SpringAMQP
什么是SpringAMQP

官方网址
官方文档![]() https://spring.io/projects/spring-amqp
https://spring.io/projects/spring-amqp
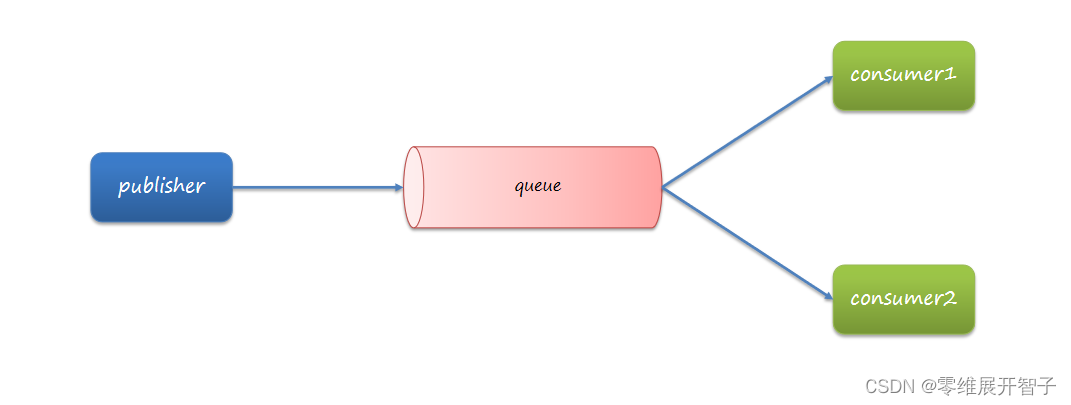
Base Queue 简单队列模型

对于生产者
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>spring:
rabbitmq:
port: 5672
host: 8.130.89.67
virtual-host: /
username: itcast
password: 123 @Autowired
private RabbitTemplate template;
@Test
public void testSimpleQueue(){
String queueName="simple.queue";
String message="hello spring ampq";
template.convertAndSend(queueName,message);
}对于消费者
依赖已经在父工程中到过了
配置和生产者的一样,粘贴过来就行
新建一个类
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg){
System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}
}启动项目就可以消费消息了
因为是消息队列,所以先生产的消息就先被消费。先进先出。
rabbit没有消息回溯功能,一旦被消费就不可逆。
Work Queue 工作队列模型
可以提高消息处理速度,避免队列消息堆积。
案例
 生产者
生产者
@Test
public void testWorkQueue() throws InterruptedException {
String queueName="simple.queue";
String message="hello , message_";
for(int i=1;i<=50;i++){
template.convertAndSend(queueName,message+i);
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}消费者
配置文件
spring:
rabbitmq:
port: 5672
host: 8.130.89.67
virtual-host: /
username: itcast
password: 123
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息 @RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("spring 消费者1接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】"+ LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(20);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("spring 消费者2接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】"+LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(200);
}启动消费者项目,
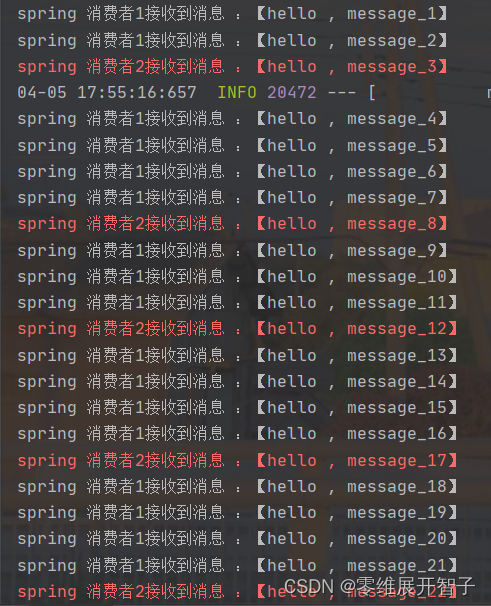
可以看到消息的处理时按照生产顺序来的,先进先出。
多个消费者绑定到一个队列,同一条消息只会被一个消费者处理
通过配置prefetch来控制消费者预取的消息数量
发布、订阅模型-Fanout
允许将同一消息发送给多个消费者。实现方式是加入了exchange(交换机)。
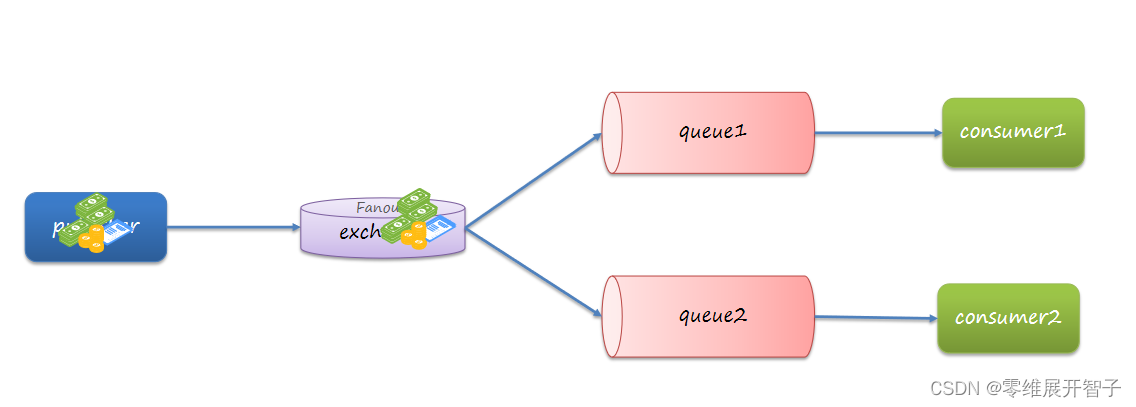
Fanout Exchange 会将接收到的消息广播到每一个跟其绑定的queue。
