【Java集合】Collection接口中的常用方法
Collection 接口
Collection 接口是 List、Set 和 Queue 接口的父接口,该接口里定义的方法 既可用于操作 Set 集合,也可用于操作 List 和 Queue 集合。
JDK不提供此接口的任何直接实现,而是提供更具体的子接口(如:Set和List)实现。
在 Java5 之前,Java 集合会丢失容器中所有对象的数据类型,把所有对象都 当成 Object 类型处理;从 JDK 5.0 增加了泛型以后,Java 集合可以记住容 器中对象的数据类型。
Collection接口的方法:
1、添加
add(Object obj)
addAll(Collection coll)
2、获取有效元素的个数
int size()
3、清空集合
void clear()
4、是否是空集合
boolean isEmpty()
5、是否包含某个元素
boolean contains(Object obj):是通过元素的equals方法来判断是否是同一个对象
boolean containsAll(Collection c):也是调用元素的equals方法来比较的。拿两个集合的元素挨个比较。
6、删除
boolean remove(Object obj) :通过元素的equals方法判断是否是要删除的那个元素。只会删除找到的第一个元素
boolean removeAll(Collection coll):取当前集合的差集
7、取两个集合的交集
boolean retainAll(Collection c):把交集的结果存在当前集合中,不 影响c
8、集合是否相等
boolean equals(Object obj)
9、转成对象数组
Object[] toArray()
10、获取集合对象的哈希值
hashCode()
11、遍历
iterator():返回迭代器对象,用于集合遍历
=========================================================================
举例;
public class CollectionTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
//add(Object e):将元素e添加到集合collection中
collection.add("AA");
collection.add("AA");
collection.add("BB");
collection.add(123);//自动装箱
collection.add(new Date());
//size():获取添加的元素的个数
System.out.println(collection.size());
//addAll(Collection collection1):将collection集合中的元素添加到当前的集合中
Collection collection1 = new ArrayList();
collection1.add(111);
collection1.add("CC");
collection.addAll(collection1);
System.out.println(collection.size());
System.out.println(collection);
//clear():清空集合元素
collection.clear();
//isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}
运行结果如下所示
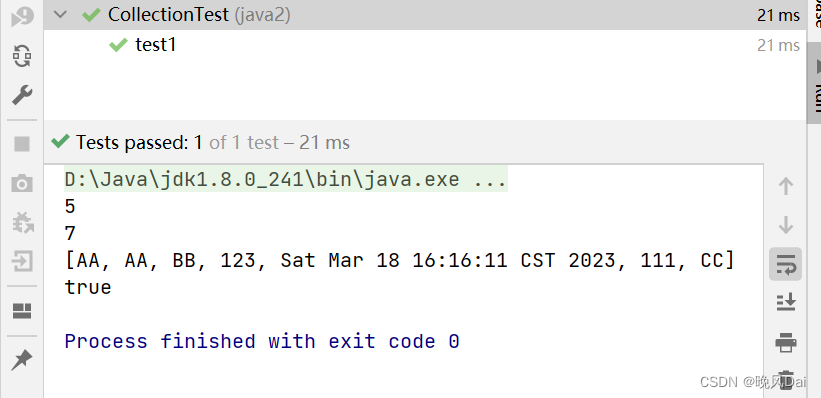
我们将collection.clear();注释。运行结果如下

例2
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
/**
* Collection接口中声明的方法的测试
*/
public class CollectionTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new String("Tom"));
collection.add(false);
Person p = new Person("Jerry", 20);
collection.add(p);
//contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否包含obj
boolean contains = collection.contains(123);
System.out.println(contains);//true
System.out.println(collection.contains(new String("Tom")));//true
System.out.println(collection.contains(p));//true
}
}
Person类
import java.util.Objects;
public class Person {
private String Name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
Name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"Name='" + Name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}运行:
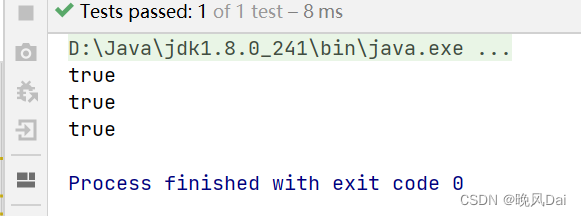
运行结果为true,说明调用了equals()进行判断
我们添加collection.add(new Person("Tom",20));再运行System.out.println(collection.contains(new Person("Tom", 20)));结果就变成了false
我们需要重写Person类的equals()
import java.util.Objects;
public class Person {
private String Name;
private int age;
public Person() {
super();
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
Name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return Name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
Name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"Name='" + Name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Person person = (Person) o;
