Java-红黑树的实现
目录
- 一、概述
- 二、红黑树的操作
- 1. 变色
- 2. 左旋与右旋
- 3. 插入节点
- 4. 删除节点
- 三、手写代码
- 1. 通用方法
- 2. 中序遍历
- 3. 左旋
- 4. 右旋
- 5. 添加节点
- 6. 删除节点
- 四、完整代码
- 五、测试
- 1. 红黑树打印类
- 2. 测试代码
- 3. 测试结果
一、概述
关于红黑树的学习,先推荐给大家一个网址:
数据结构可视化-红黑树
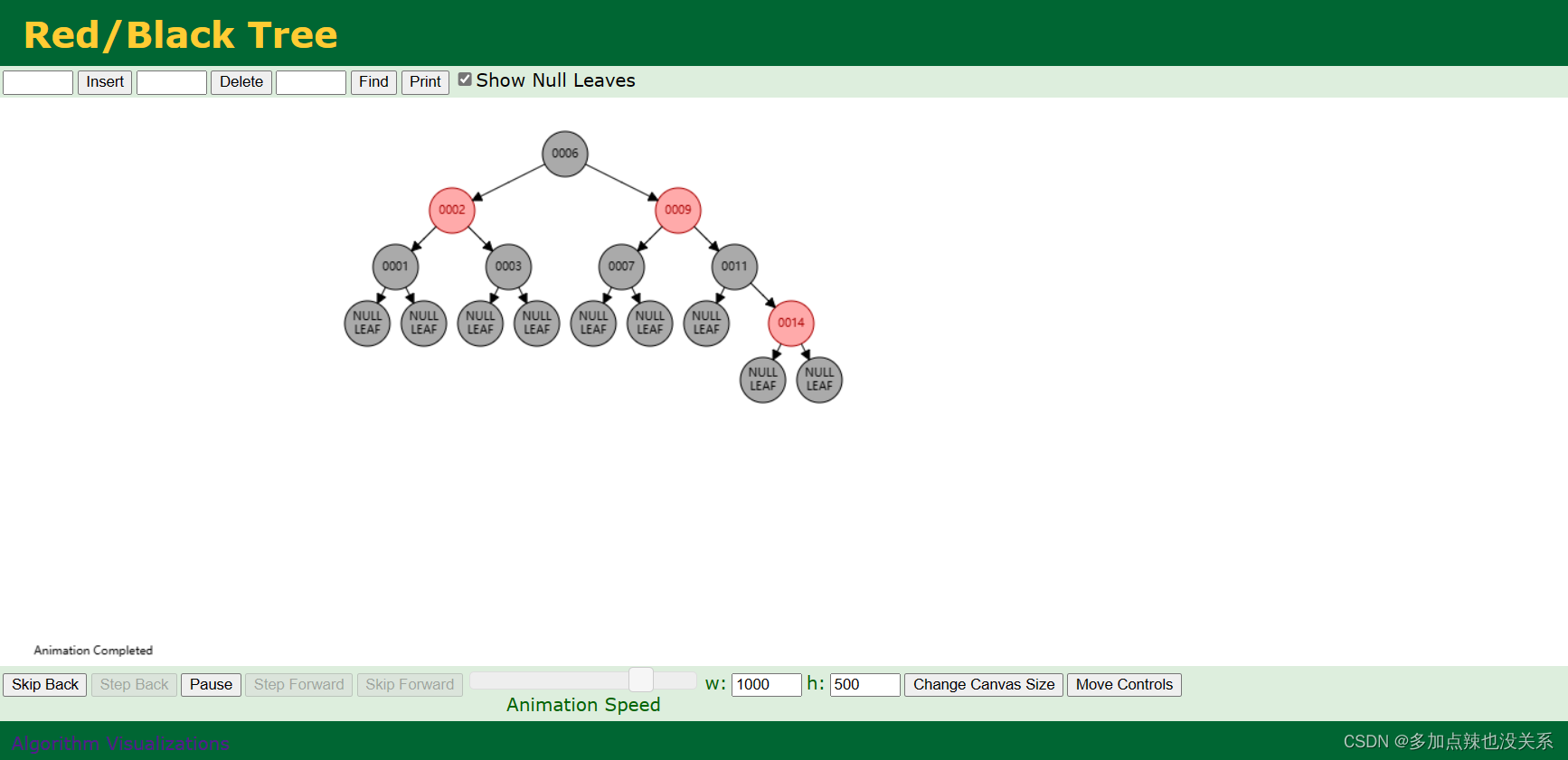
因为红黑树中有变色、左旋、右旋等变化,不是很容易理解,如果能自己对红黑树进行操作,那么这些概念上的东西相对而言就好接受一点了。
红黑树是一种自平衡二叉查找树,和 AVL 树类似,都是在进行插入和删除时通过特定操作保持二叉查找树的平衡,从而获得较高的查找性能。
红黑树虽然复杂,但它的最坏情况运行时间仍非常好,并且在实践中效率很高,它可以在 O(logn) 实践内进行查找、插入和删除操作,其性能要优于 AVL 树。

红黑树的定义:
- (1)其节点要么是
红色,要么是黑色 - (2)根节点是
黑色的 - (3)
每个叶子节点都是黑色的空节点(用 NULL 表示) - (4)
红色节点的两个子节点均为黑色的 - (5)从
任意节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同的黑色节点
其中,第(1)(4)(5)条保证了红黑树中任意一条路径都不比其他路径的 2 倍长,是近似平衡的;根据(4)条,每出现一个红节点,必然对应有一个黑色节点,而反过来不一定成立,所以一条路径下黑色节点个数 >= 红色节点个数;根据(1)(5),任意一条路径上的所有节点要么红,要么黑,且黑色的个数相同,可得一条路径的长度 <= 另一条路径长度的 2 倍。
二、红黑树的操作
红黑树的前序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、查找最大值、查找最小值、输出等接口与二叉查找树基本一样,插入和删除操作在其基础上需要考虑树失衡的情况,为了保持平衡,需要对树进行调整,调整的方式有变色、旋转。
1. 变色
为了重新符合红黑树的规则,需要尝试把红色节点变为黑色节点,或者把黑色节点变为红色节点。
例如:我先往红黑树中插入 22、25、27 三个节点
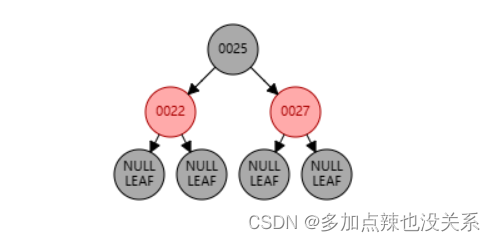
如果我再添加一个 6 节点,那么它会挂载到 22 节点的左侧
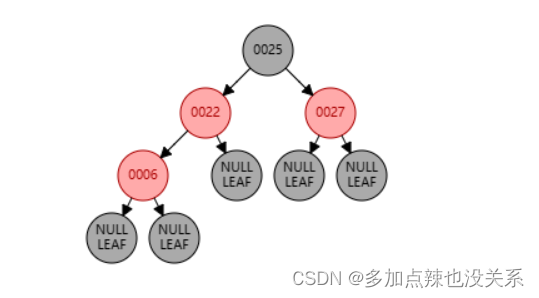
可以观察到 6、22 节点都为红色,这显然不符合规则 (4),所以需要将 22 节点从红色变成黑色,当22 节点变为黑色后打破了规则 (5),发生了连锁反映,所以 25 要从黑色变为红色色,又因为规则 (4),红色节点 25 的字节点均为黑色节点,所以 27 节点需要从 红色 转为 黑色。
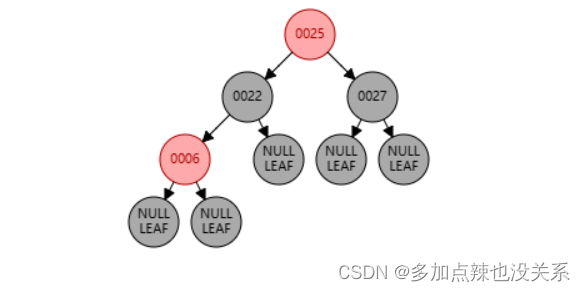
根据 (2) 可知,根节点必须为黑色,所以 25 节点又需要从 红色 转变为 黑色
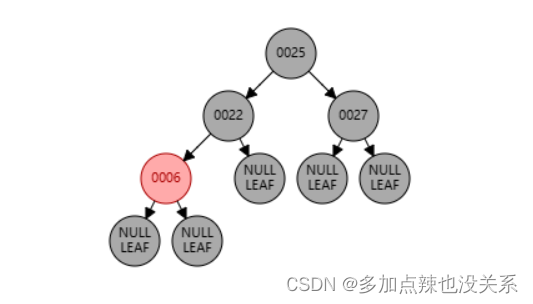
PS:可在 数据结构可视化-红黑树 中自己去操作一遍观察它的颜色变化。
2. 左旋与右旋
节点的平衡因子是它的左子树高度减去右子树高度(有时相反),叶子节点的平衡因子为 0。带有平衡因子1、0 或 -1 的节点被认为是平衡的;带有平衡因子 -2 或 2 的节点被认为是不平衡的,并需要重新平衡该树。
一般通过旋转最小失衡子树来调整失衡二叉树。其手段分为左旋和右旋,与 AVL 树的左旋和右旋过程是一致的,旋转的目的就是通过降低整棵树的高度来平衡。
最小失衡树就是在新插入的节点向上查找,以第一个平衡因子绝对值超过 1 的节点为根节点,即一颗失衡的树有可能有多棵子树同时失衡。
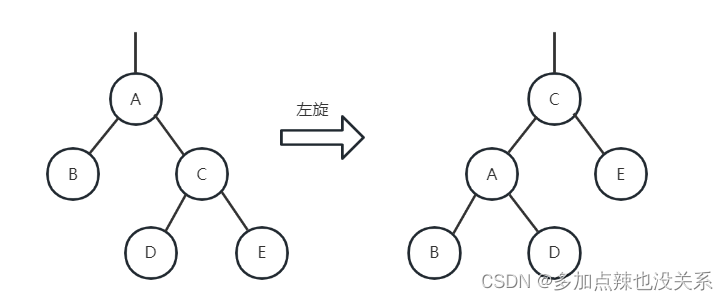
左旋:
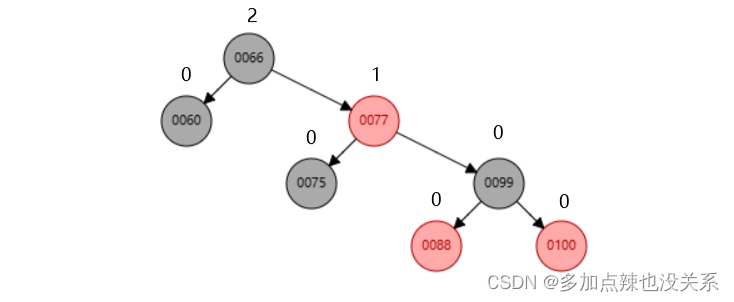
如上图所示,节点 66 就是最小失衡子树,如果再往后添加 > 100 的节点,就会采用左旋的方法来调整红黑树。
比如我再添加 111 节点,该树结构发生变化如下:
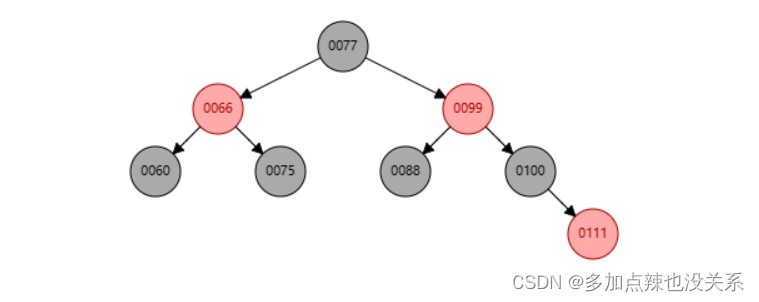
- 节点(
66)的右孩子(77)替代此节点的位置 - 右孩子(
77) 的左子树(75)变为该节点(66)的右子树 - 节点(
66)本身变为右孩子(77)的左子树
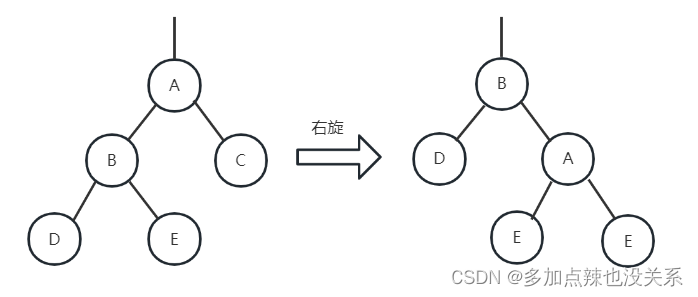
右旋:
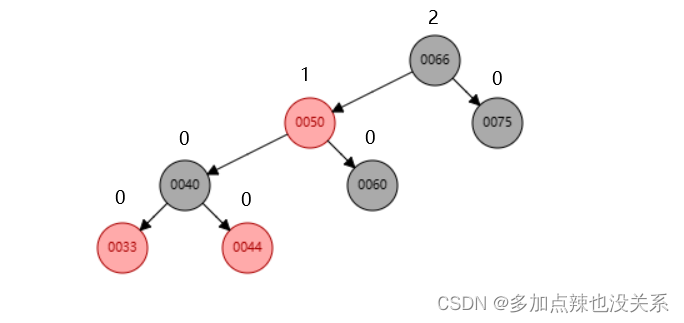
如上图所示,节点 66 就是最小失衡子树,如果再往后添加 < 33 的节点,就会采用右旋的方法来调整红黑树。
比如我再添加 20 节点,该树结构发生变化如下:

- 节点(
66)的左孩子(50)代替此节点 - 节点左孩子(
50)的右子树(60)变为节点的左子树 - 节点(
66)本身变为左孩子(50)的右子树
其实左旋和右旋基本相似,只是方向相反,平衡二叉树失衡的情况可以统计为四种,假设有一棵平衡二叉树某个节点 A,有四种插入方式会使 A 的左右高度差大于 1,即整颗树失衡。这四种情况及调整方式如下:
| 插入方式 | 描述 | 旋转方式 |
|---|---|---|
| LL | 在 A 的左子树根节点的左子树上插入节点 | 右旋转 |
| RR | 在 A 的右节点树根节点的右子树上插入节点 | 左旋转 |
| LR | 在 A 的左子树根节点的右子树上插入节点 | 先左旋转再右旋转 |
| RL | 在 A 的右子树根节点的左子树上插入节点 | 先右旋转再左旋转 |
3. 插入节点
在红黑树中插入节点时,首先找到该节点要插入得位置,即一层一层比较,大的放右边,小的放左边,直到找到 null 的节点放入即可。
- (1) 如果插入的为根节点,则直接把颜色改为黑色即可
- (2) 如果插入节点的父节点是黑色节点,则不需要调整,这是因为插入的节点会初始化为红色节点,红色节点是不会影响树的平衡的。
- (3) 插入节点的祖父节点为
null,即插入节点的父节点是根节点,直接插入即可 - (4) 插入节点的父节点和祖父节点都存在,并且其父节点是祖父节点的左节点,分两种情况:
- ① 插入节点的叔叔节点是红色,则将父节点和叔叔节点都改成黑色,然后将祖父节点改成红色即可
- ② 插入节点的叔叔节点是黑色或者不存在
- 若插入节点是其父节点的右孩子,则将其父节点左旋
- 若为左孩子,则将父节点变成黑色节点,将其祖父节点变成红色节点,然后将其祖父节点右旋
- (5) 插入节点的父节点和祖父节点都存在,并且其父节点是祖父节点的右节点,分两种情况:
- ① 插入节点的叔叔节点是红色,则将父亲节点和叔叔节点都改成黑色,然后将祖父节点改成红色即可
- ② 插入节点的叔叔节点是黑色或不存在
- 若插入节点是其父节点的左孩子,则将其父节点右旋
- 若为右孩子,则将其父节点变成黑色节点,将其祖父节点变成红色节点,然后将其祖父节点左旋
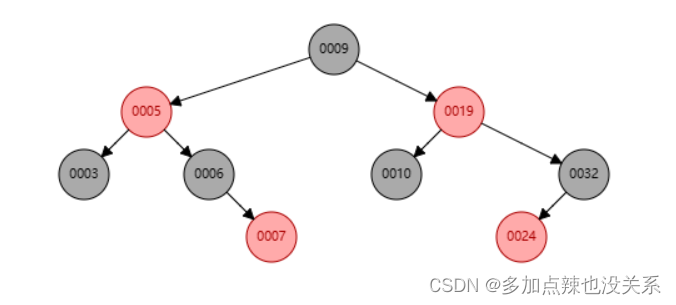
练习:往红黑树中依次添加 10 —> 5 —> 9 —> 3 —> 6 —> 7 —> 19 —> 32 —> 24,观察其变化
4. 删除节点
红黑树在进行删除节点操作的时候,会先进行二叉搜索树的删除,然后进行调整。
红黑树树的删除主要有以下几种情景:
- 情况一:待删除的节点无左右孩子
- 该节点为红色,直接删除
- 该节点为黑色,则继续考虑兄弟节点的颜色
- 情况二:待删除的节点只有左孩子或右孩子
- 由红黑树特性可知该元素必为黑色,直接把该节点的父节点指向它的左孩子或者右孩子
- 情况三:待删除的节点既有左孩子也有右孩子
- 需要先找到其右子树的最左孩子(或左子树的最右孩子),即左(右)子树中序遍历时的第一个节点,然后将其与待删除的节点互换,如果找到的节点是红色,则无需调整,如果为黑色,则删除此节点,并将其兄弟节点变为红色
总结上面的3种情况可得到一个结论,只有删除节点为黑色时才会破坏红黑树原来的平衡,因在删除节点之前红黑树是平衡状态的,删除之后很明显的其兄弟节点分支必然比删除节点的分支多了一个黑色的节点,因此我们只需要改变兄弟节点的颜色即可,我们只讨论左节点,右节点对称。
① 删除节点的兄弟节点是红色,则将兄弟节点设为黑色,兄弟左子节点设为红色,以父节点为支点左旋

② 兄弟节点是黑色的,兄弟的两个子节点是红色的,将兄弟节点右子节点设置为黑色,再将父节点左旋

③ 兄弟节点是黑色的,且兄弟节点的右子节点是红色,左子节点为空,以父节点为支点左旋

④ 兄弟节点是黑色的,且兄弟节点的左子节点是红色,右子节点为空,将兄弟节点置为红色,左子节点置为黑色,再将兄弟节点右旋转(转换成了三的情况),最后再将父节点左旋转

⑤ 兄弟节点是黑色的,且无子节点,将兄弟节点置为红

⑥ 若被删节点还有祖父节则过程如下

三、手写代码
创建一个 RedBlackTree 类,该类中写一个内部类 TreeNode 作为树的节点,每个节点当中会记录父节点、子节点、颜色以及键值等信息,color 中 true 表示红色,black 表示黑色。使用 lombok 添加类的get、set和构造方法。
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class RedBlackTree <K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
// true 表示红色
private static final boolean RED = true;
// false 表示黑色
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
// 根节点
private TreeNode <K,V> root;
// 树的大小
private int size;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public static class TreeNode <K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
// 父节点
private TreeNode<K,V> parent;
// 左节点
private TreeNode<K,V> left;
// 右节点
private TreeNode<K,V> right;
// 颜色
private boolean color;
// 键
private K key;
// 值
private V value;
}
}
1. 通用方法
/**
* 设置父节点
*/
private void setParent(TreeNode<K,V> node,TreeNode<K,V> parentNode) {
if (node != null) {
node.setParent(parentNode);
}
}
/**
* 获取叔节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> getUncle(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 获取父节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
// 获取爷爷节点
TreeNode<K, V> ancestor = parent.getParent();
if (ancestor == null) {
// 如果没有爷爷节点则说明父节点为根节点,无叔节点
return null;
}
if (parent == ancestor.getLeft()) {
// 说明爷爷节点的左节点是父节点,则爷爷节点的右节点为叔节点
return ancestor.getRight();
} else {
// 说明爷爷节点的右节点是父节点,则爷爷节点的左节点为叔节点
return ancestor.getLeft();
}
}
/**
* 获取兄弟节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> getBrother(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 获取父节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