消费者
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("itcast.fanout");
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue1");
}
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue2");
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange);
}
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2,FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange);
}
} @RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void listenFanoutQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("spring 消费者1接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void listenFanoutQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("spring 消费者1接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}发布者
@Test
public void testFanoutExchange() {
String exchangeName="itcast.fanout"; //对应消费者的交换机名字
String message="hello , everyBody";
template.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"",message);
}

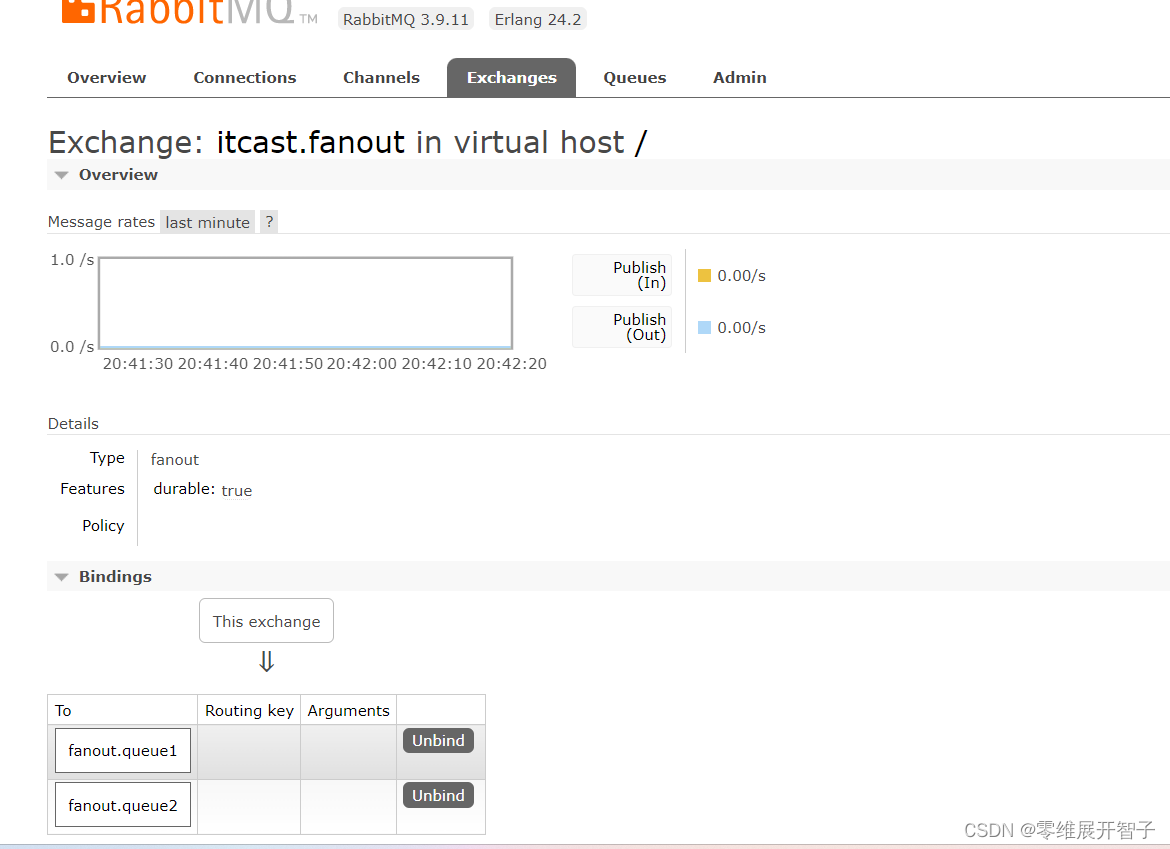
交换机的作用
接受发布者发布的消息
将消息按照规则路由到与之绑定的队列
不能缓存消息,路由失败,消息丢失
发布、订阅模型-Direct
每一个Queue都与Exchange设置一个BindingKey
发布者发送消息时,指定消息的RoutingKey
Exchange将消息路由到BindingKey与消息RoutingKey一致的队列
消费者
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.direct",type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red","blue"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("spring 消费者1接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.direct",type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red","yellow"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("spring 消费者2接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}生产者
@Test
public void testDirectExchange() {
String exchangeName="itcast.direct";
String message="hello , red";
template.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"red",message);
}差异
Direct交换机和Fanout交换机的差异
Fanout将消息路由给每一个与之绑定的队列
Direct交换机根据RoutingKey判断路由给哪一个队列
