嵌入式学习-C嘎嘎-Day03
嵌入式学习-C嘎嘎-Day03
1. 友元 friend
1.1 概念
1.2 友元函数
1.3 友元类
1.4 友元成员函数
2. 运算符重载
2.1 概念
2.2 友元函数运算符重载
2.3 成员函数运算符重载
2.4 特殊运算符重载
2.4.1 赋值运算符重载
2.4.2 类型转换运算符重载
2.5 注意事项
3. 字符串类型 string
1. 友元 friend
1.1 概念
定义:
类实现了数据的隐藏与封装,类的成员变量一般定义为私有成员,仅能通过类的成员函数才能读写。如果成员变量定义为公共的,则又破坏了封装性。但是某些情况下,需要频繁读写类的成员变量,特别是在对某些成员函数多次调用时,由于参数传递、类型检查和安全性检查等都需要时间开销,而影响程序的运行效率。
友元是一种定义在类外部的普通函数,但他需要在类体内进行说明,为了和该类的成员函数加以区别,在说明时前面加以关键字friend。友元不是成员函数,但是他能够访问类中的私有成员。
作用:
在于提高程序的运行效率,但是,他破坏了类的封装性和隐藏性,使得非成员函数能够访问类的私有成员。导致程序维护性变差,因此使用友元要慎用。
友元主要的应用场景是运算符重载。
用法:
- 友元函数
- 友元类
- 友元成员函数
1.2 友元函数
友元函数是一种在类内说明,但本身属于类外的函数,可以访问类内所有成员。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Girl
{
private:
int age;
public:
Girl(int age):age(age){}
int get_age() const
{
return 18;
}
// 友元关系说明
friend void get_real_age(Girl& g);
};
void get_real_age(Girl& g)
{
// 获取私有成员的数值并修改
cout << "真实年龄:" << g.age << endl;
g.age = 18;
cout << "修改后的真实年龄:" << g.age << endl;
}
int main()
{
Girl g(40);
cout << g.get_age() << endl; // 18
get_real_age(g);
}需要注意的是:
- 友元函数没有this指针
- 友元函数的类内说明可以在任何部分,不受权限的影响
- 一个函数可以是多个类的友元函数,只需要分别在个各类中说明
1.3 友元类
当一个类B成为了另一个类A的友元类时,类A的所有成员就可以被类B访问了。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
private:
int value = 1;
// 友元关系说明
friend class B;
};
class B
{
public:
void access(A& a)
{
cout << this << endl;
// cout << this->value << endl; 错误
// 读取和修改a的private成员
cout << a.value++ << endl;
cout << a.value << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
A a;
B b;
b.access(a);
}需要注意的是:
- 友元关系不能被继承
- 友元关系不具有交换性
- 友元关系不具有传递性
1.4 友元成员函数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 3. 上一步用到了A类,补充A声明
class A;
// 2. 上一步中用到了B类,补充B类
class B
{
public:
void access(A& a);
};
class A
{
private:
int value = 1;
// 1. 说明友元关系
friend void B::access(A& a);
};
// 4. 补充友元成员函数的内容
void B::access(A &a)
{
cout << a.value++ << endl;
cout << a.value << endl;
}
int main()
{
A a;
B b;
b.access(a);
}
2. 运算符重载
2.1 概念
函数可以重载,在C++中运算符也可以重载,运算符默认的操作类型只能是基本数据类型,但是对于很多用户自定义类型,也需要类似的运算操作,此时可以重载运算符,赋予这些运算符新的功能,执行对于自定义类型的运算操作。
可以被重载的运算符:
算术运算符:+、-、*、/、%、++、--
位操作运算符:&、|、~、^(位异或)、<<(左移)、>>(右移)
逻辑运算符:!、&&、||
