优先级队列算法
1046. 最后一块石头的重量
题目链接:1046. 最后一块石头的重量
题目解析
题目的意思大致就是给一堆石头(数组),每次从里面选出两块最大的石头(最大的数)x和y:
- 如果
x == y,x、y粉碎(删除x和y) - 如果
x!=y,较小的粉碎,较大的减去小石头的重量
返回最终的碰撞结果1块(返回重量)或者0块石头
算法原理
每次选2个最大的数进行比较,这正好符合大根堆的数据结构,即用堆来模拟
- 创建大根堆
- 数据丢入大根堆
- 拿出2次大根堆堆顶元素,碰完之后,如果还有一个没碎,丢入大根堆
代码实现
class Solution {
public:
int lastStoneWeight(vector<int>& stones)
{
//默认大根堆
priority_queue<int> heap(stones.begin(), stones.end());
while(heap.size() > 1)
{
int x = heap.top();
heap.pop();
int y = heap.top();
heap.pop();
if(x > y)
{
x -= y;
heap.push(x);
}
}
return heap.empty() ? 0 : heap.top();
}
};
703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素
题目链接:703. 数据流中的第 K 大元素
题目解析
目的是要找出排序之后的第k大元素(包含相同元素)
要实现一个类KthLargest,它的构造函数来构造数据流,add插入数据流然后返回第k大的元素

算法原理
这考察就是TopK问题,两种主流方式:
- 堆(O(N*LogK))
- 快速选择算法(O(N))
这题数据是一个一个过来,而用堆解决topK,也是一个一个处理,所以采用堆更优一点
- 创建大小为K的堆
第K大:小根堆
第K小:大根堆 - 循环:
元素依次进堆
判定堆的大小是否超过K
关于TopK问题,可以查看此篇文章:数据结构——二叉树
这篇更棒求解TopK问题的三种境界(漫画版)
代码实现
class KthLargest {
public:
int k;
//第k大, 小根堆
priority_queue<int ,vector<int>, greater<int> > heap;
KthLargest(int _k, vector<int>& nums)
{
k = _k;
for(auto e : nums)
{
heap.push(e);
if(heap.size() > k)
{
heap.pop();
}
}
}
int add(int val)
{
heap.push(val);
if(heap.size() > k)
{
heap.pop();
}
return heap.top();
}
};
/**
* Your KthLargest object will be instantiated and called as such:
* KthLargest* obj = new KthLargest(k, nums);
* int param_1 = obj->add(val);
*/
692. 前K个高频单词
题目链接:692. 前K个高频单词
题目解析
这题也是TopK问题,给一个单词列表,返回前k个出现次数最多的。
这里除了统计次数,还是统计单词的字典序,如果次数相同,按字典序排序。
算法原理
-
这里可以用排序,统计前k个次数最多的单词,需要重载一下比较函数,如果次数相同,就按照字典序排序。
-
也可以采用堆解决:
- 这里需要知道单词的次数,所以要先预处理原始字符串数组每个单词出现的个数(哈希表);
- 然后创建大小为K的堆:
出现次数键小根堆,字典序大根堆 - 循环,元素依次进堆,然后判端
- 提取结果
代码实现
排序:
class Solution {
public:
struct Greater
{
bool operator()(const pair<string,int>& kv1,const pair<string,int>& kv2)
{
return kv1.second > kv2.second || (kv1.second == kv2.second && kv1.first <kv2.first);
}
};
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k) {
map<string,int> countMap;
for(const auto& e:words)
{
countMap[e]++;
}
vector<pair<string,int>> kvVec(countMap.begin(),countMap.end());
sort(kvVec.begin(),kvVec.end(),Greater());
vector<string> ret;
for(int i=0;i<k;i++)
{
ret.push_back(kvVec[i].first);
}
return ret;
}
};
堆:
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> topKFrequent(vector<string>& words, int k)
{
unordered_map<string, int> hash;
for(const auto& e : words)
{
hash[e]++;
}
auto cmp = [](const pair<string, int> &p1, const pair<string, int> &p2)
{
if(p1.second == p2.second)
{
//大根堆
return p1.first < p2.first;
}
//小根堆
return p1.second > p2.second;
};
priority_queue<pair<string, int>, vector<pair<string, int>>, decltype(cmp)> heap(cmp);
for(const auto& e : hash)
{
heap.push(e);
if(heap.size() > k)
{
heap.pop();
}
}
vector<string> ret(k);
for(int i = k-1; i >= 0; i--)
{
ret[i] = heap.top().first;
heap.pop();
}
return ret;
}
};
295. 数据流的中位数
题目链接:295. 数据流的中位数
题目解析
题目给了一个有序整数列表,找出中间值,如果列表大小为偶数,中位数是中间两个数的平均值。
让我们实现一个MedianFinder类:
MedianFinder()初始化MedianFinder对象void addNum(int num)将数据流中的整数num添加到数据结构中
数据一个一个添加,确保序列为有序序列double findMedian()返回到目前为止所有元素的中位数。与实际答案相差 10-5以内的答案将被接受
目前序列的中位数
算法原理
解法1——直接sort:
插入一个数,排一下序,然后通过元素个数,访问中间下标的元素。
这个add时间复杂度是O(N* logN),find的时间复杂度为O(1),题目数据量很大,会超时
解法2——插入排序思想
采用插入排序,add的时间复杂度为O(N),find时间复杂度为O(1),如果插入数据很大,时间复杂度也很大
解法3——大小堆维护
借助大小根堆来维护这个序列:

此时先规定:
- 假设左侧为m,右侧为n
- 要么
m == n - 要么
m == n+1
此时要求中位数,如果这个序列元素为偶数个,直接(大根堆堆顶元素 + 小根堆堆顶元素)/2即可得到中位数;
如果为奇数个,则是大根堆堆顶元素为中位数。
查找的时间复杂度为O(1),插入的时间复杂度为O(logN)
这里需要主要的时插入数据的时候,如何维护m == n和m == n+1
这里分类讨论:
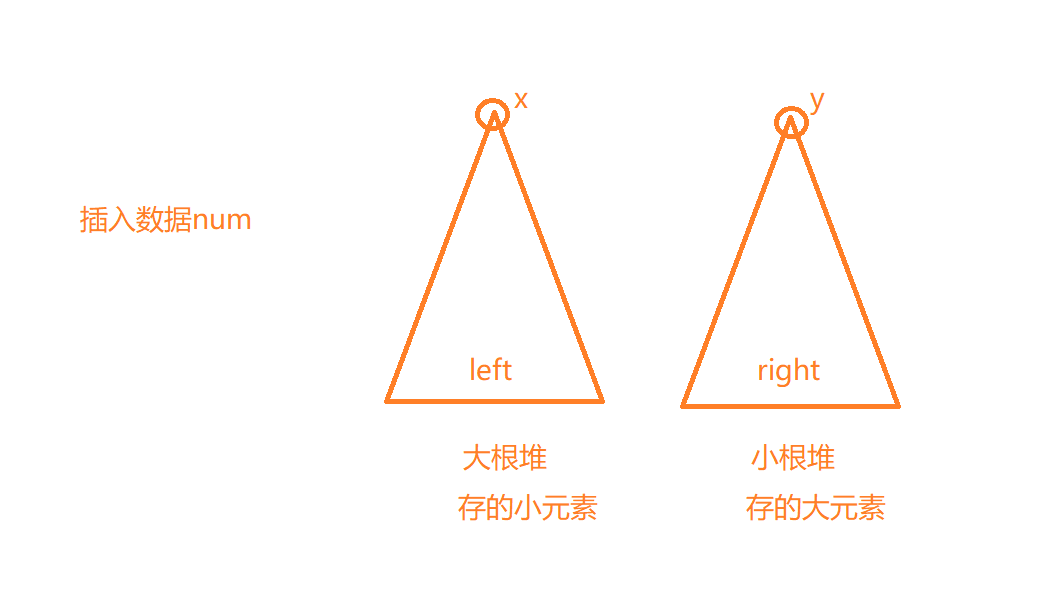
m == n:
num <= x || m == 0,插入left
num > x,插入right,然后让y进入leftm == n+1:
num <= x,进入left,此时m比n大2个,需要调整,让x进入right
num > x,进入right
代码实现
class MedianFinder
{
public:
//大根堆
priority_queue<int> left;
//小根堆
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> right;
MedianFinder()
{}
void addNum(int num)
{
if(left.size() == right.size())
{
if(left.empty() || left.top() >= num)
{
left.push(num);
}
else
{
right.push(num);
int tmp = right.top();
right.pop();
left.push(tmp);
}
}
else if(left.size() == right.size() + 1)
{
if(num <= left.top())
{
left.push(num);
int tmp = left.top();
left.pop();
right.push(tmp);
}
else
{
right.push(num);
}
}
}
double findMedian()
{
return left.size() == right.size() ? (left.top() + right.top()) / 2.0 : left.top();
}
};
/**
* Your MedianFinder object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MedianFinder* obj = new MedianFinder();
* obj->addNum(num);
* double param_2 = obj->findMedian();
*/