如果多个队列的RoutingKey相等,则和Fanout功能类似
核心
@Queue @Exchange
发布、订阅模型-Topic
TopicExchange与DirectExchange类似,区别在于routingKey,Queue与Exchange指定BindingKey时可以使用通配符:
# :代指0个或多个单词
* :代指一个单词
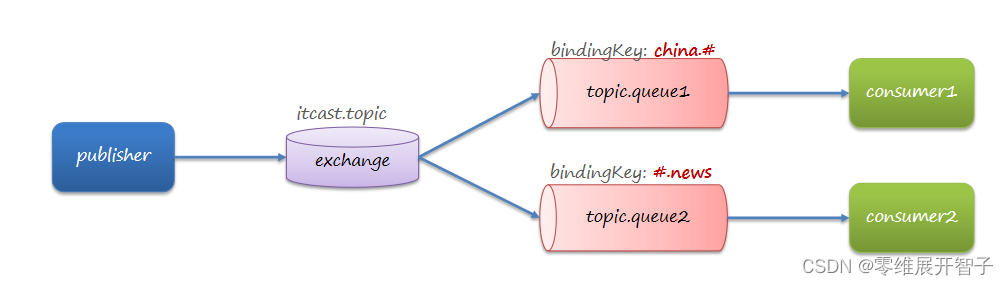
消费者
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic",type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = {"china.#"}
))
public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("spring 消费者1接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "itcast.topic",type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = {"#.news"}
))
public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("spring 消费者2接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}生产者
@Test
public void testTopicExchange() {
String exchangeName="itcast.topic";
String message="你看到了这句话";
template.convertAndSend(exchangeName,"Chain.news",message);
}差异
Direct交换机与Topic交换机的差异
Topic交换机接收的消息RoutingKey必须是多个单词,以 . 分割
Topic交换机与队列绑定时的bindingKey可以指定通配符
消息转换器
在SpringAMQP的发送方法中,接收消息的类型是Object,也就是说我们可以发送任意对象类型的消息,SpringAMQP会帮我们序列化为字节后发送。
生产者
@Test
public void testSimpleQueue(){
String queueName="simple.queue";
Map<String ,Object> map=new HashMap<>();
map.put("name","angelababy");
map.put("sex","woman");
template.convertAndSend(queueName,map);
}Spring的对消息对象的处理是由org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter来处理的。而默认实现是SimpleMessageConverter,基于JDK的ObjectOutputStream完成序列化。 如果要修改只需要定义一个MessageConverter 类型的Bean即可。推荐用JSON方式序列化,
父项目导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
</dependency>启动类中声明Bean也可以书写配置类,都一样
@Bean
public MessageConverter jsonMessageConverter(){
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}消费者
也是需要声明Bean和生产者一样
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(Map<String ,Object> msg){
System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息 :【" + msg + "】");
}需要注意的就是接受消息的参数数据类型修改成Map的