if (parent == null) {
// 如果没有父节点,则说明该节点为根节点,无兄弟节点
return null;
}
return node == parent.getLeft() ? parent.getRight() : parent.getLeft();
}
/**
* 找到节点 node 的父节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> findParentNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> dataRoot = root;
TreeNode<K, V> child = dataRoot;
while (child != null) {
int cr = child.getKey().compareTo(node.getKey());
if (cr == 0) {
return child;
} else if (cr > 0) {
dataRoot = child;
child = child.getLeft();
} else {
dataRoot = child;
child = child.getRight();
}
}
return dataRoot;
}
/**
* 根据 key 查询某个节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> findTreeNode(K key) {
// 从根节点开始
TreeNode<K,V> temp = root;
// 节点不为 null 则进行循环查找
while (temp != null) {
int cr = temp.getKey().compareTo(key);
if (cr == 0) {
return temp;
} else if (cr > 0) {
// 往左边找
temp = temp.left;
} else {
// 往右边找
temp = temp.right;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取前驱节点:比当前节点小的最大值
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> provNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> temp = node.getLeft();
if (temp == null) {
// 如果当前节点没有左子节点,则它的前驱节点为它的父节点
return node.getParent();
}
while (temp.right != null) {
temp = temp.right;
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 获取后继节点:比当前节点大的最小值
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> successNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> temp = node.getRight();
while (temp.left != null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
return temp;
}
2. 中序遍历
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
public List<TreeNode<K,V>> infixOrder() {
ArrayList<TreeNode<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
this.infixOrder(root,result);
return result;
}
private void infixOrder(TreeNode<K,V> node,List<TreeNode<K,V>> result) {
if (node != null) {
infixOrder(node.left,result);
result.add(node);
infixOrder(node.right,result);
}
}
3. 左旋
/**
* 左旋操作
*/
private void rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 假设 node 节点为 A 节点
TreeNode<K, V> right = node.getRight();
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
// A 节点的右节点变为原右节点的左节点
node.setRight(right.getLeft());
// A 节点的父节点变为原右节点
setParent(node,right);
// 原右节点的左节点的父节点变为 A
setParent(right.getLeft(),node);
// 原右节点的左节点变为 A
right.setLeft(node);
if (parent == null) {
// 如果 A 节点的父节点为 null,也就是说 A 为根节点
// 将根节点设置为 A 的原右节点
root = right;
// 原右节点变为根节点,所以它的父节点为 null
setParent(right,null);
} else {
// 如果 A 不是根节点
// 设置原右节点的父节点为 A 的原父节点
setParent(right,parent);
// 设置原父节点的子节点
if (parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(right);
} else {
parent.setRight(right);
}
}
}
4. 右旋
/**
* 右旋操作
*/
private void rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 假设 node 节点为 A 节点
