android开发
文章目录
- android开发 类微信界面
- 整体框架展示:
- 主页Fragment_MainActivity2:
- 1. 聊天界面
- 2. 用户界面
- 用户界面的跳转
- 3. 朋友圈界面
- 4. 我的界面
android开发 类微信界面
整体效果展示:
整体框架展示:
-
4个主要的fragment页面,聊天、用户、朋友圈、我的 ,如下:
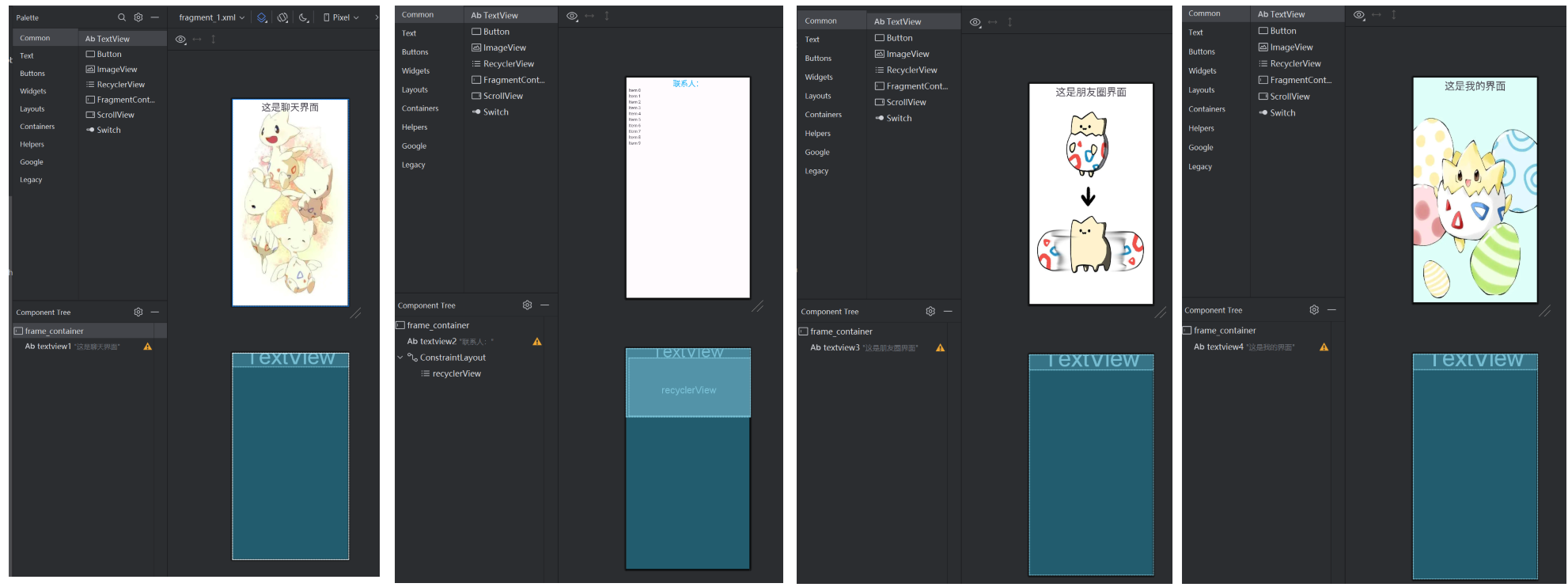
-
配置代码如下:
fragment1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/frame_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:context=".Fragment_1" android:background="@drawable/backgroud2"> <!-- TODO: Update blank fragment layout --> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这是聊天界面" android:textAlignment="center" android:textSize="34sp" /> </FrameLayout> fragment2: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/frame_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:context=".Fragment_1"> <!-- TODO: Update blank fragment layout --> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:text="联系人:" android:textAlignment="center" android:textColor="#03A9F4" android:textColorLink="#2196F3" android:textSize="25sp" /> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <androidx.recyclerview.widget.RecyclerView android:id="@+id/recyclerView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_marginStart="8dp" android:layout_marginTop="32dp" app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent" app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" /> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout> </FrameLayout> fragment3: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/frame_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:context=".Fragment_1" android:background="@drawable/backgroud"> <!