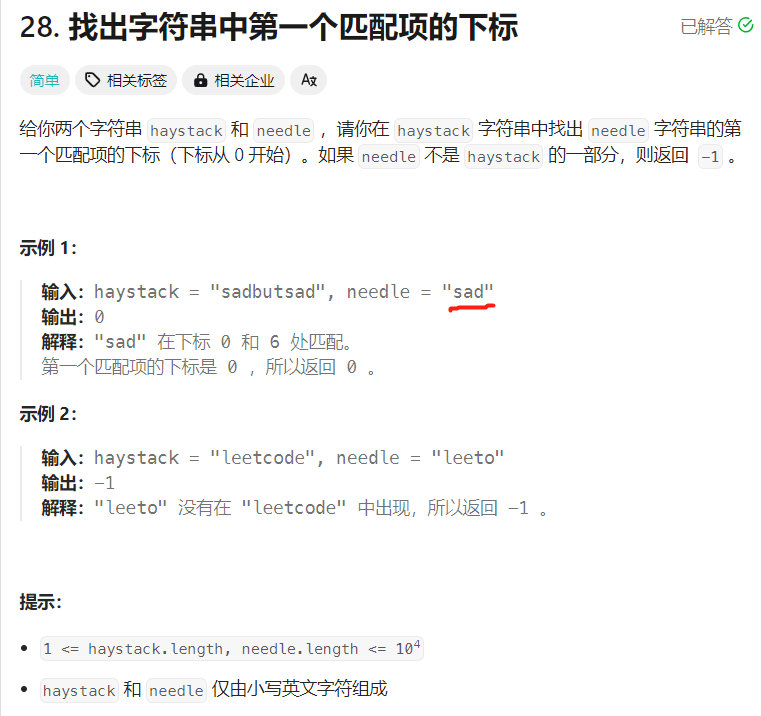
【LeetCode】28. 找出字符串中第一个匹配项的下标 【字符串单模匹配:KMP算法】
题目链接

Python3
直觉解法
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
pn, ph = 0, 0
n = len(needle)
h = len(haystack)
while ph < h:
if haystack[ph] == needle[pn]:
if pn == n-1: # 1234 123
return ph - len(needle) + 1
else:
pn += 1
ph += 1
else: ## 1234 122
ph = ph - pn + 1
pn = 0
return -1
方法一: 暴力解法 ⟮ O ( n × m ) 、 O ( 1 ) ⟯ \lgroup O(n\times m)、O(1) \rgroup ⟮O(n×m)、O(1)⟯
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
for i in range(0, len(haystack)-len(needle)+1):
if haystack[i:i+len(needle)] == needle:
return i
return -1

