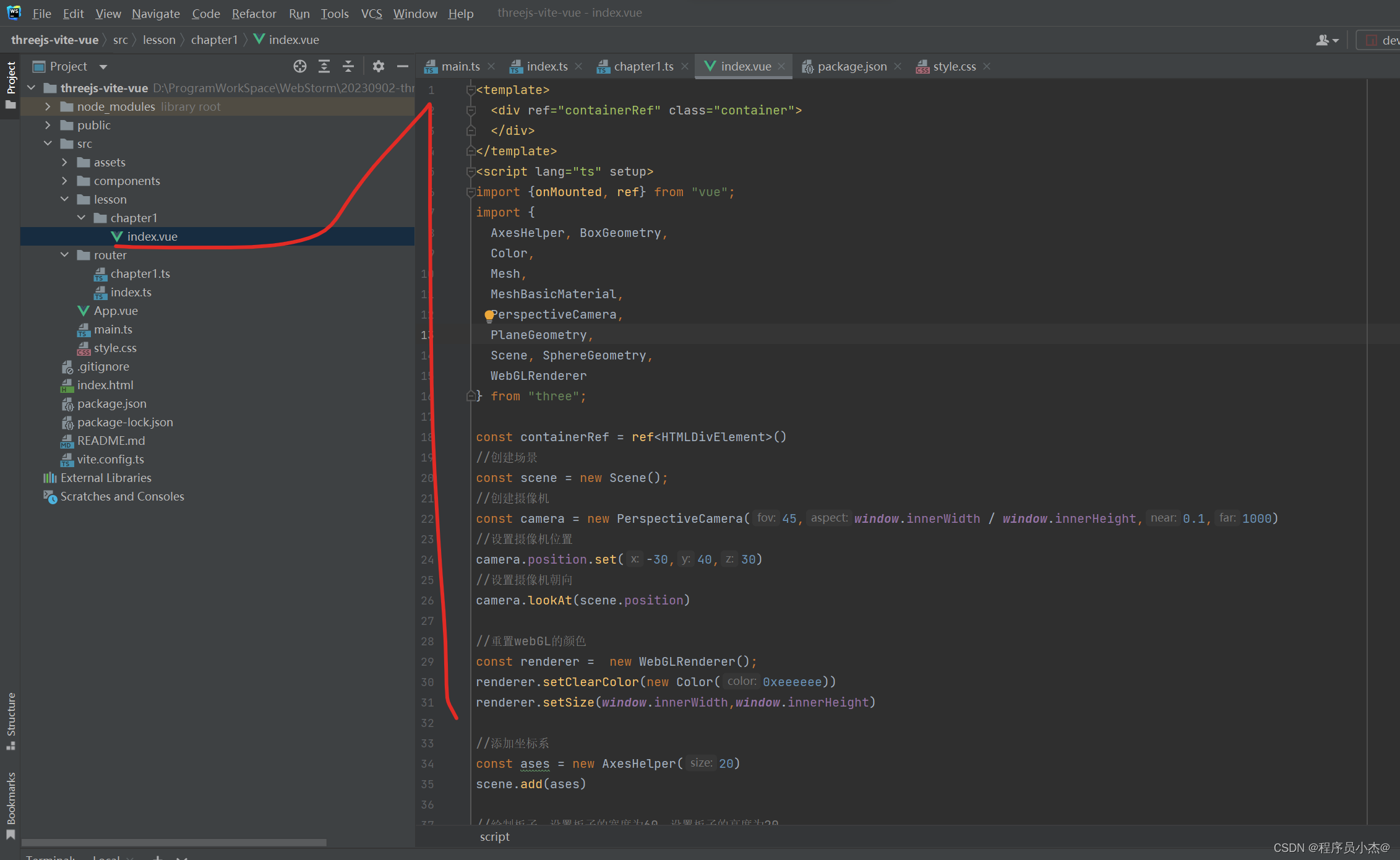
<template>
<div ref="containerRef" class="container">
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {onMounted, ref} from "vue";
import {
AxesHelper, BoxGeometry,
Color,
Mesh,
MeshBasicMaterial,
PerspectiveCamera,
PlaneGeometry,
Scene, SphereGeometry,
WebGLRenderer
} from "three";
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
//创建摄像机
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,0.1,1000)
//设置摄像机位置
camera.position.set(-30,40,30)
//设置摄像机朝向
camera.lookAt(scene.position)
//重置webGL的颜色
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setClearColor(new Color(0xeeeeee))
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
//添加坐标系
const ases = new AxesHelper(20)
scene.add(ases)
//绘制板子,设置板子的宽度为60,设置板子的高度为20
const planeGeometry = new PlaneGeometry(60,20);
const meshBasicMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({color:0xcccccc});//设置材质颜色
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeometry,meshBasicMaterial)
plane.rotation.x = -0.5 * Math.PI;
plane.position.x = 15
plane.position.y = 0
plane.position.z = 0
scene.add(plane)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:true})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometry,cubeMaterial)
cube.position.set(2,2,2)
scene.add(cube)
//绘制球体,设置球体的半径为4
const sphereGeometry = new SphereGeometry(4)
const sphereMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x7777ff,
wireframe:true
})
const sphere = new Mesh(sphereGeometry,sphereMaterial)
sphere.position.x = 15
sphere.position.y = 4
sphere.position.z = 2
scene.add(sphere)
onMounted(()=>{
//设置摄像头朝向
containerRef.value?.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
2、材质和光照
在Three.js中,材质和光照是让物体看起来更为真实的关键因素。材质定义了物体表面的外观,如颜色、纹理和光照效果。Three.js提供了多种类型的材质,适用于不同的光照效果。
物理基础渲染(Physically Based Rendering, PBR)是一种基于物理的渲染技术,使用物理基础渲染代码和材料处理技术来模拟光线和材料之间的物理相互作用,以创建逼真的材料外观和光照效果。这种渲染技术可以提供更真实的阴影,高光,反射和漫反射效果,使场景看起来更加真实。Three.js核心也包含了与Unreal、Unity、Disney和Pixar等巨头使用的相同的基于物理的渲染 (PBR) 算法。
对于纹理的应用,可以通过加载图片并设置其重复模式、采样模式以及重复次数来实现贴图效果。例如,创建一个地平面,并用下方展示的 2x2 像素的黑白格图片来作为纹理。首先加载这个纹理,设置重复模式(wrapS, wrapT),采样模式(magFilter)以及重复的次数。因为贴图是 2x2 大小,通过设置成平铺模式,并且重复次数是边长的一半,就可以让每个格子正好是1个单位的大小。
设置导航菜单组件
<template>
<a-menu mode="horizontal" style="position: fixed">
<a-sub-menu key="demo">
<template #title>
第一章
</template>
<a-menu-item key="1">
<router-link to="/"> 第一个场景 </router-link>
</a-menu-item>
<a-menu-item key="2">
<router-link to="/chapter1/2"> 第一个场景 </router-link>
</a-menu-item>
</a-sub-menu>
</a-menu>
<router-view></router-view>
</template>
<script setup>
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
复制index,生成index2
<template>
<div ref="containerRef" class="container">
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {onMounted, ref} from "vue";
import {
AxesHelper, BoxGeometry,
Color,
Mesh,
MeshBasicMaterial,
PerspectiveCamera,
PlaneGeometry,
Scene, SphereGeometry,
WebGLRenderer
} from "three";
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
//创建摄像机
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,0.1,1000)
//设置摄像机位置
camera.position.set(-30,40,30)
//设置摄像机朝向
camera.lookAt(scene.position)
//重置webGL的颜色
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setClearColor(new Color(0xeeeeee))
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
//添加坐标系
const ases = new AxesHelper(20)
scene.add(ases)
//绘制板子,设置板子的宽度为60,设置板子的高度为20
const planeGeometry = new PlaneGeometry(60,20);
const meshBasicMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({color:0xcccccc});//设置材质颜色
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeometry,meshBasicMaterial)
plane.rotation.x = -0.5 * Math.PI;
plane.position.x = 15
plane.position.y = 0
plane.position.z = 0
scene.add(plane)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:true})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometry,cubeMaterial)
cube.position.set(2,2,2)
scene.add(cube)
//绘制球体,设置球体的半径为4
const sphereGeometry = new SphereGeometry(4)
const sphereMaterial = new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x7777ff,
wireframe:true
})
const sphere = new Mesh(sphereGeometry,sphereMaterial)
sphere.position.x = 15
sphere.position.y = 4
sphere.position.z = 2
scene.add(sphere)
onMounted(()=>{
//设置摄像头朝向