-- TODO: Update blank fragment layout --> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview3" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这是朋友圈界面" android:textAlignment="center" android:textSize="34sp" /> </FrameLayout> fragment4: <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/frame_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:context=".Fragment_1" android:background="@drawable/backgroud3"> <!-- TODO: Update blank fragment layout --> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview4" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这是我的界面" android:textAlignment="center" android:textSize="34sp" /> </FrameLayout>
主页Fragment_MainActivity2:
-
要在一个Activity中根据不同的按键,分别显示不同的fragmentUI界面。先设计一个主页面,其中用 FrameLayout 来引入4个不同的fragment界面。主页面和两个top、bottomUI设计如下:
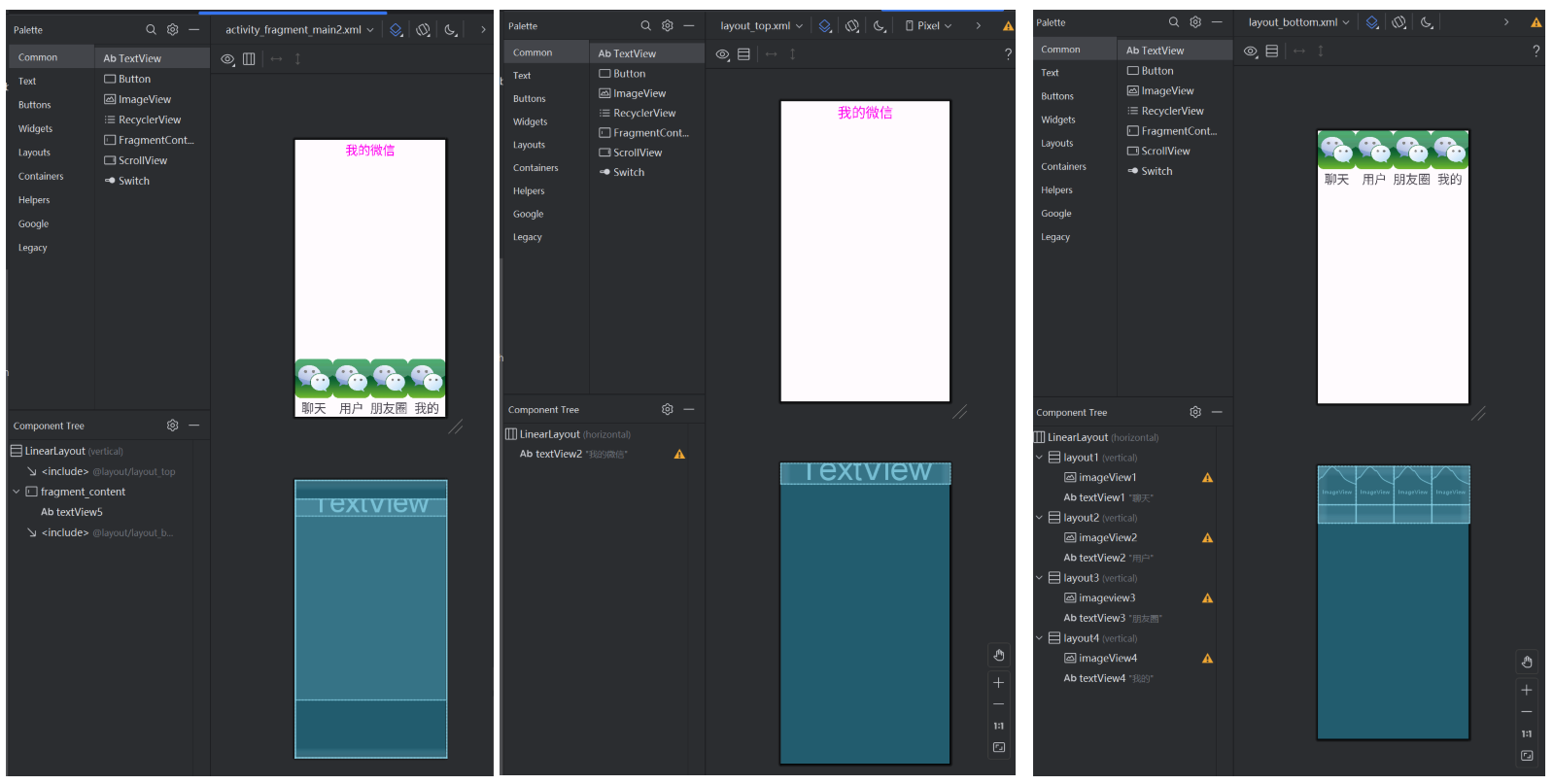
主页面activity_fragment_main2中通过include来引入 top 、 bottom 两个页面,主页面设计如下,中间用FrameLayout组件进行填充,为后面显示的fragment页面留空间:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".Fragment_MainActivity2"> <include layout="@layout/layout_top" /> <FrameLayout android:id="@+id/fragment_content" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="0dp" android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView5" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:textAlignment="textStart" android:textSize="34sp" /> </FrameLayout> <include layout="@layout/layout_bottom" /> </LinearLayout> -
Fragment_MainActivity2代码解释:
首先是4个fragment.java代码,通过继承Fragment类,重写其中的onCreateView方法来显示自己定义的UI界面 ,准备4个fragment.java文件,分别引入上面设计的4个fragment.xml文件:
在Fragment_MainActivity2中通过 manager.beginTransaction() 开始一个事务transaction,并new 4个Fragment对象作为transaction 的操作对象:
// 4个底部按钮 后面通过监听这4个按钮 来显示不同的fragment layout1 = findViewById(R.id.layout1); layout2 = findViewById(R.id.layout2); layout3 = findViewById(R.id.layout3); layout4 = findViewById(R.id.layout4); // 获取 当前Activity的 FragmentManager实例 用于管理Fragment事务 manager = getSupportFragmentManager(); // 开始一个新的Fragment事务 transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); // 在Activity 中添加一个 Fragment // 创建一个 Fragment 实例 fragment_1 = new Fragment_1(); fragment_2 = new Fragment_2(); fragment_3 = new Fragment_3(); fragment_4 = new Fragment_4(); // 初始化 transaction 中的事件 intial(); // app开始时显示fragment_1 fragment_hide(fragment_1); // 点击事件的监听器 layout1.setOnClickListener(this); layout2.setOnClickListener(this); layout3.setOnClickListener(this); layout4.setOnClickListener(this);为了让4个fragment页面不重复显示,在transaction事务中将add进的四个fragment全部隐藏,然后通过 定义接口 来显示指定的fragment页面,在Fragment_MainActivity2中定义OnClickListener接口中的 onClick方法 ,这样通过点击不同的layout,触发不同的监听、就能显示不同fragment:
// 将所有fragment添加到一个容器视图中 private void intial() { // fragment_1添加到一个容器视图中 ==> 当前资源文件activity_fragment_main2的 fragment_content中 // ==> fragment_1的内容将显示在fragmentlayout指定的位置。 transaction.add(R.id.fragment_content,fragment_1); transaction.add(R.id.fragment_content,fragment_2); transaction.add(R.id.fragment_content,fragment_3); transaction.add(R.id.fragment_content,fragment_4); } // 一个fragment封装 用来显示指定的fragment页面 传入的参数即为要显示的页面 protected void fragment_hide(Fragment fragment){ // 隐藏所有 fragment transaction.hide(fragment_1); transaction.hide(fragment_2); transaction.hide(fragment_3); transaction.hide(fragment_4); // 显示指定的 fragment页面 transaction.show(fragment); // 提交事务 transaction.commit(); } // 重写 View.OnClickListener 接口中定义的onClick方法 @Override public void onClick(View v) { if (v.getId() == R.id.layout1) { // 处理 layout1 的点击事件 transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); fragment_hide(fragment_1); } else if (v.getId() == R.id.layout2) { // 处理 layout2 的点击事件 transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); fragment_hide(fragment_2); } else if (v.getId() == R.id.layout3) { // 处理 layout3 的点击事件 transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); fragment_hide(fragment_3); } else if (v.getId() == R.id.layout4) { // 处理 layout4 的点击事件 transaction = manager.beginTransaction(); fragment_hide(fragment_4); } }