TreeNode<K, V> left = node.getLeft();
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
// A 节点的左节点变为原左节点的右节点
node.setLeft(left.getRight());
// A 节点的父节点变为原左节点
setParent(node,left);
// 原左节点的右节点的父节点变为 A
setParent(left.getRight(),node);
// 原左节点的右节点变为 A
left.setRight(node);
if (parent == null) {
// 如果 A 节点的父节点为 null,也就是说 A 为根节点
// 将根节点设置为 A 的原左节点
root = left;
// 原左节点变为根节点,所以它的父节点为 null
setParent(left,null);
} else {
// 如果 A 不是根节点
// 设置原父节点的子节点
if (parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(left);
} else {
parent.setRight(left);
}
// 设置原右节点的父节点为 A 的原父节点
setParent(left,parent);
}
}
5. 添加节点
/**
* 添加节点
*/
public void addNode(K key,V value) {
TreeNode<K, V> treeNode = new TreeNode<>();
treeNode.setLeft(null);
treeNode.setRight(null);
setParent(treeNode,null);
treeNode.setKey(key);
treeNode.setValue(value);
// 新节点一定为红色
treeNode.setColor(RED);
if (root == null) {
// 如果树为空,则根节点为刚插入的节点
root = treeNode;
// 根节点为黑色
root.color = BLACK;
size++;
return;
}
TreeNode<K, V> parentNode = findParentNode(treeNode);
int cr = parentNode.getKey().compareTo(treeNode.getKey());
setParent(treeNode,parentNode);
if (cr == 0) {
// 替换值
parentNode.setValue(treeNode.getValue());
return;
}
if (cr > 0) {
parentNode.setLeft(treeNode);
} else {
parentNode.setRight(treeNode);
}
// 平衡树
fixInsert(treeNode);
size++;
}
/**
* 根据插入节点左/右旋转来调整树
*
* 插入后修复红黑树平衡的方法
* |---情景1:红黑树为空,将根节点染为黑色
* |---情景2:插入节点的 key 已经存在,不需要处理
* |---情景3:插入节点的父节点为黑色,不需要处理
* |---情景4:插入节点的父节点为红色
* |---情景4.1:叔叔节点存在,并且为红色(父-叔 双红),将父节点和叔节点均染成黑色,将爷爷节点设置为红色,以爷爷节点作为当前节点进行下一轮处理
* |---情景4.2:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的左子树
* |---情景4.2.1:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL情况),将父节点染为黑色,将爷爷节点染为红色,然后以爷爷节点右旋
* |---情景4.2.2:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR情况),以父节点进行一次左旋,得到 LL 双红的情景(4.2.1),然后指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
* |---情景4.3:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的右子树
* |---情景4.3.1:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况),将父节点染为黑色,将爷爷节点染为红色,然后以爷爷节点左旋
* |---情景4.3.2:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况),以父节点进行一次右旋,得到 RR 双红的情景(4.3.1),然后指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
*/
private void fixInsert(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 获取插入节点的父节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
while (parent != null && parent.color == RED) {
// 获取插入节点的叔节点
TreeNode<K, V> uncle = getUncle(node);
if (uncle == null || uncle.color == BLACK) {
// 叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,则需要旋转
// 获取爷爷节点
TreeNode<K, V> ancestor = parent.getParent();
if (parent == ancestor.getLeft()) {
// 父节点是爷爷节点的左子节点
// isLeft:插入节点是否为父节点的左子节点
boolean isLeft = node == parent.getLeft();
if (isLeft) {