比较运算符:<、>、>=、<=、==、!=
赋值运算符:=、+=、-=、*=、/=、%=、&=、|=、^=、<<=、>>=
其他运算符:[]、()、->、,、new、delete、new[]、delete[]
不被重载的运算符:
成员运算符“.”、指针运算符“*”、三目运算符“? :”、sizeof、作用域“::”
通常有两种运算符重载的方式(部分运算符只支持一种):
- 友元函数运算符重载
- 成员函数运算符重载
可以把运算符重载看做是一种特殊的函数重载,运算符是一种特殊的函数。
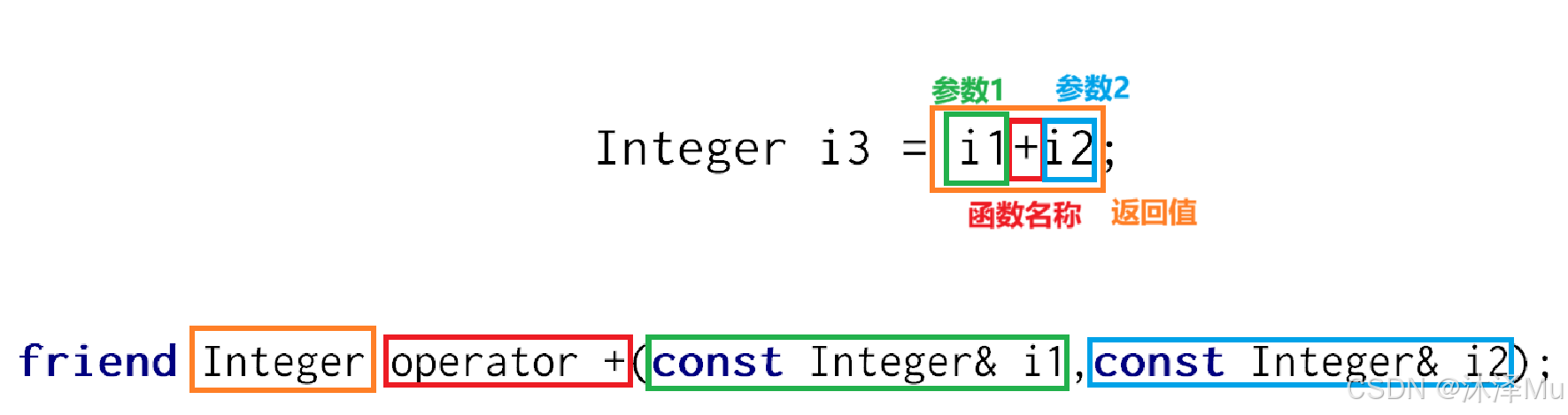
2.2 友元函数运算符重载
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
friend Integer operator +(const Integer& i1,const Integer& i2);
friend Integer operator ++(Integer& i); // 前置
friend Integer operator ++(Integer& i,int); // 后置
};
Integer operator +(const Integer& i1,const Integer& i2)
{
return i1.value + i2.value;
}
Integer operator ++(Integer& i)
{
return ++i.value;
}
Integer operator ++(Integer& i,int)
{
return i.value++;
}
int main() {
Integer i1(1);
Integer i2(2);
Integer i3 = i1+i2;
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 3
cout << (++i3).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << (i3++).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 5
return 0;
}
2.3 成员函数运算符重载
成员函数运算符重载与友元函数运算符重载的最大区别是,成员函数运算符重载的输入参数比友元函数运算符重载少一个,因为友元函数的第一个参数在成员函数中使用this指针表示。

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
Integer operator +(const Integer& i);
Integer operator ++(); // 前置
Integer operator ++(int); // 后置
};
Integer Integer::operator +(const Integer& i)
{
// this指针可以不写,因为只要不重名编译器自动添加
return this->value + i.value;
}
Integer Integer::operator ++()
{
return ++this->value;
}
Integer Integer::operator ++(int)
{
return this->value++;
}
int main() {
Integer i1(1);
Integer i2(2);
Integer i3 = i1+i2;
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 3
cout << (++i3).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << (i3++).get_value() << endl; // 4
cout << i3.get_value() << endl; // 5
return 0;
}
2.4 特殊运算符重载
2.4.1 赋值运算符重载
如果程序员不手动在类中编写赋值运算符重载函数,编译器会为这个类自动添加一个默认的赋值运算符重载函数,以便于实现同类型对象的赋值操作。
赋值运算符重载函数只能通过成员函数实现,因为需要this指针。
需要注意的是,如果出现了浅拷贝,也要修改赋值运算符重载函数的逻辑。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
// 默认的赋值运算符重载函数
Integer& operator =(const Integer& i)
{
this->value = i.value;
return *this;
}
};
int main() {
Integer i1(1);
Integer i2(2);
i1 = i2; // 赋值运算