1. 聊天界面
-
因为可能的聊天会比较多,所以采用 recyclerView组件 搭配adpter来显示,并用Intent来进行跳转至进入聊天界面:
[!NOTE]
这里我直接将聊天记录写死在程序中,但是聊天记录是可以从文件(或者数据库)中读取。
fragment设计修改如下,主要是添加一个recyclerView组件(左),再给recyclerView的每一行做一个item(中),以及群聊内部的详细页面(右):
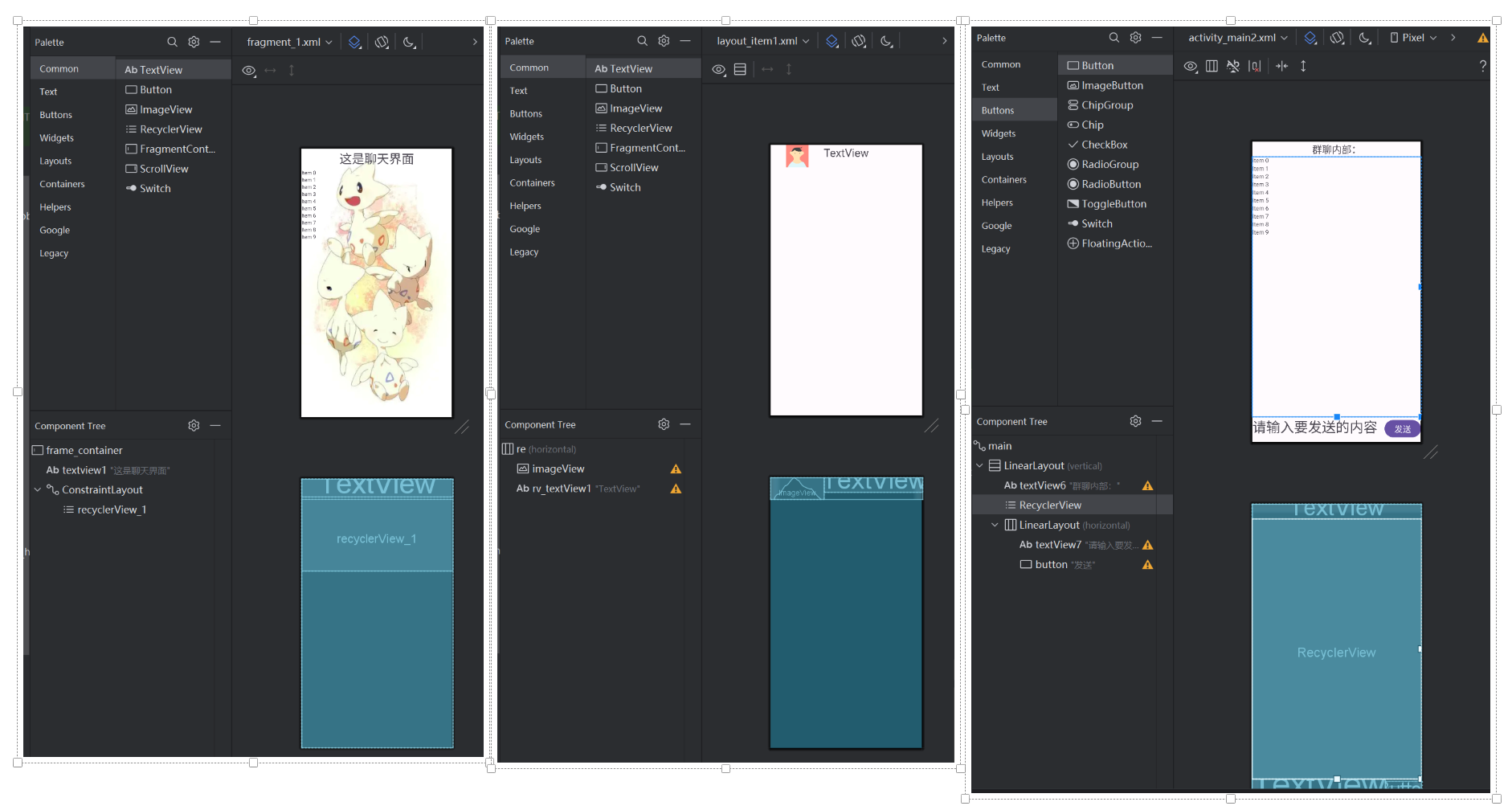
配置文件如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/main" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textView" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="81dp" android:text="联系人" android:textAlignment="center" android:textSize="48sp" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView_people" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" tools:srcCompat="@tools:sample/avatars" /> </LinearLayout> </androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:id="@+id/re" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/imageView" android:layout_width="0dp" android:layout_height="60dp" android:layout_weight="1" tools:srcCompat="@tools:sample/avatars" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/rv_textView1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_weight="1" android:text="TextView" android:textSize="30dp" /> </LinearLayout> -
fragment1中代码涉及如下,主要是给adpter2传入参数,来显示指定行:
// 引入自己的UI界面 // 引入资源 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_1, container, false); recyclerView = view.findViewById(R.id.recyclerView_1); recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(getContext())); // 为每一行添加元素 list = new ArrayList<>(); list2 = new ArrayList<>(); // 传入群聊图片id int[] name = {R.drawable.group_chats1,R.drawable.group_chats2,R.drawable.group_chats3,R.drawable.people_4}; for (int i = 0; i < 10 ; i++){ // 为每一行添加一个元素 list2.add(name[i%4]); list.add("这是第" + i + "个群聊"); } // 用 list来实例化一个 adpter对象 adpter = new adpter2(getContext(),list,list2); // 设置recyclerView recyclerView.setAdapter(adpter); Log.d("lzl","fragment...."); -
adpter2主要代码解释:
@Override // 使用自己定义的 MyViewHolder类 来设置每一行的内容 public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull adpter2.MyViewHolder holder, @SuppressLint("RecyclerView") int position) { // 显示群聊的名字 holder.textView.setText(list.get(position).toString()); // 显示群聊的图片 holder.imageView.setImageResource((Integer) list2.get(position)); // 给text设置监听 ==> 点击进入群聊内部 holder.textView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 跳转到群聊详细页面(群聊内部) Intent intent = new Intent(mcontext, MainActivity2.class); // 传参 传入textview的内容 intent.putExtra("key1",holder.textView.getText()); mcontext.startActivity(intent); } }); } -
MainActivity2代码如下,主要导入了设计的UI界面,以及接收adpter传入的参数:
textView = findViewById(R.id.textView6); // 获取一个intent对象 其他的activity 传参过来 Intent intent = getIntent(); // 获取传递的参数 通过设置的变量名 --> key1 字符串参数 String string1 = intent.getStringExtra("key1"); if (string1 != null) { // 在text中显示 // 设置textview的内容 textView.setText("群聊:" + string1); }
2. 用户界面
-
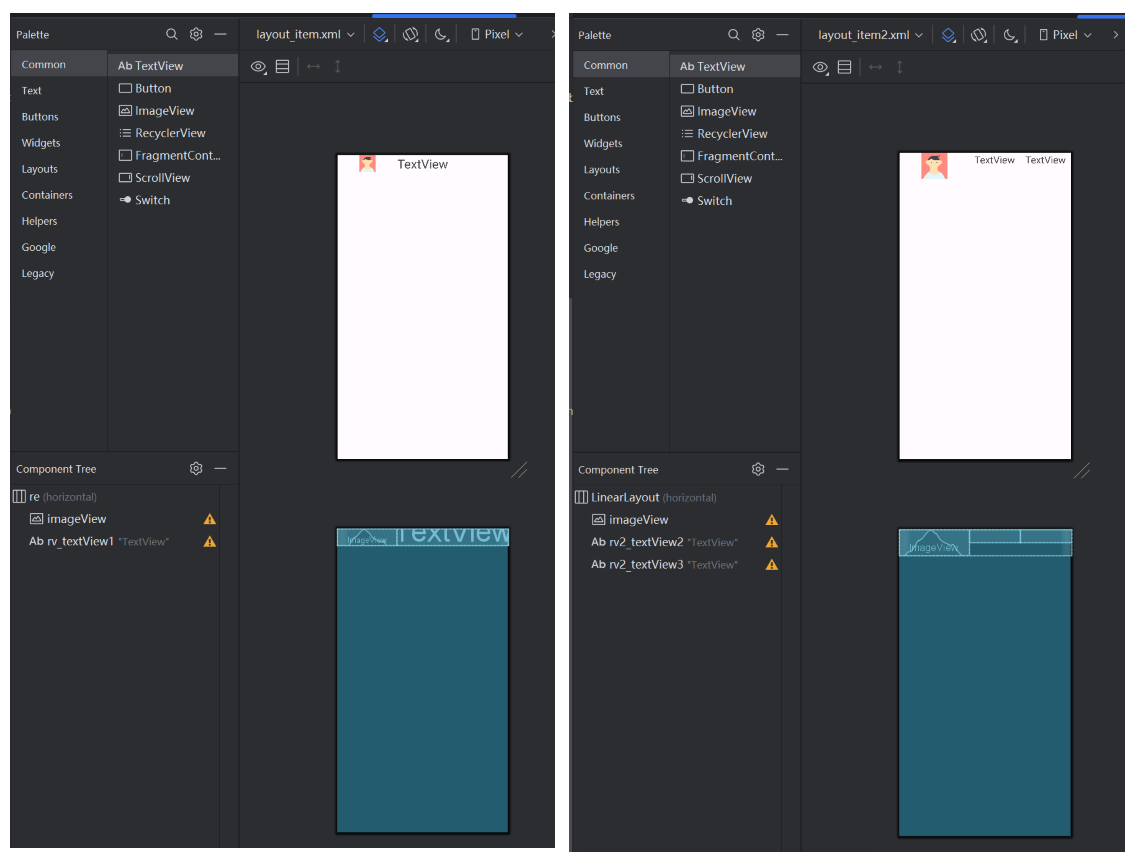
由于用户界面中连续人众多,所以考虑使用 recyclerView组件 搭配adpter来显示。下面看adpter设计:
recyclerView设计(左),recyclerView中的每一行设计(右)
-
然后在fragment_2中引用左边这个资源,并新建一个adpter.java文件,用来设置列表中的每一行:
fragment中的主要代码是onCreateView方法 中传递参数,并用adpter来设置recyclerView
@Override public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) { // 引入资源 View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_2, container, false); // 找到recyclerView组件 recyclerView = view.findViewById(R.id.recyclerView); recyclerView.setLayoutManager(new LinearLayoutManager(getContext())); // 