return age == person.age && Name.equals(person.Name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(Name, age);
}
}
运行:

我们在来看几个方法
代码如下:
package com.dai.java;
import org.junit.Test;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
public class CollectionTest {
@Test
public void test1(){
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new String("Tom"));
collection.add(false);
Person p = new Person("Jerry", 20);
collection.add(p);
collection.add(new Person("Tom",20));
//1.contains(Object obj):判断当前集合中是否包含obj
//我们再判断时辉调用obj对象的equals()
boolean contains = collection.contains(123);
System.out.println(contains);//true
System.out.println(collection.contains(new String("Tom")));//true
System.out.println(collection.contains(p));//true
System.out.println(collection.contains(new Person("Tom", 20)));//false
//变成true,重写equals()
//2.containsAll(Collection collection):判断形参collection中所有元素是否都存在与当前集合中
Collection collection1 = Arrays.asList(123,456);
collection.containsAll(collection1);
}
}运行结果:
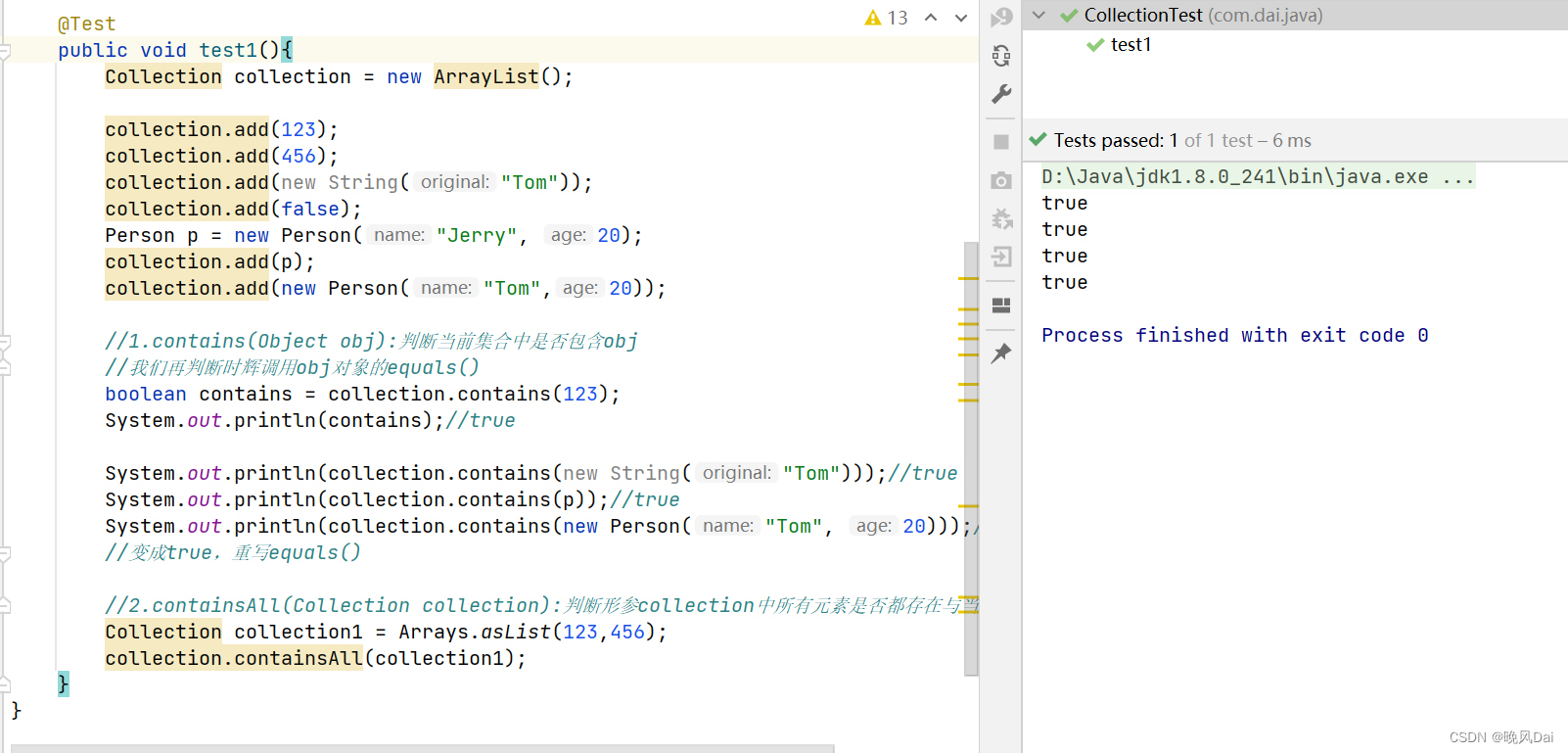
再来看一下删除
boolean remove(Object obj) :通过元素的equals方法判断是否是要删除的那个元素。只会删除找到的第一个元素
@Test
public void test2(){
//3.remove(Object obj):从当前集合中移除obj元素
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
collection.add(new String("Tom"));
collection.add(false);
collection.remove(123);
System.out.println(collection);
collection.remove(new Person("Jerry",20));
System.out.println(collection);
}运行结果如下:
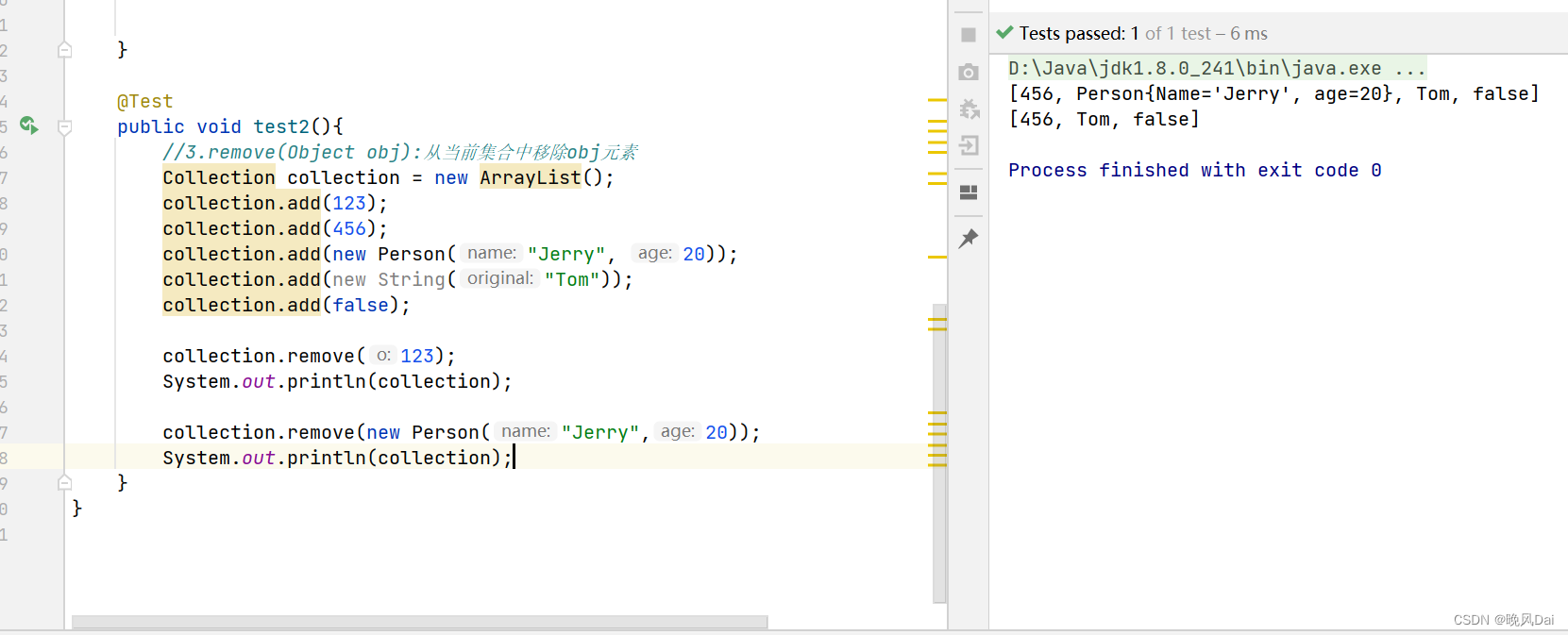
boolean removeAll(Collection coll):取当前集合的差集
@Test
public void test2(){
//3.remove(Object obj):从当前集合中移除obj元素
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
collection.add(new String("Tom"));
collection.add(false);
// collection.remove(123);
// System.out.println(collection);
collection.remove(new Person("Jerry",20));
System.out.println(collection);
//removeAll(Collection coll1):从当前集合中移除coll1中所有的元素
Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,4567);
collection.removeAll(coll1);
System.out.println(collection);
}
}运行结果如下:

retainAll(Collection coll1):交集:获取当前集合coll1集合的交集,并返回给当前集合
@Test
public void test3(){
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
collection.add(new String("Tom"));
collection.add(false);
//5.retainAll(Collection coll1):交集:获取当前集合coll1集合的交集,并返回给当前集合
Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456,789);
collection.retainAll(coll1);
System.out.println(collection);
}运行结果:

集合是否相等 :boolean equals(Object obj):要想返回true,需要当前集合和形参集合的元素都相同
@Test
public void test3(){
Collection collection = new ArrayList();
collection.add(123);
collection.add(456);
collection.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
collection.add(new String("Tom"));
collection.add(false);
//5.retainAll(Collection coll1):交集:获取当前集合coll1集合的交集,并返回给当前集合
// Collection coll1 = Arrays.asList(123,456,789);
// collection.retainAll(coll1);
// System.out.println(collection);
//6.equals(Object obj):
Collection coll1 = new ArrayList();
coll1.add(123);
coll1.add(456);
