CSS系列之Float浮动(二)
一、传统网页布局
网页布局的本质:用 CSS 来摆放盒子,把盒子摆放到相应位置。CSS 提供了三种传统布局方式(这里指的只是传统布局,其实还有一些特殊高级的布局方式):
- 标准流
- 浮动
- 定位
1、所谓的标准流:就是标签按照规定好的默认方式排列。
- 块级元素会独占一行,从上向下顺序排列。
- 行内元素会按照顺序,从左到右顺序排列,碰到父元素边缘则自动换行。
2、所谓的定位,可以看一下我的这篇文章,是利用Position属性来控制盒子在文档中位置:CSS之Position定位(一)-CSDN博客
3、为什么需要浮动:因为浮动可以改变元素标签默认的排列方式。这句话不好直观理解,我们下面将结合代码和案例做进一步的详细说明。
二、什么是浮动
float 属性用于创建浮动框,将其移动到一边,直到左边缘或右边缘触及包含块或另一个浮动框的边缘。
选择器 { float: 属性值;}
| 属性值 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| none | 元素不浮动(默认值) |
| left | 元素向左浮动 |
| right | 元素向右浮动 |
代码案例欣赏:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
/* 浮动的标签 顶对齐 */
/* 浮动: 在一行排列, 宽高生效 -- 浮动后的标签具备行内块特点 */
.one {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
float: left;
margin-top: 50px;
}
.two {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
float: left;
/* 因为有浮动, 不能生效 - 盒子无法水平居中 */
margin: 0 auto;
}
.three {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: orange;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="one">one</div>
<div class="two">two</div>
<div class="three">three</div>
</body>
</html>
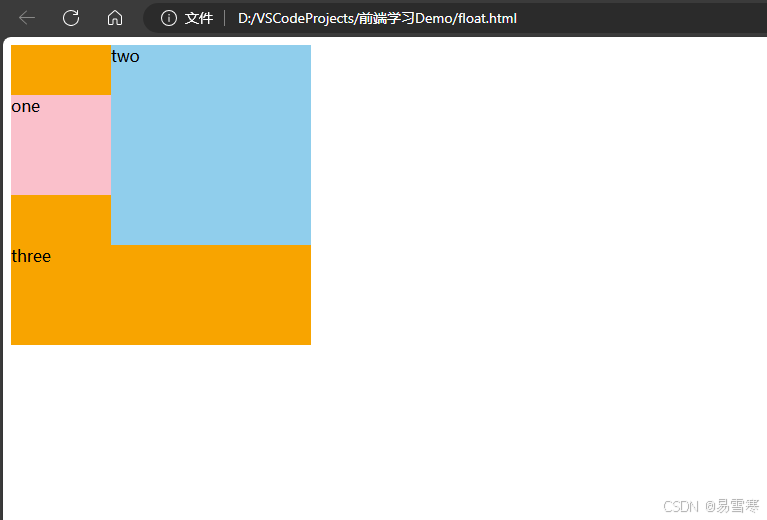
效果如下:可以看到one和two脱离文档往左浮动,three是一个文档流的布局
三、浮动特性(重难点)
加了浮动之后的元素,会具有很多特性,需要我们掌握。
- 浮动元素会脱离标准流(脱标)
- 浮动的元素会一行内显示并且元素顶部对齐
- 浮动的元素会具有行内块元素的特性
1、浮动元素会脱离标准流
