Spring框架中IOC和DI详解
Spring框架学习一—IOC和DI
来源黑马Spring课程,觉得挺好的
目录
文章目录
- Spring框架学习一---IOC和DI
- 目录
- 学习目标
- 第一章 Spring概述
- 1、为什么要学习spring?
- 2、Spring概述【了解】
- 【1】Spring是什么
- 【2】Spring发展历程
- 【3】Spring优势
- 【4】Spring体系结构
- 3、Spring核心
- 第二章 IOC概念和作用【理解】
- 1、IOC概念
- 【1】控制什么
- 【2】反转什么
- 2、IOC作用
- 【1】IOC作用概述
- 【2】生活中IOC解耦场景描述
- 【3】场景代码(1)
- 【2.1】目标
- 【3.2】实现
- 【3.2.1】创建项目
- 【3.2.2】pojo层
- 【3.2.3】service层
- 【3.2.4】controller层
- 【3.3】场景小结
- 【4】方案一:interface
- 【4.1】思考
- 【4.2】目标
- 【4.3】实现
- 【4.3.1】添加Car接口
- 【4.3.2】实现Car接口
- 【4.3.3】修改CarService
- 【4.4】方案一小结
- 【5】方案二:CarFactroy(2)
- 【5.1】思考
- 【5.2】目标
- 【5.3】实现
- 【5.3.1】创建项目
- 【5.3.2】添加factory层
- 【5.3.3】修改CarService
- 【5.3.4】方案二小结
- 【6】IOC作用小结
- 3、手写IOC实现【理解】
- 【1】思考
- 【2】目标
- 【3】实现(3)
- 【3.1】创建项目
- 【3.2】dao层
- 【3.3】servic层
- 【3.4】factory层
- 【3.5】controller层
- 【4】手写IOC小结
- 第三章 基于xml的spring-IOC【重点】
- 1、【入门案例】xml的spring-IOC(4)
- 【1】思考
- 【2】目标
- 【3】实现
- 【3.1】创建项目
- 【3.2】pom.xml依赖
- 【3.3】spring配置文件bean.xml
- 【3.4】改造AccountService
- 【3.5】改造ClientController
- 【4】入门案例小结
- 第四章 SpringIOC工厂类【了解】
- 1、BeanFactory
- 【1】作用
- 【2】方法
- 2、ApplicationContext
- 【1】作用
- 【2】实现类
- 3、加载顺序
- 【1】思考
- 【2】目的
- 【3】实现(5)
- 【3.1】创建项目
- 【3.3】改造ClientController
- 【4】加载顺序小结
- 第五章 bean标签详解【重点】
- 1、bean标签作用
- 2、bean标签基本属性
- 3、bean标签作用范围
- 【1】思考
- 【2】目标
- 【3】bean作用域实例(6)
- 【3.1】创建项目
- 【3.2】Bean【默认:singleton】
- 【3.3】singleton运行结果
- 【3.4】bean【多例:prototype】
- 【3.5】prototype运行结果
- 【4】bean作用域小结
- 4、bean标签生命周期
- 【1】目标
- 【2】bean生命周期实例(7)
- 【2.1】创建项目
- 【2.3】装配LifecycleBean
- 【2.4】创建ClientController
- 【2.5】单例模式下生命周期:
- 【2.6】多例模式下生命周期
- 【3】bean生命周期小结
- 5、bean的实例化方式(8)
- 【1】目标
- 【2】创建项目
- 【3】缺省构造函数方式【重点】
- 【3.1】配置方式
- 【3.2】注意事项
- 【4】静态工厂方法方式
- 【4.1】配置方式
- 【4.2】静态工厂代码
- 【5】实例工厂方法方式
- 【5.1】配置方式
- 【5.2】实例工厂代码
- 【6】bean实例化小结
- 6、bean标签配置小结
- 第六章 spring的依赖注入(DI)【重点】
- 1、DI是什么?
- 【1】DI概念
- 【2】思考
- 2、依赖注入(DI)的2种方式【重点】
- 【1】set方法注入(9)
- 【1.1】目标
- 【1.2】实现
- 【1.2.1】创建项目
- 【1.2.2】修改AccountServicImpl提供属性的set方法
- 【1.2.3】编写bean.xml
- 【1.2.4】ClientController测试
- 【1.3】set方法注入小结
- 【2】构造函数注入(10)
- 【2.1】目标
- 【2.2】实现
- 【2.1】创建项目
- 【2.2】修改AccountServicImpl添加构造函数
- 【2.3】编写bean.xml
- 【2.4】ClientController测试
- 【2.3】构造函数注入小结
- 3、依赖注入的简单配置【了解】
- 【1】P标签方式(set方法)(11)
- 【1.1】目标
- 【1.2】实现
- 【1.2.1】创建项目
- 【1.2.2】修改bean.xml
- 【1.2.3】ClientController测试
- 【2】C标签方式(构造函数)(12)
- 【2.1】目标
- 【2.2】实现
- 【2.1.1】创建项目
- 【2.1.2】修改bean.xml
- 【2.1.3】ClientController测试
- 【3】简单配置小结
- 4、复杂类型的注入(13)【了解】
- 【1】目标
- 【2】实现
- 【2.1】创建项目
- 【2.2】创建Account
- 【2.3】编写bean.xml
- 【2.4】controller测试
- 【3】复杂对象注入小结
学习目标
1、了解Spring框架;
2、了解Spring框架的两大核心;
3、理解IOC的概念;
4、掌握Spring基于xml的IOC配置;
5、了解Spring中的工厂结构;
6、掌握Spring的bean标签的配置;
7、掌握spring的di注入机制
第一章 Spring概述
1、为什么要学习spring?
如果让本人用一句话去回答这个问题,那么我只能说:在J2EE的学习之路上,spring给我带来了开发的春天,让我们从JSP、sevlet的高耦合的开发中彻底的解救出来。
-
spring是目前最主流的框架
-
spring是学习后面课程(比如:springboot、springcloud等)的基础
2、Spring概述【了解】
【1】Spring是什么
Spring是一个开源框架,Spring的核心是控制反转(IoC)和面向切面(AOP)。简单来说,Spring是一个分层的JavaSE/EE full-stack(一站式) 轻量级开源框架。
轻量级:与EJB对比,依赖资源少,销毁的资源少。
分层: 一站式,每一个层都提供的解决方案
-
web层:struts2,spring-MVC
-
service层:spring
-
dao层:hibernate,mybatis , jdbcTemplate --> spring-data
【2】Spring发展历程
Spring的发展历史:
1997年IBM提出了EJB的思想
1998年,SUN制定开发标准规范EJB1.0
1999年,EJB1.1发布
2001年,EJB2.0发布
2003年,EJB2.1发布
2006年,EJB3.0发布
Rod Johnson(spring之父)
Expert One-to-One J2EE Design and Development(2002)
阐述了J2EE使用EJB开发设计的优点及解决方案
Expert One-to-One J2EE Development without EJB(2004)
阐述了J2EE开发不使用EJB的解决方式(Spring雏形)
2017年9月份发布了spring的最新版本–spring 5.0通用版(GA)
【3】Spring优势
Spring 出现是为了解决JavaEE 实际问题:
-
方便解耦,简化开发 (IOC)
Spring就是一个大工厂(容器),可以将所有对象创建和依赖关系维护,交给Spring管理
Spring工厂是用于生成bean
-
AOP编程的支持
Spring提供面向切面编程,可以方便的实现对程序进行权限拦截、运行监控等功能
-
声明式事务的支持