⭐ 方法二:Knuth-Morris-Pratt 算法 [KMP算法] ⟮ O ( m + n ) 、 O ( m ) ⟯ \lgroup O(m+n)、O(m) \rgroup ⟮O(m+n)、O(m)⟯ 【空间换时间】
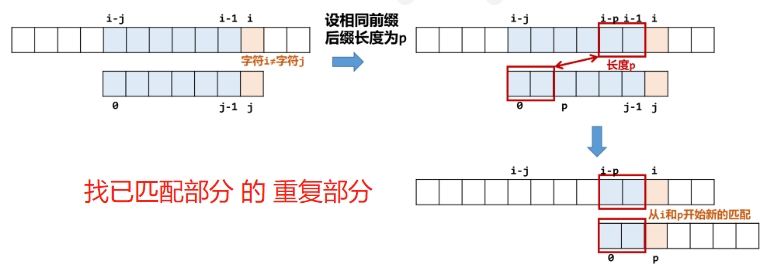
从而实现 更快地 跳转
参考链接1
参考链接2: KMP字符串匹配算法2
官方解法链接
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
h = len(haystack)
n = len(needle)
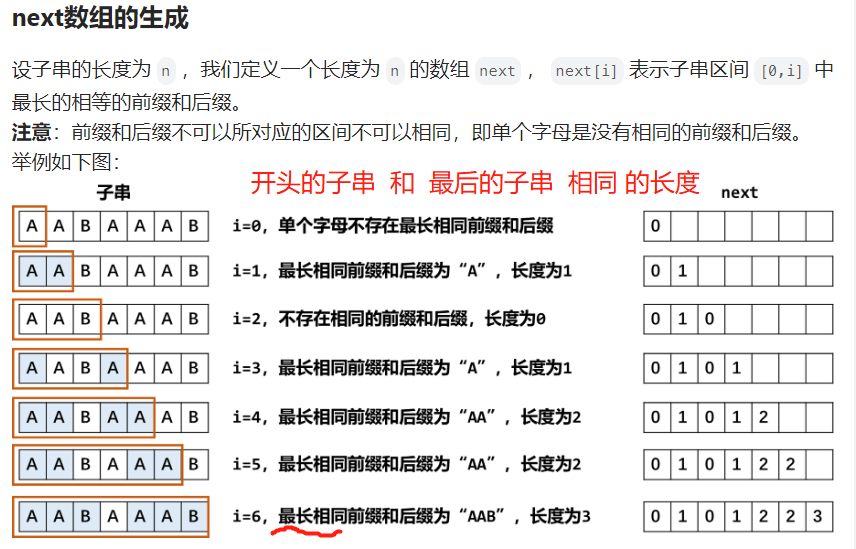
# 获取 needle 的前缀信息
lis = [0] * n
j = 0 # 前后 子串长度
for i in range(1, n): # 需要前后比较, 1个字符无法比较,因此从 i=1 开始
while j > 0 and needle[i] != needle[j]:
j = lis[j-1] # 和之前 相等的长度一样
if needle[i] == needle[j]:
j += 1
lis[i] = j
# 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
# a a b a a a b needle
# 0 1 0 1 2 2 3 前缀子串 后缀子串 相同的长度 若是 needle[j] 不匹配了,注意是 lis[j-1] 存储的才是 待比较的下一个 j
# a a c a a
# 根据上述的 信息进行 匹配
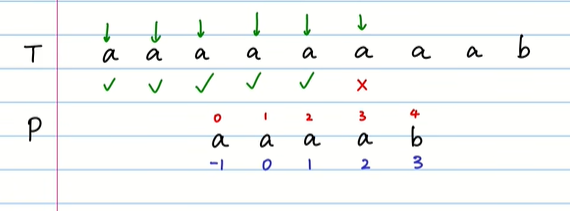
j = 0 # 遍历 needle 下标
for i in range(0, h): # 遍历 haystack 下标
while j > 0 and haystack[i] != needle[j]: #
j = lis[j-1] # 这里 根据 前后缀 信息 快速跳转
if haystack[i] == needle[j]:
j += 1
if j == n: # needle 已全部匹配 因为前面的if 成立,j多加了1
return i - n + 1
return -1

链接
class Solution:
def strStr(self, haystack: str, needle: str) -> int:
def get_next():
for i in range(1, len(needle)):
k = fπ[i-1]
while needle[i] != needle[k]:
if k == 0:
k -= 1
break
else:
k = fπ[k-1]
fπ[i] = k+1
n = len(needle)
fπ = [0] * n
get_next() # 生成 needle 的next 数组
i = 0
j = 0
while i < len(haystack):
if haystack[i] == needle[j]:
i += 1
j += 1
elif j == 0:
i += 1
else:
j = fπ[j-1]
if j >= n:
return i - n
return -1
C++
KMP 算法 ⟮ O ( h + n ) 、 O ( n ) ⟯ \lgroup O(h+n)、O(n) \rgroup ⟮O(h+n)、O(n)⟯
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int h = haystack.size(), n = needle.size();
vector<int> lis(n);
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < n; ++i){
while (j > 0 && needle[i] != needle[j]){
j = lis[j-1];
}
if (needle[i] == needle[j]){
++j;
}
lis[i] = j;
}
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < h; ++i){
while (j > 0 && haystack[i] != needle[j]){
j = lis[j-1];
}
if (haystack[i] == needle[j]){
++j;
}
if (j == n){
return i - n + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
暴力解法
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string haystack, string needle) {
int h = haystack.size(), n = needle.size();
int j = 0, i = 0;
while (i < h){
if (haystack[i] == needle[j]){
if (j == n-1){
return i - n + 1;
}
else{
++j;
++i;
}
}
else{
j = 0;
i = i - j + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
};