为每一行添加元素 列表传参 list = new ArrayList<>(); list2 = new ArrayList<>(); // 传入图片id int[] name = {R.drawable.people_1,R.drawable.people_2,R.drawable.people_3,R.drawable.people_4}; for (int i = 0; i < 100 ; i++){ // 为每一行添加一个元素 list2.add(name[i%4]); list.add("这是第" + i + "个联系人"); } // 用 list来实例化一个 adpter对象 adpter = new adpter(getContext(),list,list2); // 设置recyclerView recyclerView.setAdapter(adpter); Log.d("lzl","fragment...."); // 返回界面 return view; }adpter文件设计如下:
其中要声明adpter的构造方法,方便new的时候传参。其次定义一个自己的内部类MyViewHolder,用来定义每一行的元素,因为后续**public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType)**会给每一行返回一个parent,用来设置每一行。
然后在**public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, @SuppressLint(“RecyclerView”) int position)**中接收上面返回的holder,然后根据fragment传入的参数设置每一行的每一个组件。
[!NOTE]
这里fragment给adpter传参是在程序中写死了的,也可以从文件中(或者数据库中)读出需要的内容,再传递给adpter进行显示
// adpter构造函数 可以接收两个list类型的参数 public adpter(Context context, List list, List list2) { this.list = list; this.list2 = list2; this.mcontext = context; } // 定义内部类 自己的 ViewHolder 继承自 RecyclerView.ViewHolder 用于onCreateViewHolder创建 // 定义ViewHolder 每一行有什么 class MyViewHolder extends RecyclerView.ViewHolder{ // 成员变量 TextView textView; ImageView imageView; // 自己类的构方法 表示 recyclerView每行有哪些属性 public MyViewHolder(@NonNull View itemView) { super(itemView); // 拿到 layout_item中的rv_textView1 textView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.rv_textView1); // 设置图片 imageView = itemView.findViewById(R.id.imageView); } } @NonNull // 该方法不能返回空 @Override // 返回一个 MyViewHolder 实例 holder public MyViewHolder onCreateViewHolder(@NonNull ViewGroup parent, int viewType) { Context context = parent.getContext(); // 返回一个 View 定义每一行 layout_item压入 View view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.layout_item,parent,false); // 