// 插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL情况)
// 将父节点染为黑色
parent.setColor(BLACK);
// 将爷爷节点染为红色
ancestor.setColor(RED);
// 以爷爷节点右旋
rotateRight(ancestor);
return;
} else {
// 插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR情况),则以父节点进行一次左旋
rotateLeft(parent);
// 指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
node = parent;
parent = node.getParent();
}
} else {
// 父节点是爷爷节点的右子节点
// isRight:插入节点是否为父节点的右子节点
boolean isRight = node == parent.getRight();
if (isRight) {
// 插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况)
//将父节点染为黑色
parent.setColor(BLACK);
// 将爷爷节点染为红色
ancestor.setColor(RED);
// 然后以爷爷节点左旋
rotateLeft(ancestor);
return;
} else {
// 插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况),则以父节点进行一次右旋
rotateRight(parent);
// 然后指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
node = parent;
parent = node.getParent();
}
}
} else {
// 叔节点存在,并且为红色
// 将父节点和叔节点均染成黑色
parent.setColor(BLACK);
uncle.setColor(BLACK);
// 并且将爷爷节点染成红色
parent.getParent().setColor(RED);
// 以爷爷节点作为当前节点进行下一轮处理
node = parent.getParent();
parent = node.getParent();
}
}
// 根节点为黑色
this.root.setColor(BLACK);
// 根节点的父节点设置为 null
this.root.setParent(null);
}
6. 删除节点
/**
* 删除节点
* |---1:没有找到删除节点则直接返回
* |---2:如果删除的是唯一的根节点,则将 root 置空,返回
* |---3:删除叶子节点
* |---3.1:对要删除的黑色叶子节点进行调整
* |---3.2:删除红黑两种叶子节点
* |---4:删除只有一个子节点的节点
* |---4.1:将红色子节点拷贝到父节点
* |---4.2:将删除节点转换为删除红色叶子节点,即 3.2
* |---5:删除两个子节点的节点
* |---5.1:使用前驱或后继节点作为替换的删除节点
* |---5.2:将删除节点指向替换节点,转为3或4处理
*/
public TreeNode<K, V> removeNode(K key) {
TreeNode<K, V> node = findTreeNode(key);
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("Not find node by key ~~");
return null;
}
TreeNode<K, V> delNode = node;
// 判断需要删除的节点是否为唯一的根节点
if (node == root && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 将根节点置空
root = null;
size--;
return delNode;
}
// 替换节点
TreeNode<K, V> replaceNode = null;
// 双子节点置换为前驱节点或后继节点
if (node.right != null && node.left != null) {
// 获取替代节点
replaceNode = this.getReplaceNode(node);
// 置换删除节点与替换节点的键值
node.key = replaceNode.getKey();
node.value = replaceNode.getValue();
// 删除节点指向替代节点
node = replaceNode;
}
// 有一个红色节点的黑节点置换为红色叶子节点的删除
if ((node.left != null && node.right == null) || (node.left == null && node.right != null)) {
// 获得替换的红叶子节点
replaceNode = node.left == null ? node.right : node.left;
// 置换删除节点与替换节点的键值
node.key = replaceNode.getKey();
node.value = replaceNode.getValue();
// 删除节点指向替代节点
node = replaceNode;
}
// 叶子节点的删除
if (node.color == BLACK) {
// 需要进行平衡调整
fixRemove(node);
}
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
if (node == parent.getLeft()) {
// 删除的节点为左子节点
parent.setLeft(null);
} else {
// 删除的节点为右子节点
parent.setRight(null);
}
node.parent = null;
return delNode;
}
/**
* 删除平衡调整
* |---1:只有一个根节点,直接删除