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无需手动编程
-
方便程序的测试
Spring对Junit4支持,可以通过注解方便的测试Spring程序
-
方便集成各种优秀框架
Spring不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如:Struts、Hibernate、MyBatis、Quartz等)的直接支持
-
降低JavaEE API的使用难度
Spring 对JavaEE开发中非常难用的一些API(JDBC、JavaMail、远程调用等),都提供了封装,使这些API应用难度大大降低
基于这些特性,我们也会俗称Spring为开发架构的粘合剂。
【4】Spring体系结构
官网:https://spring.io/
Spring框架至今已集成了20多个模块,这些模块分布在以下模块中:
核心容器(Core Container)
数据访问/集成(Data Access/Integration)层
Web层
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)模块
植入(Instrumentation)模块
消息传输(Messaging)
测试(Test)模块
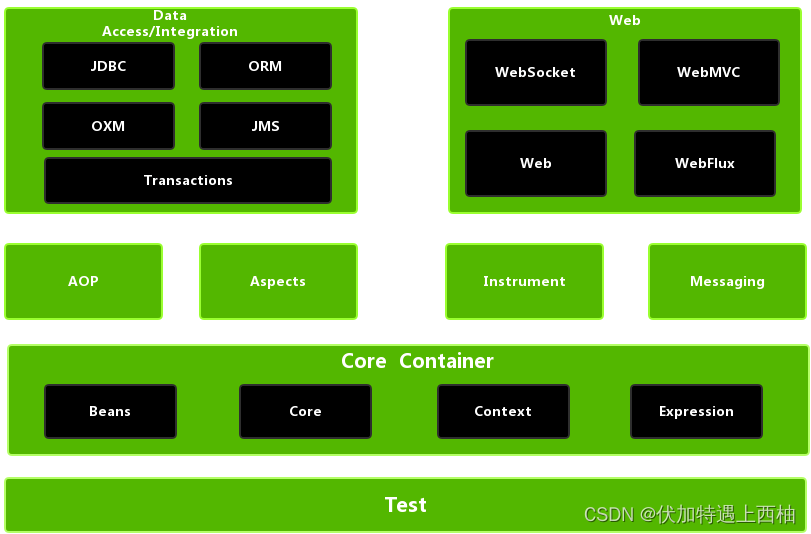
3、Spring核心
Spring为企业级开发提供了丰富的功能,这些功能的底层都依赖于它的两个核心特性:
-
控制反转(Inversion of Control,IOC)
-
面向切面编程(aspect-oriented programming,AOP)
IOC和AOP是一种技术吗?不!他们是一种思想
第二章 IOC概念和作用【理解】
1、IOC概念
IoC 全称为 Inversion of Control,翻译为 “控制反转”。
【1】控制什么
控制对象的创建和销毁
【2】反转什么
将对象的控制权(创建和销毁)交给IOC容器
2、IOC作用
【1】IOC作用概述
IOC的作用:解耦
我们知道在面向对象设计的软件系统中,它的底层都是由N个对象构成的,各个对象之间通过相互合作,最终实现系统地业务逻辑 ,如图所示:
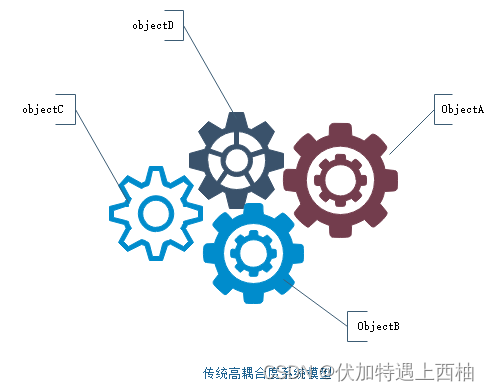
IOC理论提出的观点:借助于“第三方”实现具有依赖关系的对象之间的解耦。 如图所示:
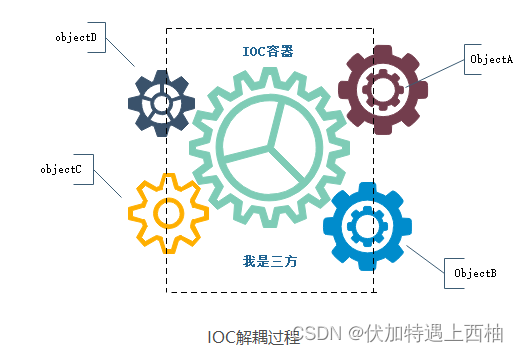
大家看到了吧,由于引进了中间位置的“第三方”,也就是IOC容器,使得A、B、C、D这4个对象没有了耦合关系,齿轮之间的传动全部依靠“第三方”了,全部对象的控制权全部上缴给“第三方”IOC容器,所以,IOC容器成了整个系统的关键核心,它起到了一种类似“粘合剂”的作用,把系统中的所有对象粘合在一起发挥作用,如果没有这个“粘合剂”,对象与对象之间会彼此失去联系,这就是有人把IOC容器比喻成“粘合剂”的由来。
我们再来做个试验:把上图中间的IOC容器隐藏,然后再来看看这套系统
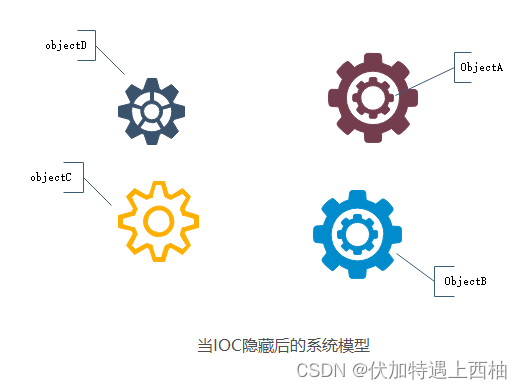
我们现在看到的画面,就是我们要实现整个系统所需要完成的全部内容。这时候,A、B、C、D这4个对象之间已经没有了耦合关系,彼此毫无联系,这样的话,当你在实现A的时候,根本无须再去考虑B、C和D了,对象之间的依赖关系已经降低到了最低程度。
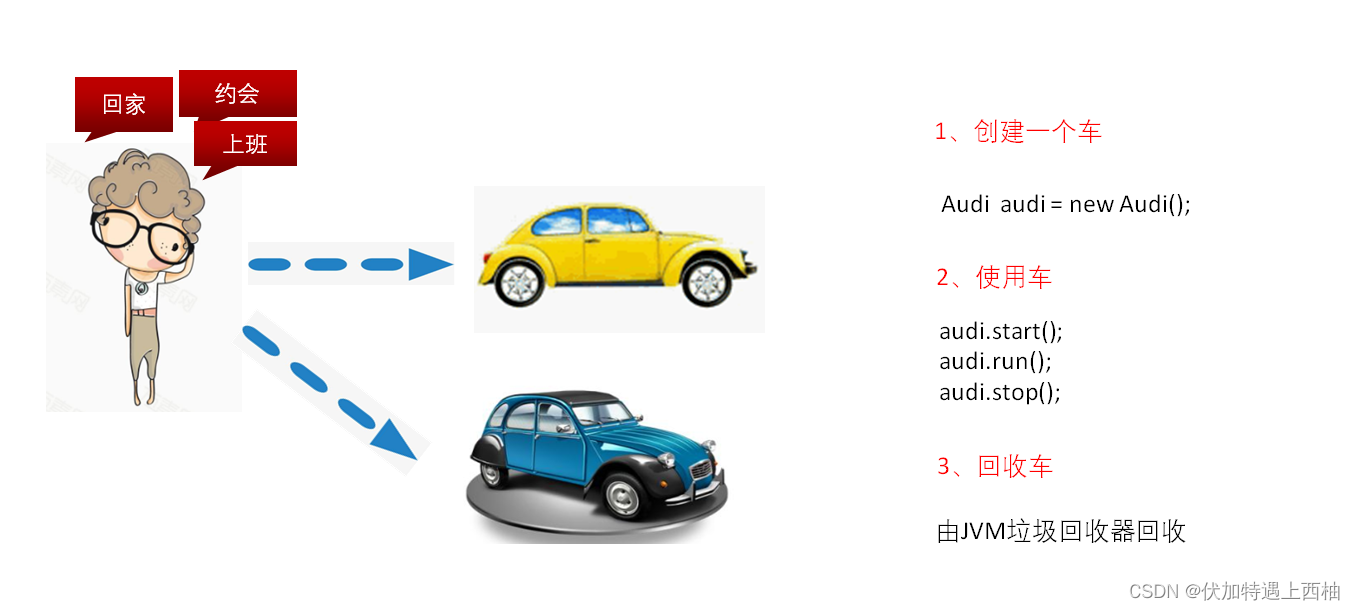
【2】生活中IOC解耦场景描述
回家场景代码描述
1、创建一个车
2、使用车
3、回收车
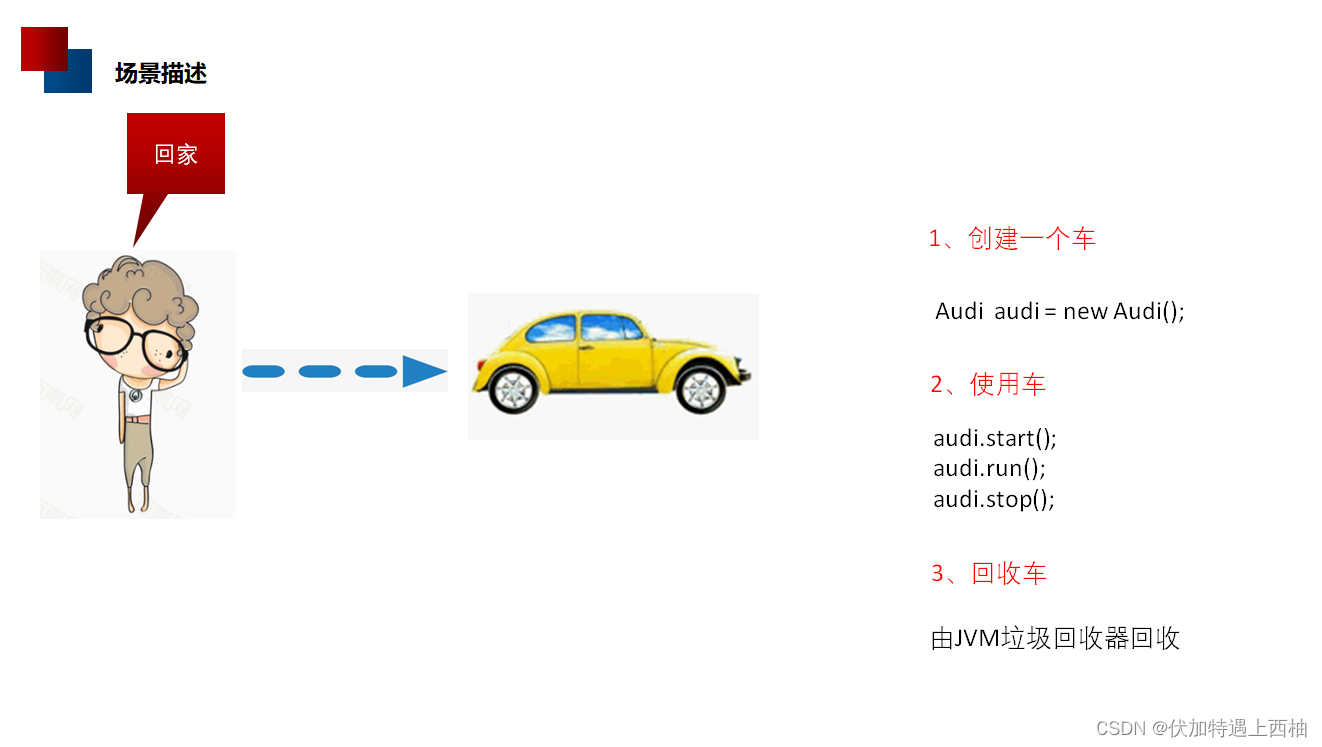
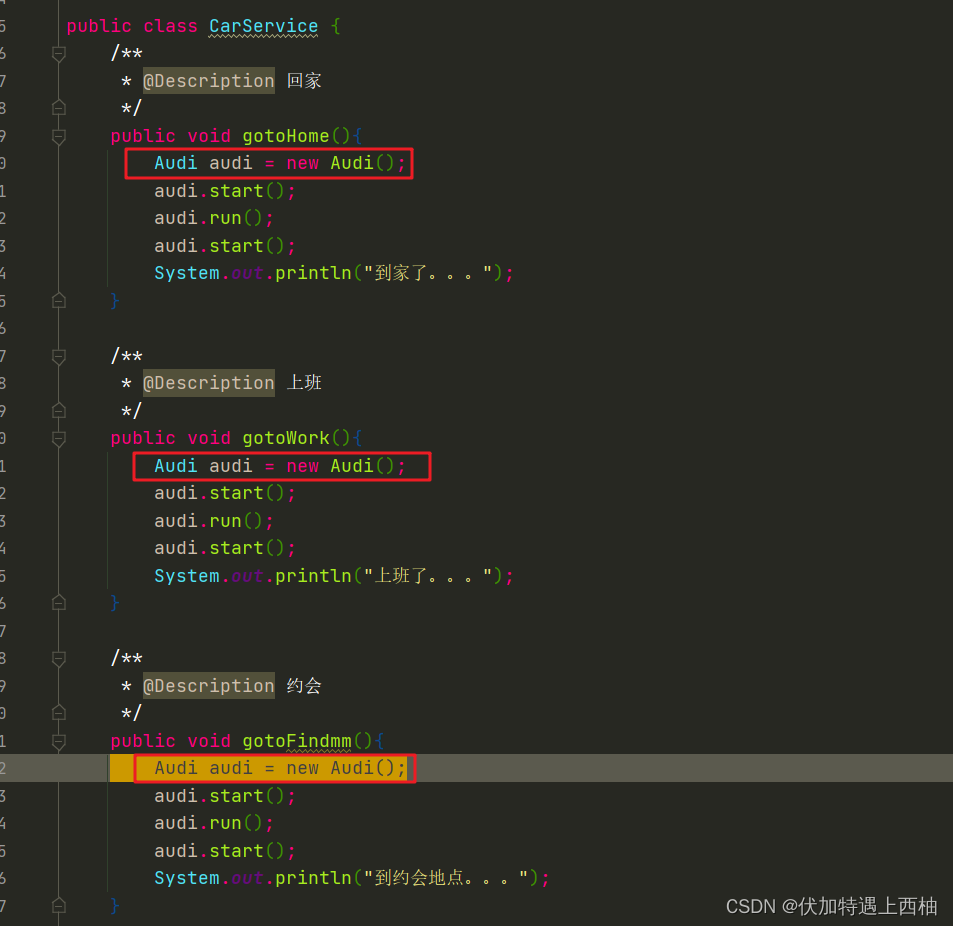
【3】场景代码(1)
【2.1】目标
1、用代码描述用车场景
2、分析依赖的问题
【3.2】实现
#步骤:
【1】创建pojo、service.controller层
【2】创建基础类:AUdi;CarService;XiaoWang
【3】使用CarService调用Audi
【3.2.1】创建项目
新建spring-day01-01car结构如下
【3.2.2】pojo层
package com.itheima.spring.pojo;
/**
* @Description:奥迪车
*/
public class Audi {
/**
* @Description 启动
*/
public void start(){
System.out.println("奥迪启动。。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 运行
*/
public void run(){
System.out.println("奥迪运行。。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 停止
*/
public void stop(){
System.out.println("奥迪熄火。。。。");
}
}
package com.itheima.spring.pojo;
/**
* @Description:宝马车
*/
public class Bmw {
public void start(){
System.out.println("宝马启动");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("驾驶宝马");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("宝马熄火");
}
}
【3.2.3】service层
package com.itheima.spring.service;
import com.itheima.spring.pojo.Audi;
/**
* @Description:车辆使用场景
*/
public class CarService {
/**
* @Description 回家
*/
public void gotoHome(){
Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到家了。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 上班
*/
public void gotoWork(){
Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到家了。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 约会
*/
public void gotoFindmm(){
Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到约会地点。。。");
}
}
【3.2.4】controller层
package com.itheima.spring.controller;
import com.itheima.spring.service.CarService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
/**
* @Description:小王的生活场景
*/
public class XiaoWang {
@Test
public void needGotoHome(){
CarService carService = new CarService();
carService.gotoHome();
}
@Test
public void needGotoWork(){
CarService carService = new CarService();
carService.gotoWork();
}
@Test
public void needGotoFindMM(){
CarService carService = new CarService();
carService.gotoFindMM();
}
}
【3.3】场景小结
1、回家、上班、约会多个场景小王都需要依赖车
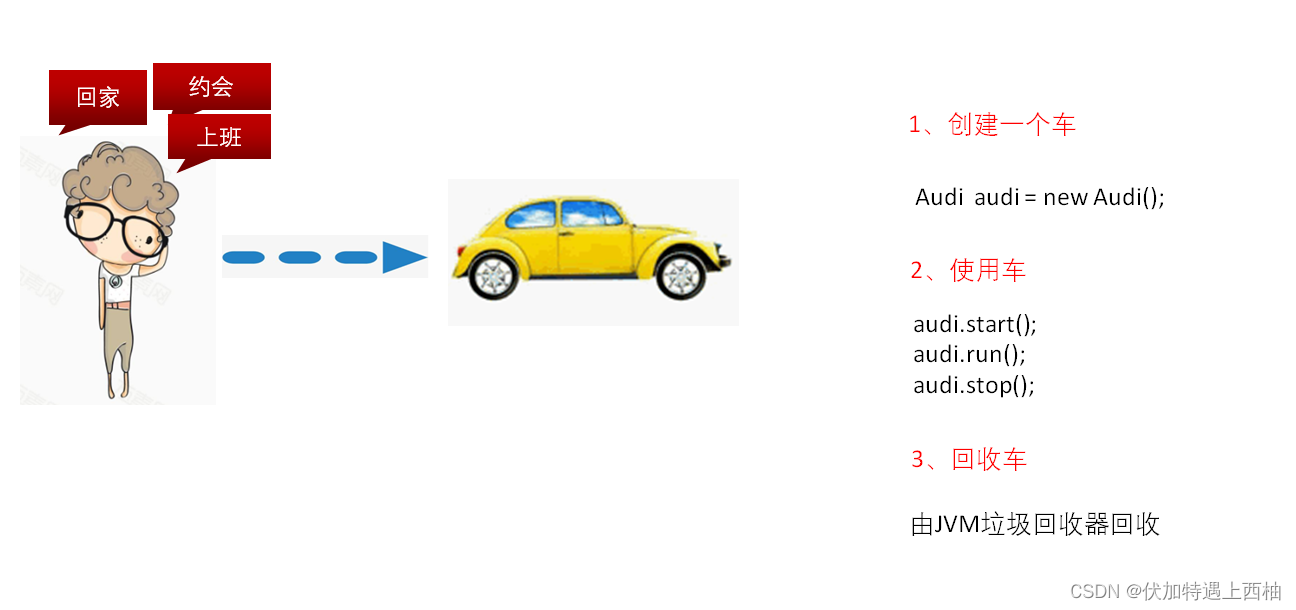