脱离标准普通流的控制移动到指定位置(俗称脱标),浮动的盒子不再保留原先的位置。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动特性1</title>
<style>
/* 设置了浮动(float)的元素会:
1.脱离标准普通流的控制(浮)移动到指定位置(动)。
2.浮动的盒子不再保留原先的位置 */
.box1 {
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.box2 {
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
background-color: gray;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">浮动的盒子</div>
<div class="box2">标准流的盒子</div>
</body>
</html>
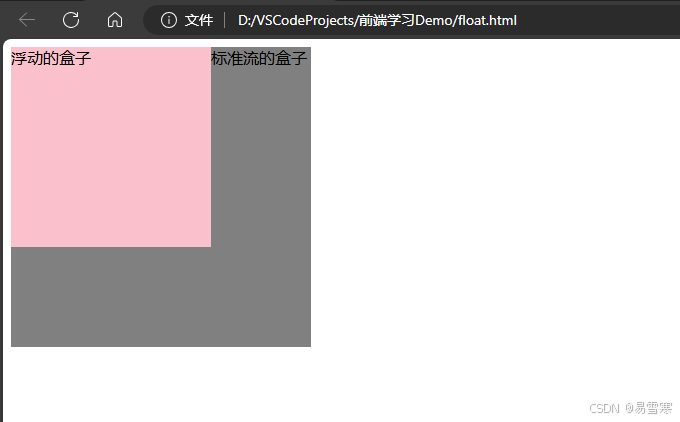
效果如下:
2、浮动的元素会一行内显示并且元素顶部对齐
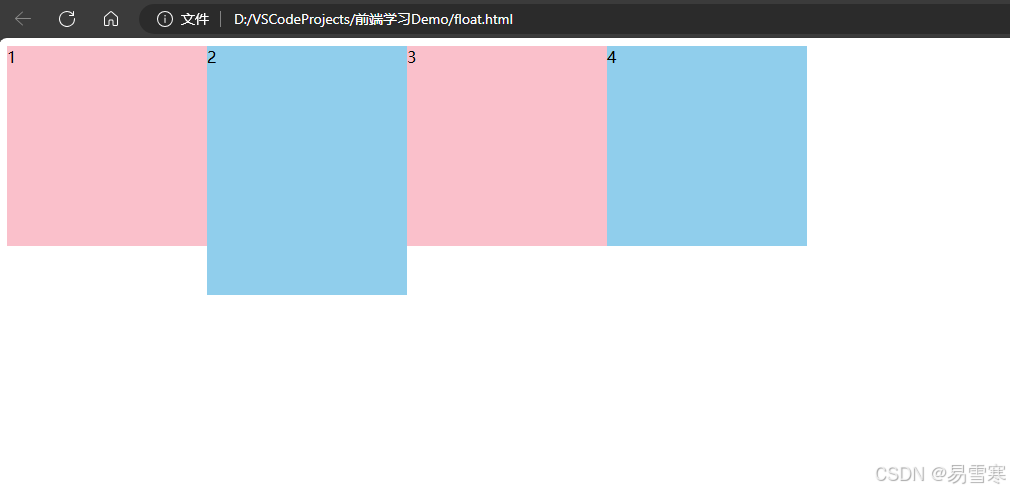
如果多个盒子都设置了浮动,则它们会按照属性值一行内显示并且顶端对齐排列。浮动的元素是互相贴靠在一起的(不会有缝隙),如果父级宽度装不下这些浮动的盒子,多出的盒子会另起一行对齐。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动元素特性-浮动元素一行显示</title>
<style>
div {
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.two {
background-color: skyblue;
height: 249px;
}
.four {
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div>1</div>
<div class="two">2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div class="four">4</div>
</body>
</html>
效果如下:
3、浮动的元素会具有行内块元素的特性
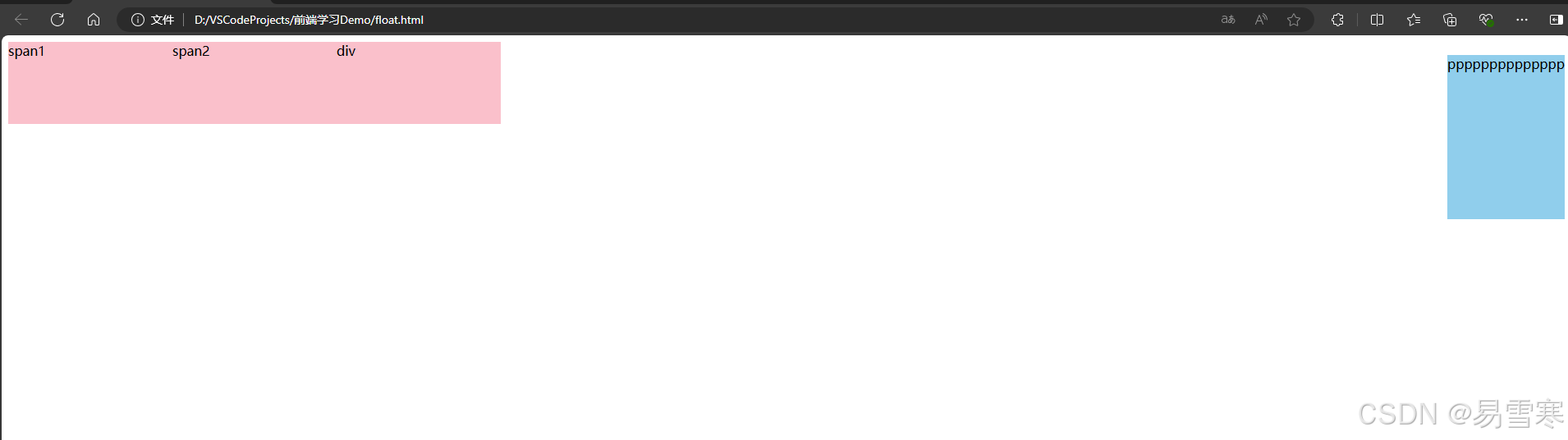
任何元素都可以浮动。不管原先是什么模式的元素,添加浮动之后具有行内块元素相似的特性:
默认宽度由内容决定,同时支持指定高宽,盒子之间无空隙。
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动的元素具有行内块元素特点</title>
<style>
/* 任何元素都可以浮动。不管原先是什么模式的元素,添加浮动之后具有行内块元素相似的特性。 */