* |---2:兄弟节点为黑色
* |---2.1:兄弟节点有红色子节点
* |---2.1.1:兄弟节点有红色左子节点
* LL型,该兄弟节点的父节点和左子节点染为黑色,兄弟节点染为父节点的颜色,以父节点右旋
* |---2.1.2:兄弟节点有红色右子节点
* LR型,该兄弟节点的右子节点染为父节点的颜色,父节点染为黑色,以兄弟节点先左旋,再以父节点右旋
* |---2.2:兄弟节点无红色子节点
* |---2.2.1:父节点是红色
* 父节点染为黑色,兄弟节点染为红色
* |---2.2.2:父节点是黑色
* 将兄弟节点染红,把父节点当作新的被删节点,递归调用前面方法,进行相应处理,直至遇到红色父节点并将其染黑,或遇到根节点
* |---3:兄弟为红色节点
* 删除右子节点,需要右旋,兄弟节点和右侄颜色互换
*/
private static final int LL = 1;
private static final int LR = 2;
private static final int RR = 3;
private static final int RL = 4;
private void fixRemove(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
if (root == node) {
root.color = BLACK;
return;
}
// 获取该节点的兄弟节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
TreeNode<K, V> brother = getBrother(node);
if (brother == null) return;
if (brother.color == BLACK) {
// 兄弟节点为黑色
switch (getRemoveRotateType(brother)) {
case LL:
// 兄弟节点旋转后取代父节点颜色
brother.color = parent.color;
// 父节点和侄节点变黑
parent.color = BLACK;
brother.left.color = BLACK;
// 以父节点右旋
rotateRight(parent);
break;
case LR:
// 侄节点变为父节点颜色
brother.right.color = parent.color;
// 父节点变为黑色
parent.color = BLACK;
// 以兄弟节点左旋
rotateLeft(brother);
// 以父节点右旋
rotateRight(parent);
break;
case RR:
// 兄弟节点旋转后取代父节点颜色
brother.color = parent.color;
// 父节点和侄节点变黑
parent.color = BLACK;
brother.left.color = BLACK;
// 以父节点右旋
rotateLeft(parent);
break;
case RL:
// 侄节点变为父节点颜色
brother.left.color = parent.color;
// 父节点变为黑色
parent.color = BLACK;
// 以兄弟节点右旋
rotateRight(brother);
// 以父节点左旋
rotateLeft(parent);
break;
default:
// 兄弟节点无子节点
if (parent.color == RED) {
// 父节点为红色,改变父节点和兄弟节点的颜色
parent.color = BLACK;
brother.color = RED;
} else {
// 父节点为黑色
brother.color = RED;
this.fixRemove(parent);
}
}
} else {
// 兄弟节点为红色
if (node == parent.getLeft()) {
brother.color = BLACK;
brother.left.color = RED;
rotateLeft(parent);
} else {
brother.color = BLACK;
brother.right.color = RED;
rotateRight(parent);
}
}
}
private int getRemoveRotateType(TreeNode<K,V> brotherNode) {
if ( brotherNode.parent != null && brotherNode == brotherNode.parent.left) {
if (brotherNode.left != null && brotherNode.left.color == RED) {
return LL;
}
if (brotherNode.right != null && brotherNode.right.color == RED) {
return LR;
}
} else {
if (brotherNode.right != null && brotherNode.right.color == RED) {
return RR;
}
if (brotherNode.left != null && brotherNode.left.color == RED) {
return RL;
}
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 获取替代节点
* 该方法的目的是为了减少调整的次数
* 先找前驱,如果找到以下两种则返回前驱
* ① 红色叶子节点
* ② 有一个红色叶子节点的黑节点
* 否则返回后继
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> getReplaceNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> provNode = this.provNode(node);
if (provNode != null) {
if (provNode.color == RED || provNode.left != null) {
return provNode;
}
}
return this.successNode(node);