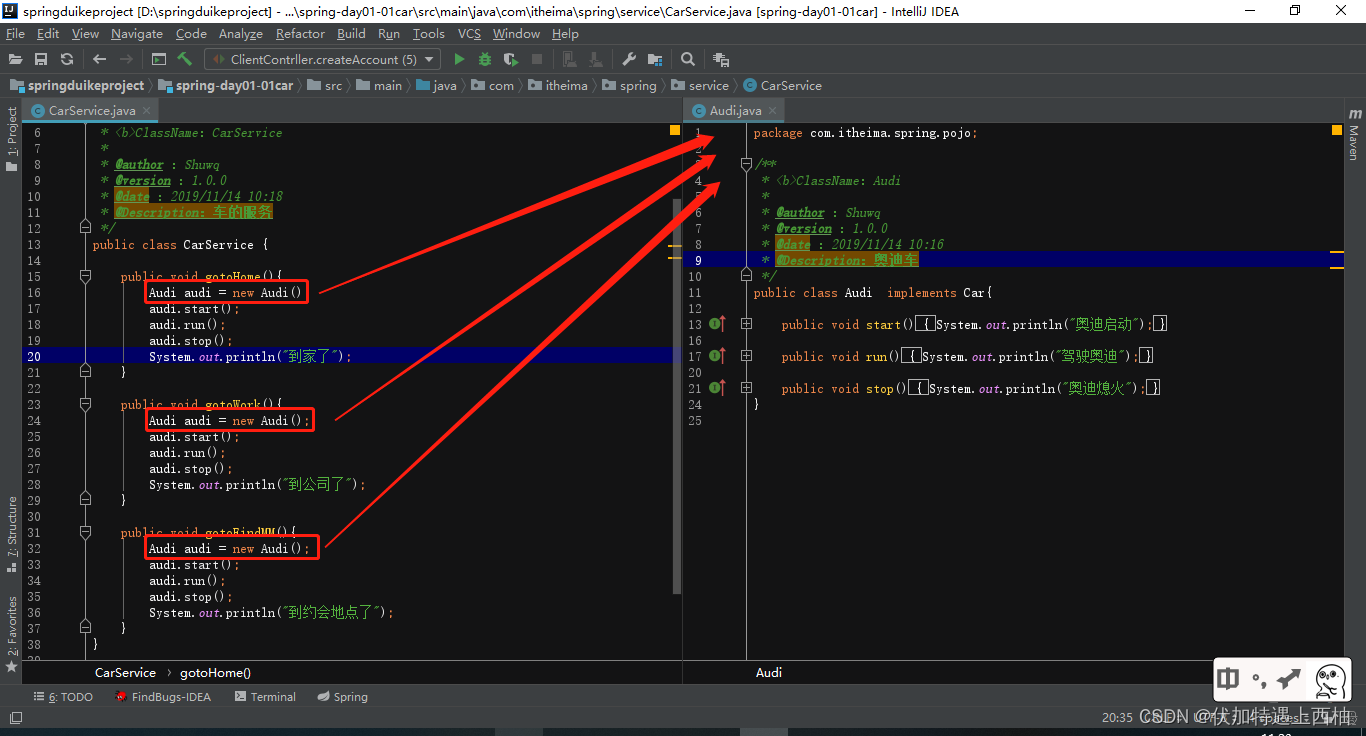
2、换车之后都要修改CarService的业务代码
【4】方案一:interface
【4.1】思考
1、咱们想一下,小王是需要一辆宝马?需要一辆奥迪?其实小王只是需要一辆车?
同学们之前我们是不是学习过接口的概念,这里我们能不能抽象出一个Car的接口呢?
【4.2】目标
1、使用接口与实现分离的方式解耦
【4.3】实现
#步骤:
【1】添加Car的接口
【2】Audi、Bmw实现Car接口
【3】修改CarService
【4.3.1】添加Car接口
package com.itheima.spring.pojo;
/**
* @Description:车接口
*/
public interface Car {
public void start();
public void run();
public void stop();
}
【4.3.2】实现Car接口
package com.itheima.spring.pojo;
/**
* @Description:奥迪
*/
public class Audi implements Car{
public void start(){
System.out.println("奥迪启动");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("驾驶奥迪");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("奥迪熄火");
}
}
package com.itheima.spring.pojo;
/**
* @Description:宝马
*/
public class Bmw implements Car {
public void start(){
System.out.println("宝马启动");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("驾驶宝马");
}
public void stop(){
System.out.println("宝马熄火");
}
}
【4.3.3】修改CarService
package com.itheima.spring.service;
import com.itheima.spring.pojo.Audi;
import com.itheima.spring.pojo.Car;
/**
* @Description:车辆使用场景
*/
public class CarService {
Car audi = new Audi();
/**
* @Description 回家
*/
public void gotoHome(){
// Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到家了。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 上班
*/
public void gotoWork(){
// Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到家了。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 约会
*/
public void gotoFindmm(){
// Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到约会地点。。。");
}
}
【4.4】方案一小结
1、局部变量提到成员变量解耦
2、接口与实现分离解耦
3、Car bmw = new Bmw();的时候还是需要指定实现类,由此可以看出,没有本质上解决强依赖的问题
#【话外音】
#难道上班、约会、回家之前小王自己造个车吗?
【5】方案二:CarFactroy(2)
【5.1】思考
现实生活中,我们不可能在上班、回家、约会之前自己去造车子,而是我们在使用车子之前,去工厂买一辆,
车的制造是由汽车工厂完成,我们只需要告诉工厂咱们需要什么牌子的车就好
【5.2】目标
1、用代码模拟汽车工厂
2、理解IOC控制反转的概念
【5.3】实现
#步骤
【1】增加汽车工厂
工厂提供车的方式:可以直接调用的
生产车过程:知道类全路径,使用反射机制实例化类的对象
【2】修改CarService,使用工厂
【5.3.1】创建项目
拷贝项目spring-day01-01car建立spring-day01-02car结构如下:
【5.3.2】添加factory层
package com.itheima.spring.factory;
import com.itheima.spring.pojo.Car;
/**
* @Description:汽车工厂
*/
public class CarFactory{
/**
* @Description 根据class对象实例化车
* @param carClass 车辆class对象
* @return
*/
public static Car getCar(Class<?> carClass){
String carClassName = carClass.getName();
Car car =null;
try {
car = (Car) Class.forName(carClassName).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return car;
}
/**
* @Description 根据class对象实例化车
* @param carClassName 车辆class对象全限定名称
* @return
*/
public static Car getCar(String carClassName ){
Car car =null;
try {
car = (Car) Class.forName(carClassName).newInstance();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return car;
}
}
【5.3.3】修改CarService
/**
* @Description:车辆使用场景
*/
public class CarService {
Car audi = CarFactory.getCar(Audi.class);
/**
* @Description 回家
*/
public void gotoHome(){
// Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到家了。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 上班
*/
public void gotoWork(){
// Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到公司。。。");
}
/**
* @Description 约会
*/
public void gotoFindmm(){
// Audi audi = new Audi();
audi.start();
audi.run();
audi.start();
System.out.println("到约会地点。。。");
}
}
【5.3.4】方案二小结
1、程序中汽车工厂生产车的方式:反射实例化汽车对象
2、程序中汽车工厂--IOC容器
【6】IOC作用小结
IOC-控制反转:
控制什么:控制对象的创建和销毁;
反转什么:new-->factory创建;
IOC的作用:
解耦
IOC是什么:
工厂: 反射机制实例化对象
3、手写IOC实现【理解】
咱们完成了一个生活中的场景解耦描述,知道了:
- IOC就是一个工厂
【1】思考
1、手写IOC工厂采用什么方式实例化对象?
方案:反射机制实例化类的对象
2、能不能把实例化的对象,事先加载到集合中?选取什么数据结构的集合合适?
方案:对象名和对象全限定名是键值对结构,又需要便于存储与查找,使用map集合更适合!
3、类似“com.itheima.spring.pojo.Audi”的配置信息怎么处理?