containerRef.value?.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
import {RouteRecordRaw} from "vue-router";
import Index from '../lesson/chapter1/index.vue'
import Index2 from '../lesson/chapter1/index2.vue'
const chapter1 : RouteRecordRaw[] = [
{
path:'/',
component: Index,
meta:{
title:"第一个场景"
}
},
{
path:'/chapter1/2',
component: Index2,
meta:{
title:"第二个场景"
}
}
]
export default chapter1;
实现第二个场景
<template>
<div ref="containerRef" class="container">
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {onMounted, ref} from "vue";
import {
AxesHelper, BoxGeometry,
Color,
Mesh,
MeshBasicMaterial, MeshLambertMaterial,
PerspectiveCamera,
PlaneGeometry,
Scene, SphereGeometry, SpotLight,
WebGLRenderer
} from "three";
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
//创建摄像机
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,0.1,1000)
//设置摄像机位置
camera.position.set(-30,40,30)
//设置摄像机朝向
camera.lookAt(scene.position)
//重置webGL的颜色
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setClearColor(new Color(0xeeeeee))
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true
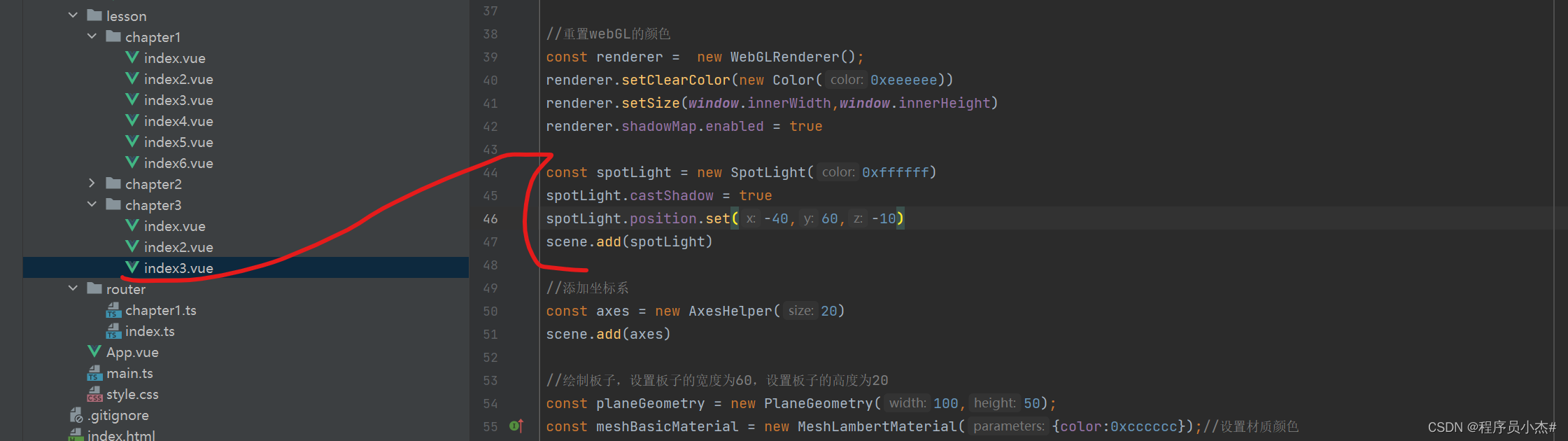
const spotLight = new SpotLight(0xffffff)
spotLight.castShadow = true
spotLight.position.set(-40,60,-10)
scene.add(spotLight)
//添加坐标系
const axes = new AxesHelper(20)
scene.add(axes)
//绘制板子,设置板子的宽度为60,设置板子的高度为20
const planeGeometry = new PlaneGeometry(60,20);
const meshBasicMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xcccccc});//设置材质颜色
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeometry,meshBasicMaterial)
plane.receiveShadow = true //设置可以接收阴影
plane.rotation.x = -0.5 * Math.PI;
//plane.position.x = 15
//plane.position.y = 0
//plane.position.z = 0
scene.add(plane)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometry,cubeMaterial)
cube.castShadow = true
cube.position.set(2,2,2)
scene.add(cube)
//绘制球体,设置球体的半径为4
const sphereGeometry = new SphereGeometry(4)
const sphereMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x7777ff,
wireframe:false
})
const sphere = new Mesh(sphereGeometry,sphereMaterial)
sphere.castShadow = true
sphere.position.x = 15
sphere.position.y = 4
sphere.position.z = 2
scene.add(sphere)
onMounted(()=>{
//设置摄像头朝向
containerRef.value?.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
3、材质和光照和动画
Three.js提供了一套强大的动画系统,可以应用于物体的位置、旋转、缩放、材质的颜色或不透明度等各个方面。这套系统中主要包括了KeyFrameTrack、AnimationClip、AnimationMixer和AnimationAction四个组件。
在制作动画时,我们通常会使用关键帧动画,即在不同时间点设置关键帧,然后由动画系统通过补间过程自动填补各关键帧之间的变化。例如,要为一个弹跳的球设置动画,只需要指定弹跳的顶部和底部的点,Three.js将在这两点之间的所有点上平滑地生成动画。此外,我们还可以通过合成和混合多个动画来创造出更复杂的效果。
复制index2创建index3

<template>
<div ref="containerRef" class="container">
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {onMounted, ref} from "vue";
import {
AxesHelper, BoxGeometry,
Color,
Mesh,
MeshBasicMaterial, MeshLambertMaterial,
PerspectiveCamera,
PlaneGeometry,
Scene, SphereGeometry, SpotLight,
WebGLRenderer
} from "three";
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
//创建摄像机
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,0.1,1000)
//设置摄像机位置
camera.position.set(-30,40,30)
//设置摄像机朝向
camera.lookAt(scene.position)
//重置webGL的颜色
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setClearColor(new Color(0xeeeeee))
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true
const spotLight = new SpotLight(0xffffff)
spotLight.castShadow = true
spotLight.position.set(-40,60,-10)
scene.add(spotLight)
//添加坐标系
const axes = new AxesHelper(20)
scene.add(axes)
//绘制板子,设置板子的宽度为60,设置板子的高度为20
const planeGeometry = new PlaneGeometry(100,50);
const meshBasicMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xcccccc});//设置材质颜色
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeometry,meshBasicMaterial)
plane.receiveShadow = true //设置可以接收阴影
plane.rotation.x = -0.5 * Math.PI;
//plane.position.x = 15
//plane.position.y = 0
//plane.position.z = 0
scene.add(plane)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometry,cubeMaterial)
cube.castShadow = true
cube.position.set(2,2,2)
scene.add(cube)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry1 = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial1 = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube1 = new Mesh(cubeGeometry1,cubeMaterial1)
cube1.castShadow = true