}
四、完整代码
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class RedBlackTree <K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
// true 表示红色
private static final boolean RED = true;
// false 表示黑色
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
// 根节点
private TreeNode<K,V> root;
// 树的大小
private int size;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public static class TreeNode <K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
// 父节点
private TreeNode<K,V> parent;
// 左节点
private TreeNode<K,V> left;
// 右节点
private TreeNode<K,V> right;
// 颜色
private boolean color;
// 键
private K key;
// 值
private V value;
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
public List<TreeNode<K,V>> infixOrder() {
ArrayList<TreeNode<K, V>> result = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) {
return result;
}
this.infixOrder(root,result);
return result;
}
private void infixOrder(TreeNode<K,V> node,List<TreeNode<K,V>> result) {
if (node != null) {
infixOrder(node.left,result);
result.add(node);
infixOrder(node.right,result);
}
}
/**
* 左旋操作
*/
private void rotateLeft(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 假设 node 节点为 A 节点
TreeNode<K, V> right = node.getRight();
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
// A 节点的右节点变为原右节点的左节点
node.setRight(right.getLeft());
// A 节点的父节点变为原右节点
setParent(node,right);
// 原右节点的左节点的父节点变为 A
setParent(right.getLeft(),node);
// 原右节点的左节点变为 A
right.setLeft(node);
if (parent == null) {
// 如果 A 节点的父节点为 null,也就是说 A 为根节点
// 将根节点设置为 A 的原右节点
root = right;
// 原右节点变为根节点,所以它的父节点为 null
setParent(right,null);
} else {
// 如果 A 不是根节点
// 设置原右节点的父节点为 A 的原父节点
setParent(right,parent);
// 设置原父节点的子节点
if (parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(right);
} else {
parent.setRight(right);
}
}
}
/**
* 右旋操作
*/
private void rotateRight(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 假设 node 节点为 A 节点
TreeNode<K, V> left = node.getLeft();
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
// A 节点的左节点变为原左节点的右节点
node.setLeft(left.getRight());
// A 节点的父节点变为原左节点
setParent(node,left);
// 原左节点的右节点的父节点变为 A
setParent(left.getRight(),node);
// 原左节点的右节点变为 A
left.setRight(node);
if (parent == null) {
// 如果 A 节点的父节点为 null,也就是说 A 为根节点
// 将根节点设置为 A 的原左节点
root = left;
// 原左节点变为根节点,所以它的父节点为 null
setParent(left,null);
} else {
// 如果 A 不是根节点
// 设置原父节点的子节点
if (parent.getLeft() == node) {
parent.setLeft(left);
} else {
parent.setRight(left);
}
// 设置原右节点的父节点为 A 的原父节点
setParent(left,parent);
}
}
/**
* 设置父节点
*/
private void setParent(TreeNode<K,V> node,TreeNode<K,V> parentNode) {
if (node != null) {
node.setParent(parentNode);
}
}
/**
* 插入
*/
public void addNode(K key,V value) {
TreeNode<K, V> treeNode = new TreeNode<>();
treeNode.setLeft(null);
treeNode.setRight(null);