方案:放到properties文件
【2】目标
1、手写IOC
反射机制实例化对象
存储到集合容器
使用properties文件存储配置
【3】实现(3)
1、创建项目及J2EE三层架构
2、创建pojo对象
3、创建dao对象
4、创建service对象
5、创建controller对象
6、创建properties文件
7、factory工厂类【重点】
【1】事先创建集合容器
【2】事先加载properties文件内容
【3】反射机制实例化bean对象,并且放入集合容器
【4】公共的访问方法
【3.1】创建项目
新建项目spring-day01-03myioc结构如下
package com.heima.spring.pojo;
/**
* @Description:账户实体类
*/
public class Account {
//账户编号
private String Id;
//账户所有者
private String accountName;
//账户余额
private Float money;
public Account() {
}
public String getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getAccountName() {
return accountName;
}
public void setAccountName(String accountName) {
this.accountName = accountName;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"Id='" + Id + '\'' +
", accountName='" + accountName + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}
【3.2】dao层
package com.itheima.spring.dao;
/**
* @Description:账户dao层
*/
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* @Description 新增
*/
void saveAccount();
/**
* @Description 删除
*/
void delAccount();
/**
* @Description 修改
*/
void updateAccout();
/**
* @Description 查询
*/
void findAccount();
}
package com.itheima.spring.dao.impl;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.spring.pojo.Account;
/**
* @Description:
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
private static Account account;
static {
account = new Account();
account.setId("010101");
account.setAccountName("张三");
account.setMoney(2000F);
}
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
System.out.println("保存:"+account.toString());
}
@Override
public void delAccount() {
System.out.println("删除:"+account.toString());
}
@Override
public void updateAccout() {
System.out.println("修改:"+account.toString());
}
@Override
public void findAccount() {
System.out.println("查询:"+account.toString());
}
}
【3.3】servic层
package com.itheima.spring.service;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
/**
* @Description:用户业务层接口
*/
public interface AccountService {
/**
* @Description 新增
*/
void saveAccount();
/**
* @Description 删除
*/
void delAccount();
/**
* @Description 修改
*/
void updateAccout();
/**
* @Description 查询
*/
void findAccount();
void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao);
}
package com.itheima.spring.service.impl;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.spring.service.AccountService;
/**
* @Description:用户业务层接口实现
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
@Override
public void delAccount() {
accountDao.delAccount();
}
@Override
public void updateAccout() {
accountDao.updateAccout();
}
@Override
public void findAccount() {
accountDao.findAccount();
}
@Override
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
}
【3.4】factory层
在resources目录中建立
db.properties
accountDao = com.itheima.spring.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl
accountService = com.itheima.spring.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl
package com.itheima.spring.factory;
import javafx.beans.binding.ObjectExpression;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @Description:bean工厂
*/
public class BeanFactory {
//1、事先存储容器
private static Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
//2、加载配置文件
static {
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("db.properties"));
Enumeration<?> enumeration = properties.propertyNames();
while (enumeration.hasMoreElements()) {
String key = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
String value = (String) properties.get(key);
//3、实例化bean
Object beanObject = Class.forName(value).newInstance();
//4、放入容器
map.put(key,beanObject);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//5、公共获得bean
public static Object getBean(String calssName){
return map.get(calssName);
}
}
【3.5】controller层
package com.itheima.spring.controller;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.spring.factory.BeanFactory;
import com.itheima.spring.service.AccountService;
import com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AccountServiceImpl;
import org.junit.Test;
/**
* @Description:
*/
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void saveAccount() {
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) BeanFactory.getBean("accountService");
accountService.setAccountDao((AccountDao) BeanFactory.getBean("accountDao"));
accountService.saveAccount();
}
}
【4】手写IOC小结
我们通过使用工厂模式,实现了表现层——业务层、业务层——持久层的解耦。
【实现思路】:
工厂+反射+配置文件
【核心思想】:
【1】读取配置文件中类的全限定名通过反射机制创建对象。
【2】把创建出来的对象事先都存起来,当我们使用时可以直接从存储容器中获取。
存哪去?
由于我们是很多对象,肯定要找个集合来存。这时候有 Map 和 List 供选择。
到底选 Map 还是 List 就看我们有没有查找需求。有查找需求,选 Map。
所以我们的答案就是在应用加载时,创建一个 Map,用于存放bean对象。
我们把这个 map 称之为容器。
什么是IOC工厂
事先加载bean,并且提供一个直接获取bean的方法。
什么是控制反转
主动new对象方式--被动从容器中获取
第三章 基于xml的spring-IOC【重点】
1、【入门案例】xml的spring-IOC(4)
【1】思考
1、我们采用工厂+反射的方式实现了手写IOC工厂,那么spring-IOC的工厂是不是也类似?
spring框架提供了一个大工厂接口:ApplicationContext==》Beanfactroy
2、手写IOC中的配置文件类型是properties,那么spring-IOC的配置采取的是什么类型?
spring使用XML格式的文件存储配置
<bean id="唯一标识"
class="实现类的全限定名">
</bean>
3、spring-IOC是怎么加载配置文件的呢?
ApplicationContext工厂使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载配置文件
4、手写IOC中的BeanFactory提供一个公共获得bean的方法,那spring-ioc是不是有类似的方法?
ApplicationContext工厂使用getBean()方法,用于根据bean的名称获取实例化对象
【2】目标
1、掌握spring-IOC工厂的创建
2、掌握bean标签的基本配置
3、掌握spring-IOC工厂获得实例化对象的方式
【3】实现
步骤:
1、导入依赖
2、编写bean.xml文件替换properties
3、使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载bean.xml配置文件
4、使用ApplicationContext工厂的getBean()方法获得bean
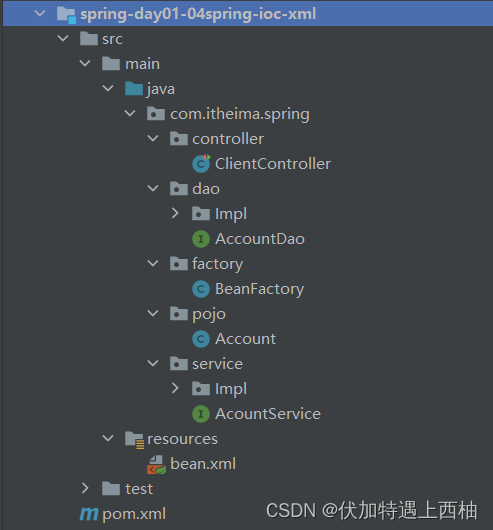
【3.1】创建项目
创建spring-day01-04spring-ioc-xml结构如下
【3.2】pom.xml依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.itheima.spring</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-day01-04spring-ioc-xml</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>spring-day01-04spring-ioc-xml</name>
<!-- FIXME change it to the project's website -->
<url>http://www.example.com</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<!-- spring版本 -->
<spring.version>5.1.11.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
</build>
</project>
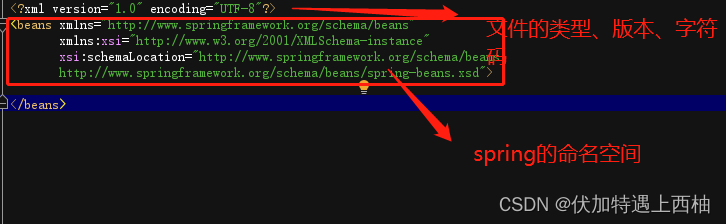
【3.3】spring配置文件bean.xml
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Wf1Eggxg-1679275066825)(img\image-20191104144000328.png)]
初建时候bean.xml的结构如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>
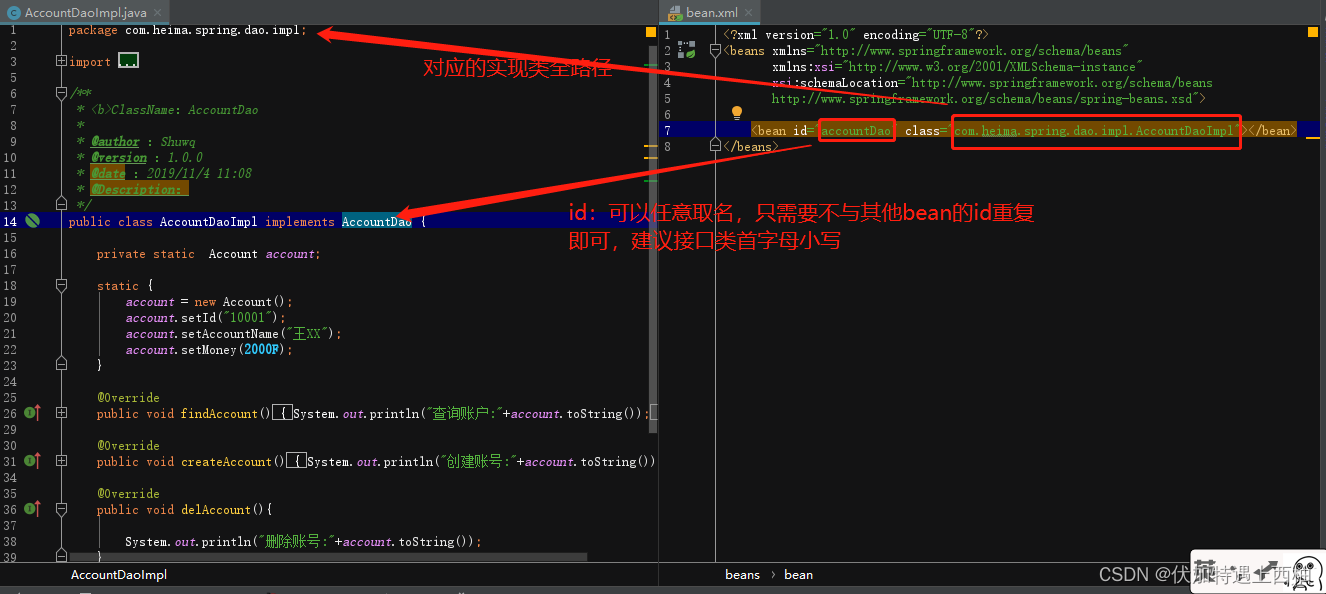
全部改写完成后bean.xml的配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--bean
