Python 学习完基础语法知识后,如何进一步提高?
入门Python后,就可以拿些小案例练手了,这时候千万不要傻乎乎地成天啃语法书。
编程是一门实践的手艺,讲究孰能生巧。不管是去手撸算法、或者照葫芦画瓢写几个小游戏都可以让你的Python突飞猛进。
之前看github比较多,推荐给大家几个不错的项目。
1、用Python实现所有常见算法
这个项目包含了上千个算法的Python代码实现,几乎囊括了大部分常见算法。
包括回溯、布尔代数、元胞自动机、线性回归、图算法、网络流等等

以排序为例,该项目提供了近50种算法,比如下面的树形选择排序:
"""
Tree_sort algorithm.
Build a BST and in order traverse.
"""
class node:
# BST data structure
def __init__(self, val):
self.val = val
self.left = None
self.right = None
def insert(self, val):
if self.val:
if val < self.val:
if self.left is None:
self.left = node(val)
else:
self.left.insert(val)
elif val > self.val:
if self.right is None:
self.right = node(val)
else:
self.right.insert(val)
else:
self.val = val
def inorder(root, res):
# Recursive traversal
if root:
inorder(root.left, res)
res.append(root.val)
inorder(root.right, res)
def tree_sort(arr):
# Build BST
if len(arr) == 0:
return arr
root = node(arr[0])
for i in range(1, len(arr)):
root.insert(arr[i])
# Traverse BST in order.
res = []
inorder(root, res)
return res
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(tree_sort([10, 1, 3, 2, 9, 14, 13]))
© 2021 GitHub, Inc.
其他排序:

项目地址:TheAlgorithms/Python
2、Python制作小游戏、画图
这是大家最喜闻乐见的代码练习方式,通过制作小游戏、画一个卡通图片,能熟悉基础语法的使用,并熟悉相关库。
比如说,用Python制作坦克大战游戏:

代码虽然复杂点,但仔细琢磨琢磨应该都能搞会,还能帮你熟悉应用开发的流程。

坦克大战部分代码
如果你觉得制作游戏比较复杂,那可以用python的turtle库绘制卡通人物
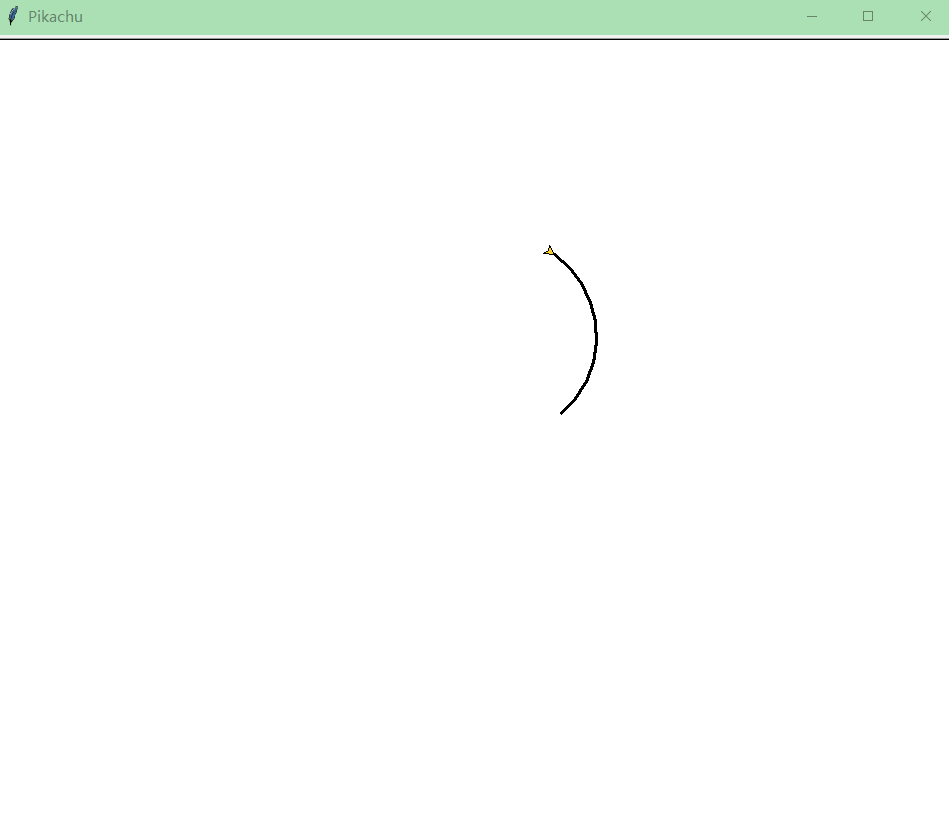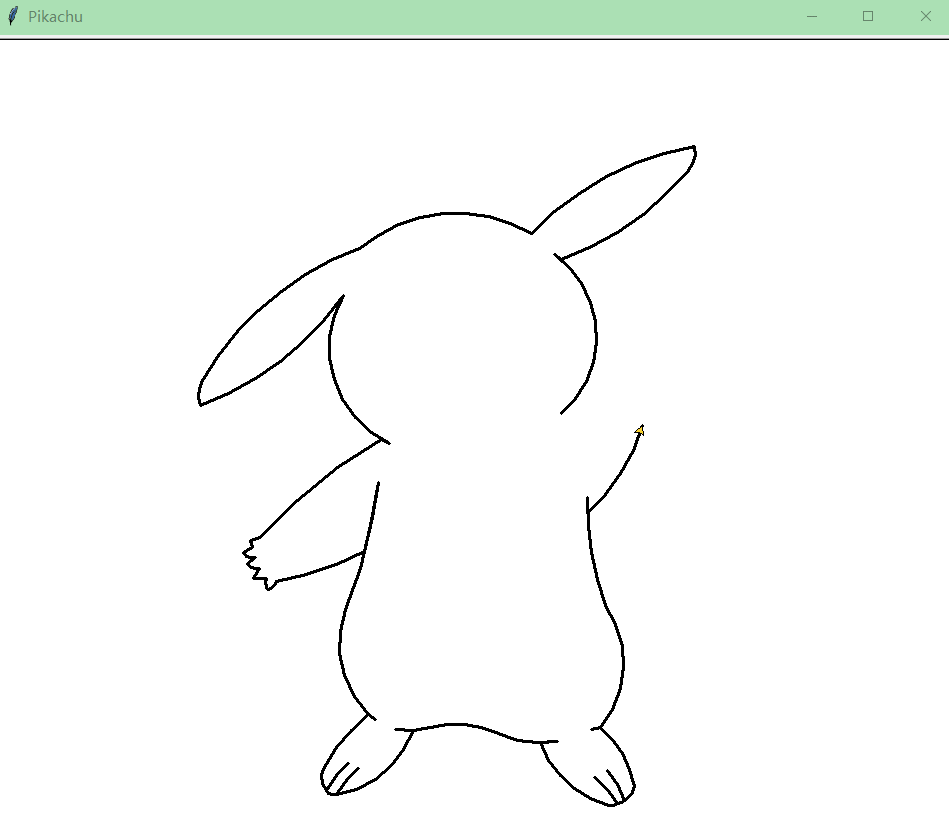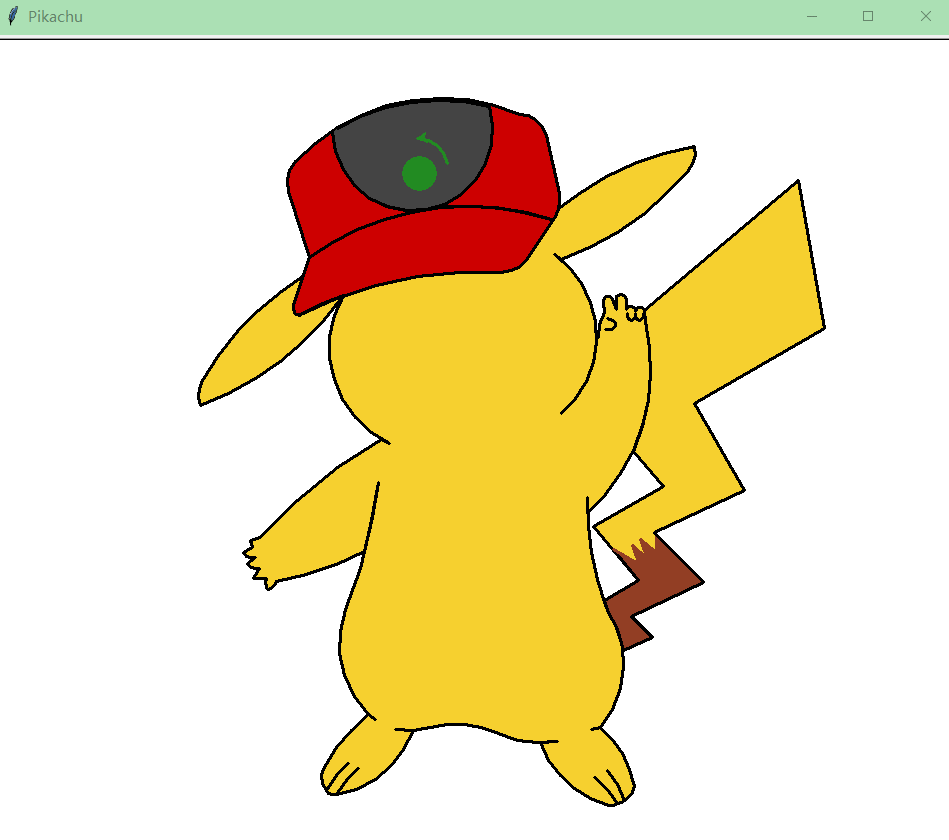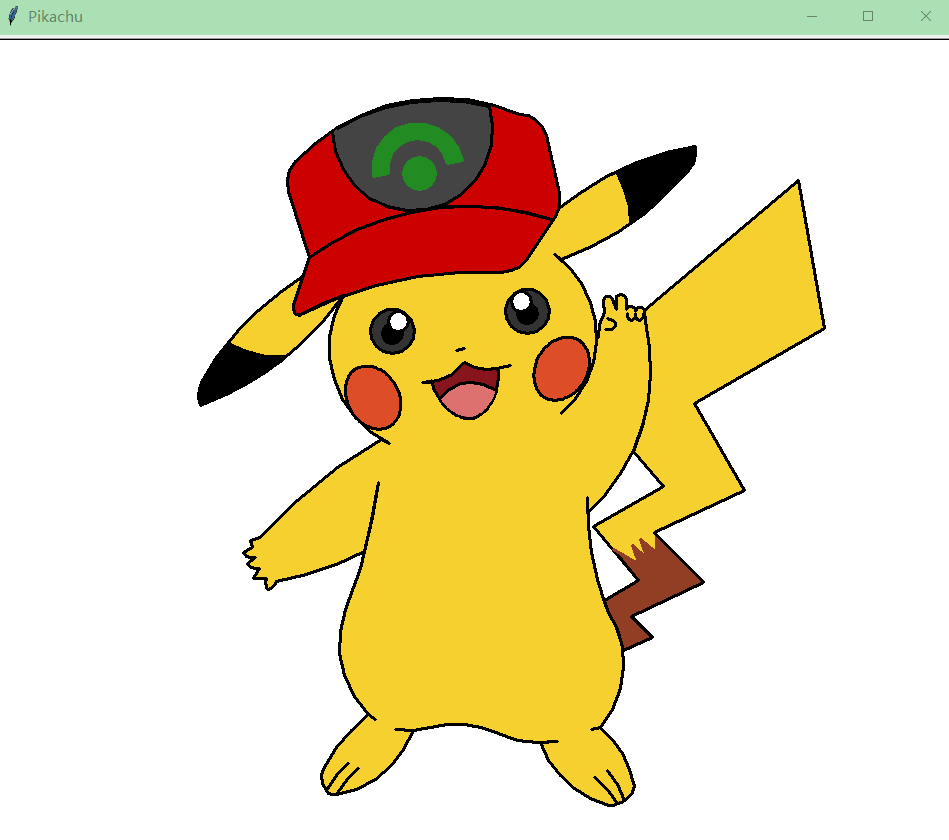
皮卡丘
turtle语法非常简单,就是一些画笔的操作:

绘制皮卡丘部分代码
游戏和绘图建议初学者都可以去试试,是很好的锻炼机会。
项目地址:liuzuoping/python_Games
3、制作可视化图表
众所周知,python擅长数据科学,能制作各种图表。
matplotlib是python可视化的基础库,非常强大,对可视化感兴趣的小伙伴一定要去试试。
曲线图

import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Fixing random state for reproducibility
np.random.seed(19680801)
dt = 0.01
t = np.arange(0, 30, dt)
nse1 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 1
nse2 = np.random.randn(len(t)) # white noise 2
# Two signals with a coherent part at 10Hz and a random part
s1 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse1
s2 = np.sin(2 * np.pi * 10 * t) + nse2
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1)
axs[0].plot(t, s1, t, s2)
axs[0].set_xlim(0, 2)
axs[0].set_xlabel('time')
axs[0].set_ylabel('s1 and s2')
axs[0].grid(True)
cxy, f = axs[1].cohere(s1, s2, 256, 1. / dt)
axs[1].set_ylabel('coherence')
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
三维图

import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib import cm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
X = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
Y = np.arange(-5, 5, 0.25)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
R = np.sqrt(X**2 + Y**2)
Z = np.sin(R)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig, auto_add_to_figure=False)
fig.add_axes(ax)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap=cm.viridis)
plt.show()
动图


项目地址:Python plotting - Matplotlib 3.4.1 documentation