coll1.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll1.add(new String("Tom"));
coll1.add(false);
System.out.println(collection.equals(coll1));
}运行结果:

如果我们将123和456调换一下位置:

获取集合对象的哈希值 hashCode()
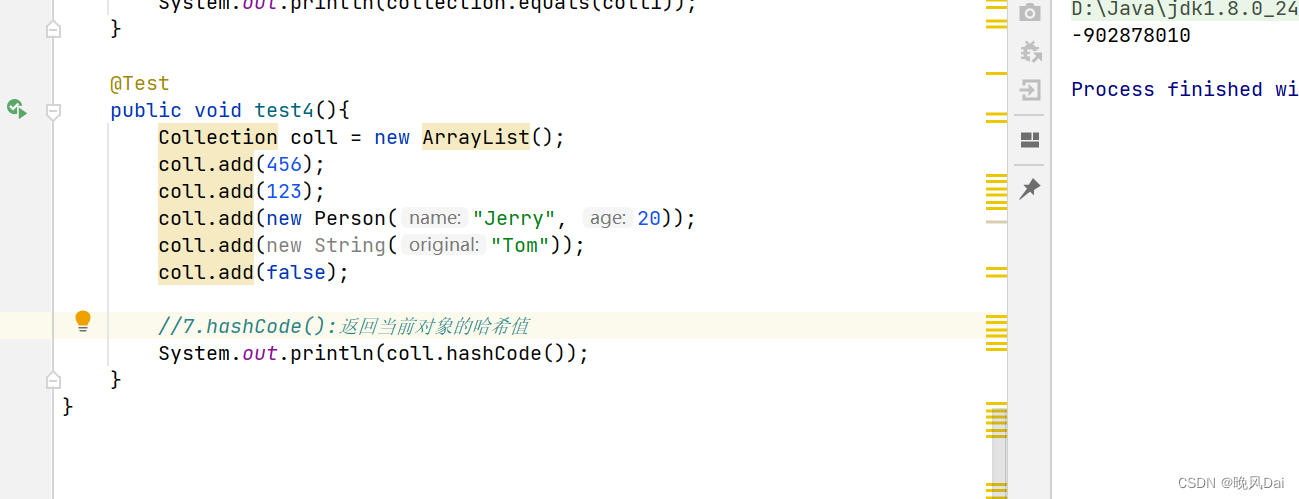
@Test
public void test4(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(456);
coll.add(123);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//7.hashCode():返回当前对象的哈希值
System.out.println(coll.hashCode());
}运行结果:
转成对象数组Object[] toArray()
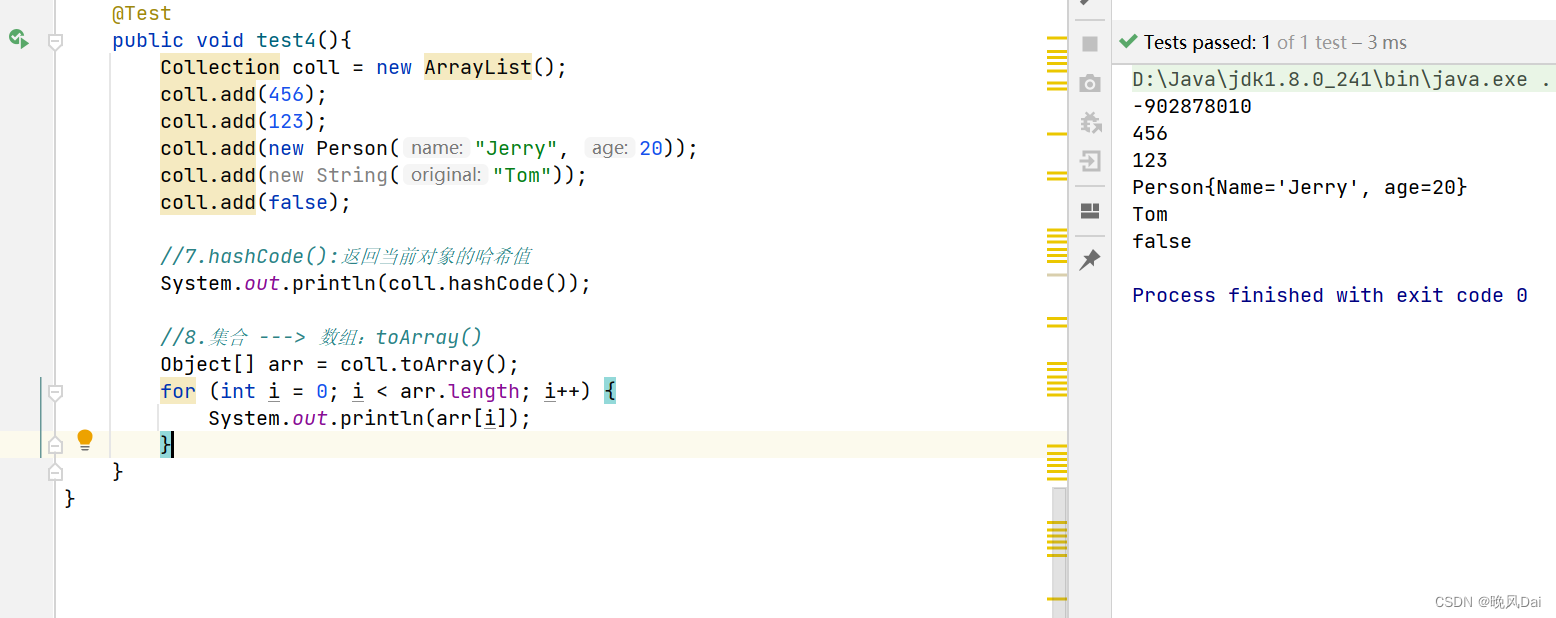
@Test
public void test4(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(456);
coll.add(123);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//7.hashCode():返回当前对象的哈希值
System.out.println(coll.hashCode());
//8.集合 ---> 数组:toArray()
Object[] arr = coll.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}运行结果如下:
拓展:数组 ---> 集合:调用Arrays类的静态方法asList()
@Test
public void test4(){
Collection coll = new ArrayList();
coll.add(456);
coll.add(123);
coll.add(new Person("Jerry", 20));
coll.add(new String("Tom"));
coll.add(false);
//7.hashCode():返回当前对象的哈希值
System.out.println(coll.hashCode());
//8.集合 ---> 数组:toArray()
Object[] arr = coll.toArray();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
//拓展:数组 ---> 集合:调用Arrays类的静态方法asList()
List<String> list = Arrays.asList(new String[]{"AA", "BB", "CC"});
System.out.println(list);
}
运行结果:

=========================================================================
结论: 向Collection接口的实现类的对象中添加数据obj时,要求obj所在类重写equals()
感谢观看!!!