作用:
声明类交给spring容器
属性:
id: 唯一标识
class:全路径限定名称
细节:
默认使用无参构造函数实例化-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="acountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AcountServiceImpl"></bean>
</beans>
【3.4】改造AccountService
package com.itheima.spring.service;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
public interface AcountService {
/**
* @Description 新增
*/
void saveAccount();
/**
* @Description 删除
*/
void delAccount();
/**
* @Description 修改
*/
void updateAccout();
/**
* @Description 查询
*/
void findAccount();
void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao);
}
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.spring.service.AcountService;
public class AcountServiceImpl implements AcountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
@Override
public void delAccount() {
accountDao.delAccount();
}
@Override
public void updateAccout() {
accountDao.updateAccout();
}
@Override
public void findAccount() {
accountDao.findAccount();
}
@Override
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
}
【3.5】改造ClientController
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void saveAccount(){
/*
1、导入依赖
2、编写bean.xml文件替换properties
3、使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载bean.xml配置文件
4、使用ApplicationContext工厂的getBean()方法获得bean
*/
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AcountService acountService = (AcountService) applicationContext.getBean("acountService");
AccountDao accountDao = applicationContext.getBean("accountDao",AccountDao.class);
acountService.setAccountDao(accountDao);
acountService.saveAccount();
}
}
【4】入门案例小结
spring-IOC入门案例,我们了解如下内容:
1、工厂类:ApplicationContext
2、工厂配置:
文件类型:xml
方式:
<!--配置accountDao、accountServic说明:
标签:
bean:配置javaBean对象
属性:
id:bean的唯一标识名称
class:类的全路径信息
细节:
默认使用无参数构造方法,创建对象
-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.heima.spring.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
3、工厂加载配置:
ApplicationContext通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载bean.xml配置
4、工厂获得bean:
ApplicationContext使用getBean()方法,用于根据bean的名称获取实例化对象
第四章 SpringIOC工厂类【了解】
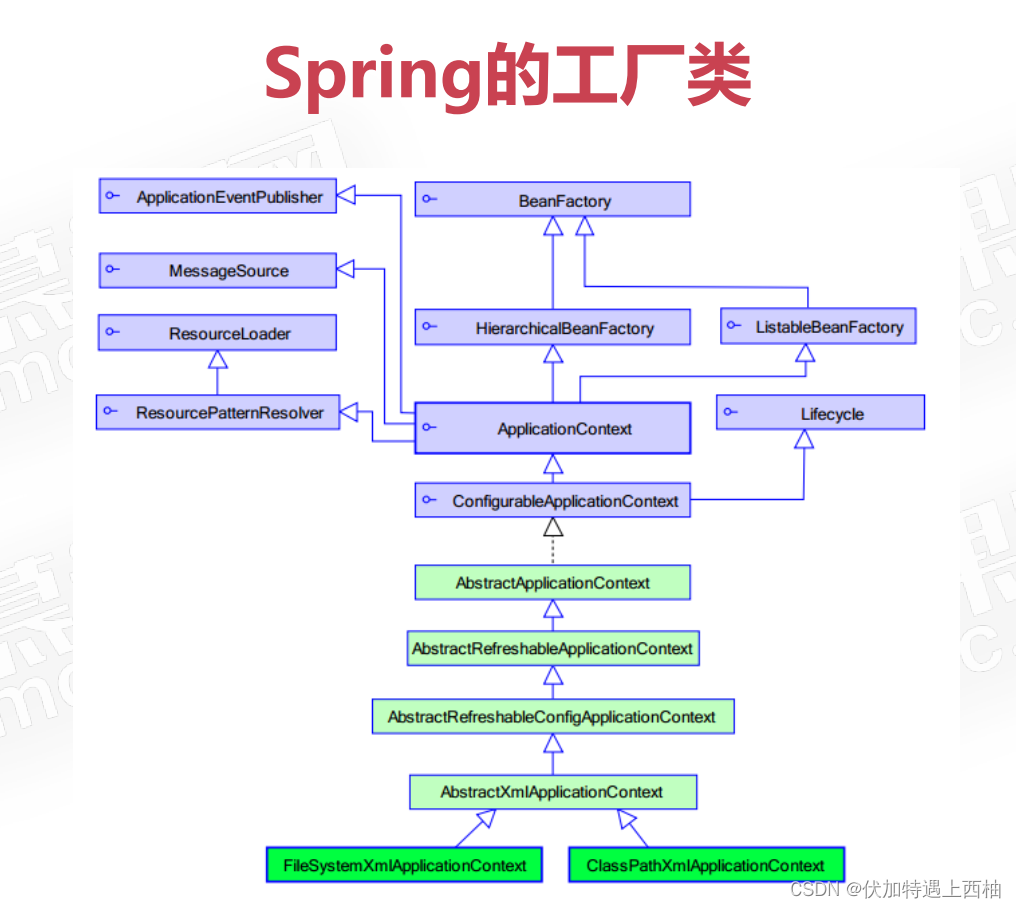
1、BeanFactory
【1】作用
Spring里面最顶层的接口,提供了最简单的容器的功能,只定义了实例化对象和拿对象的功能;
【2】方法
public interface BeanFactory {
//对FactoryBean的转义定义,因为如果使用bean的名字检索FactoryBean得到的对象是工厂生成的对象
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
//根据bean的名字,在IOC容器中得到bean实例,
*Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
//根据bean的名字,在IOC容器中得到bean实例,args:显式参数(必须为非单例模式)
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
//根据bean的名字获得对象,并转换为Class类型
*<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType);
//根据bean的类型获得对象(必须是拥有唯一实现类)
*<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
//根据bean的类型获得对象,args:显式参数
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
//这里提供对bean的检索,看看是否在IOC容器有这个名字的bean
*boolean containsBean(String name);
//判断这个bean是不是单例
*boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//同时判断这个bean是不是多例
*boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//这里得到bean实例的Class类型
*Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//这里得到bean的别名,如果根据别名检索,那么其原名也会被检索出来
*String[] getAliases(String name);
2、ApplicationContext
【1】作用
应用上下文,继承BeanFactory接口,它是Spring的更高级的容器,提供了更多的有用的功能;
-
国际化(MessageSource)
-
访问资源,如URL和文件(ResourceLoader)
-
载入多个(有继承关系)上下文 ,使得每一个上下文都专注于一个特定的层次,比如应用的web层
-
消息发送、响应机制(ApplicationEventPublisher)
-
AOP(拦截器)
【2】实现类
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:
从类的根路径下加载配置文件 推荐使用这种
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext
从硬盘路径下加载配置文件
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
基于Java的配置类加载Spring的应用上下文配置
@Test
public void createAccountTest(){
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
//获得bean
AccountDao accountDao = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDao");
AccountServic accountServic = (AccountServic) applicationContext.getBean("accountServic");
//set方法指定accountDao
accountServic.setAccountDao(accountDao);
//创建账户
accountServic.createAccount();
}
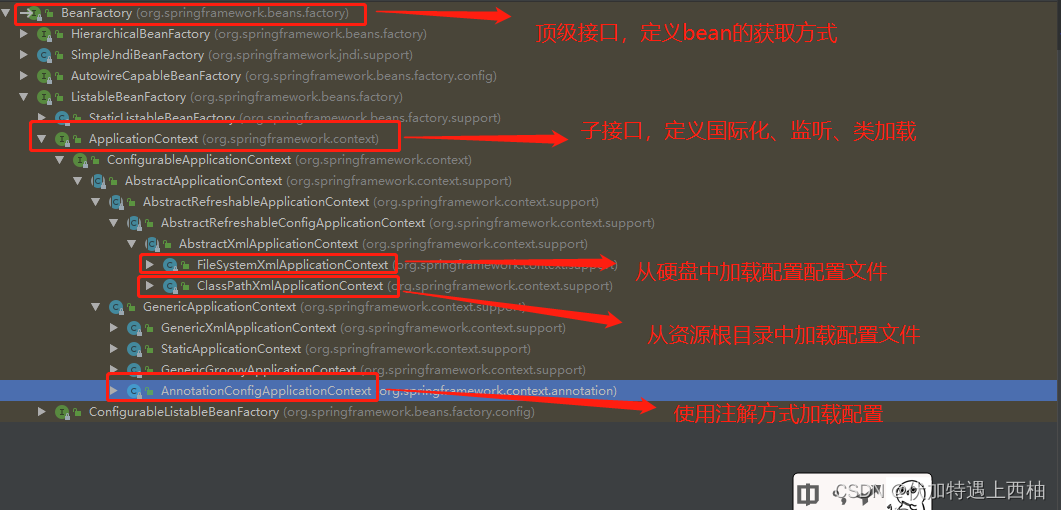
3、加载顺序
【1】思考
BeanFactory、ApplicationContext都是容器,那么他们的加载顺序有什么不同?
【2】目的
了解BeanFactory和ApplicationContext的加载顺序
【3】实现(5)
步骤:
1、观察ApplicationContext的加载方式
2、观察BeanFactory的加载方式
3、比较一下加载顺序
【3.1】创建项目
拷贝项目spring-day01-04spring-ioc-xml创建spring-day01-05BeanFactory-ApplicationContext结构如下
在AccountDaoImpl中增加构造函数
public AccountDaoImpl() {
System.out.println("AccountDaoImpl的实例已经创建");
}
【3.3】改造ClientController
package com.itheima.spring.controller;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.spring.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
/**
* @Description:测试
*/
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void saveAccount() {
/**
* Spring-IOC容器:ApplicationContext
* 构建方式:通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载配置文件
* 使用bean:getBean
*/
System.out.println("======ApplicationContext开始创建容器=====");
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
System.out.println("======ApplicationContext创建容器完成=====");
applicationContext.getBean("accountDao");
System.out.println("======分割线==========");
System.out.println("======BeanFactory开始创建容器=====");
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource("bean.xml");
BeanFactory beanFactory = new XmlBeanFactory(resource);
System.out.println("======BeanFactory创建容器完成=====");
beanFactory.getBean("accountDao");
}
}
【3.4】加载顺序
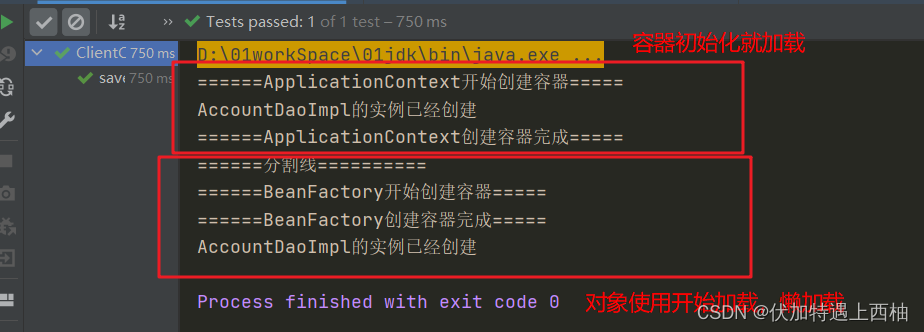
【4】加载顺序小结
1.BeanFactory是顶层接口
2.ApplicationContext是子接口
3.它们最大的区别是创建对象的时间不一样(单例的):
【BeanFactory】采用的是延迟加载的思想。即什么时候使用对象,什么时候创建
【ApplicationContext】采用立即创建的思想。即一加载配置文件,立即就创建
第五章 bean标签详解【重点】
1、bean标签作用
bean作用:
用于配置对象让spring 来创建的。
【细节】
默认情况下调用类的无参构造函数。
2、bean标签基本属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| id | bean的唯一标识名称 |
| class | 实现类的全限定名称 |
| name | bean的名称 * 多个别名使用 ”,” 分割 * bean与bean的别名不可以重复 |
入门案例中我们已经基本使用过
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao" name="accountDao2,accountDao3" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"></bean>
</beans>
3、bean标签作用范围
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| scope | 指定对象的作用范围。 * singleton 【默认】: 单例,所有的请求都用一个对象来处理 * prototype : 多例,每个请求用一个新的对象来处理 * request : WEB 项目中,将对象存入到 request 域中. * session : WEB 项目中,将对象存入到 session 域中. * global session : WEB 项目中,应用在集群环境.如果没有集群环境那么相当于session |
【1】思考
单例、多例他们分别在什么场景中使用?他们有什么区别?
spring默认单例,不需要修改,不要随意定义成员变量。
多例:资源共用
【2】目标
1、掌握scope的单例、多例的配置
2、掌握单例和多例的区别
【3】bean作用域实例(6)
步骤:
1、改造ClientController多次获得对象
2、装配bean到spring的IOC容器中,修改bean标签中scope的作用域
3、观察不同作用域下获得的对象内存地址是否一致
【3.1】创建项目
拷贝项目spring-day01-04spring-ioc-xml创建spring-day01-06bean-scope结构如下
改造ClientController
package com.itheima.spring.controller;
import com.itheima.spring.dao.AccountDao;
import com.itheima.spring.service.AccountService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.core.io.Resource;
import javax.sound.midi.Soundbank;
/**
* @Description:测试
*/
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void saveAccount() {
/**
* Spring-IOC容器:ApplicationContext
* 构建方式:通过ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载配置文件
* 使用bean:getBean
*/
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AccountDao accountDaoA = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDao");
AccountDao accountDaoB = (AccountDao) applicationContext.getBean("accountDao");
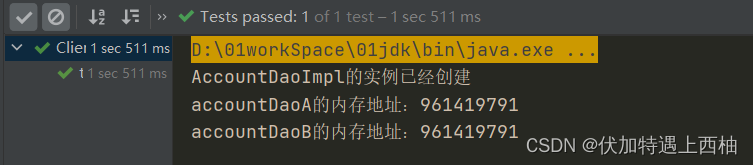
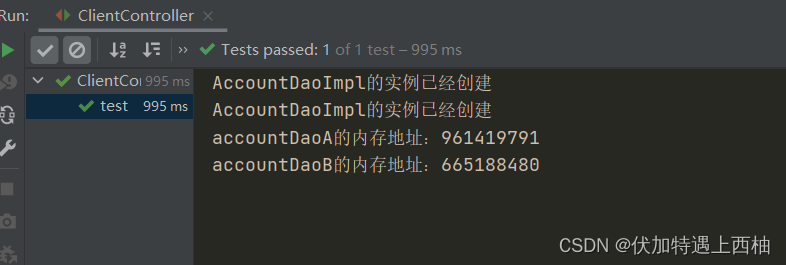
System.out.println("accountDaoA的内存地址:"+accountDaoA.hashCode());
System.out.println("accountDaoB的内存地址:"+accountDaoB.hashCode());
}
}
【3.2】Bean【默认:singleton】
使用bean标签在bean.xml中装配accountDao的scope=“singleton”
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean
作用:
声明一个bean交于spring容器管理
属性:
id:唯一标识
class:实现类的全限定名称(反射)
scope="singleton" 所有请求只创建一个对象,内存地址相同
scope="prototype" 每次请求都创建新的对象,内存地址不同
-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl" scope="singleton"/>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"/>
</beans>
【3.3】singleton运行结果
【3.4】bean【多例:prototype】
使用bean标签在bean.xml中装配accountDao的scope=“prototype”
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean
作用:
声明一个bean交于spring容器管理
属性:
id:唯一标识
class:实现类的全限定名称(反射)
scope="singleton" 所有请求只创建一个对象,内存地址相同
scope="prototype" 每次请求都创建新的对象,内存地址不同
-->
<!-- <bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl" scope="singleton"/>-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl" scope="prototype"/>
<bean id="accountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.impl.AccountServiceImpl"/>
</beans>
【3.5】prototype运行结果
【4】bean作用域小结
1、单例和多里创建方式、内存地址
【singleton单例】:所有请求只创建一个对象,内存地址相同
【prototype多例】:每次请求都创建新的对象,内存地址不同
2、为什么使用单例?
节省内存、CPU的开销,加快对象访问速度
3、为什么使用多例?
如果你给controller中定义很多的属性,那么单例肯定会出现竞争访问,不要在controller层中定义成员变量(dao、service注入的bean)
当web层的对象是有状态的时候 使用多例,防止并发情况下的互相干扰
4、单例、多例的场景
单例===》spring中的Dao,Service,controller都是单例的
多例====》struts2的Action是多实例
4、bean标签生命周期
sevlet的生命周期回顾
1.被创建:执行init方法,只执行一次
--默认情况下,第一次被访问时,Servlet被创建,然后执行init方法;
--可以配置执行Servlet的创建时机;
2.提供服务:执行service的doGet、doPost方法,执行多次
3.被销毁:当Servlet服务器正常关闭时,执行destroy方法,只执行一次
spring-IOC中不同作用域中bean的生命周期
| 作用范围 | 生命周期 | |
|---|---|---|
| 单例scope=“singleton” | 所有请求只创建一次对象 | 出生:应用加载,创建容器,对象就被创建 活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着。 死亡:应用卸载,销毁容器,对象就被销毁 |
| 多例scope=“prototype” | 每次请求都创建对象 | 出生:应用加载,创建容器,对象使用创建 活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着。 死亡:对象长时间不用,被垃圾回收器回收 |
生命周期方法相关
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| init-method | 指定类中的初始化方法名称 |
| destroy-method | 指定类中销毁方法名称 |
【1】目标
1、掌握bean的生命周期配置方式
2、单例和多例下bean的生命周期的区别。
【2】bean生命周期实例(7)
步骤:
1、创建LifecycBeanServic类
2、装配LifecycBeanServic
3、创建测试类
4、观察默认单例下生命周期
5、观察多例下生命周期
【2.1】创建项目
新建项目spring-day01-07bean-lifecycle
/**
* @Description:生命周期测试服务
*/
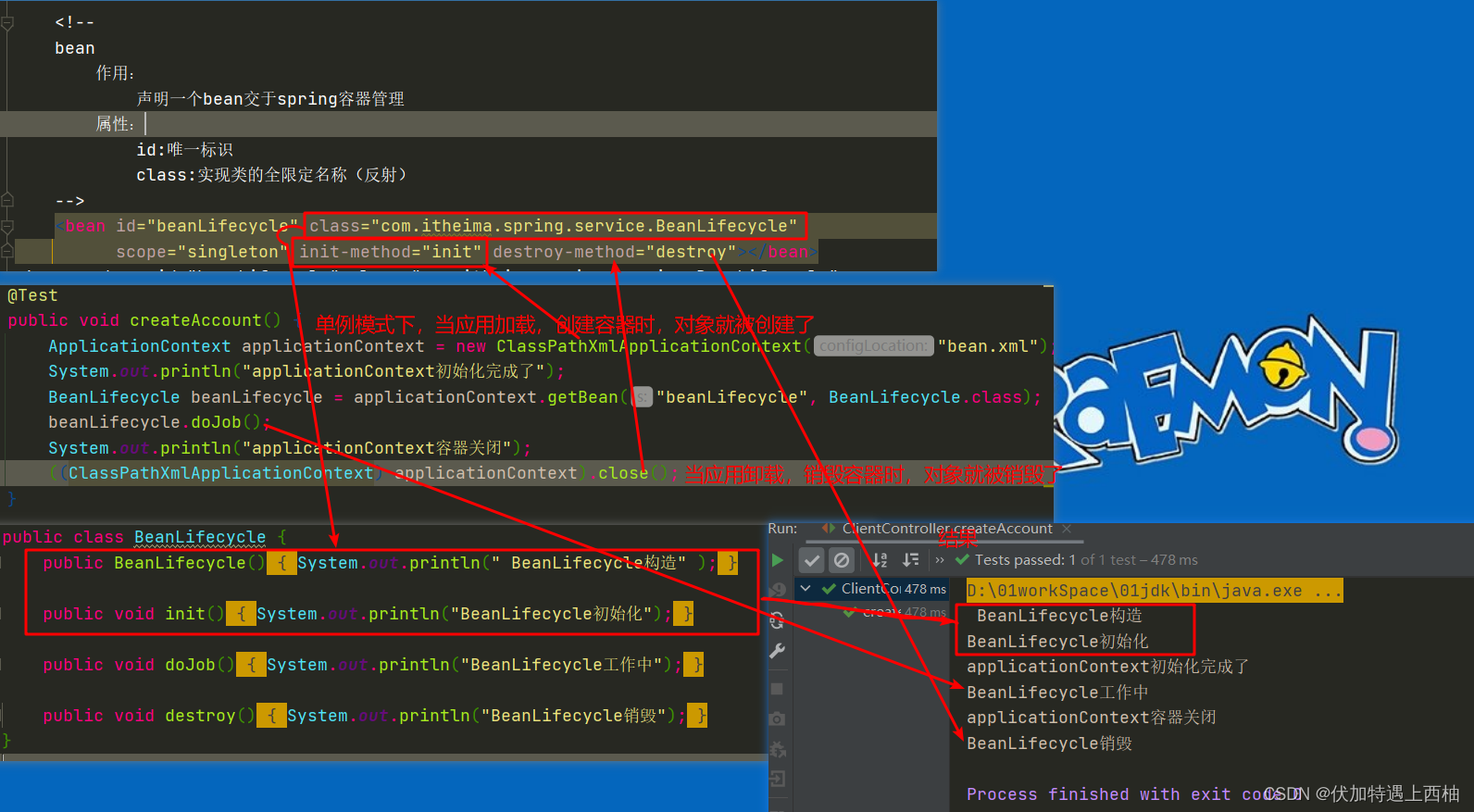
public class BeanLifecycle {
public BeanLifecycle(){
System.out.println(" BeanLifecycle构造" );
}
public void init(){
System.out.println("BeanLifecycle初始化");
}
public void doJob(){
System.out.println("BeanLifecycle工作中");
}
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("BeanLifecycle销毁");
}
}
【2.3】装配LifecycleBean
装配bean并且设置问单例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean
作用:
声明一个bean交于spring容器管理
属性:
id:唯一标识
class:实现类的全限定名称(反射)
-->
<bean id="beanLifecycle" class="com.itheima.spring.service.BeanLifecycle"
scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
</beans>
【2.4】创建ClientController
/**
* @Description:客户端
*/
public class ClientContrller {
/**
* ApplicationContext:spring-IOC容器
* ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:容器实现类,加载配置文件
* applicationContext.getBean:获得容器中的bean对象
*/
@Test
public void createAccount() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
System.out.println("applicationContext初始化完成了");
BeanLifecycle beanLifecycle = applicationContext.getBean("beanLifecycle", BeanLifecycle.class);
beanLifecycle.doJob();
System.out.println("applicationContext容器关闭");
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) applicationContext).close();
}
}
【2.5】单例模式下生命周期:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean
作用:
声明一个bean交于spring容器管理
属性:
id:唯一标识
class:实现类的全限定名称(反射)
-->
<bean id="beanLifecycle" class="com.itheima.spring.service.BeanLifecycle"
scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
</beans>
【2.6】多例模式下生命周期
将配置文件中的单例修改为多例
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean
作用:
声明一个bean交于spring容器管理
属性:
id:唯一标识
class:实现类的全限定名称(反射)
-->
<!-- <bean id="beanLifecycle" class="com.itheima.spring.service.BeanLifecycle"-->
<!-- scope="singleton" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>-->
<bean id="beanLifecycle" class="com.itheima.spring.service.BeanLifecycle"
scope="prototype" init-method="init" destroy-method="destroy"></bean>
</beans>
再次执行方法发现,LifecycleBean被延迟加载了,并且只执行了初始化方法-init,没有执行销毁方法destory.
