C++_day6:继承、多态
1.封装一个动物的基类,类中有私有成员:姓名,颜色,指针成员年纪
再封装一个狗这样类,共有继承于动物类,自己拓展的私有成员有:指针成员:腿的个数(整型 int count),共有成员函数:会叫:void speak()
要求:分别完成基类和派生类中的:构造函数、析构函数、拷贝构造函数、拷贝赋值函数
程序代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//封装一个动物的基类
class Animal
{
private:
string name;//名字
string color;//颜色
int *age;//年龄(指针)
public:
//无参构造函数
Animal()
{}
//有参构造函数
Animal(string name,string color,int age):name(name),color(color),age(new int(age))
{
cout << "父类::有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Animal(const Animal &other):name(other.name),color(other.color),age(new int(*other.age))
{
cout << "父类::拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Animal &operator=(const Animal &other)
{
if( this != &other )
{
name = other.name;
color = other.color;
age = new int(*other.age);
}
cout << "父类::拷贝赋值函数" << endl;
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~Animal()
{
delete age;
age=nullptr;
cout << "父类::析构函数" << endl;
}
};
//封装一个狗 类 共有继承 动物类
class Dog:public Animal
{
private:
int *count;//狗腿个数 (指针)
public:
void speak()
{
cout << "汪汪汪" << endl;
}
//无参构造函数
Dog()
{
cout << "子类::无参构造函数" << endl;
}
//有参构造函数
Dog(string name,string color,int age,int count):Animal(name,color,age),count(new int(count))
{
cout << "子类::有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Dog(const Dog &other):Animal(other),count(new int(*other.count))
{
cout << "子类::拷贝构造函数" << endl;
}
//拷贝赋值函数
Dog &operator=(const Dog &other)
{
if( this != &other )
{
Animal::operator=(other);//父类的拷贝赋值函数
count = new int(*other.count);
}
cout << "子类::拷贝赋值函数" << endl;
return *this;
}
//析构函数
~Dog()
{
delete count;
count = nullptr;
cout << "子类::析构函数" << endl;
}
};
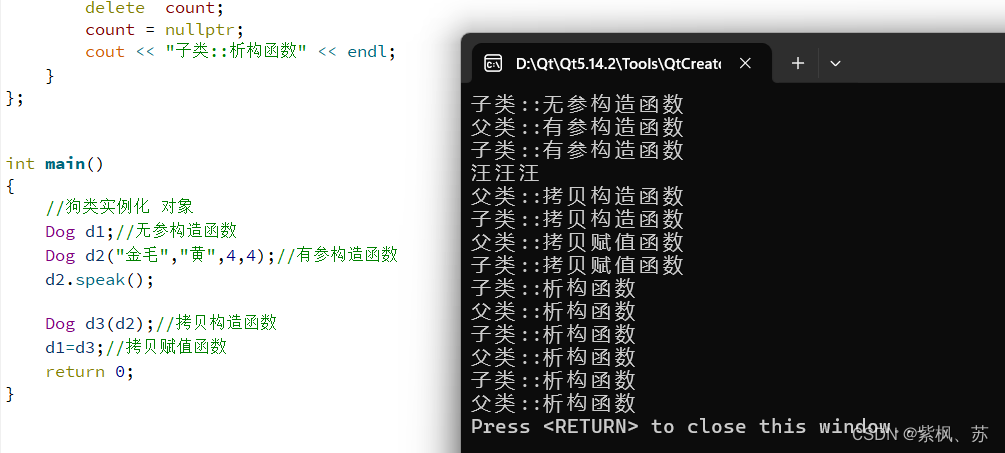
int main()
{
//狗类实例化 对象
Dog d1;//无参构造函数
Dog d2("金毛","黄",4,4);//有参构造函数
d2.speak();
Dog d3(d2);//拷贝构造函数
d1=d3;//拷贝赋值函数
return 0;
}运行结果:
2.以下是一个简单的比喻,将多态概念与生活中的实际情况相联系:
比喻:动物园的讲解员和动物表演
想象一下你去了一家动物园,看到了许多不同种类的动物,如狮子、大象、猴子等。现在,动物园里有一位讲解员,他会为每种动物表演做简单的介绍。
在这个场景中,我们可以将动物比作是不同的类,而每种动物表演则是类中的函数。而讲解员则是一个基类,他可以根据每种动物的特点和表演,进行相应的介绍。
具体过程如下:
定义一个基类 Animal,其中有一个虛函数perform(),用于在子类中实现不同的表演行为。
程序代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//封装 动物 类
class Animal
{
private:
string name;//名字
int age;//年龄
public:
//无参构造函数
Animal()
{}
//有参构造函数
Animal(string name,int age):name(name),age(age)
{
cout << "Animal::有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//虚表演函数
virtual void perform()=0;
//虚析构函数
virtual ~Animal()
{
cout << "Animal::析构函数" << endl;
}
void show()
{
cout << "age = " << age << endl;
}
};
//封装 虎子 类
class Tiger:public Animal
{
private:
string color;//颜色
public:
//无参构造函数
Tiger(){}
//有参构造函数
Tiger(string name,int age,string color):Animal(name,age),color(color)
{
cout << "Tiger::有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//表演行为
void perform()
{
cout << "Tiger::钻火圈" << endl;
}
//析构函数
~Tiger()
{
cout << "Tiger::析构函数" << endl;
}
};
//封装 猴 类 共有继承 动物类
class Monkey:public Animal
{
private:
string color;//颜色
public:
//无参构造函数
Monkey(){}
//有参构造函数
Monkey(string name,int age,string color):Animal(name,age),color(color)
{
cout << "Monkey::有参构造函数" << endl;
}
//表演行为
void perform()
{
cout << "Monkey::套圈" << endl;
}
//析构函数
~Monkey()
{
cout << "Monkey::析构函数" << endl;
}
};
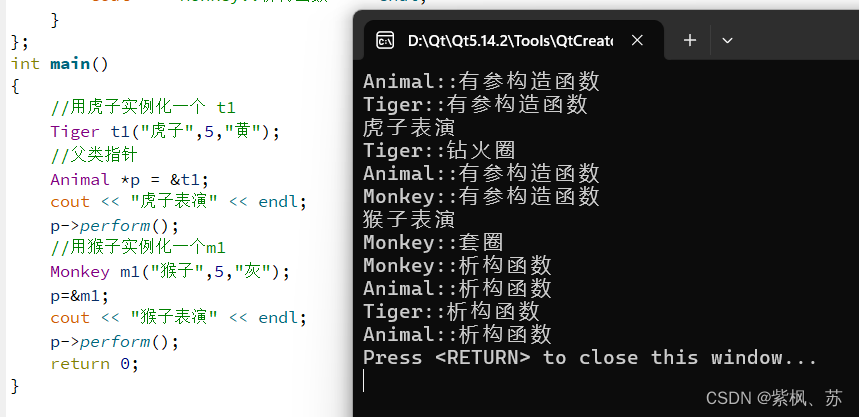
int main()
{
//用虎子实例化一个 t1
Tiger t1("虎子",5,"黄");
//父类指针
Animal *p = &t1;
cout << "虎子表演" << endl;
p->perform();
//用猴子实例化一个m1
Monkey m1("猴子",5,"灰");
p=&m1;
cout << "猴子表演" << endl;
p->perform();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
流程图:

