Java反射机制入门:解锁运行时类信息的秘密
反射技术:
- 其实就是对类进行解剖的技术
- 类中有什么?
- 构造方法
- 成员方法
- 成员变量
结论:反射技术就是把一个类进行了解剖,然后获取到 构造方法、成员变量、成员方法
反射技术的应用案例:
- idea
- 框架技术:Spring
想要使用反射技术有一个必备条件:
- Class对象
- 原因:.class文件由类加载器读取并创建Class对象。Class对象中存储了.class文件中的内容:构造方法、成员变量、成员方法
反射技术的作用
使用反射技术,可以对类进行解剖,可以获取到类中的:构造方法、成员变量、成员方法
- 构造方法: 可以创建对象
- 成员方法: 可以调用执行
- 成员变量: 赋值、取值
反射技术的作用:
- 不用使用new关键字,就可以创建对象
- 不用使用"对象名.方法"形式,就可以调用方法
- 不用使用"对象名.属性"形式,就可以给属性赋值、取值
- 通常在类中属性,都被修饰为private(私有的:外部不能访问)
- 反射技术,可以做到对私有成员进行操作
"cn.itcast.pojo.Student" stu = new cn.itcast.pojo.Student();
给一个字符串:"cn.icast.pojo.Student"
创建一个对象:????? //使用new做不到
使用反射技术可以实现给一个Student.class
程序在运行中,不能停止, 动态的获取一个Student.class
//使用反射技术,可v小结
反射技术 :对类进行解剖的技术
反射技术的作用:可以不通过传统方式,来实现类的实例化、方法的调用
- 实现的提前:需要使用Class对象
反射:Class类
路径
- Class类
- 获取Class类对象的方式
- Class类中的常用方法
Class类
- Class就是用来描述正在运行的java类型
Class类的实例表示Java中任何正在运行的类型,每一个类型都有与之对应的Class对象
-
- 比如:类,接口,枚举,注解,数组,基本数据类型,void 都有与之对应的Class对象
类名.class
接口名.class
int.class
boolean.class
array.class 获取Class对象
获取Class类对象的方式有3种:
方式一:类型名.class //Student.class
方式二:对象.getClass() //对象名.getClass()
方式三:Class.forName(String className) //className是全路径类名 = 包名+类型名//方式1:类型名.class
//应用场景: 当类名明确时,可以直接使用"类名.class"
Class clz = String.class
Class clz = int.class
Class clz = double.class
//方式2:对象.getClass()
//应用场景:通常是应用方法中
public void method(Student stu){
Class clz = stu.getClass();
}
//方式3: Class.forName("类的全名称");//带有包名的类
//应用场景: 通常使用在读取配置文件中的类型
pro.properties文件
--------------文件内容------------------
className=cn.icast.pojo.Student
---------------------------------------
//代码实现
ResourceBundler r = ResourceBundler.getBundler("pro");
String className = r.getString("className");//"cn.icast.pojo.Student"
Class StudentClass = Class.forName(className);//className="cn.icast.pojo.Student"
//当获取到Class对象了,就可以对类进行解剖了Class类中的常用方法
String getSimpleName() // 获得类名字符串:类名
String getName() // 获得类全名:包名+类名
T newInstance() // 创建Class对象关联类的对象 (前提:类中有一个无参构造方法)
//示例:
Studentod类 cn.itcast.pojo.Student //public Student(){}
Class stuClass = Student.class;
Object obj = stuClass.newInstance();//调用Student() 创建Student对象
Student stu = (Student) obj;代码实现
public class Test01 {
@Test
public void testMethod3() throws ClassNotFoundException, IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Class stuClass = Class.forName("com.itheima.cls.demo2.Student");
Student stu = (Student) stuClass.newInstance();
stu.study();
}
@Test
public void testMethod2() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
Student stu =new Student();
//对象名.getClass()
Class studentClass = stu.getClass();
Student student = (Student) studentClass.newInstance();
student.study();
}
@Test
public void testMethod1() throws IllegalAccessException, InstantiationException {
// 类型名.class
Class studentClass = Student.class;
//System.out.println(studentClass);
System.out.println("带有包名的类:"+studentClass.getName());
System.out.println("类名:"+studentClass.getSimpleName());
//实例化Student对象
Object obj = studentClass.newInstance();
Student stu = (Student) obj;
stu.age=20;
stu.name="张三";
System.out.println(stu.name+"==="+stu.age);
stu.study();
}
}获取Class对象的方式:
- 类型名.class //明确了具体的类型时,直接使用:类名.class
- 对象名.getClass() //当方法中传递的对象时,使用:对象名.getClass()
- Class类中的静态方法:forName("带有包名的类") //从配置文件中读取到类的全名称时
反射:构造器
路径
- Constructor类
- 获取构造器Constructor对象的方式
- Constructor类中常用方法
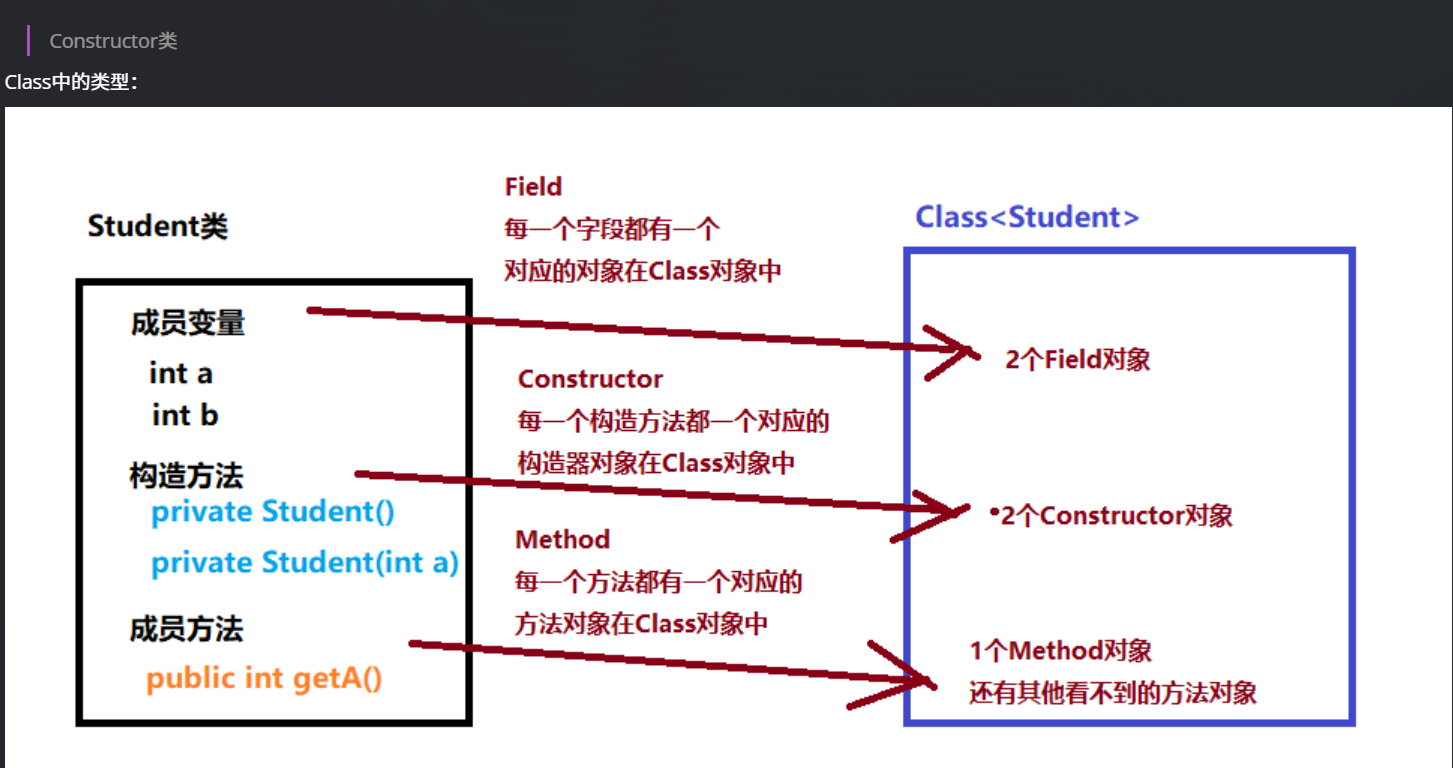
构造方法对应的类型: Constructor类型
字段:Field
方法:MethodConstructor类
- 代表构造方法(构造器)
- 类中的每一个构造方法都是一个Constructor类的对象
反射技术中构造器的目的:
- 获得Constructor对象来创建类的对象
大白话:不使用new关键字,通过Constructor来创建对象获取Constructor对象的方式
Constructor对象的获取和Class类中方法有关:
Constructor[] getConstructors()
//获得类中的所有构造方法对象,只能获得public的
Constructor[] getDeclaredConstructors()
//获得类中的所有构造方法对象
//可以是public、protected、(默认)、private修饰符的构造方法
Constructor getConstructor( Class... parameterTypes)
//根据参数类型获得对应的Constructor对象 获取public修饰的
//只能获得public修饰的构造方法
/*示例: Student public Student(String name, int age) public Student(int age)
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//根据给定的参数类型,来获取匹配的构造器对象
Constructor c = stuClass.getConstructor( String.class , int.class );
*/
Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)
//根据参数类型获得对应的Constructor对象
//可以是public、protected、默认、private修饰符的构造方法Constructor类常用方法
T newInstance(Object... initargs)
//根据指定的参数创建对象
/*
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//根据给定的参数类型,来获取匹配的构造器对象
Constructor c = stuClass.getConstructor( String.class , int.class );
//使用构造器对象,来实例化Student
c.newInstance( "张三", 22 );//Student(String name, int age)
//无参构造
Constructor c = stuClass.getConstructor();
Student stu = (Student) c.newInstance();
*/
void setAccessible(true)//应用场景:仅适用于访问有权限检查的成员
//设置"暴力反射" ——是否取消权限检查,true取消权限检查,false表示不取消代码实现:
public class Test1 {
@Test
public void testMethod1() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取构造器的步骤
/*1、先获取到Class对象
2、使用Class对象中的方法,获取Constructor对象
3、使用Constructor对象,实例化类
*/
//获取Class对象(Student.class)
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//获取Constructor对象: public Student()
Constructor con1 = stuClass.getConstructor();
System.out.println(con1);
Student stu = (Student)con1.
();
stu.name="小崔";
System.out.println(stu.name);
}
}Constructor类:
- 代表类中的一个构造方法
获取Constructor类的方式:
//获取public修饰的构造方法
Constructor getConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)
//获取非public修饰的方法
Constructor getDeclaredConstructor(Class... parameterTypes)Object newInstance(Object... param) //利用构造器对象,实例化自定义对象
void setAccessible(true) //消除JVM对权限的检查操作 (一次性的。只是对当前操作去除) 反射:使用构造器创建对象
路径
- 案例:使用无参构造器创建对象
- 案例:使用有参构造器创建对象
- 案例:使用私有构造器创建对象
- 案例:使用私有构造器创建对象
案例:使用无参构造器创建对象
@Test
public void testMethod1() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象(Student.class)
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//利用Class对象,来获取构造器对象
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor();//方法中的参数为可变参数,可以不传递值
//使用Constructor对象中的方法,来实例化Student类对象
Student stu = (Student) con.newInstance();//方法中的参数是可变参数
stu.study();
}案例:使用有参构造器创建对象
//有参构造方法
@Test
public void testMethod2() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象(Student.class)
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//public Student(String name, int age, String gender)
//获取带有参数的构造器对象
//参数:是用来设置构造方法中参数的类型是什么
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor(String.class, int.class, String.class);
//实例化有参构造方法
//参数:要传递给Student(String name, int age, String gender)的数据
Student stu = (Student) con.newInstance("熊大", 22, "男");
//调用对象中的方法
stu.study();
}案例:使用私有构造器创建对象
@Test
public void testMethod3() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象(Student.class)
Class stuClass = Student.class;
// private Student(String name)
//获取私有构造器对象
Constructor con = stuClass.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class);
//当需要对私有成员操作时,需要先取消JVM对访问权限的检查操作
con.setAccessible(true);//暴力破解(取消权限检查) //仅在当前次取消
//使用私有构造器,实例化Student对象
Student stu = (Student) con.newInstance("文平");
System.out.println(stu.name);
stu.study();
}反射:方法
路径
- Method类
- 获取Method对象的方式
- Method类常用方法
Method
Method类
- 代表一个成员方法
-
- 每一个成员方法都是一个Method类的对象
反射技术中使用Method的目的:
- 通过Method对象来调用成员方法
获取Method对象的方式
Method对象的获取和Class类中方法有关:
Method[] getMethods();
//获得当前类和其父类中的所有public成员方法对象,返回数组
Method[] getDeclaredMethods();
//获得当前类中的所有成员方法对象,返回数组
//只获得本类的,包括public、protected、默认、private的
Method getMethod(String name,Class...args);
//根据方法名和参数类型获得对应的成员方法对象,只能获得public的
//参数说明:
name : 类中方法的名字
args : 方法中参数类型的Class 例:int.class
Method getDeclaredMethod(String name,Class...args);
//根据方法名和参数类型获得对应的成员方法对象,包括public、protected、(默认)、private的Method类常用方法
//使用方法对象,调用对象中的方法执行(入栈执行)
Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args)
// obj: 对象 //"对象名.方法"
// args:调用方法时传递的实参
//返回值: Object类型
void setAccessible(true)
// 设置"暴力访问" ——是否取消权限检查,true取消权限检查,false表示不取消代码实现:
//获取Method对象的步骤:
1、先获取Class对象
2、使用Class对象,获取Method对象
3、使用Method对象,执行方法
public class Test01 {
@Test
public void testMethod1() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取Class对象
Class stuClass = Class.forName("com.itheima.method.demo1.Student");
//使用Class对象,获取Method对象
Method[] methods = stuClass.getMethods();//获取本类及父类中所有的public方法
for (Method m : methods){
System.out.println(m);
}
}
@Test
public void testMethod2() throws ClassNotFoundException {
//获取Class对象
Class stuClass = Class.forName("com.itheima.method.demo1.Student");
//使用Class对象,获取Method对象
Method[] methods = stuClass.getDeclaredMethods();//获取本类中所有方法(包含私有)
for (Method m : methods){
System.out.println(m);
}
}
} 反射:方法调用
路径
- 案例:调用无参无返回值的方法
- 案例:调用有参有返回值的方法
- 案例:调用私有方法
- 案例:调用静态方法
案例:调用无参无返回值的方法
@Test
public void testMethod1() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//因为在调用Method时,需要传递Student对象
