双非本科准备秋招(18.1)—— 力扣二叉树
1、404. 左叶子之和
方法一:
可以在父节点判断一下,如果左子树不为null,并且左子树没有左右子树,说明这是个左叶子节点。
class Solution {
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return 0;
int LV = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.left);
int RV = sumOfLeftLeaves(root.right);
int t = 0;
if (root.left != null && root.left.left == null && root.left.right == null) {
t = root.left.val;
}
return t+LV+RV;
}
}方法二,找bug:
一开始我用的递归,用布尔值传值,于是我写了如下代码。
class Solution {
static int ans = 0;
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
preOrder(root, false);
return ans;
}
static void preOrder(TreeNode root, boolean isLeft){
if(root == null) return;
if(isLeft && root.left == null && root.right == null){
ans += root.val;
return;
}
preOrder(root.left, true);
preOrder(root.right, false);
}
}这个测试用例竟然会输出24。
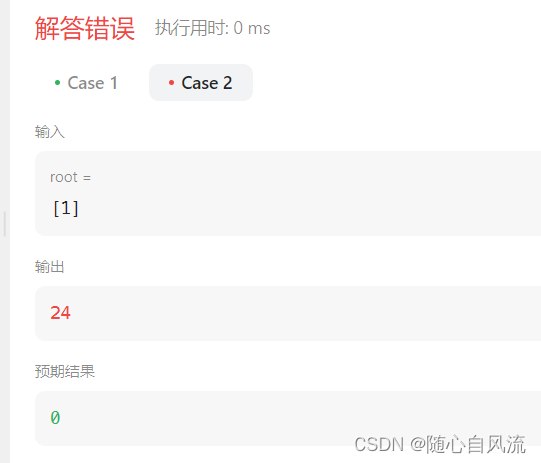
想了一天,晚上突然明白了,测试用例1答案是24,测试用例2答案应该是0,但是为什么是24呢?因为测试用例2答案在第一个基础上,也就是24+0 = 24
而我的ans变量是static的,也就是所有实例共享的,把代码改成下面这样就过了。
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
public int sumOfLeftLeaves(TreeNode root) {
preOrder(root, false);
return ans;
}
void preOrder(TreeNode root, boolean isLeft){
if(root == null) return;
if(isLeft && root.left == null && root.right == null){
ans += root.val;
return;
}
preOrder(root.left, true);
preOrder(root.right, false);
}
}
2、513. 找树左下角的值
这个题应该挺好想的,左下角是最底层,最左边的值,用层序遍历就很好实现,遍历到最后一层记录第一个值就是答案。
class Solution {
public int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode root) {
//层序遍历 最后一层 第一个节点
LinkedList<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<>();
int ans = 0;
if(root == null) return 0;
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
int len = q.size();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++){
TreeNode t = q.poll();
if(i == 0) ans = t.val;
if(t.left != null){
q.offer(t.left);
}
if(t.right != null){
q.offer(t.right);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}3、112. 路径总和
跟昨天的输出路径题一个套路(257. 二叉树的所有路径),核心还是判断是不是叶子节点,当左右子树都为null并且传的值等于target的时候说明找到了,为了保证不出现空指针异常,每次递归都要判断一下。
class Solution {
boolean f = false;
public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if(root == null) return f;
preOrder(root, targetSum, 0);
return f;
}
void preOrder(TreeNode root, int target, int n){
if(f) return;
n += root.val;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && n == target){
f = true;
return;
}
if(root != null && root.left != null) preOrder(root.left, target, n);
if(root != null && root.right != null) preOrder(root.right, target, n);
}
}4、654. 最大二叉树
跟昨天做的根据前序中序构造树一个思路,代码都很像,for循环找到最大值,然后根据最大值位置划分左右子树,递归地遍历左右子树,左子树范围0——index,右子树范围index+1——length。
但是要注意判断一下index是否是边界,也就是为0或length-1的时候,左子树或右子树直接就是null了。
class Solution {
public TreeNode constructMaximumBinaryTree(int[] nums) {
int r = -1, index = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i] > r){
r = nums[i];
index = i;
}
}
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(r);
if(index == 0) root.left = null;
else root.left = constructMaximumBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, 0, index));
if(index == nums.length-1) root.right = null;
else root.right = constructMaximumBinaryTree(Arrays.copyOfRange(nums, index+1, nums.length));
return root;
}
}5、617. 合并二叉树
核心在于如何同步遍历两个二叉树。
每次把结果都加到root1这棵树上就好,节省空间。
class Solution {
public TreeNode mergeTrees(TreeNode root1, TreeNode root2) {
if(root1 == null) return root2;
if(root2 == null) return root1;
root1.val += root2.val;
root1.left = mergeTrees(root1.left, root2.left);
root1.right = mergeTrees(root1.right, root2.right);
return root1;
}
}