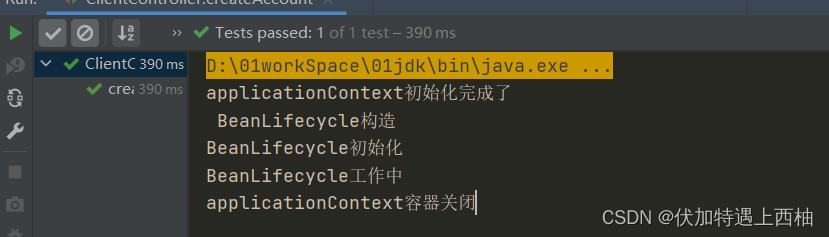
【3】bean生命周期小结
单例对象:scope="singleton"
一个应用只有一个对象的实例。它的作用范围就是整个应用。
生命周期:
对象出生:当应用加载,创建容器时,对象就被创建了。
对象活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着。
对象死亡:当应用卸载,销毁容器时,对象就被销毁了。
多例对象:scope="prototype"
每次访问对象时,都会重新创建对象实例。
生命周期:
对象出生:当使用对象时,创建新的对象实例(getBean)。
对象活着:只要对象在使用中,就一直活着。
对象死亡:当对象长时间不用时,被垃圾回收器回收。
生命周期方法:
init-method:指定类中的初始化方法名称
destroy-method:指定类中销毁方法名称
5、bean的实例化方式(8)
bean的实例化方式有以下3种:
- bean缺省构造函数创建
- 静态factory方法创建
- 实例化factory方法创建
【1】目标
1、掌握bean实例化的三种方式
2、了解3中方式应用场景
【2】创建项目
新建项目spring-day01-08bean-instance结构如下
【3】缺省构造函数方式【重点】
【3.1】配置方式
<!--空的构造方法实例化-->
<bean id="account" class="com.heima.spring.pojo.Account"></bean>
【3.2】注意事项
缺省构造函数实例化Bean的方式是Spring中默认的实例化方式;
被实例化的Bean中必须有无参构造;
【4】静态工厂方法方式
【4.1】配置方式
<!--静态工厂实例化-->
<bean id="accountStatic" class="com.heima.spring.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="createAccount"></bean>
【4.2】静态工厂代码
步骤一:创建静态工厂
/**
* @Description:静态工厂
*/
public class StaticFactory {
public static Account createAccount(){
System.out.println("静态工厂创建");
return new Account();
}
}
步骤二:配置静态工厂
<!--静态工厂实例化-->
<bean id="accountStatic" class="com.itheima.spring.factory.StaticFactory" factory-method="createAccount"></bean>
【5】实例工厂方法方式
【5.1】配置方式
<!--实例化工厂实例化-->
<bean id="instanceFactory" class="com.itheima.spring.factory.InstanceFactory"></bean>
<bean id="accountInstance" factory-bean="instanceFactory" factory-method="createAccount"></bean>
【5.2】实例工厂代码
步骤一:创建实例工厂
/**
* @Description:实例化工厂
*/
public class InstanceFactory {
public Account createAccount(){
System.out.println("实例工厂构建!");
return new Account();
}
}
【6】bean实例化小结
【缺省构造函数方式】
说明:
在默认情况下会根据默认缺省构造函数来创建类对象。如果bean中没有默认无参构造函数,将会创建失败。
场景:
当各个bean的业务逻辑相互比较独立时,或者与外界关联较少时可以使用
【静态工厂方法方式】
说明:
使用工厂中的静态方法创建对象,并装配到 spring的IOC 容器中。
id 属性:指定 bean 的 id,用于从容器中获取
class 属性:指定静态工厂的全限定类名
factory-method 属性:指定生产对象的静态方法
场景:
统一管理各个bean的创建
各个bean在创建之前需要相同的初始化处理,则可用静态factory方法进行统一的处理
【实例工厂方法方式】
说明
使用工厂中的实例方法创建对象,并装配到容器中。
1、先把实例工厂做为一个bean装配到 spring容器中。
2、然后再引用工厂bean 来调用里面的非静态方法来获取bean并装配到spring的IOC容器中。
factory-bean 属性:用于指定实例工厂 bean 的 id。
factory-method 属性:用于指定实例工厂中创建对象的方法
场景:
1.实例factory方法也作为业务bean控制,可以用于集成其他框架的bean创建管理方法,
2.能够使bean和factory的角色互换
6、bean标签配置小结
1、bean标签的作用:把自己的类的对象的创建交给Spring管理
2、基本配置:
id:IOC工厂中bean实例的唯一标识
class:实现类的全限定路径
name:别名
3、bean的作用域:
单例:默认,IOC工厂创建后,立即创建bean的实例对象(bean只会被实例化一次)
多例:scope="prototype" 每次从工厂中获取bean的时候,都会创建一个新的对象返回
4、bean的生命周期:
单例:
创建:IOC工厂创建后,立即创建bean的实例对象
初始化:对象创建完成之后立刻调用
工作...................
销毁:IOC工厂卸载,单例bean销毁
多例:
出生:应用加载,创建容器,对象使用创建<br/>
活着:只要容器在,对象一直活着。<br/>
死亡:对象长时间不用,被垃圾回收器回收
5、bean实例化的3种方式:获取对象
bean缺省构造函数创建
静态factory方法创建
实例化factory方法创建
第六章 spring的依赖注入(DI)【重点】
1、DI是什么?
【1】DI概念
依赖注入:Dependency Injection(简称DI注入)。它是spring框架核心 ioc容器,bean属性值赋值的具体方案
【2】思考
在上面的课程中,我们在程序编写时,通过控制反转,把对象的创建交给了 spring,但是这种方式仅仅是降低了代码中的依赖关系,并不会完全消除依赖。例如:我们的业务层仍会调用持久层的方法,如图所示:
而所谓的依赖注入,可以先简单的理解为由spring框架来帮助我们以解耦的方式将dao传递到service中
目的
以解耦的方式给属性进行赋值,简称DI注入。
2、依赖注入(DI)的2种方式【重点】
DI注入的方式有2种:
-
set方法注入
-
构造方法注入
【1】set方法注入(9)
【1.1】目标
使用类中属性的set方法,给属性赋值。
注意,赋值的操作不是我们硬编码的,而是通过配置的方式,让spring框架来为我们注入。
要求:
1、bean中必须提供属性的set方法
2、bean标签中通过proprety标签注入属性
【1.2】实现
步骤:
1、为属性提供set方法
2、修改bean.xml的property注入
【1.2.1】创建项目
拷贝spring-day01-04spring-ioc-xml创建spring-day01-09bean-di-set结构如下
【1.2.2】修改AccountServicImpl提供属性的set方法
public class AcountServiceImpl implements AcountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
//提供set方法
@Override
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
// public AcountServiceImpl(AccountDao accountDao) {
// this.accountDao = accountDao;
// }
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
@Override
public void delAccount() {
accountDao.delAccount();
}
@Override
public void updateAccout() {
accountDao.updateAccout();
}
@Override
public void findAccount() {
accountDao.findAccount();
}
}
【1.2.3】编写bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
bean:实例化对象
id:bean的唯一标示
class:实现类的全路径(反射使用)
细节:默认使用无参数构造函数实例化
-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
<!--方式一 使用set方式-->
<bean id="acountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AcountServiceImpl">
<property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
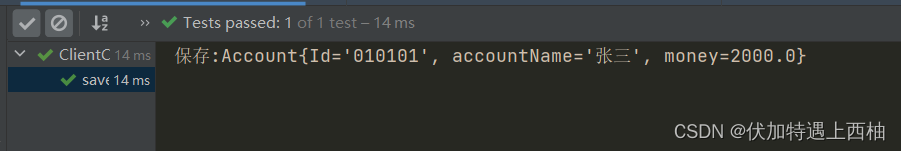
【1.2.4】ClientController测试
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void saveAccount(){
/*
1、导入依赖
2、编写bean.xml文件替换properties
3、使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载bean.xml配置文件
4、使用ApplicationContext工厂的getBean()方法获得bean
*/
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AcountService acountService = (AcountService) applicationContext.getBean("acountService");
acountService.saveAccount();
}
}
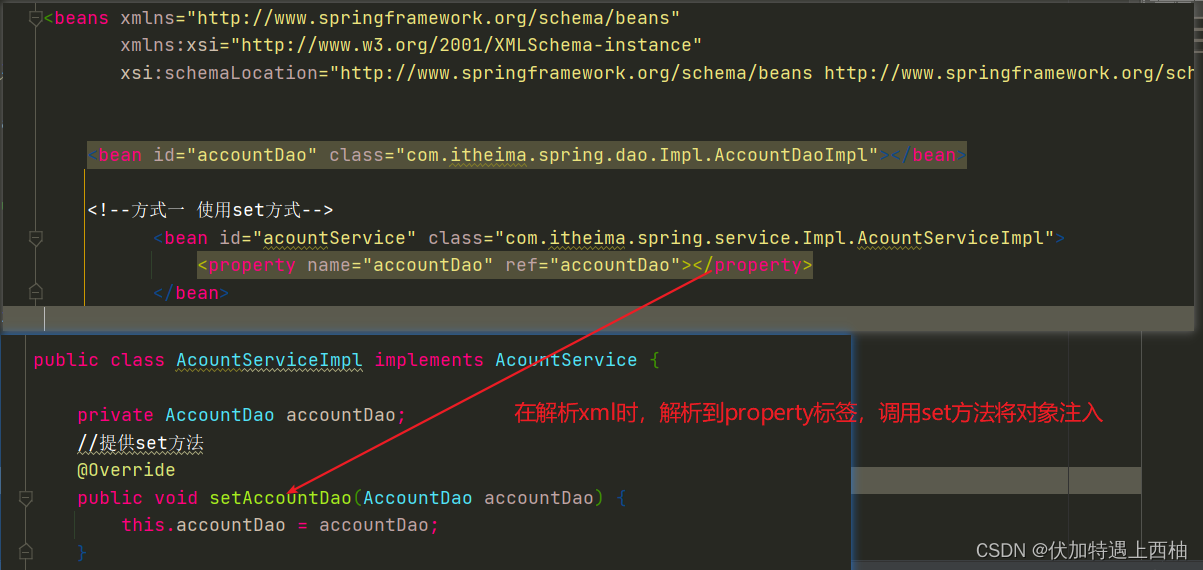
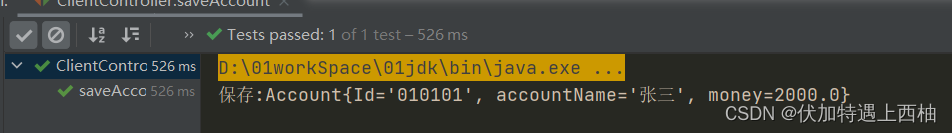
【1.3】set方法注入小结
set注入要求:
1、bean中必须提供属性的set方法
2、在bean标签中通过proprety标签注入属性
【2】构造函数注入(10)
【2.1】目标
使用类中的构造函数,给成员变量赋值。
注意,赋值的操作不是我们硬编码的,而是通过配置的方式,让spring框架来为我们注入。
要求:
1、bean对象需要创建有参数的构造方法
2、在配置文件中通过constructor-arg标签注入属性
【2.2】实现
【2.1】创建项目
拷贝spring-day01-09bean-di-set创建spring-day01-10bean-di-construction结构如下
【2.2】修改AccountServicImpl添加构造函数
public class AcountServiceImpl implements AcountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
//提供构造函数注入
public AcountServiceImpl(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
//提供set方法
@Override
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
@Override
public void saveAccount() {
accountDao.saveAccount();
}
@Override
public void delAccount() {
accountDao.delAccount();
}
@Override
public void updateAccout() {
accountDao.updateAccout();
}
@Override
public void findAccount() {
accountDao.findAccount();
}
}
【2.3】编写bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
<!--方式一 使用set方式-->
<!-- <bean id="acountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AcountServiceImpl">-->
<!-- <property name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></property>-->