cube1.position.set(-10,2,2)
scene.add(cube1)
//绘制球体,设置球体的半径为4
const sphereGeometry = new SphereGeometry(4)
const sphereMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x7777ff,
wireframe:false
})
const sphere = new Mesh(sphereGeometry,sphereMaterial)
sphere.castShadow = true
sphere.position.x = 15
sphere.position.y = 4
sphere.position.z = 2
scene.add(sphere)
//控制物体运动
let step = 0;
function renderScene() {
step += 0.04;
cube.rotation.x += 0.02;
cube.rotation.y += 0.02;
cube.rotation.z += 0.02;
cube1.rotation.x += -0.02;
cube1.rotation.y += -0.02;
cube1.rotation.z += -0.02;
cube1.scale.set((2 + 1 * Math.cos(step)), (2 + 1 * Math.cos(step)), (2 + 1 * Math.cos(step)));
//控制物体
sphere.position.x = 20 + 10 * Math.cos(step); //cos为数据当中的函数 余弦函数
sphere.position.y = 2 + 10 * Math.abs(Math.sin(step)); //abs为绝对值 sin为正弦函数
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
}
renderScene()
onMounted(()=>{
//设置摄像头朝向
containerRef.value?.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>

4、性能监控
Three.js的性能监控工具Stats.js是一个强大的插件,它能够监测帧率、内存等数据的变化。在动画或网页开发中,帧率是衡量和描述动画是否流畅的一个重要单位。Stats.js可以帮助开发者实时了解Three.js的渲染性能,尤其是渲染帧率(FPS),即每秒钟完成的渲染次数。理想状态下,渲染帧率应该达到每秒60次。
在使用Stats.js时,首先需要引入相关的脚本文件。然后,实例化一个Stats对象,并将该对象生成的DOM元素添加到页面中。通过这种方式,我们可以在开发过程中实时监控Three.js的性能,及时发现并解决可能存在的问题,从而提升用户体验。
安装stats.js插件
npm install stats.js
复制index3.vue创建index4.vue
import index4 from '../lesson/chapter1/index4.vue'
,
{
path:'/chapter1/4',
component: index4,
meta:{
title:"性能监控"
}
}
<div ref="statsRef"></div>
const statsRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
const stats = new Stats()
stats.showPanel(0)
stats.update()
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
stats.dom.style.top = "50px"
statsRef.value?.append(stats.dom)
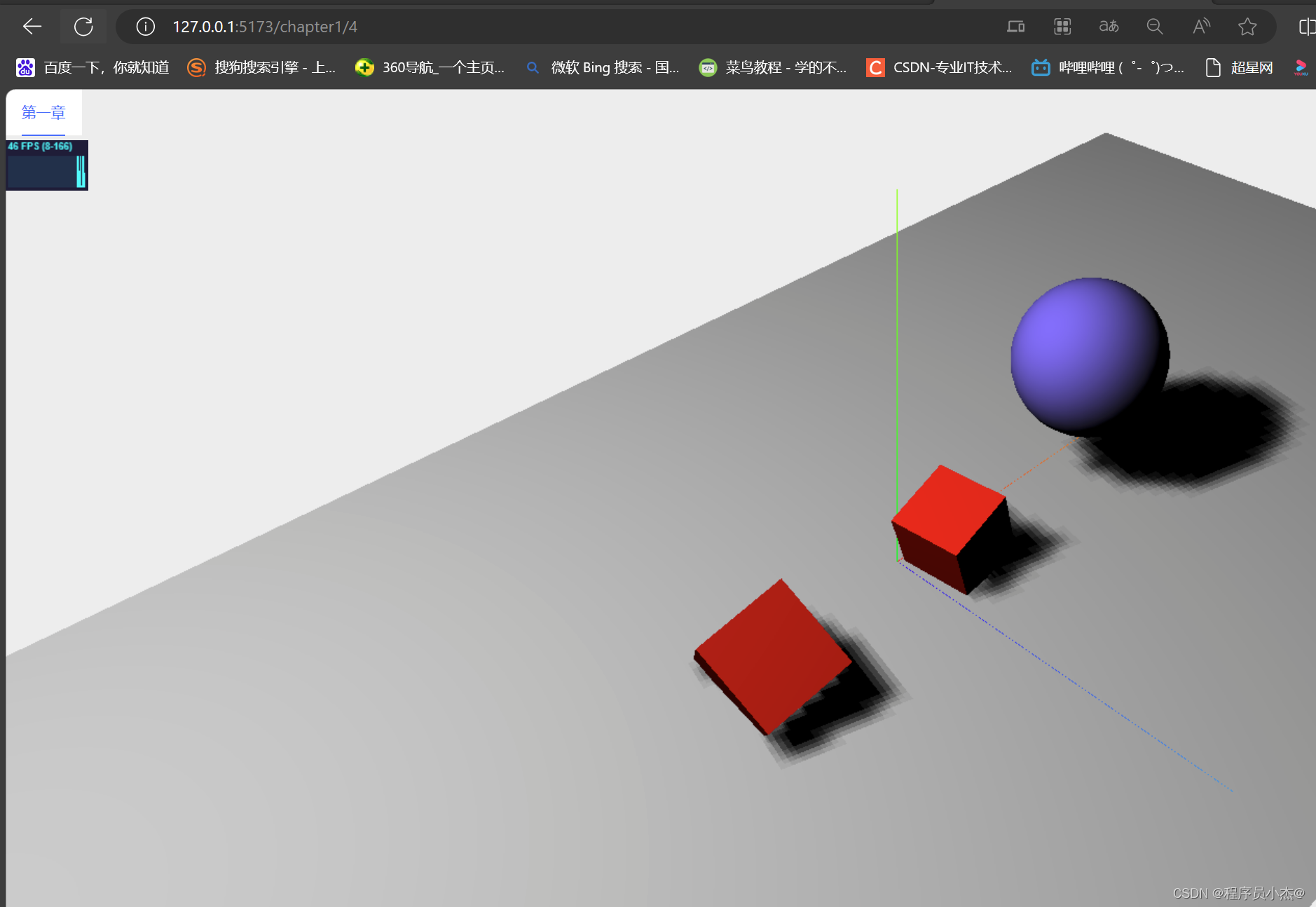
访问第四个场景
http://127.0.0.1:5173/chapter1/4
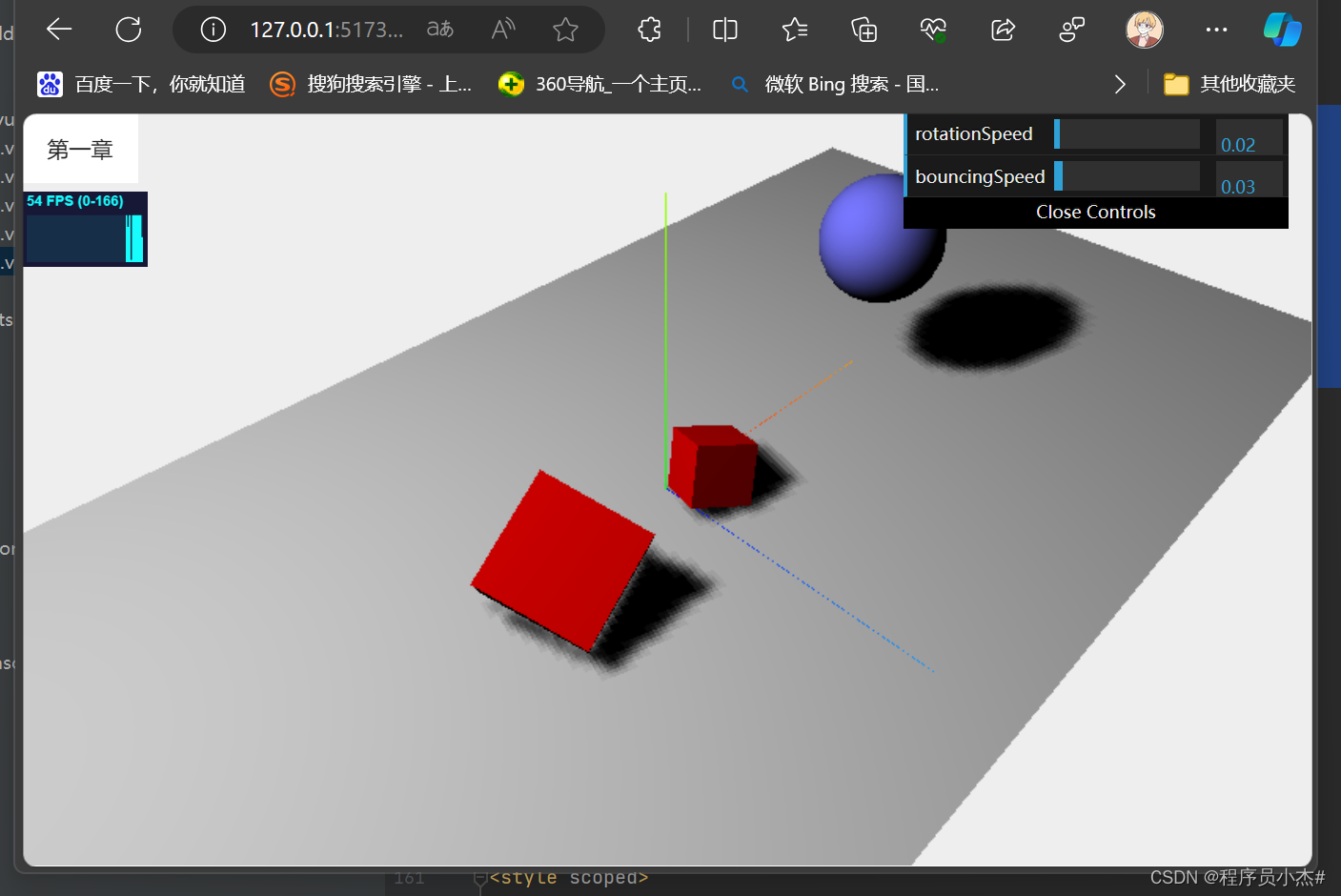
5、交互控制
dat.gui@0.7.9是一个轻量级的JavaScript库,它的主要功能是帮助用户添加交互式控制面板,以便在3D场景中调整对象参数并实时预览结果。
复制一下index4.vue 为index5.vue

{
path:'/chapter1/5',
component: index5,
meta:{
title:"交互控制"
}
}
<a-menu-item key="5">
<router-link to="/chapter1/5"> 第五个场景 </router-link>
</a-menu-item>
安装dat.gui
npm install dat.gui@0.7.9
npm install @types/dat.gui@0.7.9 -D
import * as dat from "dat.gui"
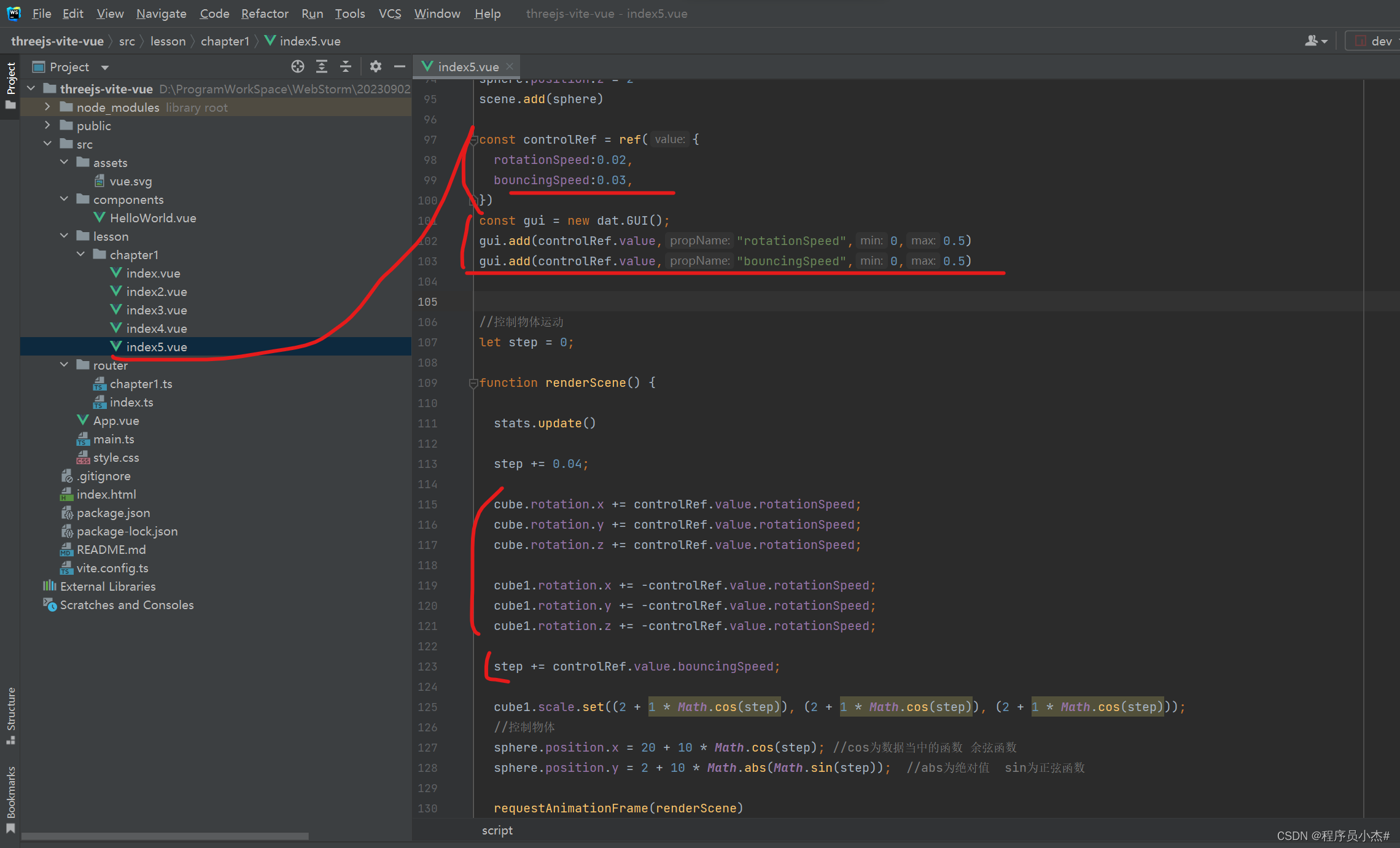
const controlRef = ref({
rotationSpeed:0.02,
bouncingSpeed:0.03,
})
const gui = new dat.GUI();
gui.add(controlRef.value,"rotationSpeed",0,0.5)
gui.add(controlRef.value,"bouncingSpeed",0,0.5)
step += 0.04;
cube.rotation.x += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube.rotation.y += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube.rotation.z += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube1.rotation.x += -controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube1.rotation.y += -controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube1.rotation.z += -controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
step += controlRef.value.bouncingSpeed;

放置重复初始化
if(document.querySelectorAll(".dg.ac>.dg.main.a").length === 0){
const gui = new dat.GUI()
gui.add(controlRef.value,"rotationSpeed",0,0.5)
gui.add(controlRef.value,"bouncingSpeed",0,0.5)
}
index5.vue全部代码
<template>
<div ref="statsRef"></div>
<div ref="containerRef" class="container">
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {onMounted, ref} from "vue";
import {
AxesHelper, BoxGeometry,
Color,
Mesh,
MeshBasicMaterial, MeshLambertMaterial,
PerspectiveCamera,
PlaneGeometry,
Scene, SphereGeometry, SpotLight,
WebGLRenderer
} from "three";
import Stats from "stats.js"
import * as dat from "dat.gui"
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
const statsRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
const stats = new Stats()
stats.showPanel(0)
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
//创建摄像机
const camera = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,0.1,1000)
//设置摄像机位置
camera.position.set(-30,40,30)
//设置摄像机朝向
camera.lookAt(scene.position)
//重置webGL的颜色
const renderer = new WebGLRenderer();
renderer.setClearColor(new Color(0xeeeeee))
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
renderer.shadowMap.enabled = true
const spotLight = new SpotLight(0xffffff)
spotLight.castShadow = true
spotLight.position.set(-40,60,-10)
