Python初学者学习记录——python基础综合案例:数据可视化——动态柱状图
一、案例效果
通过pyecharts可以实现数据的动态显示,直观的感受1960~2019年世界各国GDP的变化趋势

二、通过Bar构建基础柱状图

反转x轴和y轴

标签数值在右侧
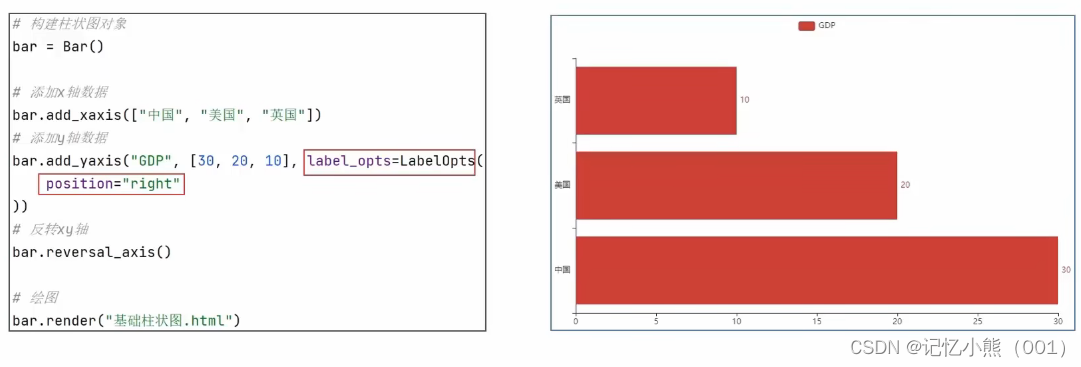
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from pyecharts.options import LabelOpts
# 构建柱状图对象
bar = Bar()
# 添加x轴数据
bar.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "英国"])
# 添加y轴数据
bar.add_yaxis("GDP", [30, 20, 10], label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))
#反转x轴和y轴
bar.reversal_axis()
# 绘图
bar.render("基础柱状图.html") 
三、基础时间线柱状图的绘制
1、Timeline()—时间线
柱状图描述的是分类数据,回答的是每一个分类中【有多少?】这个问题,这是柱状图的主要特点,同时柱状图很难动态的描述一个趋势性的数据,这里pyecharts为我们提供了一种解决方案——时间线
如果说一个Bar、Line对象是一张图表的话,时间线就是创建一个一维的x轴,轴上的每一个点就是一个图表对象

2、创建时间线

3、自动播放

4、时间线设置主题

from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
bar1 = Bar()
bar1.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "英国"])
bar1.add_yaxis("GDP", [30, 20, 10], label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))
bar1.reversal_axis()
bar2 = Bar()
bar2.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "英国"])
bar2.add_yaxis("GDP", [50, 40, 30], label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))
bar2.reversal_axis()
bar3 = Bar()
bar3.add_xaxis(["中国", "美国", "英国"])
bar3.add_yaxis("GDP", [70, 60, 40], label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))
bar3.reversal_axis()
# 构建时间线
timeline = Timeline({"theme": ThemeType.MACARONS})
# 在时间线内部添加柱状图对象
timeline.add(bar1, "点1")
timeline.add(bar2, "点2")
timeline.add(bar3, "点3")
# 自动播放设置
timeline.add_schema(
play_interval=1000, # 自动播放的时间间隔,单位毫秒
is_timeline_show=True, # 是否在自动播放的时候,显示时间线
is_auto_play=True, # 是否自动播放
is_loop_play=True # 是否循环自动播放
)
# 绘图是用时间线对象绘图,而不是bar对象
timeline.render("基础时间线柱状图.html") 
四、动态GDP柱状图的绘制
1、列表的sort方法
在前面我们学习过sorted函数,可以对数据容器进行排序。
在后面的数据处理中,我们需要对列表进行排序,并指定排序规则,sorted函数就无法完成了。所以我们补充学习列表的sort方法。
使用方法:
列表.sort(key=选择排序依据的函数,reverse=True|False)
· 参数key,是要求传入一个函数,表示将列表的每一个元素都传入函数中,返回排序的依据
· 参数reverse,是否反转排序结果,True表示降序,False表示升序

# 准备列表
my_list = [["a", 33], ["b", 55], ["c", 11]]
# 排序,基于带名函数
# def choose_sort_key(element):
# return element[1]
# my_list.sort(key=choose_sort_key, reverse=True)
# print(my_list)
# 排序,基于lambda匿名函数
my_list.sort(key=lambda element: element[1], reverse=True)
print(my_list) 
2、需求分析

3、处理数据

4、绘图
from pyecharts.charts import Bar, Timeline
from pyecharts.options import *
from pyecharts.globals import ThemeType
# 读取数据
f = open("D:/1960-2019全球GDP数据.csv", "r", encoding="GB2312")
data_lines = f.readlines()
# 关闭文件
f.close()
# 删除第一条数据
data_lines.pop(0)
# 将数据转换为字典存储,格式为:
# {年份: [[国家, GDP],[国家, GDP],……], 年份: [[国家, GDP],[国家, GDP],……],……}
# 先定义一个字典对象
data_dict = dict()
for line in data_lines:
year = int(line.split(",")[0]) # 年份
country = line.split(",")[1] # 国家
GDP = float(line.split(",")[2]) # GDP数据
# 如何判断字典里面有没有指定的key呢?
try:
data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])
except KeyError:
data_dict[year]=[]
data_dict[year].append([country, GDP])
# 创建时间线对象
timeline = Timeline({"theme": ThemeType.LIGHT})
# 排序年份
sorted_year_list = sorted(data_dict.keys())
for year in sorted_year_list:
data_dict[year].sort(key=lambda element: element[1], reverse=True)
# 取出本年份前八名的国家
year_data = data_dict[year][:8]
x_data = []
y_data = []
for country_gdp in year_data:
x_data.append(country_gdp[0]) # x轴添加国家
y_data.append(country_gdp[1] / 100000000) # y轴添加gdp数据
# 构建柱状图对象
bar = Bar()
x_data.reverse()
y_data.reverse()
bar.add_xaxis(x_data)
bar.add_yaxis("GDP(亿)", y_data, label_opts=LabelOpts(position="right"))
# 反转x轴和y轴
bar.reversal_axis()
# 设置每一年的图表标题
bar.set_global_opts(
title_opts=TitleOpts(title=f"{year}年全球前8名GDP数据"),
toolbox_opts=ToolboxOpts(is_show=True)
)
timeline.add(bar, str(year))
# 设置时间线自动播放
timeline.add_schema(
play_interval=500,
is_timeline_show=True,
is_auto_play=True,
is_loop_play=False
)
# 绘图
timeline.render("1960-2019年全球GDP前8国家.html")
生成的图表链接(PC端打开):
http://localhost:63342/pythonProject/1960-2019%E5%B9%B4%E5%85%A8%E7%90%83GDP%E5%89%8D8%E5%9B%BD%E5%AE%B6.html?_ijt=e2vorgbc1leno4grnck9tsdg21&_ij_reload=RELOAD_ON_SAVE