<!-- </bean>-->
<!--方式二 创建accountServic使用构造函数 -->
<bean id="acountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AcountServiceImpl">
<constructor-arg name="accountDao" ref="accountDao"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
</beans>
【2.4】ClientController测试
package com.heima.spring.controller;
import com.heima.spring.service.AccountServic;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @Description:调用层
*/
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void saveAccount(){
/*
1、导入依赖
2、编写bean.xml文件替换properties
3、使用ClassPathXmlApplicationContext加载bean.xml配置文件
4、使用ApplicationContext工厂的getBean()方法获得bean
*/
ApplicationContext applicationContext=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
AcountService acountService = (AcountService) applicationContext.getBean("acountService");
acountService.saveAccount();
}
}
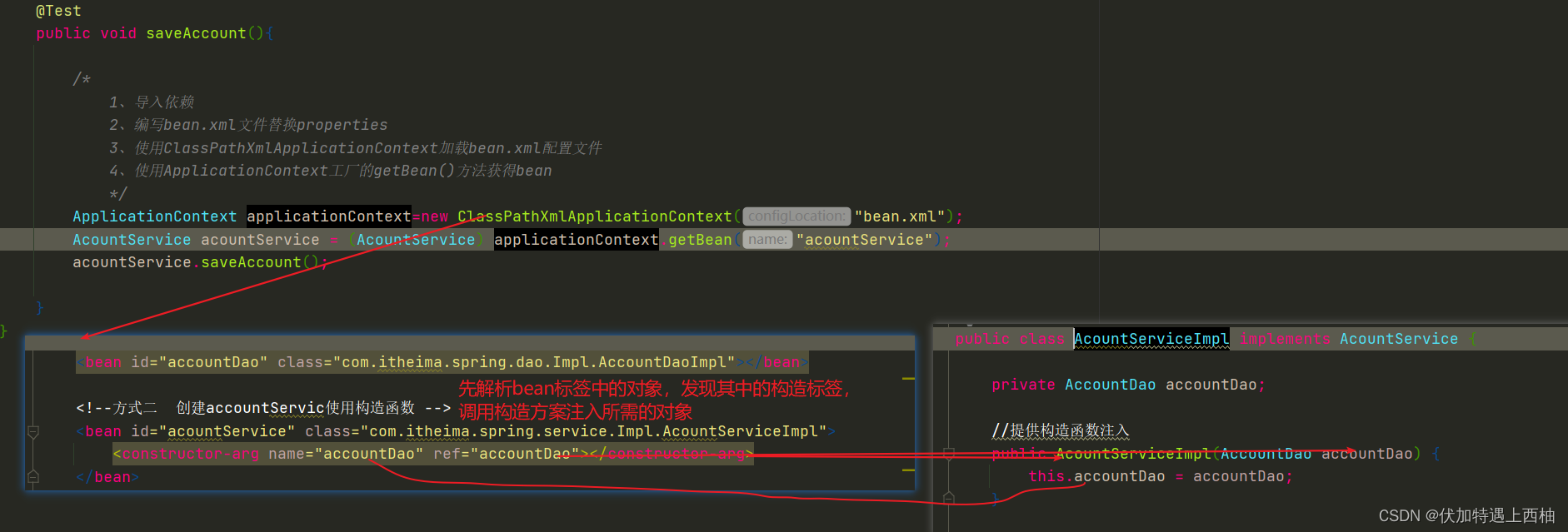
【2.3】构造函数注入小结
构造方式:
默认:
使用无参数构造方法,创建对象
set方式:
property 指定属性
name:按属性名
ref:指定注入bean的Id
构造函数:
constructor-arg:构造函数
name:按属性名
index:按下标注
type:按类型
3、依赖注入的简单配置【了解】
简单名称空间注入只是set方法注入和构造方法注入的简化方式,其本质是相同的
【1】P标签方式(set方法)(11)
【1.1】目标
p名称空间注入,就是set方法注入。其本质在于简化配置,
bean.xml中添加
空间名: xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
【1.2】实现
【1.2.1】创建项目
拷贝spring-day01-9bean-di-set创建spring-day01-11bean-di-p结构如下
【1.2.2】修改bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="acountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AcountServiceImpl" p:accountDao-ref="accountDao">
</bean>
</beans>
【1.2.3】ClientController测试
【2】C标签方式(构造函数)(12)
【2.1】目标
c名称空间注入,就是构造函数注入。其本质在于简化配置,
空间名: xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
【2.2】实现
【2.1.1】创建项目
拷贝spring-day01-10bean-di-construction创建spring-day01-12bean-di-c结构如下
【2.1.2】修改bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
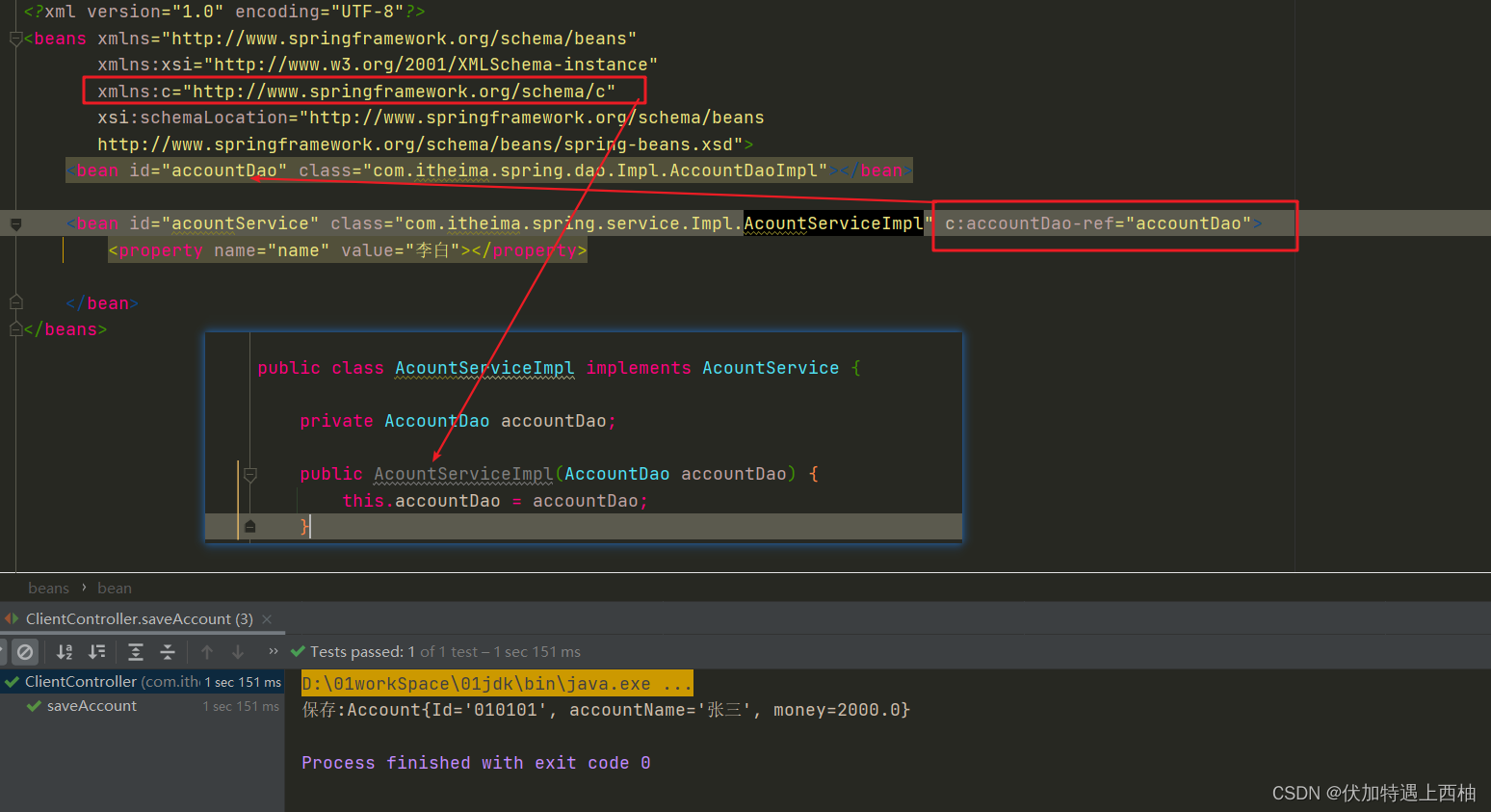
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.spring.dao.Impl.AccountDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="acountService" class="com.itheima.spring.service.Impl.AcountServiceImpl" c:accountDao-ref="accountDao">
</bean>
</beans>
【2.1.3】ClientController测试
【3】简单配置小结
P名称空间注入,就是set方法注入。其本质在于简化配置,
空间名:xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p
c名称空间注入,就是构造函数注入。其本质在于简化配置,
空间名: xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
4、复杂类型的注入(13)【了解】
我们知道了自定对象,及基础对象的注入方式,那么数组、List、Set、Map、Properties是怎么配置的呢?
【1】目标
给类中的复杂的属性注入数据,比如集合或者数组, 我们这里介绍注入数组、List、Set、Map、Properties。
【2】实现
【2.1】创建项目
拷贝spring-day01-12bean-di-c创建spring-day01-13bean-di-all结构如下
【2.2】创建Account
package com.itheima.spring.pojo;
import java.util.*;
/**
* @Description:账户实体类
*/
public class Account {
//账户编号
private String Id;
//账户所有者
private String accountName;
//账户余额
private Float money;
private String[] myStrs;
private List<String> myList;
private Set<String> mySet;
private Map<String, String> myMap;
private Properties myProps;
public Account() {
}
public String getId() {
return Id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
Id = id;
}
public String getAccountName() {
return accountName;
}
public void setAccountName(String accountName) {
this.accountName = accountName;
}
public Float getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(Float money) {
this.money = money;
}
public String[] getMyStrs() {
return myStrs;
}
public void setMyStrs(String[] myStrs) {
this.myStrs = myStrs;
}
public List<String> getMyList() {
return myList;
}
public void setMyList(List<String> myList) {
this.myList = myList;
}
public Set<String> getMySet() {
return mySet;
}
public void setMySet(Set<String> mySet) {
this.mySet = mySet;
}
public Map<String, String> getMyMap() {
return myMap;
}
public void setMyMap(Map<String, String> myMap) {
this.myMap = myMap;
}
public Properties getMyProps() {
return myProps;
}
public void setMyProps(Properties myProps) {
this.myProps = myProps;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Account{" +
"Id='" + Id + '\'' +
", accountName='" + accountName + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
", myStrs=" + Arrays.toString(myStrs) +
", myList=" + myList +
", mySet=" + mySet +
", myMap=" + myMap +
", myProps=" + myProps +
'}';
}
}
【2.3】编写bean.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="account" class="com.itheima.spring.pojo.Account">
<property name="id" value="1111"></property>
<property name="accountName" value="小王"></property>
<property name="money" value="2000"></property>
<!--
注入集合属性:
使用set方法注入集合属性:
array:一般用来设置数组
list:一般用来设置list集合
map:一般用来设置map集合
props:一般用来设置properties
-->
<property name="myStrs">
<array>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</array>
</property>
<property name="myList">
<list>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="mySet">
<set>
<value>AAA</value>
<value>BBB</value>
<value>CCC</value>
</set>
</property>
<property name="myMap">
<map>
<entry key="name1" value="AAA"></entry>
<entry key="name2" value="BBB"></entry>
<entry key="name3" value="CCC"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<property name="myProps">
<props>
<prop key="name1">AAA</prop>
<prop key="name2">BBB</prop>
<prop key="name3">CCC</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
【2.4】controller测试
public class ClientController {
@Test
public void createAccountTest(){
//加载配置文件
ApplicationContext applicationContext =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
//获得bean
Account account = (Account) applicationContext.getBean("account");
//打印结果
System.out.println("account的对象信息"+account.toString());
}
}
【运行结果】
account的对象信息Account{Id='1111', accountName='小王', money=2000.0, myStrs=[AAA, BBB, CCC],
myList=[AAA, BBB, CCC], mySet=[AAA, BBB, CCC],
myMap={name1=AAA, name2=BBB, name3=CCC}, myProps={name3=CCC, name2=BBB, name1=AAA}}
【3】复杂对象注入小结
使用set方法注入集合属性:
array:一般用来设置数组
list:一般用来设置list集合
map:一般用来设置map集合
props:一般用来设置properties