scene.add(spotLight)
//添加坐标系
const axes = new AxesHelper(20)
scene.add(axes)
//绘制板子,设置板子的宽度为60,设置板子的高度为20
const planeGeometry = new PlaneGeometry(100,50);
const meshBasicMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xcccccc});//设置材质颜色
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeometry,meshBasicMaterial)
plane.receiveShadow = true //设置可以接收阴影
plane.rotation.x = -0.5 * Math.PI;
//plane.position.x = 15
//plane.position.y = 0
//plane.position.z = 0
scene.add(plane)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometry,cubeMaterial)
cube.castShadow = true
cube.position.set(2,2,2)
scene.add(cube)
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry1 = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial1 = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube1 = new Mesh(cubeGeometry1,cubeMaterial1)
cube1.castShadow = true
cube1.position.set(-10,2,2)
scene.add(cube1)
//绘制球体,设置球体的半径为4
const sphereGeometry = new SphereGeometry(4)
const sphereMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x7777ff,
wireframe:false
})
const sphere = new Mesh(sphereGeometry,sphereMaterial)
sphere.castShadow = true
sphere.position.x = 15
sphere.position.y = 4
sphere.position.z = 2
scene.add(sphere)
const controlRef = ref({
rotationSpeed:0.02,
bouncingSpeed:0.03,
})
if(document.querySelectorAll(".dg.ac>.dg.main.a").length === 0){
const gui = new dat.GUI()
gui.add(controlRef.value,"rotationSpeed",0,0.5)
gui.add(controlRef.value,"bouncingSpeed",0,0.5)
}
//控制物体运动
let step = 0;
function renderScene() {
stats.update()
step += 0.04;
cube.rotation.x += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube.rotation.y += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube.rotation.z += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube1.rotation.x += -controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube1.rotation.y += -controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
cube1.rotation.z += -controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
step += controlRef.value.bouncingSpeed;
cube1.scale.set((2 + 1 * Math.cos(step)), (2 + 1 * Math.cos(step)), (2 + 1 * Math.cos(step)));
//控制物体
sphere.position.x = 20 + 10 * Math.cos(step); //cos为数据当中的函数 余弦函数
sphere.position.y = 2 + 10 * Math.abs(Math.sin(step)); //abs为绝对值 sin为正弦函数
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
}
renderScene()
onMounted(()=>{
//创建场景
const scene = new Scene();
stats.dom.style.top = "50px"
statsRef.value?.append(stats.dom)
//设置摄像头朝向
containerRef.value?.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
renderer.render(scene,camera)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
6、响应窗口变化
和之前一样创建index6.vue
/*
监听在窗口变化的时候重新设置大小
* */
window.addEventListener('resize',()=>{
camera.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight;
//更新相机投影矩阵
camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
})
三、基础场景搭建
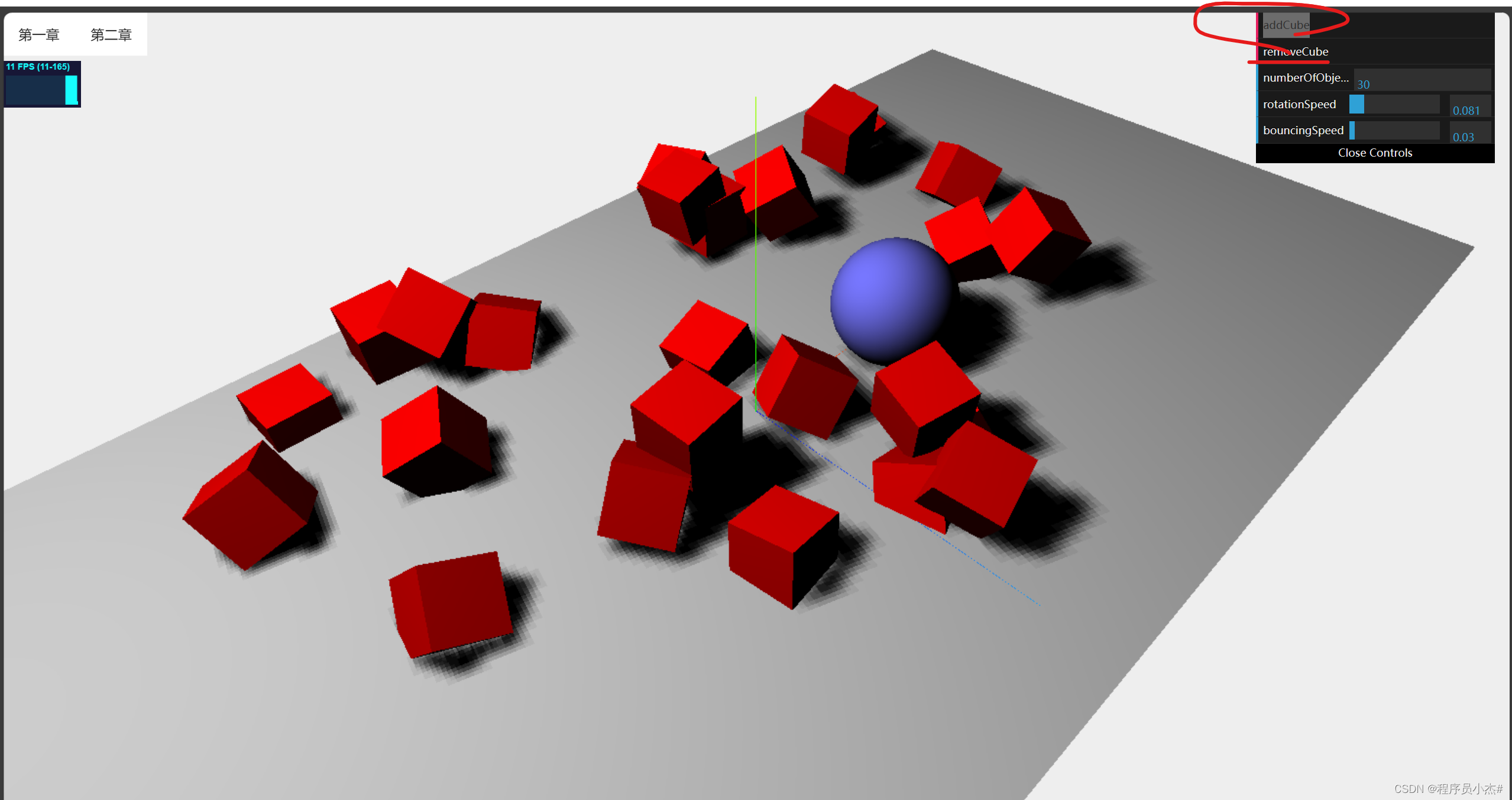
1、创建基础场景【实现添加几何体和删除几何体】
将index6复制到chapter2下的index
const controlRef = ref({
rotationSpeed:0.02,
bouncingSpeed:0.03,
numberOfObjects:0,
addCube:function (){
//绘制立方体,设置板子的长宽高分别是4,4,4
const cubeGeometry = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometry,cubeMaterial)
cube.name = "cube-"+scene.children.length
cube.castShadow = true
cube.position.x = -30 + Math.round((Math.random() * 60))
cube.position.y = Math.round((Math.random() * 5))
cube.position.z = -20 + Math.round((Math.random() * 40))
scene.add(cube)
this.numberOfObjects = scene.children.length
},
removeCube:function (){
const allChildren = scene.children;
const lastObject = allChildren[allChildren.length - 1];
if(lastObject instanceof Mesh && lastObject.name.startsWith('cube')){
scene.remove(lastObject);
}
this.numberOfObjects = scene.children.length
}
})
if(document.querySelectorAll(".dg.ac>.dg.main.a").length === 0){
const gui = new dat.GUI()
gui.add(controlRef.value,"addCube")
gui.add(controlRef.value,"removeCube")
gui.add(controlRef.value,"numberOfObjects").listen()
gui.add(controlRef.value,"rotationSpeed",0,0.5)
gui.add(controlRef.value,"bouncingSpeed",0,0.5)
}
stats.update()
//遍历场景当中的所有内容
scene.traverse((e) =>{
/*
*
if ( e instanceof Mesh && e != plane){
e.rotation.x += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