span,
div {
float: left;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background-color: pink;
}
/* 如果行内元素有了浮动,则不需要转换块级\行内块元素就可以直接给高度和宽度 */
p {
float: right;
height: 200px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<span>span1</span>
<span>span2</span>
<div>div</div>
<p>pppppppppppppp</p>
</body>
</html>
注意:之所以顶部没有对齐,原因是 p 标签自带的外边距大于 span div 自带的外边距。
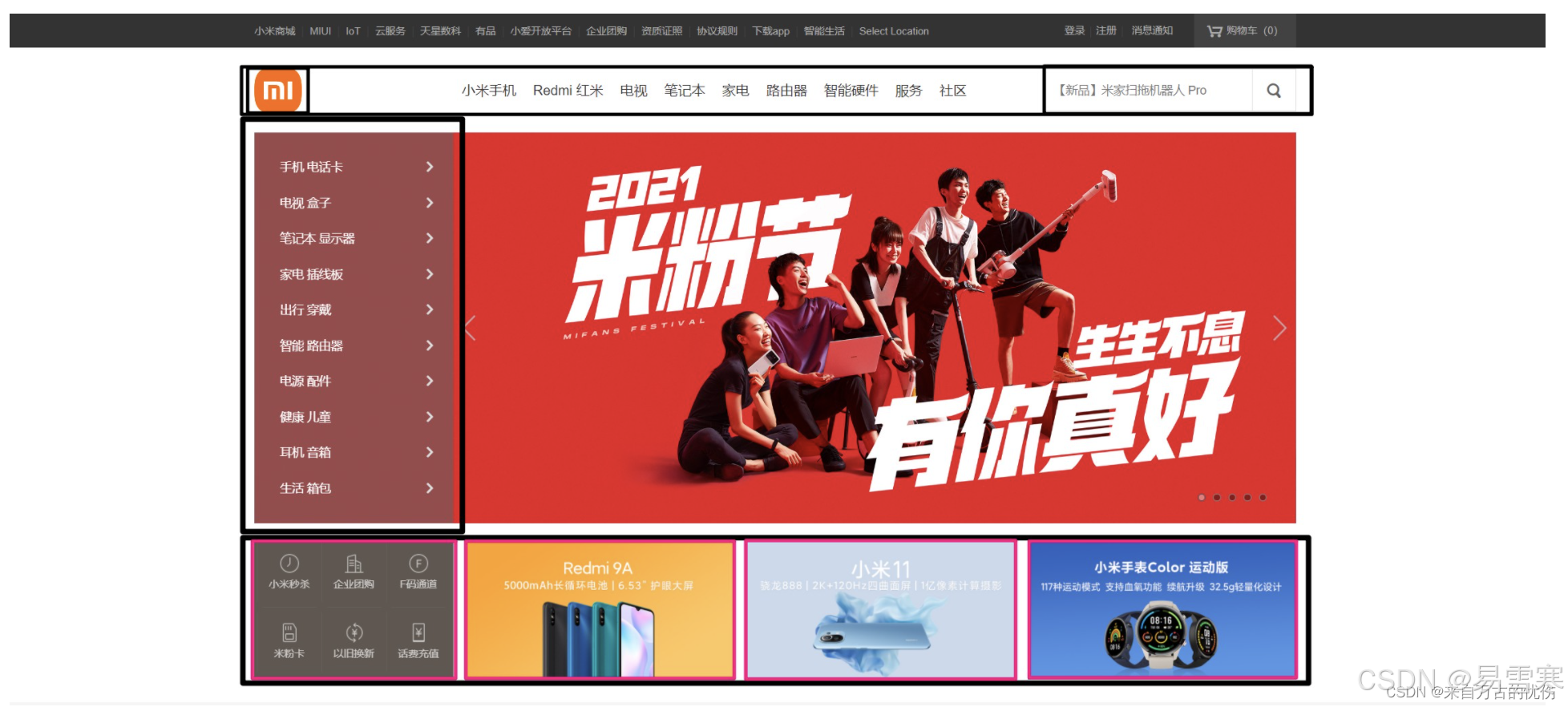
四、浮动元素经常和标准流父级搭配使用
为了约束浮动元素位置,我们网页布局一般采取的策略是:先用标准流的父元素排列上下位置,之后内部子元素采取浮动排列左右位置。符合网页布局第一准侧。
效果一:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动元素搭配标准流父盒子1</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 1200px;
height: 460px;
background-color: black;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.left {
float: left;
width: 230px;
height: 460px;
background-color: pink;
}
.right {
float: left;
width: 970px;
height: 460px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="left">左侧</div>
<div class="right">右侧</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
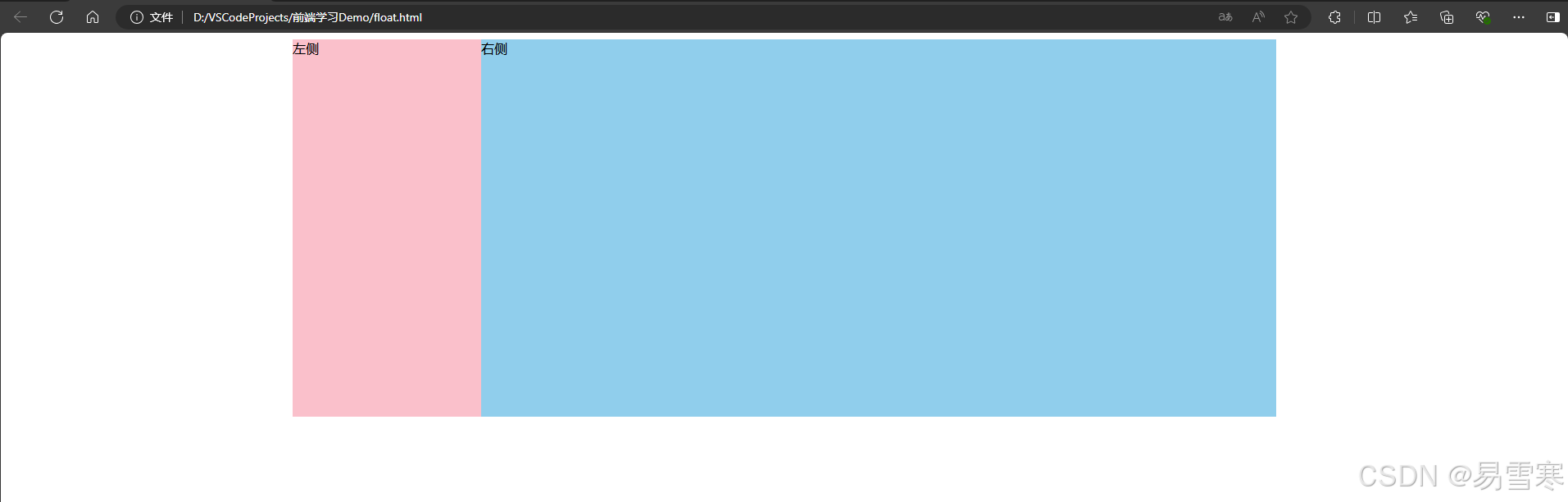
效果二:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动元素搭配标准流父盒子2</title>
<style>
* {
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
/* 取消 li 前的圆点 */
li {
list-style: none;
}
.box {
width: 1226px;
height: 285px;
background-color: pink;
/* 让大盒子水平居中 */
margin: 0 auto;
}
.box li {
width: 296px;
height: 285px;
background-color: gray;
float: left;
/* 每个小盒子用右边距隔开 */
margin-right: 14px;
}
/* 取消最后一个小盒子的右外边距 */
/* 这里必须写 .box .last 要注意权重的问题 20 */
.box .last {
margin-right: 0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="box">
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
<li class="last">4</li>
</ul>
</body>
</html>

效果三:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>浮动布局练习3</title>
<style>
.box {
width: 1226px;
height: 615px;
background-color: pink;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.left {
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 615px;
background-color: gray;
}
.right {
float: left;
width: 992px;
height: 615px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
.right>div {
float: left;
width: 234px;
height: 300px;
background-color: pink;
margin-left: 14px;
margin-bottom: 14px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box">
<div class="left">左青龙</div>
<div class="right">
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<div>4</div>
<div>5</div>
<div>6</div>
<div>7</div>
<div>8</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

关于浮动的一些基本理解就先说到这里,更多新的知识和技能我们将在后续逐步探究和讲解,感谢你的观看和订阅。
