C语言实现memcpy、memmove库函数
目录
- 引言
- 一、库函数介绍
- 二、库函数详解
- 三、源码实现
- 1.memcpy源码实现
- 2.memmove源码实现
- 四、测试
- 1.memcpy函数
- 2.memmove函数
- 五、源码
- 1.memcpy源码
- 2.memmove源码
- 六、参考文献
引言
关于memcpy和memmove这两个函数,不论是算法竞赛还是找工作面试笔试,对这两个函数必然是经常都会用到,而且面试的时候很有可能会让你把代码复现出来,也许会问你这两个库函数的区别,这都是你自学才能知道的,所以也是很能体现你实力的一种,所以说很重要,话不多说了,那就开始介绍吧。
一、库函数介绍
#include <cstring> // CPP版头文件
#include <string.h> //C版头文件
void *memcpy(void *dest, const void *src, size_t count);
void *memmove(void *dest, const void *src, size_t count);
功能:把从src开始的count个字节拷贝到以dest开始的内存区域中,返回dest(可进行链式嵌套调用)
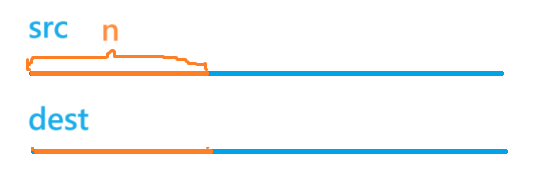
区别: memcpy要求在使用时这两块区域不能有重叠,也就是不能出现自拷贝的情况,而memmove则保证在有重叠的情况下,结果是正确的。
二、库函数详解
memcpy:强转为char*,解引用从前到后依次赋值count次。
但是遇到如下图的情况:在src赋值的同时会把自己原本的值给覆盖掉,就会出现与使用者本意不相符的情况发生,所以memcpy不允许这两块区域重叠。

但如果是如下图这种情况:dest会跟本意一样,只不过src有些变了,但目的还是dest所以这个是没关系的,所以这种情况不考虑,因为设计者也是这么写的。

memmove:遇到有可能发生重叠的情况,从后往前赋值,就不会出错了,可以看图想想。

三、源码实现
这里值得注意的就是*d++这块,++优先级高,所以先d++,结果为d,然后*d,语句结束后d才++。
1.memcpy源码实现
void* memcpy(void* dest, const void* src, size_t count)
{
if (dest == NULL || src == NULL || count == 0) return dest;
char* d = (char*)dest;
char* s = (char*)src;
while (count--)
{
*d++ = *s++;
}
return dest;
}
2.memmove源码实现
void* memmove(void* dest, const void* src, size_t count)
{
if (dest == NULL || src == NULL || count == 0) return dest;
char* d = (char*)dest;
char* s = (char*)src;
if (dest < src)
{
while (count--)
{
*d++ = *s++;
}
}
else
{
d += count;
s += count;
while (count--) // 从后往前赋值
{
*--d = *--s; // 注意这里先减减
}
}
return dest;
}
四、测试
1.memcpy函数
int main()
{
const size_t size = 20;
int a[size] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int b[size];
memcpy(b, a, 10 * sizeof(int)); //注意这里是字节数
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) printf("%d ", b[i]);
return 0;
}

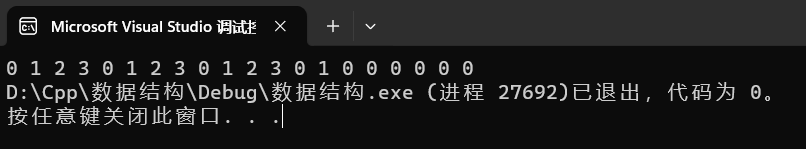
可以看出如下的例子:说明memcpy不能自拷贝
int main()
{
const size_t size = 20;
int a[size] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int b[size];
memcpy(a+4, a, 10 * sizeof(int)); //注意这里是字节数
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) printf("%d ", a[i]);
return 0;
}
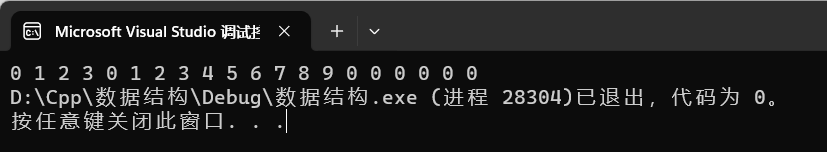
2.memmove函数
如下例子可以看出与memcpy的区别
int main()
{
const size_t size = 20;
int a[size] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int b[size];
memmove(a+4, a, 10 * sizeof(int)); //自拷贝
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) printf("%d ", a[i]);
return 0;
}
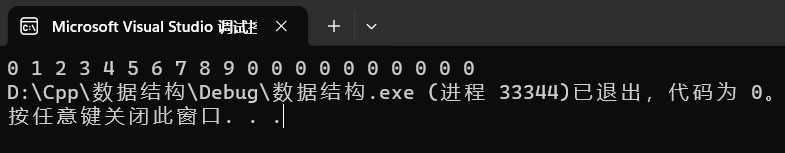
正常例子:
int main()
{
const size_t size = 20;
int a[size] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 };
int b[size] = {0};
memmove(b, a, 10 * sizeof(int)); //注意这里是字节数
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) printf("%d ", b[i]);
return 0;
}
五、源码
1.memcpy源码
/***
*memcpy.c - contains memcpy routine
*Purpose:
* memcpy() copies a source memory buffer to a destination buffer.
* Overlapping buffers are not treated specially, so propogation may occur.
*
**********/
#include <cruntime.h>
#include <string.h>
#pragma function(memcpy)
/***
*memcpy - Copy source buffer to destination buffer
*
*Purpose:
* memcpy() copies a source memory buffer to a destination memory buffer.
* This routine does NOT recognize overlapping buffers, and thus can lead
* to propogation.
*
* For cases where propogation must be avoided, memmove() must be used.
*
*Entry:
* void *dst = pointer to destination buffer
* const void *src = pointer to source buffer
* size_t count = number of bytes to copy
*
*Exit:
* Returns a pointer to the destination buffer
*
*Exceptions:
*******************************************************************************/
void * __cdecl memcpy (
void * dst,
const void * src,
size_t count
)
{
void * ret = dst;
#if defined (_M_IA64)
{
__declspec(dllimport)
void RtlCopyMemory( void *, const void *, size_t count );
RtlCopyMemory( dst, src, count );
}
#else /* defined (_M_IA64) */
/*
* copy from lower addresses to higher addresses
*/
while (count--) {
*(char *)dst = *(char *)src;
dst = (char *)dst + 1;
src = (char *)src + 1;
}
#endif /* defined (_M_IA64) */
return(ret);
}
2.memmove源码
/***
*memmove - Copy source buffer to destination buffer
*
*Purpose:
* memmove() copies a source memory buffer to a destination memory buffer.
* This routine recognize overlapping buffers to avoid propogation.
* For cases where propogation is not a problem, memcpy() can be used.
*
* Algorithm:
*******************************************************************************/
void* memmove(void* dest, void* source, size_t count)
{
void* ret = dest;
if (dest <= source || dest >= (source + count))
{
//Non-Overlapping Buffers
//copy from lower addresses to higher addresses
while (count --)
*dest++ = *source++;
}
else
{
//Overlapping Buffers
//copy from higher addresses to lower addresses
dest += count - 1;
source += count - 1;
while (count--)
*dest-- = *source--;l
}
return ret;
}
六、参考文献
51CTO博客:C语言库函数 Memcpy 和 Memmove 的区别,你知道多少?
CSND博客:memmove和memcpy的区别