e.rotation.y += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
e.rotation.z += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
}
*/
if ( e.name.startsWith('cube')){
e.rotation.x += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
e.rotation.y += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
e.rotation.z += controlRef.value.rotationSpeed;
}
})
实现点击添加cube和删除cube
2、实现雾化场景
雾化效果是一种常见的视觉效果,它可以使场景中的物体看起来更加模糊和透明。在Three.js中,可以通过设置材质的透明度和混合模式来实现雾化效果
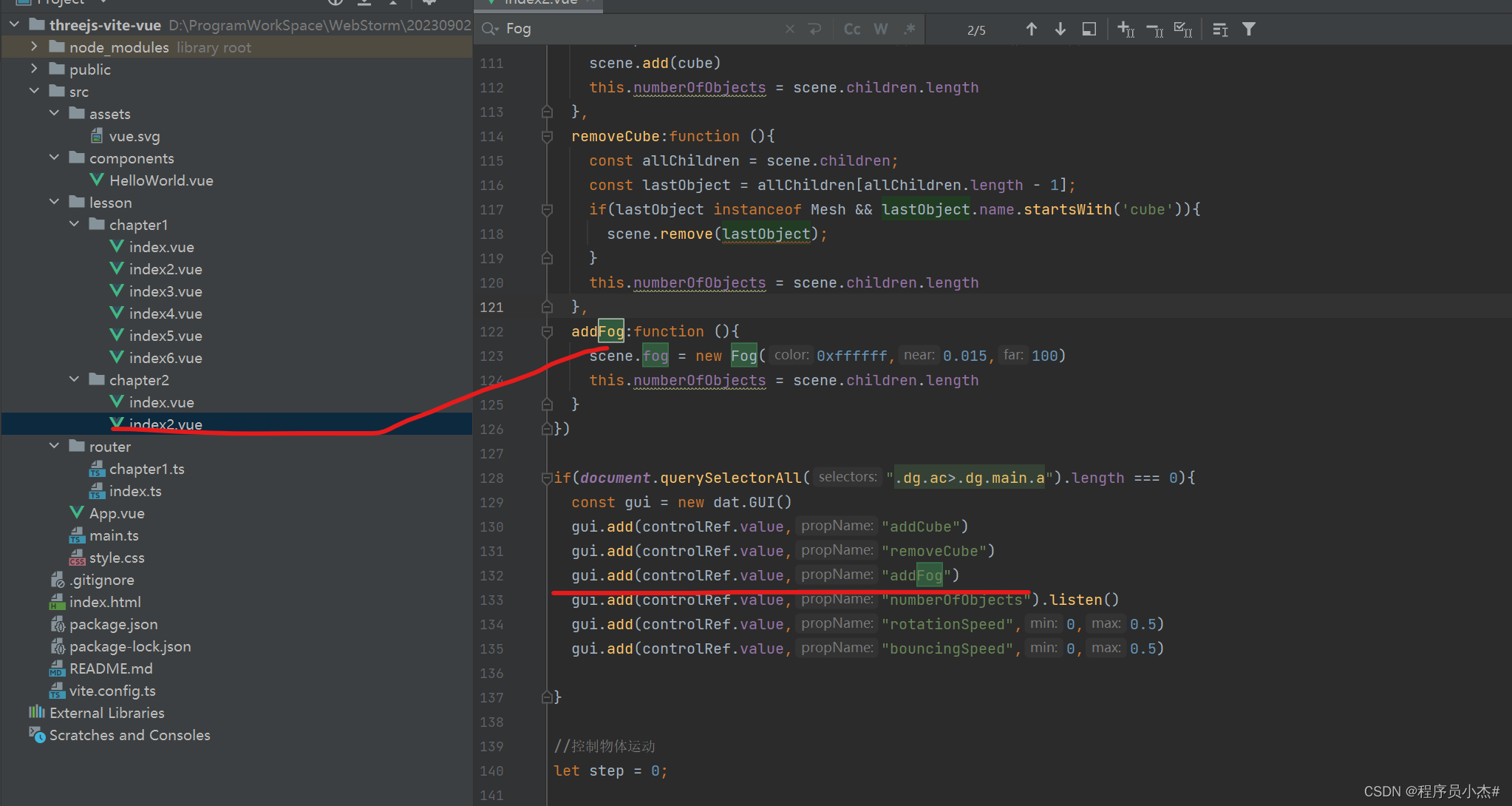
addFog:function (){
scene.fog = new Fog(0xffffff,0.015,100)
this.numberOfObjects = scene.children.length
}
gui.add(controlRef.value,"addFog")
http://127.0.0.1:5173/chapter2/2
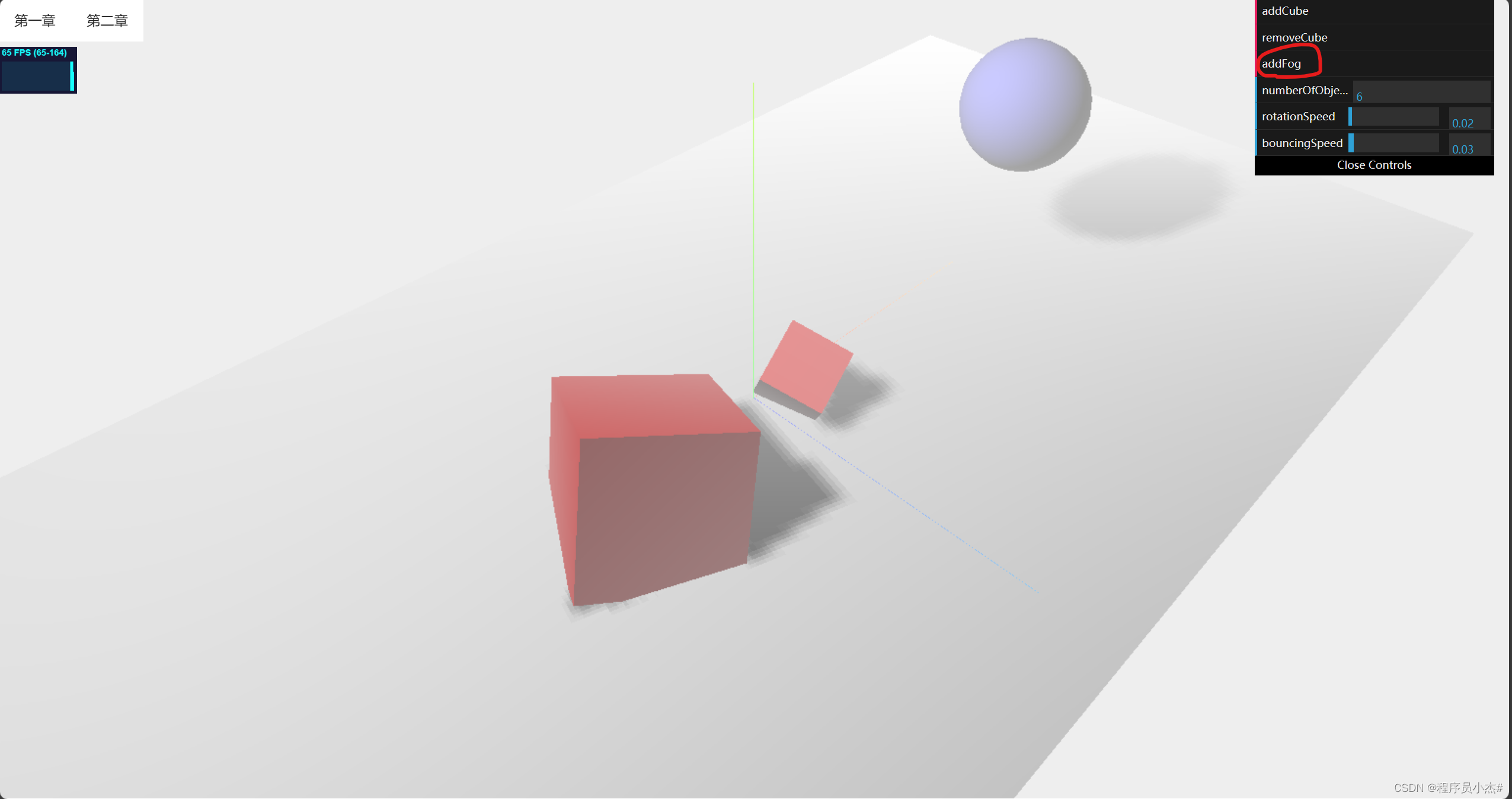
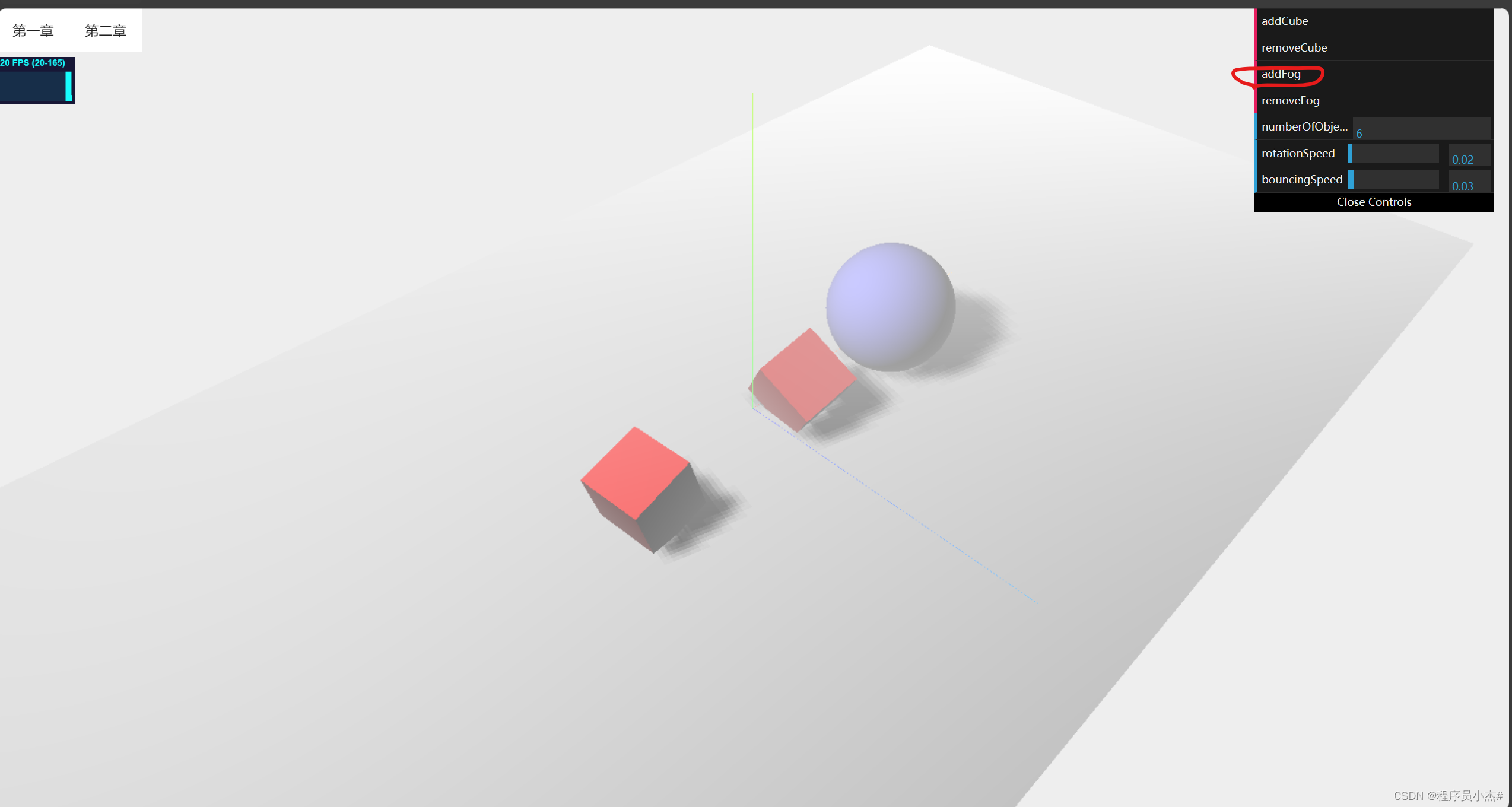
移除雾化
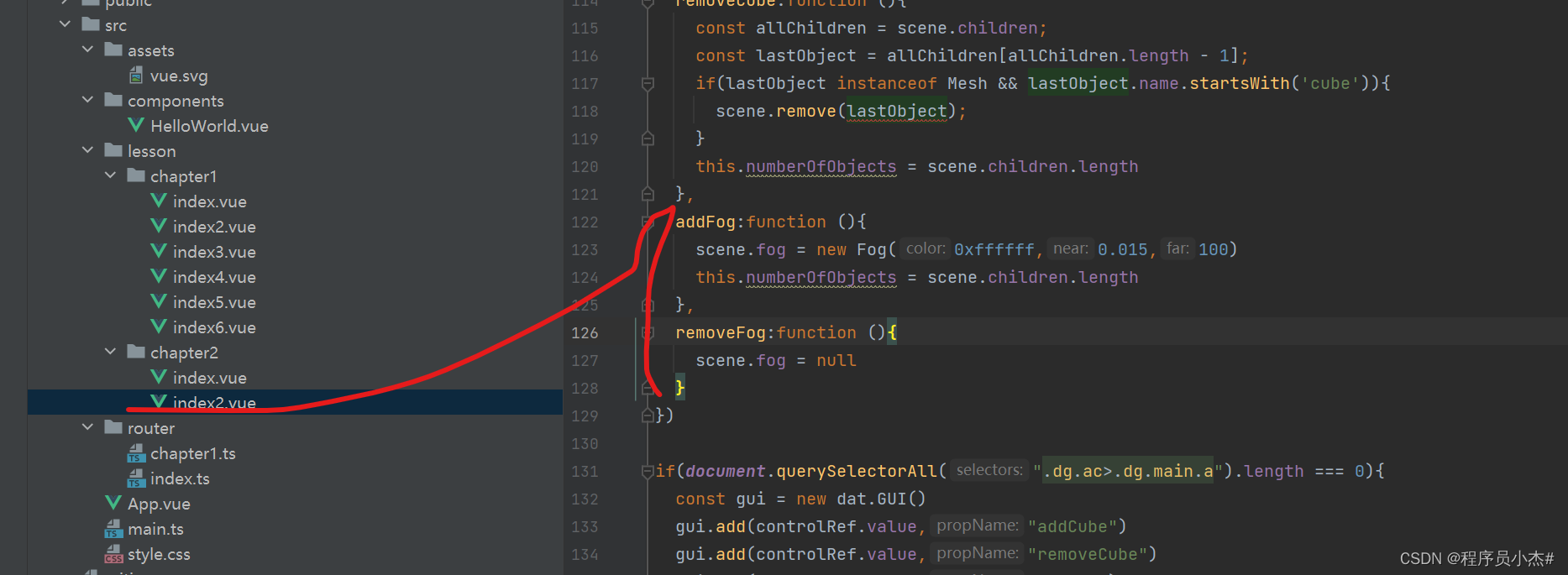
removeFog:function (){
scene.fog = null
}
gui.add(controlRef.value,"removeFog")
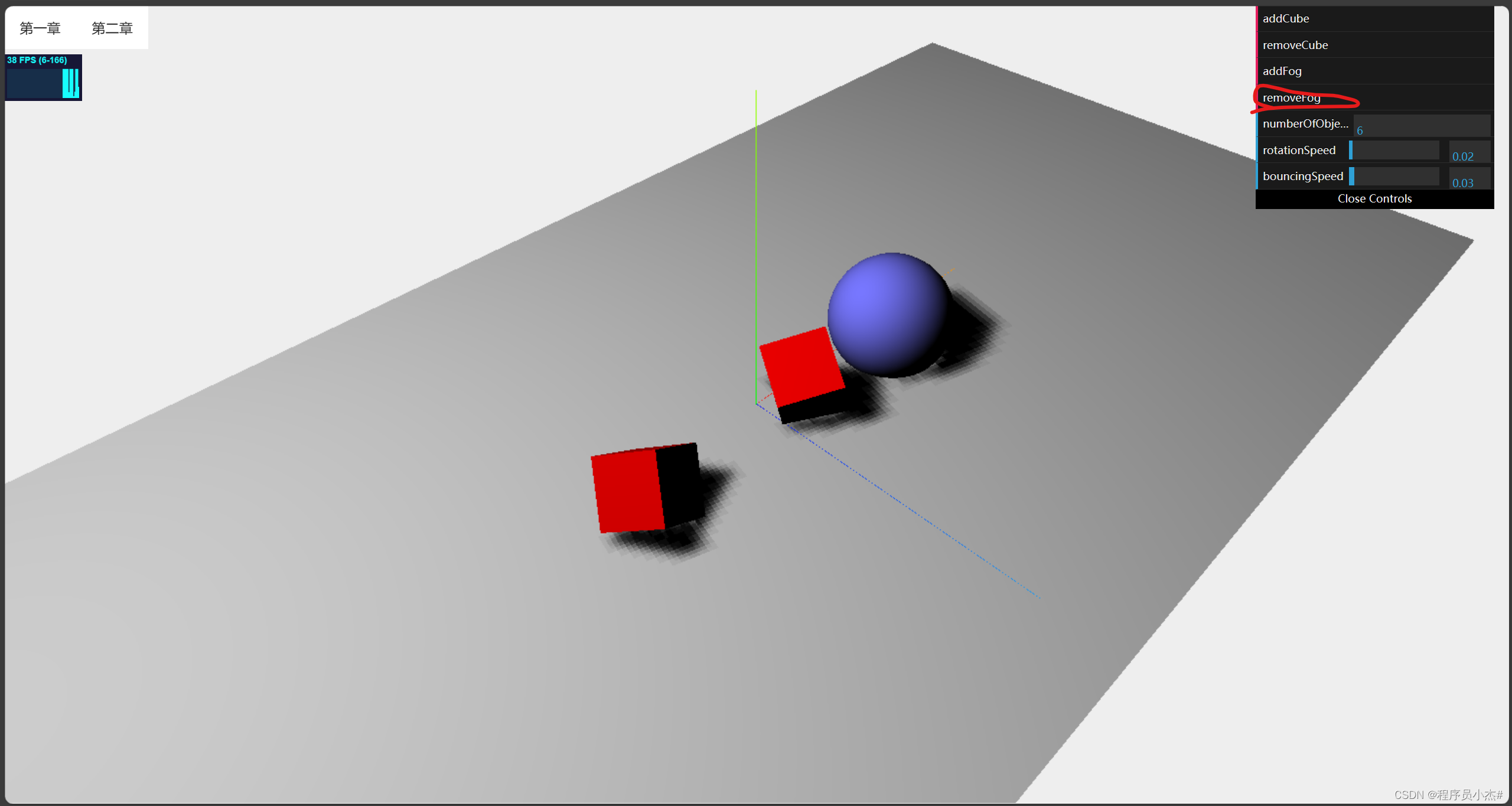
3、重写材质
在Three.js中,材质是定义物体外观的关键。通过创建自定义材质,可以对物体的外观进行更精细的控制,包括如何设置材质的颜色、纹理和透明度等属性。
toggleMaterial:function (){
if(!scene.overrideMaterial){
scene.overrideMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({
color:0xffffff,
})
}else{
scene.overrideMaterial =null
}
}
gui.add(controlRef.value,"toggleMaterial")
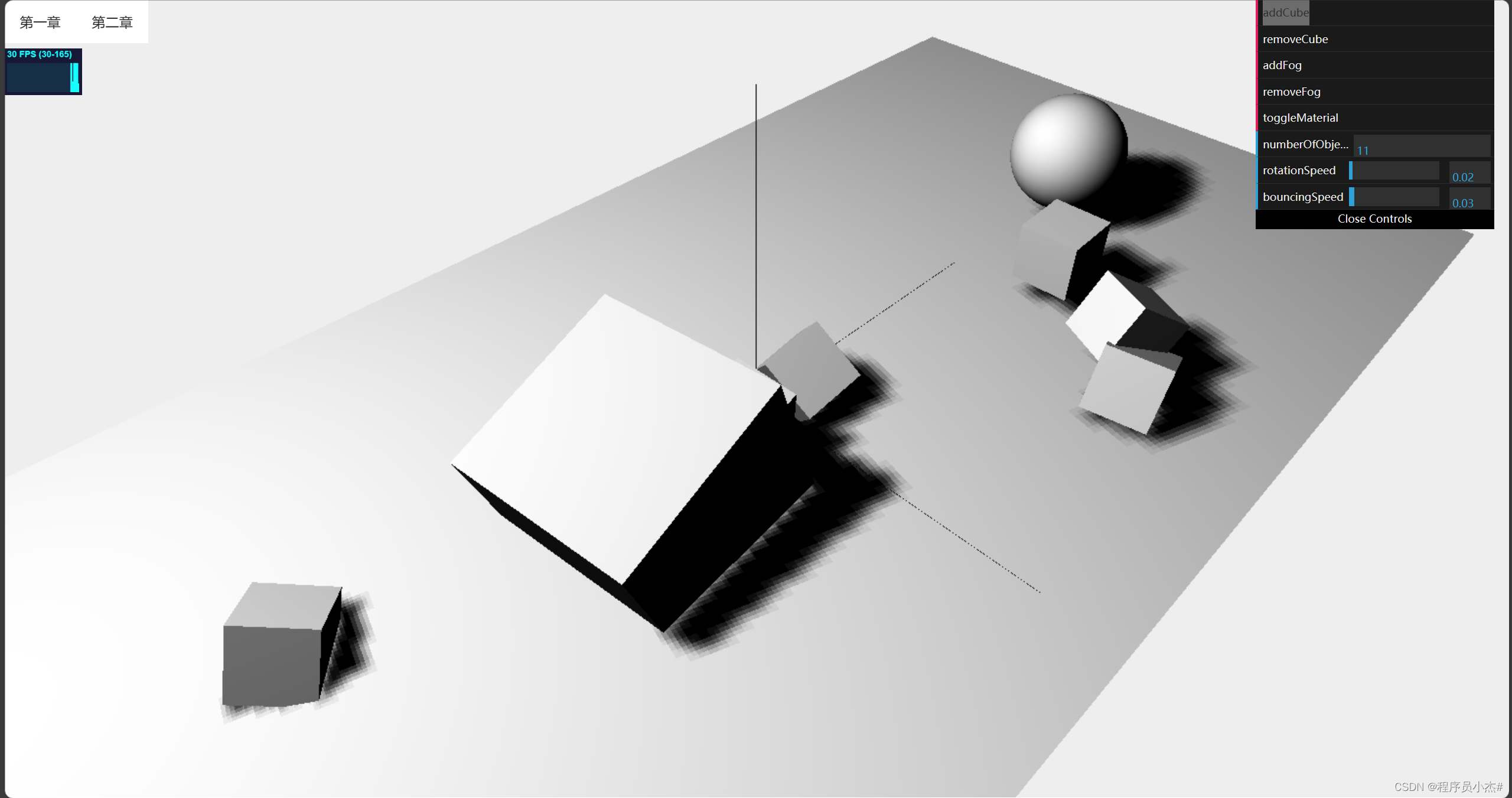
4、常见几何体
在Three.js中,几何体是一个数据结构,它包含了用于描述三维物体的基本信息,如顶点(vertices)、线(lines)和面(faces)。几何体可以被用来定义物体的形状和大小。
常见的几何体类型有以下几种:
BoxGeometry(立方体几何体):通过指定宽度、高度和深度来创建一个立方体。
SphereGeometry(球体几何体):通过指定半径来创建一个球体。
CylinderGeometry(圆柱体几何体):通过指定高度、半径和圆周上的段数来创建一个圆柱体。
PlaneGeometry(平面几何体):一种基础的二维几何体,可以用来绘制平面。
ConeGeometry(圆锥体几何体):通过指定高度、底部半径和顶部半径,以及圆周上的段数来创建一个圆锥体。
TubularGeometry(管状几何体):这是一种具有圆形截面的管道形状,需要指定管道的中心轴线、直径、高度和圆周上的段数。
const geoms:BufferGeometry[] = []
geoms.push(new CylinderGeometry(1,4,8))
geoms.push(new BoxGeometry(2,2,2))
geoms.push(new OctahedronGeometry(3))
geoms.push(new TetrahedronGeometry(3))
geoms.push(new TorusGeometry(3,1,10,10))
//材质
const materials = [
new MeshLambertMaterial({
color:Math.random() * 0xffffff,
flatShading:true
}),
new MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x000000,
wireframe:true
})
]
geoms.forEach((g,i) =>{
const mesh = createMultiMaterialObject(g,materials)
mesh.castShadow = true
mesh.position.x = -24 + i * 10,
mesh.position.y = 4,
scene.add(mesh)
})
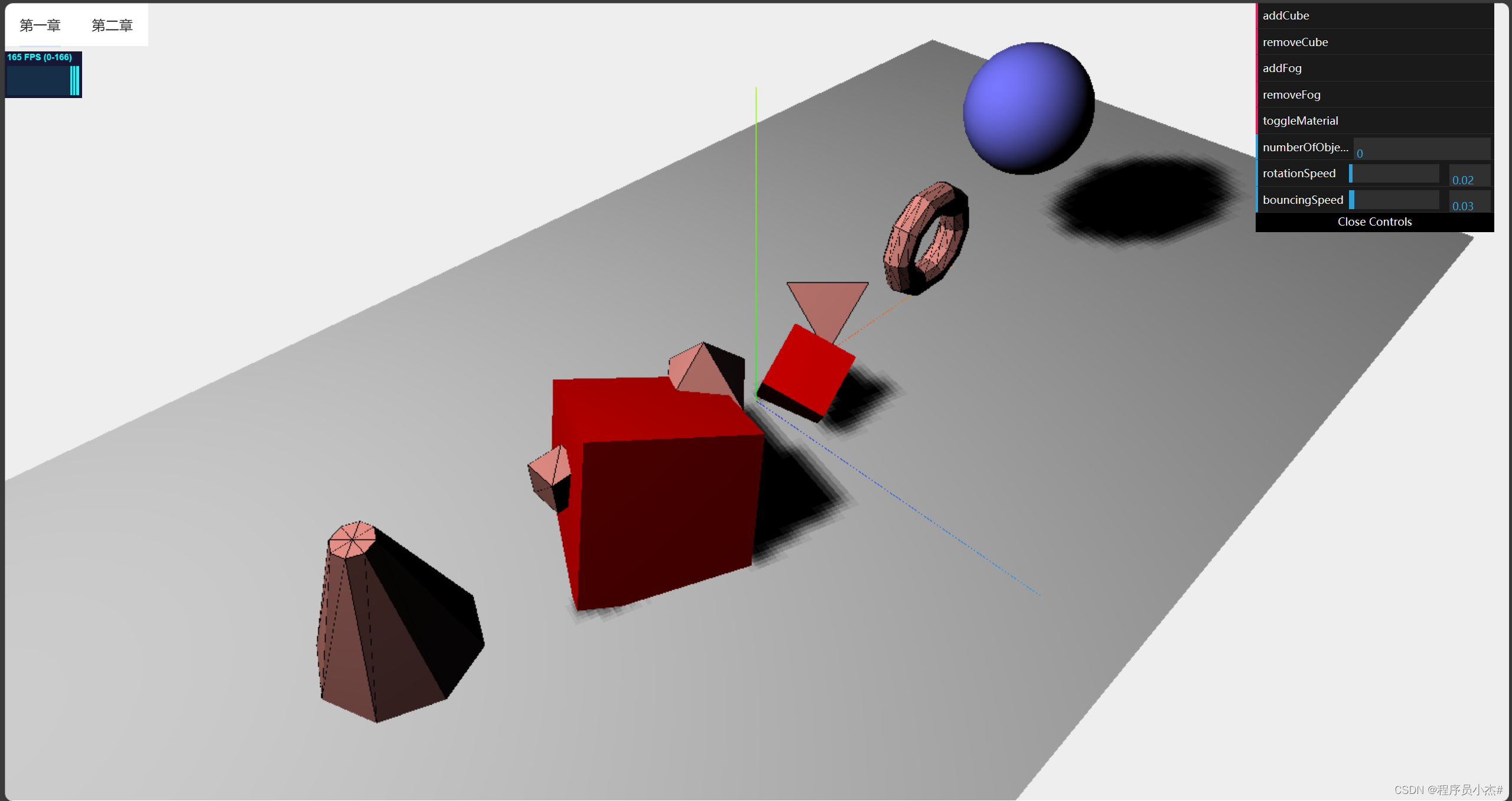
5、修改几何体属性
在Three.js中,几何体的属性可以通过修改其顶点、线和面的数据来改变物体的形状和大小。以下是一些常见的修改几何体属性的方法:
修改顶点数据:通过修改几何体的vertices属性,可以改变物体的形状。例如,可以将一个立方体的顶点数据修改为一个球体的顶点数据,从而创建一个球形物体。
修改线数据:通过修改几何体的lines属性,可以改变物体的边界线。例如,可以将一个立方体的边线修改为一个圆柱体的边线,从而创建一个圆柱形物体。
修改面数据:通过修改几何体的faces属性,可以改变物体的表面。例如,可以将一个立方体的面修改为一个球体的面,从而创建一个球形物体。
修改材质属性:通过修改几何体的material属性,可以改变物体的颜色、纹理和透明度等视觉效果。例如,可以将一个立方体的材质修改为一个半透明的红色材料,从而创建一个半透明的红色立方体。
需要注意的是,修改几何体属性需要对Three.js的底层实现有一定的了解,并且需要注意性能问题。如果频繁地修改几何体属性,可能会导致性能下降。因此,在实际应用中,应该根据需求选择合适的方法来修改几何体属性。
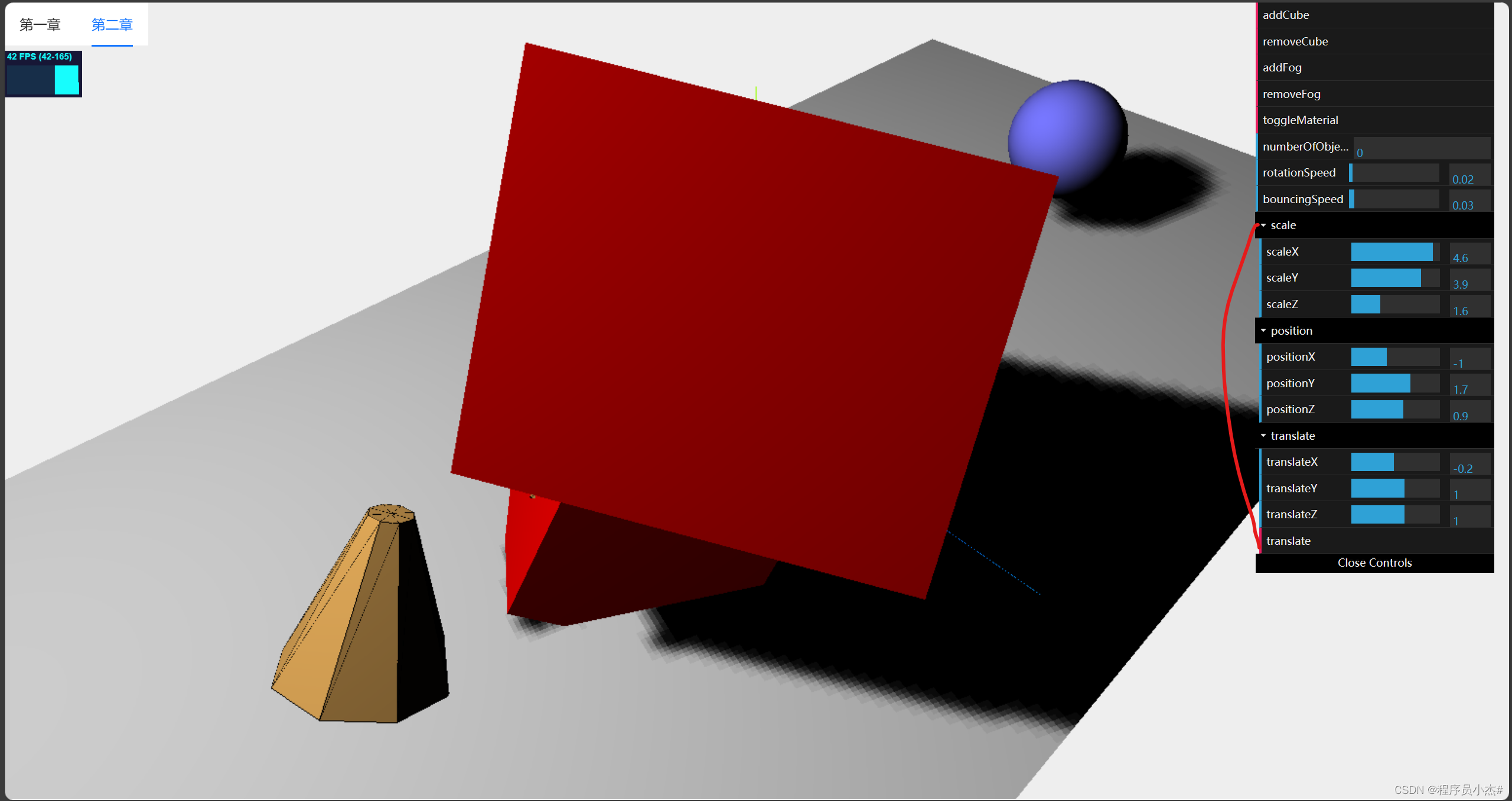
scaleX:1,
scaleY:1,
scaleZ:1,
positionX:1,
positionY:1,
positionZ:1,
translateZ:1,
translateY:1,
translateX:1,
obj:{
x:0,
y:0,
z:0,
},
translate:function (){
this.obj.x = this.translateX
this.obj.y = this.translateY
this.obj.z = this.translateZ
}
/*设置大小*/
const scaleFolder = gui.addFolder("scale")
scaleFolder.add(controlRef.value,"scaleX",0,5);
scaleFolder.add(controlRef.value,"scaleY",0,5);
scaleFolder.add(controlRef.value,"scaleZ",0,5);
/*设置位置*/
const positionFolder = gui.addFolder("position")
positionFolder.add(controlRef.value,"positionX",-5,5);
positionFolder.add(controlRef.value,"positionY",-5,5);
positionFolder.add(controlRef.value,"positionZ",-5,5);
/*设置斜角位置*/
const translateFolder = gui.addFolder("translate")
translateFolder.add(controlRef.value,"translateX",-5,5);
translateFolder.add(controlRef.value,"translateY",-5,5);
translateFolder.add(controlRef.value,"translateZ",-5,5);
translateFolder.add(controlRef.value,"translate");
watch(()=>controlRef.value.obj,(n)=>{
cube.translateX(n.x)
cube.translateY(n.y)
cube.translateZ(n.z)
},{deep:true})
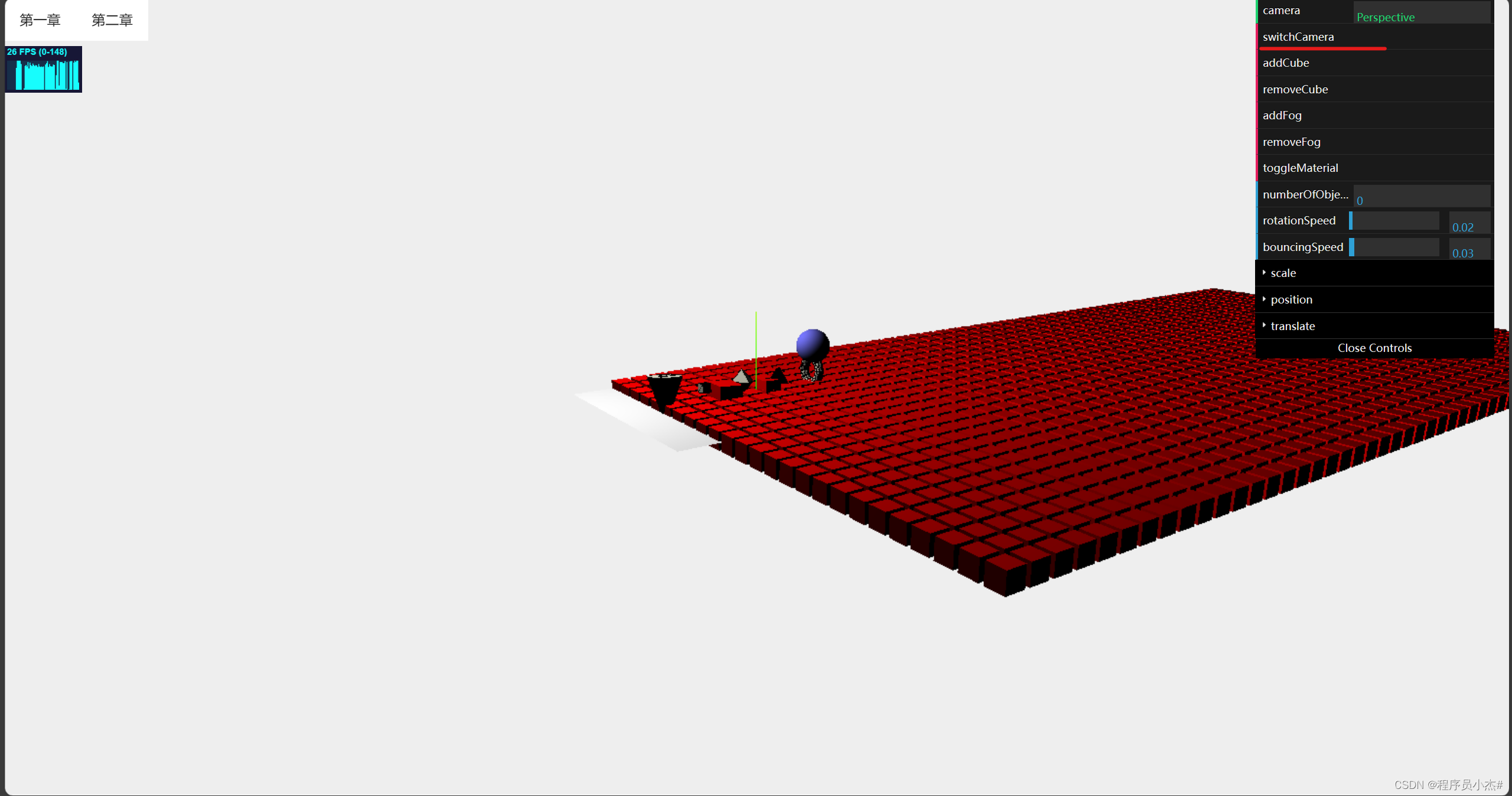
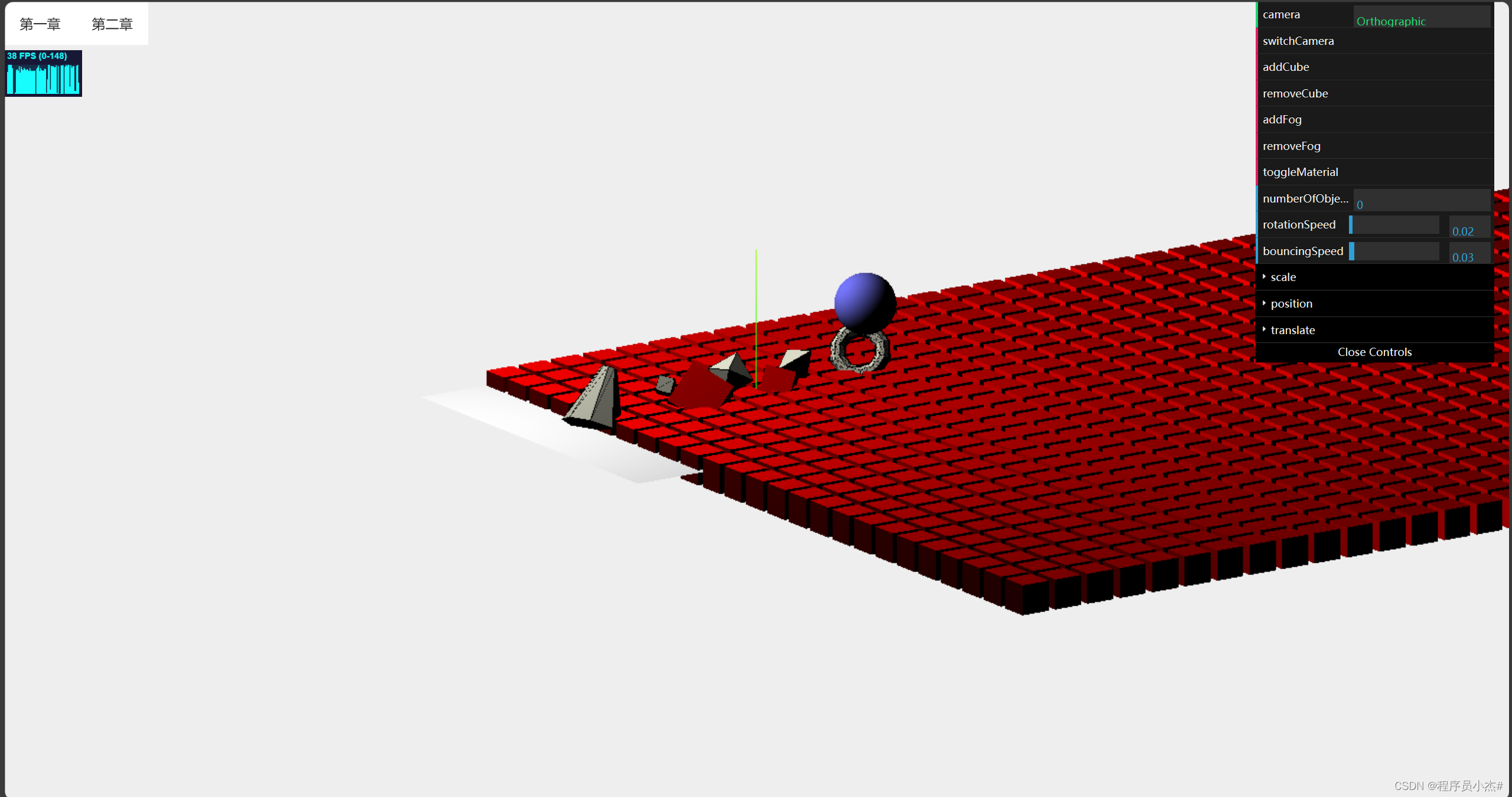
6、相机切换
在Three.js中,相机是用于渲染场景的工具。主要包括透视相机(PerspectiveCamera)和正交相机(OrthographicCamera)。
透视相机可以创建具有深度感的三维效果,而正交相机则可以在二维平面上进行投影。
实现相机视角的切换,主要有两种方法。一种是使用Tween.js库来实现平滑过渡的效果。Tween.js库可以很容易实现两个值之间的过度,中间值都会自动计算出来。
另一种是通过鼠标拉拽来改变相机的位置、旋转角度等,比如使用OrbitControls类。
OrbitControls类是Three.js提供的鼠标、方向键与场景交互的控件,通过鼠标的操作可以改变相机的视角,从而改变视觉,使得视觉效果更具有真实感。
此外,如果想要切换不同的场景,可以通过创建多个场景对象,并在每个场景中添加不同的模型、灯光等元素。
使用renderer.render(scene, camera)方法在渲染循环中渲染当前场景,使用scene.dispose()方法清除当前场景中的元素,释放内存。当需要切换到下一个场景时,重复上述步骤,并将下一个场景设置为当前场景。
设置场景和多个物体
//绘制板子,设置板子的宽度为60,设置板子的高度为20
const planeGeometry = new PlaneGeometry(100,50,1);
const meshBasicMaterial = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xffffff});//设置材质颜色
const plane = new Mesh(planeGeometry,meshBasicMaterial)
plane.receiveShadow = true //设置可以接收阴影
plane.rotation.x = -0.5 * Math.PI;
plane.position.x = 15
plane.position.y = 0
plane.position.z = 0
scene.add(plane)
const cubeGeometryC = new BoxGeometry(4,4,4)
const cubeMaterialC = new MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000,wireframe:false})
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometryC,cubeMaterialC)
cube.castShadow = true
cube.position.set(2,2,2)
scene.add(cube)
for (let j = 0;j < planeGeometry.parameters.height / 2;j++){
for (let i = 0;i < planeGeometry.parameters.width / 2;i++){
const cube = new Mesh(cubeGeometryC,cubeMaterialC)
cube.position.z = -(planeGeometry.parameters.height / 2) + 2 + j * 5;
cube.position.x = -(planeGeometry.parameters.height / 2) + 2 + i * 5;
cube.position.y = 0;
scene.add(cube)
}
}
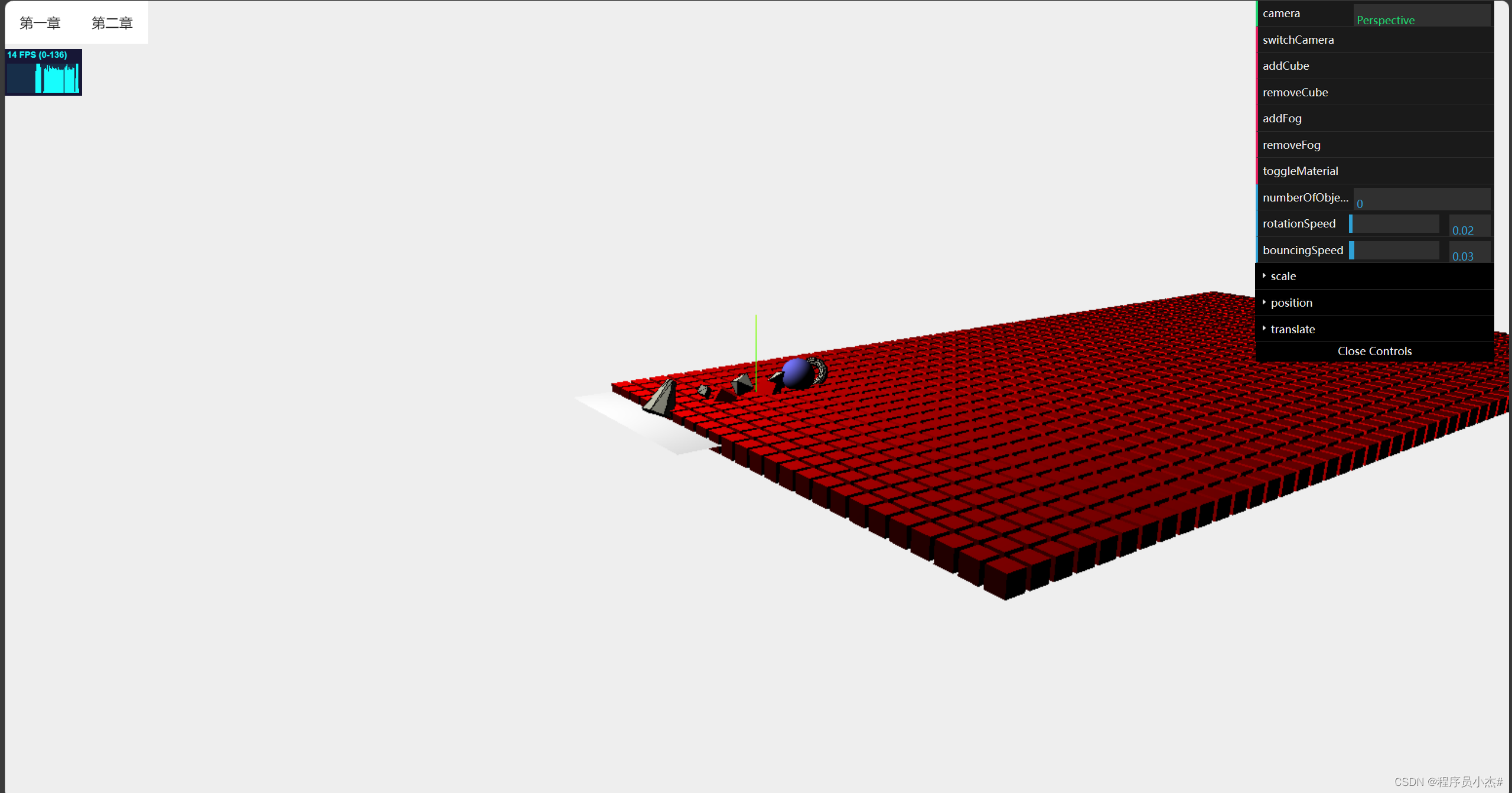
设置切换相机
gui.add(controlRef.value,"camera").listen()
gui.add(controlRef.value,"switchCamera")
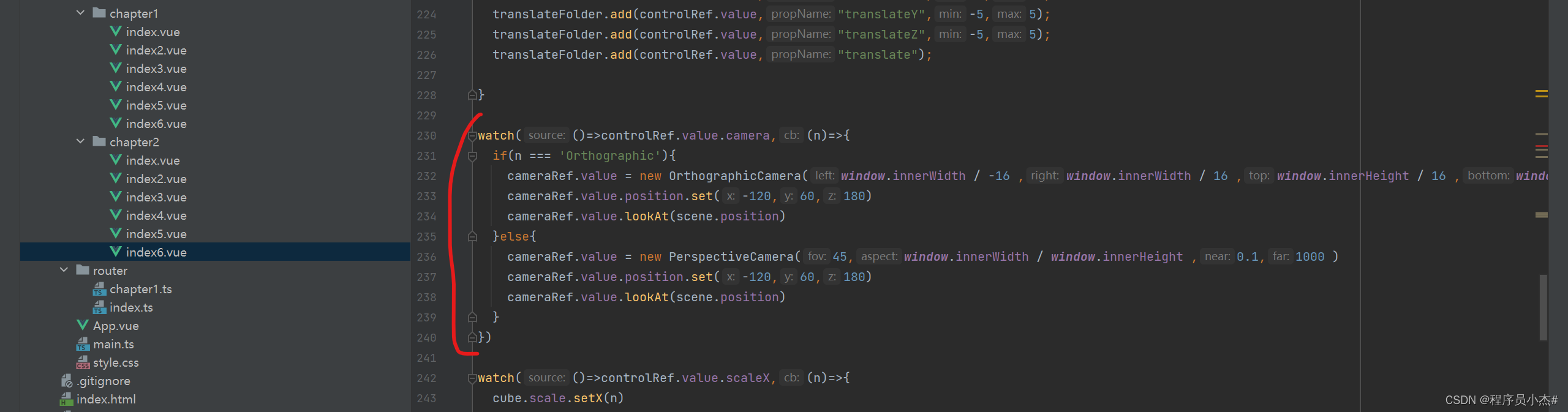
watch(()=>controlRef.value.camera,(n)=>{
if(n === 'Orthographic'){
cameraRef.value = new OrthographicCamera(window.innerWidth / -16 ,window.innerWidth / 16 ,window.innerHeight / 16 ,window.innerHeight / -16,-200,500 )
cameraRef.value.position.set(-120,60,180)
cameraRef.value.lookAt(scene.position)
}else{
cameraRef.value = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight ,0.1,1000 )
cameraRef.value.position.set(-120,60,180)
cameraRef.value.lookAt(scene.position)
}
})
7、相机跟随
在Three.js中,相机跟随物体的技术广泛应用于实现如游戏中的摄像机跟随角色、VR中的视点跟踪等效果。
要实现这一功能,首先需要获取到目标物体(例如一个游戏角色或者一个3D模型)的位置信息,然后将相机的位置设置为该物体的对应位置,从而实现视角的跟随。
此外,关于具体的实现方式,有多种可选的策略。
如果你想要创建一个第一人称视角的效果,可以使用键盘的WASD键控制相机的移动方向;而如果你希望实现第三人称视角的效果,则可以通过鼠标来控制相机的视角朝向。
另外,对于复杂的场景,比如管道内的视野展示或者物体在三维空间中任意方向移动的情况,你可能需要结合使用一些额外的工具和方法。
例如,你可以创建一个管道模型来帮助你观察物体的运动方向,并通过调整相机的位置和朝向,使得镜头能够紧密地跟随物体的移动。
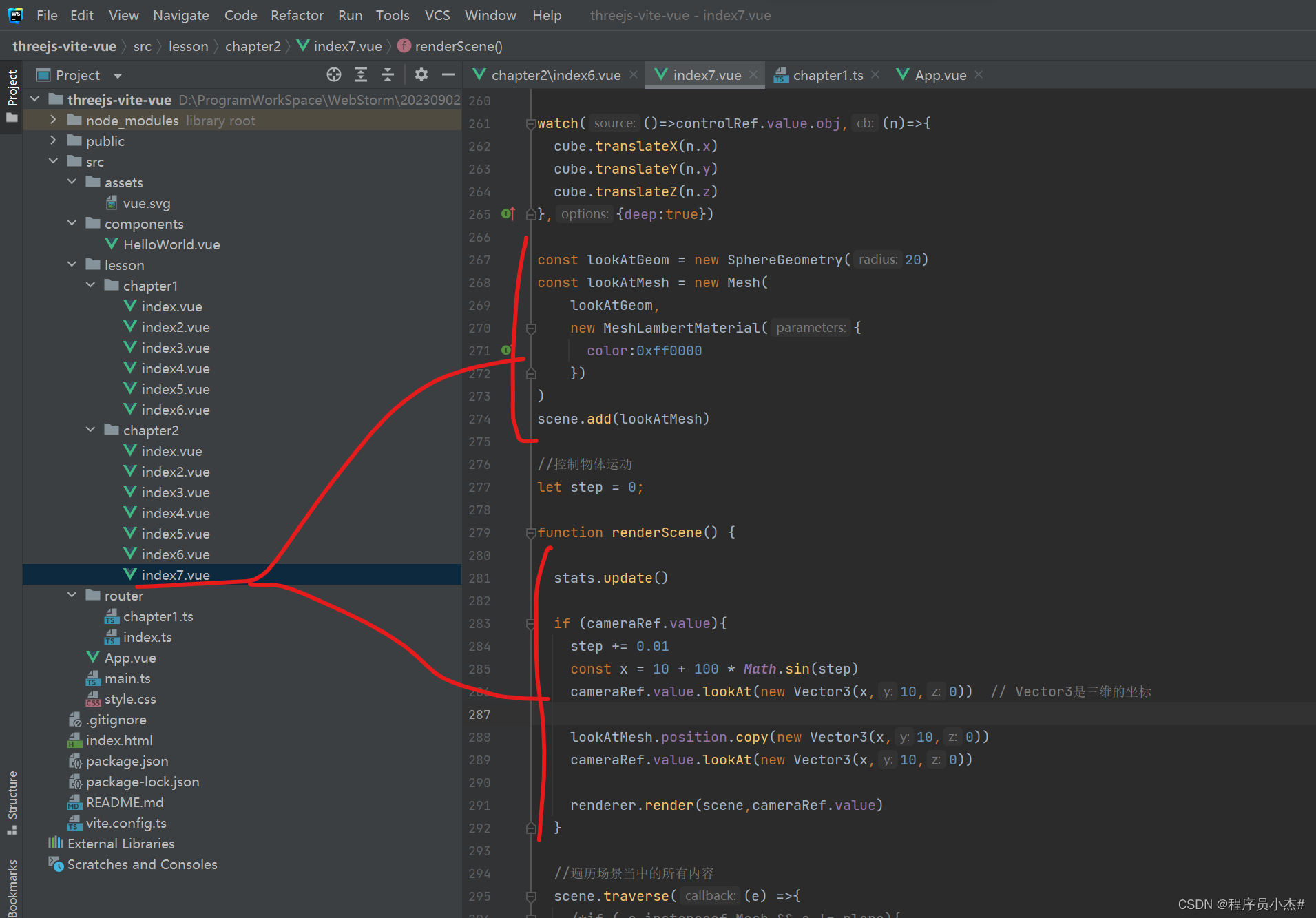
const lookAtGeom = new SphereGeometry(20)
const lookAtMesh = new Mesh(
lookAtGeom,
new MeshLambertMaterial({
color:0xff0000
})
)
scene.add(lookAtMesh)
//控制物体运动
let step = 0;
function renderScene() {
stats.update()
if (cameraRef.value){
step += 0.01
const x = 10 + 100 * Math.sin(step)
cameraRef.value.lookAt(new Vector3(x,10,0)) // Vector3是三维的坐标
lookAtMesh.position.copy(new Vector3(x,10,0))
cameraRef.value.lookAt(new Vector3(x,10,0))
renderer.render(scene,cameraRef.value)
}
}

四、光照
1、环境光
Three.js中环境光(AmbientLight)是一种全局光照,它能够均匀地照亮场景中的物体。
与点光源和平行光源不同,环境光不会直接照亮物体,而是与场景中的颜色相乘,从而使得物体的颜色变暗或变亮。
环境光通常用于模拟全局的光照效果,例如在室外场景中模拟太阳的光线、室内场景中模拟灯光的反射等。
通过调整环境光的颜色和强度,可以改变整个场景的亮度和色调,从而增强渲染的真实感。
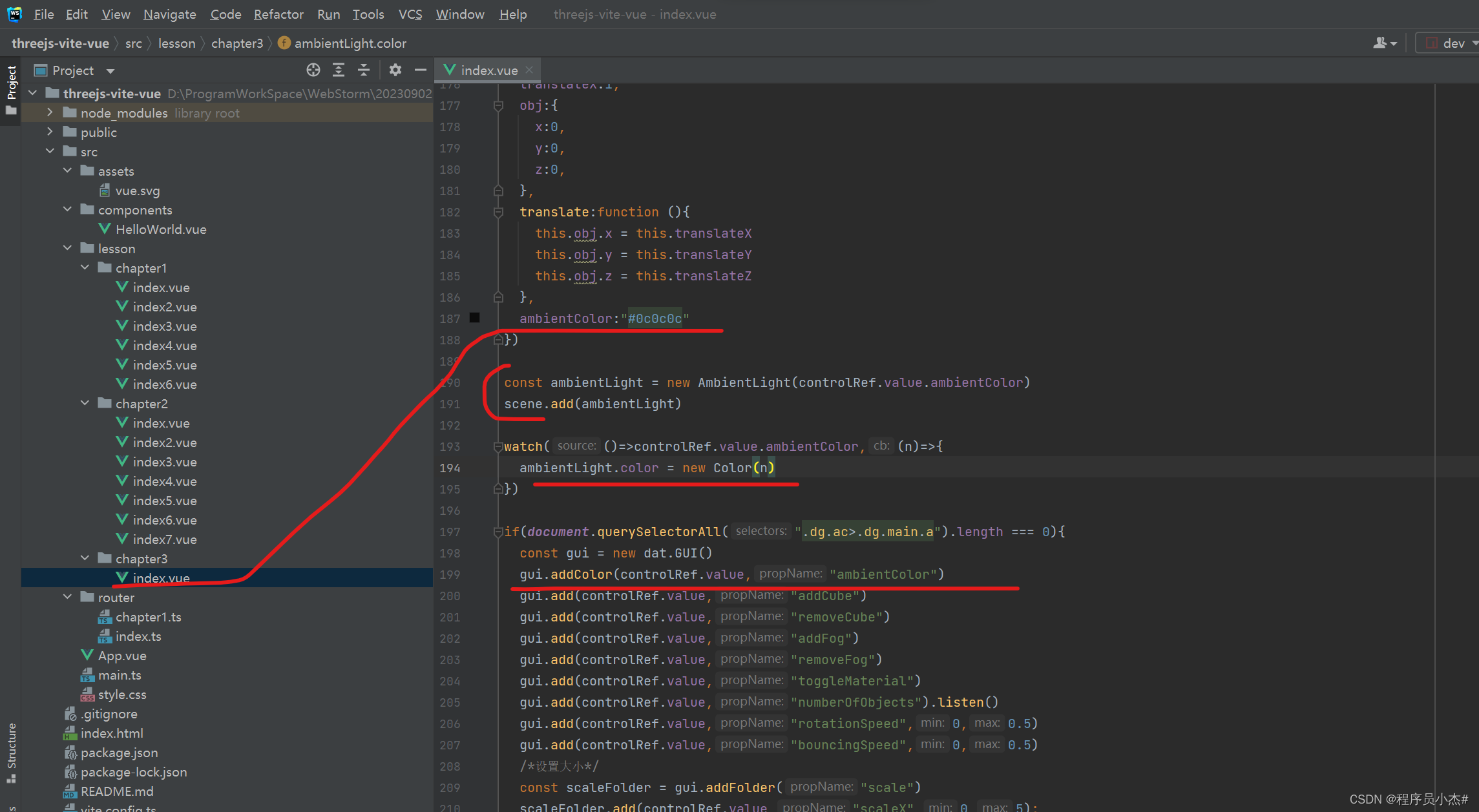
ambientColor:"#0c0c0c"
const ambientLight = new AmbientLight(controlRef.value.ambientColor)
scene.add(ambientLight)
watch(()=>controlRef.value.ambientColor,(n)=>{
ambientLight.color = new Color(n)
})
gui.addColor(controlRef.value,"ambientColor")
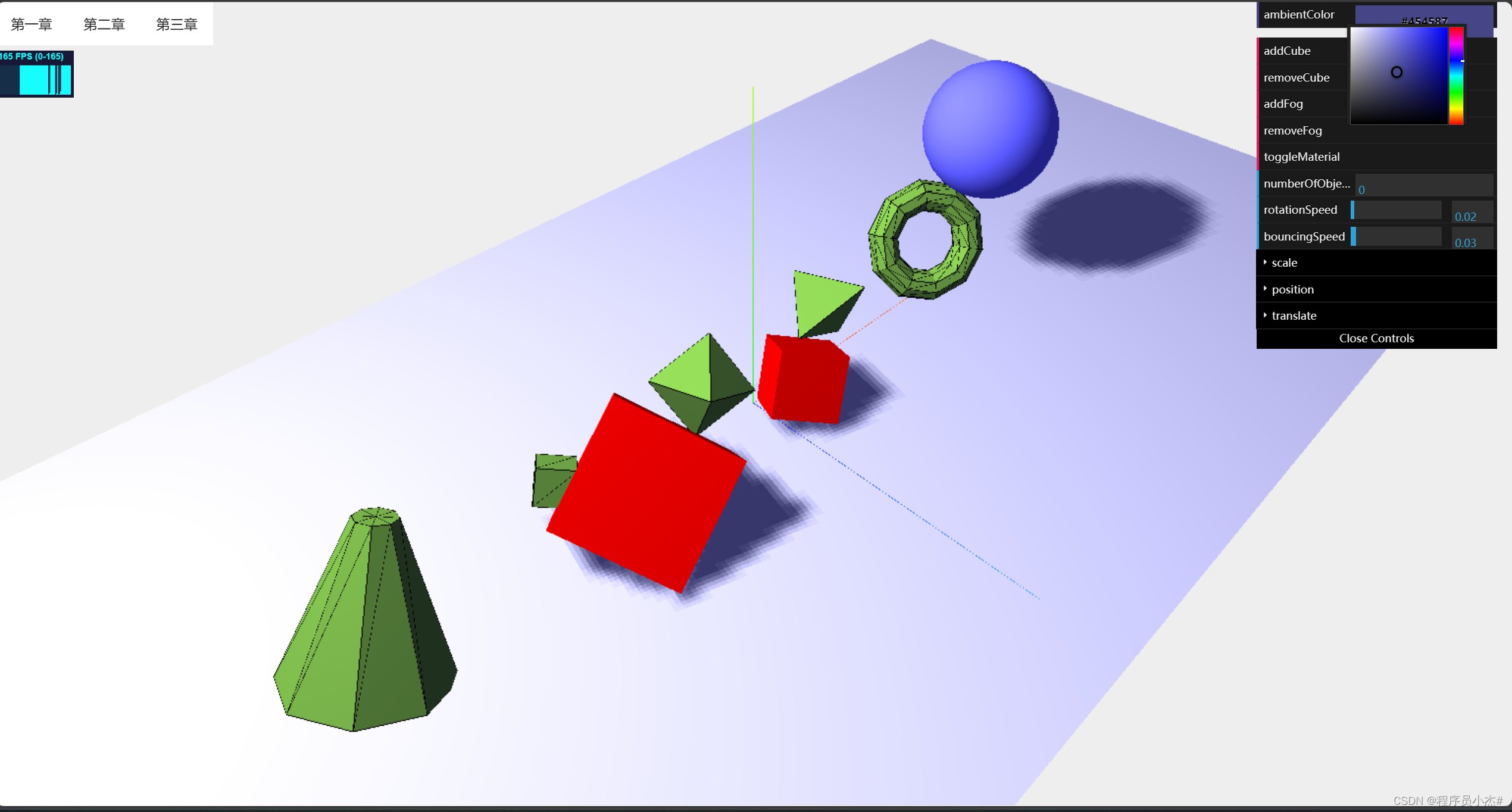
2、点光源
Three.js库中的THREE.PointLight(点光源)是一种单点发光、照射所有方向的光源,比如夜空中的照明弹。
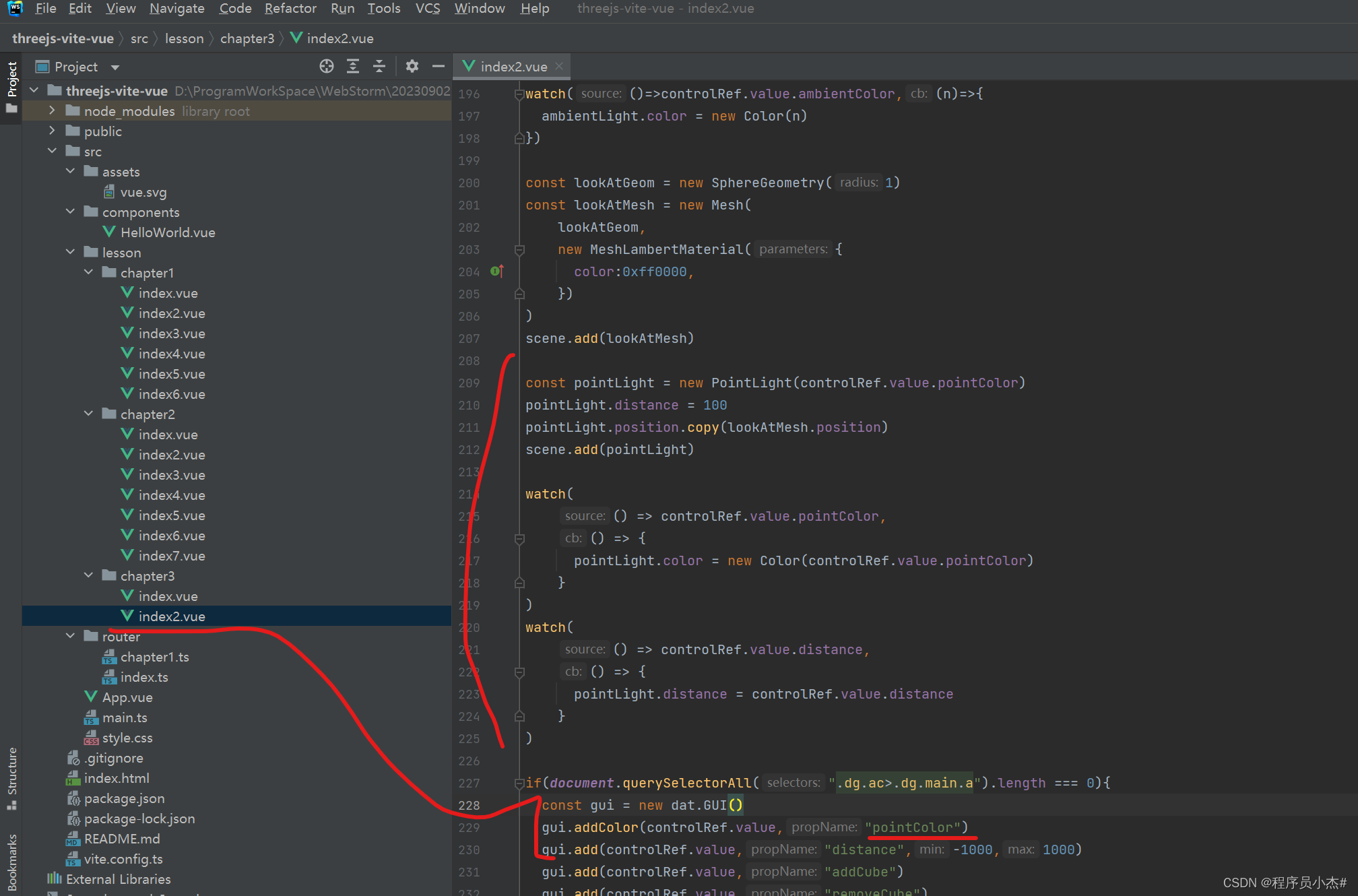
ambientColor:"#0c0c0c",
pointColor:"#ccffcc",
distance: 100,
const pointLight = new PointLight(controlRef.value.pointColor)
pointLight.distance = 100
pointLight.position.copy(lookAtMesh.position)
scene.add(pointLight)
watch(
() => controlRef.value.pointColor,
() => {
pointLight.color = new Color(controlRef.value.pointColor)
}
)
watch(
() => controlRef.value.distance,
() => {
pointLight.distance = controlRef.value.distance
}
)
gui.addColor(controlRef.value,"pointColor")
gui.add(controlRef.value,"distance",-1000,1000)
3、聚光灯
Three.js中的聚光灯(SpotLight)是一种光源类型,用于在场景中创建聚焦光照。
它有一个锥形的照射范围,可以模拟手电筒或灯塔等发出的光线。
聚光灯具有方向和角度,可以通过调整其属性来控制照射范围和强度
target:'plane',
watch(
() => controlRef.value.target,
(t) => {
if(t === 'cube'){
spotLight.target = cube