返回一个 MyViewHolder实例 holder为每一行的初始对象 MyViewHolder holder = new MyViewHolder(view); return holder; } @Override // 使用自己定义的 MyViewHolder类 来设置每一行的内容 public void onBindViewHolder(@NonNull MyViewHolder holder, @SuppressLint("RecyclerView") int position) { // position 表示list中的第几个元素 即用list来设置 recyclerView 中每行的内容 holder.textView.setText(list.get(position).toString()); // 显示图片 holder.imageView.setImageResource((Integer) list2.get(position)); // 给text设置监听 holder.textView.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() { @Override public void onClick(View v) { // 这里给每一个 textView设置监听,跳转到另外一个页面(用来表示点击列表项 --> 跳转到详细页面) Intent intent = new Intent(mcontext, MainActivity.class); // 传参 给跳转到的MainActivity 传入参数、便于定向显示每一行的详细页面 intent.putExtra("key1",holder.textView.getText()); mcontext.startActivity(intent); } }); } @Override // 返回 RecyclerView 中的项数。这是告诉 RecyclerView 需要显示多少项 public int getItemCount() { // 返回 list的大小 即 recyclerView能显示的总行数 return list.size(); }
用户界面的跳转
-
前面在adpter中监听textView组件,进而跳转到详细页面,下面看跳转的目标Activity中如何显示详细信息:
详细页面的UI设计如下:

在目标Activity中完成的两个任务:1. 接收源Activity的参数、进而显示指定的联系人详细页面。2. 设计一个service,采用bind方法在启动Activity时自动服务启动。
接收参数如下:
// 获取一个intent对象 其他的activity 传参过来 Intent intent = getIntent(); // 获取传递的参数 通过设置的变量名 --> key1 字符串参数 String string1 = intent.getStringExtra("key1"); if (string1 != null) { // 在text中显示 // 设置textview的内容 textView.setText(string1); } // 接收传入的图像信息 int image = intent.getIntExtra("key2",0); if (image != 0) { // 显示联系人的图片 imageView.setImageResource((Integer) image); }bind启动服务,这里额外需要一个 MyService.java文件 来继承Service类:
Intent serviceIntent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, MyService.class); // 使用bindservice方法 ServiceConnection connection = new ServiceConnection() { @Override public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) { Log.d("lzl","onServiceConnected ....."); // 接收Myservice与服务进行通信。 Activity开始时就启动服务 mybinder = (MyService.Mybinder) service; mybinder.todo(); } @Override public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) { Log.d("lzl","onServiceDisconnected ....."); // 当服务与客户端的连接意外断开时 清空对象 解绑 mybinder = null; } }; this.bindService(serviceIntent,connection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);Myservice.java文件设置如下,其中要重写onBind方法和onDestroy方法,以及定义一个内部类Mybinder:
public MyService() { //context = this; //Log.d("lzl","MyService create......"); } @Override public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) { // TODO: Return the communication channel to the service. Log.d("lzl","MyService onBind ......"); Mybinder binder = new Mybinder(); return binder; } // 继承Binder 来定义子类 添加一个额外的方法 来启动 public class Mybinder extends Binder{ public Mybinder() { } // 定义启动服务的方法 public void todo(){ Log.d("lzl","Mybinder todo() ......"); // 初始化 mediaplayer 对象 mediaplayer = MediaPlayer.create(getApplicationContext(),R.raw.wu_zhu_x_zhi_er); // 启动服务 mediaplayer.start(); } } @Override public void onDestroy() { Log.d("lzl","onDestroy......"); // 销毁时释放资源 mediaplayer.stop(); super.onDestroy(); } -
如何给不同的列设置不同的音乐服务?难道给每个列都写一个serivce.java文件?肯定不显示。这里分析一下音乐服务如何启动:
无论是非绑定式服务还是绑定式服务,都主要是在Service.java文件中来设置的音乐,所以如果能动态选择音乐(根据列的跳转信息),那么就值需要这一个Service.java文件即可。修改后的代码如下:
这里暂时只改bind服务:
fragment增加传入music资源
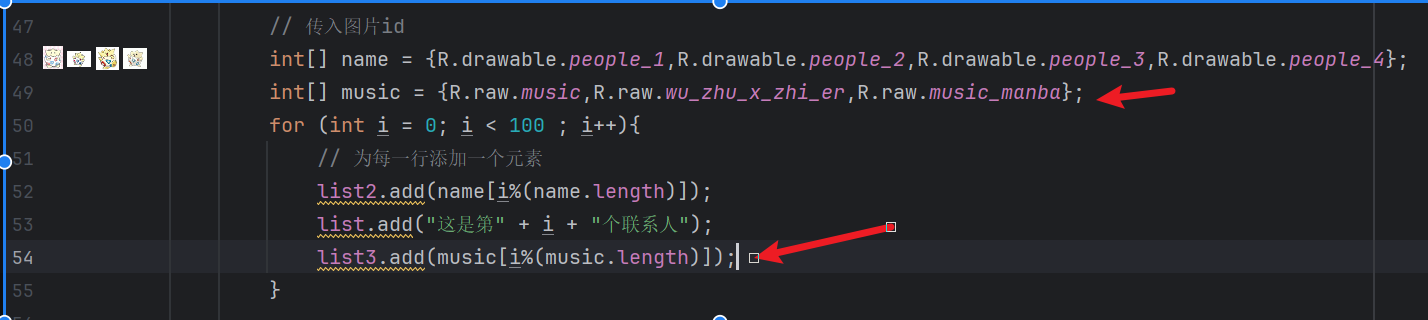
在adpter接收参数,传递给MainActivity启动服务:
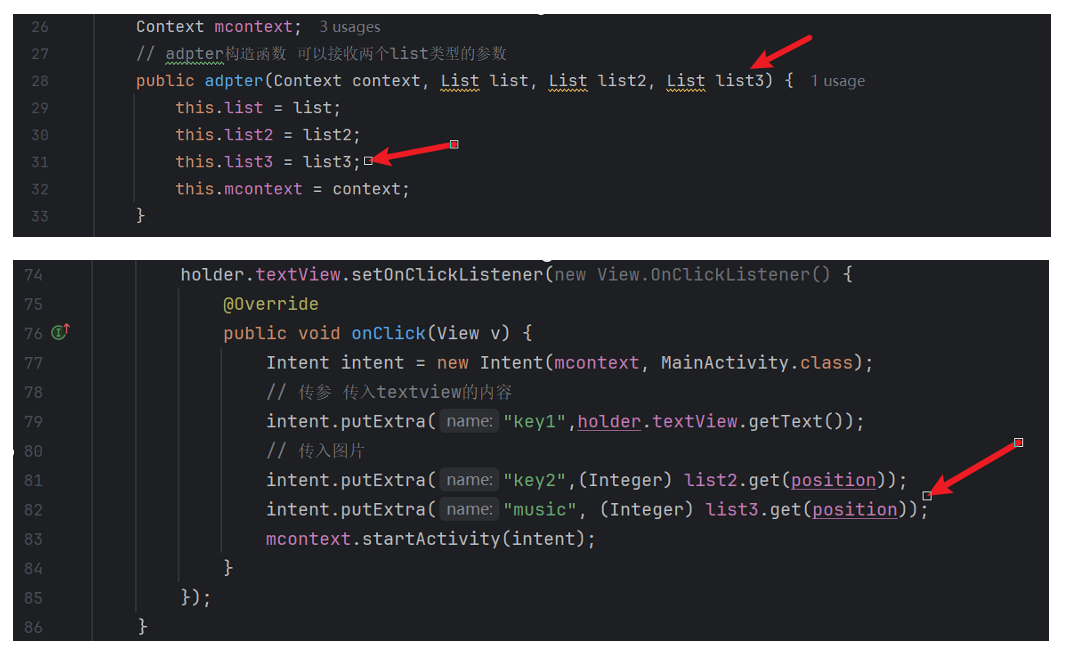
MainActivity中接收music参数,在传递给service来自定义选择音乐文件,service中给todo方法增加一个参数,在绑定到音乐式选择指定音乐。代码如下,上面是MainActivity文件,下面是service文件:
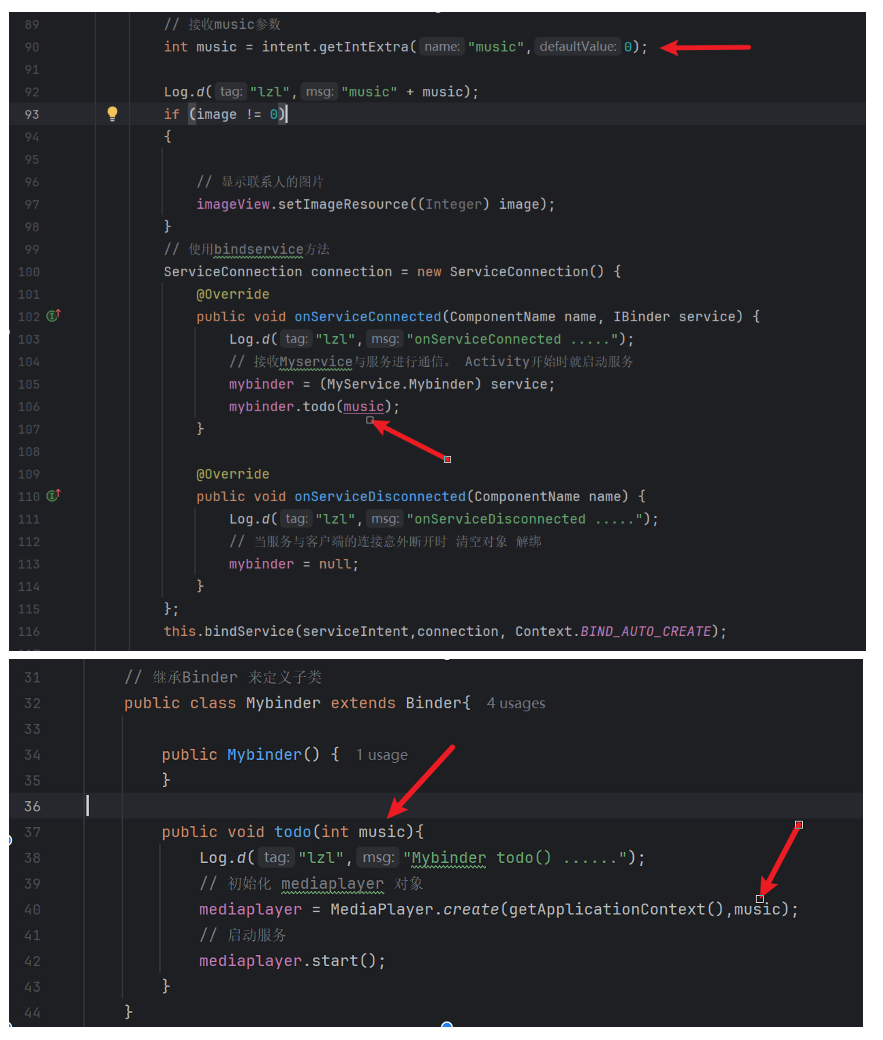
这样就能根据不同的列进而选择不同的service音乐启动了!!!
3. 朋友圈界面
4. 我的界面
这两个界面不做额外描述。
项目源码位于:https://gitee.com/poppy-qwq/