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor();
Student stu = (Student)con.newInstance();
//获取public void study()方法的对象
Method method = stuClass.getMethod("study");
//使用Method对象 执行study()方法
method.invoke( stu );
}案例:调用有参有返回值的方法
/有参有返回值
@Test
public void testMethod2() throws NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//获取Class对象
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//因为在调用Method时,需要传递Student对象
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor();
Student stu = (Student)con.newInstance();
//获取public String sayHello(String name)方法的Method对象
Method method = stuClass.getMethod("sayHello", String.class);
//调用method方法
Object result = method.invoke(stu,"波波");
System.out.println(result);
}案例:调用私有方法
//私有方法
@Test
public void testMethod3() throws IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, NoSuchMethodException {
//获取Class对象
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//因为在调用Method时,需要传递Student对象
Constructor con = stuClass.getConstructor();
Student stu = (Student)con.newInstance();
//获取 private void eat(String name)方法的Method对象
Method method = stuClass.getDeclaredMethod("eat", String.class);
//去除JVM对当前次权限的检查
method.setAccessible(true);
//执行method方法
method.invoke(stu,"红烧肉");
}案例:调用静态方法
//静态方法
@Test
public void testMethod4() throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//获取Class对象
Class stuClass = Student.class;
//静态方法的调用不需要对象。"类名.静态方法()"
//获取public static void sleep()方法的Method对象
Method method = stuClass.getMethod("sleep");
//执行静态方法
method.invoke(null);//不需要传递对象(null就表示执行静态方法)
}Method对象的使用步骤:
1、获取Class对象
2、基于Class对象,获取Method对象
//有参方法
Method method = Class对象.getMethod("方法名",参数1类型.class,参数2类型.class ...);
//无参方法
Method method = class对象.getMethod("方法名");3、使用Method对象,执行方法
//调用非静态方法
method对象.invoke(实例对象,方法中需要的实参)
//调用静态方法
method对象.invoke(null,方法中需要的实参) 反射的作用案例演示
- 作用反射是框架的灵魂!框架的底层一定会用到反射技术。
- 需求:要把猫的睡觉方法 变成 狗的吃饭方法
- 效果:使用反射+Properties完成配置文件。把需要修改的灵活的内容写在配置文件中,代码不需要做任何的改动。
-
- 案例演示
public class Dog {
public void eat(){
System.out.println("狗爱吃肉");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("狗睡觉流口水");
}
}
public class Cat {
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫爱吃鱼");
}
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("猫睡觉打呼噜");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//不使用反射
//需求: 要把猫的睡觉方法 变成 狗的吃饭方法
//Dog d = new Dog();
//d.eat();
//使用反射
//properties
Properties pro = new Properties();
//load():可以把文件中的键值对读取到集合中
FileReader fr = new FileReader("day21\\aaa.txt");
pro.load(fr);
//通过键获取值
String cn = pro.getProperty("className");
String mn = pro.getProperty("methodName");
//获取字节码对象
Class c = Class.forName(cn);
//获取空参构造
Constructor con = c.getConstructor();
//执行构造方法
Object o = con.newInstance();
//获取方法
Method m = c.getMethod(mn);
//执行方法
m.invoke(o);
}
}
配置文件:
className=com.itheima_05.Cat
methodName=sleep