}else if( t === 'sphere'){
spotLight.target = sphere
}else {
spotLight.target = plane
}
}
)

4、平行光
Three.js中的平行光(DirectionalLight)是一种光源类型,它发出的光线是平行的并且沿特定方向传播。
这种光源模拟太阳光等效果,因为它的表现像是无限远,从它发出的光线都是平行的。平行光通常用于模拟太阳光、月光等远离物体的光源。
你可以通过调整平行光的颜色、强度以及方向属性来控制照射效果。
在着色器中计算时,平行光的方向向量会直接与模型顶点的法线方向进行点乘操作,从而确定该点的亮度。
//添加平行光
const directionalColor = "#ff5808"
const directionalLight = new DirectionalLight(directionalColor)
directionalLight.position.set(-40,60,-10)
directionalLight.castShadow = true
directionalLight.intensity = 0.5
scene.add(directionalLight)
5、半球光
Three.js中的半球光(HemisphereLight)是一种光源类型,它模拟了天空和地面的反射效果。这种光源的特性在于,其发出的光线颜色从天空光线颜色渐变到地面光线颜色。
具体来说,半球光的原理由两部分组成,一部分是从下往上的平行光,另一部分是从上半球往中心点的光。
这样,实现了模拟模型法线向上的部分天空光线照射到物体上,法线向下的部分接收来自于地面的反射环境光。
然而需要注意的是,半球光无法投射阴影。
在创建半球光时,可以分别指定天空和地面的颜色。
//添加半球光
// 创建球体几何体和材质
const sphereGeometry1 = new SphereGeometry(2, 32, 32);
const sphereMaterial1 = new MeshLambertMaterial({
color: 0x7777ff,
wireframe:false
})
// 创建网格对象并添加到场景中
const spherea = new Mesh(sphereGeometry1, sphereMaterial1);
scene.add(spherea);
// 渲染循环
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
// 更新球体材质的emissive属性以实现半球光效果
const time = Date.now() * 0.001;
sphereMaterial.emissive.setRGB(Math.sin(time) * 0.5 + 0.5, Math.cos(time) * 0.5 + 0.5, Math.sin(time * 2) * 0.5 + 0.5);
renderer.render(scene, camera);
}
animate();
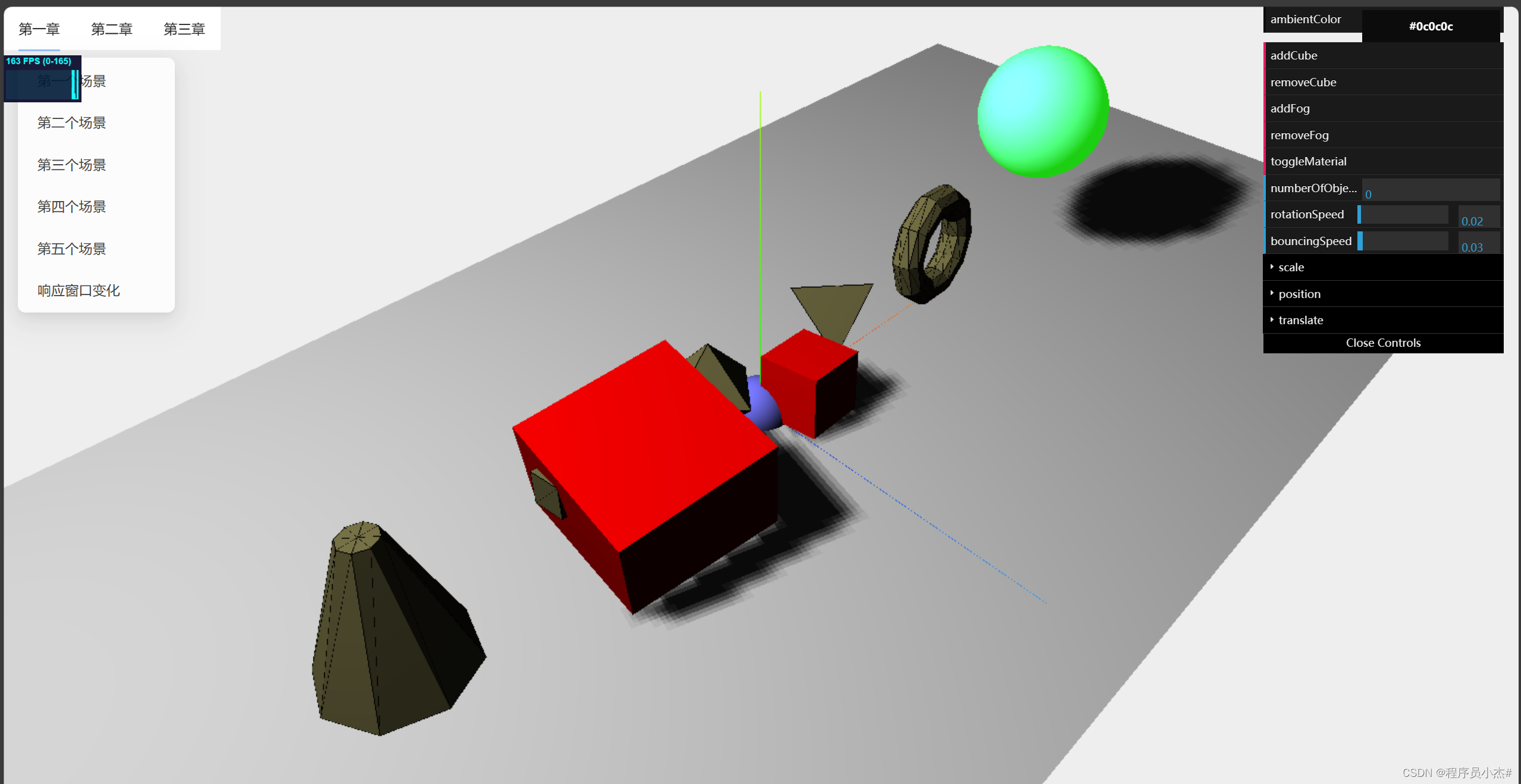
五、小车案例
1、基础环境搭建
<template>
<div ref="statsRef"></div>
<div ref="containerRef" class="container">
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts" setup>
import {
ACESFilmicToneMapping, AxesHelper,
Color,
EquirectangularReflectionMapping, Fog, GridHelper, Material,
PerspectiveCamera,
Scene,
sRGBEncoding,
WebGLRenderer
} from "three";
import Stats from "stats.js"
import * as dat from "dat.gui"
import {onMounted, ref, watchEffect} from "vue";
//
import venice_sunset_1k from '../../assets/venice_sunset_1k.hdr?url'
import car from '../../assets/car.glb?url'
import {RGBELoader} from "three/examples/jsm/loaders/RGBELoader";
const scene = new Scene();
const grid = new GridHelper(20,40,0xfffff,0xffff);
const containerRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
const statsRef = ref<HTMLDivElement>()
const stats = new Stats();
const controlRef = ref({
bodyColor:"#0c0c0c",
glassColor:"#0c0c0c",
detailColor:"#0c0c0c",
})
const cameraRef = ref<PerspectiveCamera>()
const rendererRef = ref<WebGLRenderer>()
//它会检查当前网页中是否存在具有特定类名(即".dg.ac>.dg.main.a")的元素。
// 如果不存在,它将创建一个新的dat.GUI对象,
// 并在该对象中添加三个颜色控件:bodyColor、glassColor和detailColor。
// 这些颜色控件的值都是从名为controlRef的引用所指向的对象中获取的
function initGUI() {
if(document.querySelectorAll(".dg.ac>.dg.main.a").length === 0){
const gui = new dat.GUI()
gui.addColor(controlRef.value,"bodyColor")
gui.addColor(controlRef.value,"glassColor")
gui.addColor(controlRef.value,"detailColor")
}
}
/*
它使用PerspectiveCamera构造函数创建了一个新的透视相机对象。
这个构造函数需要四个参数:视角角度(在这里为45度)、纵横比(在这里为窗口宽度除以窗口高度)、近裁剪平面距离(在这里为0.1)
以及远裁剪平面距离(在这里为1000)。然后,它设置了摄像机的位置坐标为(-30,40,30),使摄像机面向场景的位置
* */
function initCamera() {
cameraRef.value = new PerspectiveCamera(45,window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight,0.1,1000)
cameraRef.value.position.set(-30,40,30)
cameraRef.value.lookAt(scene.position)
}
/*
创建了一个新的WebGL渲染器并将其赋值给rendererRef。这个渲染器启用了抗锯齿功能,
设置了像素比例为窗口的设备像素比,
并将宽度和高度设置为窗口的内宽度和内高度。它还设置了输出编码为sRGBEncoding,
色调映射为ACESFilmicToneMapping,色调映射曝光为0.85。
* */
function initRenderer(){
rendererRef.value = new WebGLRenderer({antialias:true})
rendererRef.value.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio)
rendererRef.value.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
rendererRef.value.outputEncoding = sRGBEncoding
rendererRef.value.toneMapping = ACESFilmicToneMapping
rendererRef.value.toneMappingExposure = 0.85
}
/*
将背景颜色设为深灰色(#333),然后加载名为"venice_sunset_1k"的环境贴图,并将其映射方式设为EquirectangularReflectionMapping。这将会使场景具有反射光照的效果。
接下来的几行代码修改了grid组件所用材质的透明度、深度写入以及透明度属性,使其呈现出半透明效果。
最后,它向场景中添加了一个长度为20的新坐标轴助手。
*
*/
function initScene(){
scene.background = new Color(0x333333)
scene.environment = new RGBELoader().load(venice_sunset_1k)
scene.environment.mapping = EquirectangularReflectionMapping;
// scene.fog = new Fog(0x333333,10,15)
const material = grid.material as Material
material.opacity = 0.2
material.depthWrite = false