cout << i1.get_value() << endl; // 2
return 0;
}
【思考】截止到目前,如果一个成员手写了一个空类,编译器会自动添加哪些内容:
- 构造函数
- 析构函数
- 拷贝构造函数
- 赋值运算符重载函数
2.4.2 类型转换运算符重载
类型转换运算符重载函数也必须使用成员函数重载,格式比较特殊
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
* @brief The Integer class 整数类
*/
class Integer
{
private:
int value;
public:
Integer(int v):value(v){}
int get_value() const
{
return value;
}
// 类型转换函数
operator int()
{
return value;
}
};
int main() {
// int → Integer
Integer i1 = 1; // 编译器自动调用构造函数
cout << i1.get_value() << endl; // 1
// Integer → int
int i2 = i1;
cout << i2 << endl; // 1
return 0;
}
2.5 注意事项
- 运算符重载只能限制在C++已有的范围内,不能创建的新的运算符。
- 运算符重载不能改变运算符的优先级和结合性。
- 运算符重载不能改变运算符的操作数和语法结构。
- 运算符重载的操作数一定包含自定义类型。
- 运算符重载的功能应该与原有功能相似,避免滥用。
- 运算符重载不能设置参数默认值。
- 通常单目运算符优先考虑成员函数,双目运算符优先考虑友元函数。
3. 字符串类型 string
之前对string的学习比较基础,实际上string有诸多字符串处理函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string s; // 创建一个空字符串
cout << s.empty() << endl; // 判断内容是否为空
// 构造函数,参数const char*
string s1 = "Thursday";
string s2("Thursday");
cout << (s1 == s2) << endl;
// 拷贝构造函数
string s3 = s1;
string s4(s3);
cout << s3 << " " << s4 << endl;
// 参数1:const char* 原字符串
// 参数2:保留前几个字符
string s5("ABCDEFG",2);
cout << s5 << endl; // AB
s = "ABCDEFG";
// 参数1:string 原字符串
// 参数2:不保留前几个字符
string s6(s,2);
cout << s6 << endl; // CDEFG
// 参数1:数量
// 参数2:字符元素
string s7(5,'A');
cout << s7 << endl; // AAAAA
swap(s6,s7); // 交换
cout << s6 << endl;
cout << s7 << endl;
// 连接
cout << s6 + s7 << endl;
// 尾插单字符
s6.push_back('B');
cout << s6 << endl;
// 尾插string,支持链式调用
s6.append("CC").append("DDD");
cout << s6 << endl;
// 在第二个位置插入内容"111"
s6.insert(1,"111");
cout << s6 << endl;
// 参数1:替换的起始位置
// 参数2:替换的字符数
// 参数3:替换的新内容
s6.replace(0,3,"*****");
cout << s6 << endl;
s6.pop_back(); // 删除最后一个字符
cout << s6 << endl;
s6 = "1234567890";
// 参数1:删除的起始位置
// 参数2:删除的字符数
s6.erase(3,4);
cout << s6 << endl;
s6.clear(); // 清空
cout << s6.size() << endl; // 0
s6 = "ABCDEFGHIJK";
char c[20];
// 参数1:拷贝的目标
// 参数2:拷贝的字符数量
// 参数3:拷贝的起始位置
s6.copy(c,5,2);
cout << c << endl;
// C++ string→C string
strcpy(c,s6.c_str());
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