material.transparent = true
scene.add(grid)
const axes = new AxesHelper(20)
scene.add(axes)
}
initGUI()
onMounted(()=>{
//创建场景
stats.dom.style.top = "50px"
statsRef.value?.append(stats.dom)
initScene()
initCamera()
initRenderer()
})
/*
持续运行的循环渲染函数,用于不断更新和重新绘制3D场景。
每一帧开始时,它会先调用stats对象的update方法,用于统计当前性能信息。
接着,它会调用requestAnimationFrame方法再次请求下一帧的动画。这个方法会在浏览器认为适合的时候安排一次重绘,通常是在下一次刷新周期之前。
如果存在cameraRef引用,则使用该相机进行当前帧的渲染。rendererRef指针表示的是已经初始化好的WebGL渲染器,而scene则是需要渲染的三维场景。
最后,根据性能计数器的时间戳,对网格物体的位置做了一次平移操作,使得网格能够以一定的速度沿Z轴方向移动。这里使用了取模运算符%来让网格的位置在其运动过程中始终保持在一个范围内。
注意requestAnimationFrame(renderScene)这一句的作用。这是一个JavaScript API,它可以在浏览器下次重绘之前,要求浏览器执行指定的函数(在这个例子中就是renderScene())。这样做的好处是可以减少不必要的CPU和GPU工作,从而提高页面性能。
每个requestAnimationFrame()调用都会返回一个定时ID,你可以用这个ID取消未执行的动画。如果要停止动画,只需清除对应的定时ID即可。
在这个例子中,requestAnimationFrame(renderScene)会在每次渲染完成后立即调用自己,从而形成一个无限循环,不断地重复执行渲染过程。只要页面没有关闭,这个函数就会一直被调用下去。
* */
function renderScene() {
stats.update()
requestAnimationFrame(renderScene)
if(cameraRef.value){
rendererRef.value!.render(scene,cameraRef.value)
}
const time = -performance.now() / 1000
grid.position.z = -(time) % 1
}
renderScene()
/*
这段代码是一个Vue watchEffect钩子函数,当某些数据发生变化时,会触发此函数执行。
函数内部主要做了两件事:
将rendererRef的domElement属性(即渲染器的DOM元素)添加到containerRef指定的容器中。这意味着该渲染器将会在对应的HTML元素中显示。
在窗口大小发生改变时,监听并响应事件。当窗口尺寸发生改变时,会更新相机的宽高比,计算新的投影矩阵,并且重新设置渲染器的尺寸,使其与窗口尺寸保持一致。
因此,这段代码的作用是将渲染结果正确地显示出来,并确保在窗口尺寸改变时能够及时更新视口大小和视角。
* */
watchEffect(()=>{
containerRef.value?.appendChild(rendererRef.value!.domElement)
window.addEventListener('resize',()=>{
cameraRef.value!.aspect = window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight
//更新相投影矩阵
cameraRef.value!.updateProjectionMatrix();
rendererRef.value!.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight)
},false)
})
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>

2、载入模型,实现轨道控制器
import venice_sunset_1k from '../../assets/venice_sunset_1k.hdr?url'
import Car from '../../assets/car.glb?url'
//轨道控制器
const controlsRef = ref<OrbitControls>()
function initGLTF() {
const dracoLoader = new DRACOLoader();
dracoLoader.setDecoderPath('/gltf/');
const loader = new GLTFLoader();
loader.setDRACOLoader (dracoLoader) ;
loader.load(Car,(gltf: GLTF) => {
console.log(gltf)
const carModel = gltf.scene.children[0];
scene.add(carModel)
})
}
function initControl() {
if(cameraRef.value) {
controlsRef.value = new OrbitControls(cameraRef.value,containerRef.value);
controlsRef.value.enableDamping = true
controlsRef.value.maxDistance = 9
controlsRef.value.target.set(0,0.5,0)
controlsRef.value.update()
}
}
initGUI()
initGLTF()
onMounted(()=>{
//创建场景
stats.dom.style.top = "50px"
statsRef.value?.append(stats.dom)
initScene()
initCamera()
initRenderer()
initControl()
})
3、实现模型颜色材质调整,轮子转动
//轨道控制器
const controlsRef = ref<OrbitControls>()
const bodyMaterial = new MeshPhysicalMaterial({
color:0xff0000,metalness:1.0,roughness:0.5,clearcoat:1.0,clearcoatRoughness:0.03,sheen:0.5
})
const glassMaterial = new MeshPhysicalMaterial({
color:0xffffff,metalness:0.25,roughness:0,transmission:1.0
})
const detailMaterial = new MeshPhysicalMaterial({
color:0xff0000,metalness:1.0,roughness:0.5
})
watch(()=> controlRef.value.bodyColor,(c)=>{
bodyMaterial.color.set(c);
})
watch(()=> controlRef.value.glassColor,(c)=>{
glassMaterial.color.set(c);
})
watch(()=> controlRef.value.detailColor,(c)=>{
detailMaterial.color.set(c);
})
const carModel = gltf.scene.children[0];
(carModel.getObjectByName('body') as Mesh).material = bodyMaterial;
(carModel.getObjectByName('glass') as Mesh).material = glassMaterial;
(carModel.getObjectByName('rim_fl') as Mesh).material = detailMaterial;
(carModel.getObjectByName('rim_fr') as Mesh).material = detailMaterial;
(carModel.getObjectByName('rim_rr') as Mesh).material = detailMaterial;
(carModel.getObjectByName('rim_rl') as Mesh).material = detailMaterial;
(carModel.getObjectByName('trim') as Mesh).material = detailMaterial;
wheels.push(
carModel.getObjectByName('wheel_fl'),
carModel.getObjectByName('wheel_fr'),
carModel.getObjectByName('wheel_rl'),
carModel.getObjectByName('wheel_rr'),
)
for (let i = 0;i < wheels.length;i++){
wheels[i]!.rotation.x = time * Math.PI * 2
}
实现效果

4、源代码下载
https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_44757034/88582419