setParent(treeNode,null);
treeNode.setKey(key);
treeNode.setValue(value);
// 新节点一定为红色
treeNode.setColor(RED);
if (root == null) {
// 如果树为空,则根节点为刚插入的节点
root = treeNode;
// 根节点为黑色
root.color = BLACK;
size++;
return;
}
TreeNode<K, V> parentNode = findParentNode(treeNode);
int cr = parentNode.getKey().compareTo(treeNode.getKey());
setParent(treeNode,parentNode);
if (cr == 0) {
// 替换值
parentNode.setValue(treeNode.getValue());
return;
}
if (cr > 0) {
parentNode.setLeft(treeNode);
} else {
parentNode.setRight(treeNode);
}
// 平衡树
fixInsert(treeNode);
size++;
}
/**
* 根据插入节点左/右旋转来调整树
*
* 插入后修复红黑树平衡的方法
* |---情景1:红黑树为空,将根节点染为黑色
* |---情景2:插入节点的 key 已经存在,不需要处理
* |---情景3:插入节点的父节点为黑色,不需要处理
* |---情景4:插入节点的父节点为红色
* |---情景4.1:叔叔节点存在,并且为红色(父-叔 双红),将父节点和叔节点均染成黑色,将爷爷节点设置为红色,以爷爷节点作为当前节点进行下一轮处理
* |---情景4.2:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的左子树
* |---情景4.2.1:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL情况),将父节点染为黑色,将爷爷节点染为红色,然后以爷爷节点右旋
* |---情景4.2.2:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR情况),以父节点进行一次左旋,得到 LL 双红的情景(4.2.1),然后指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
* |---情景4.3:叔叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,父节点为爷爷节点的右子树
* |---情景4.3.1:插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况),将父节点染为黑色,将爷爷节点染为红色,然后以爷爷节点左旋
* |---情景4.3.2:插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况),以父节点进行一次右旋,得到 RR 双红的情景(4.3.1),然后指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
*/
private void fixInsert(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 获取插入节点的父节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
while (parent != null && parent.color == RED) {
// 获取插入节点的叔节点
TreeNode<K, V> uncle = getUncle(node);
if (uncle == null || uncle.color == BLACK) {
// 叔节点不存在,或者为黑色,则需要旋转
// 获取爷爷节点
TreeNode<K, V> ancestor = parent.getParent();
if (parent == ancestor.getLeft()) {
// 父节点是爷爷节点的左子节点
// isLeft:插入节点是否为父节点的左子节点
boolean isLeft = node == parent.getLeft();
if (isLeft) {
// 插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(LL情况)
// 将父节点染为黑色
parent.setColor(BLACK);
// 将爷爷节点染为红色
ancestor.setColor(RED);
// 以爷爷节点右旋
rotateRight(ancestor);
return;
} else {
// 插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(LR情况),则以父节点进行一次左旋
rotateLeft(parent);
// 指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
node = parent;
parent = node.getParent();
}
} else {
// 父节点是爷爷节点的右子节点
// isRight:插入节点是否为父节点的右子节点
boolean isRight = node == parent.getRight();
if (isRight) {
// 插入节点为其父节点的右子节点(RR情况)
//将父节点染为黑色
parent.setColor(BLACK);
// 将爷爷节点染为红色
ancestor.setColor(RED);
// 然后以爷爷节点左旋
rotateLeft(ancestor);
return;
} else {
// 插入节点为其父节点的左子节点(RL情况),则以父节点进行一次右旋
rotateRight(parent);
// 然后指定父节点为当前节点进行下一轮处理
node = parent;
parent = node.getParent();
}
}
} else {
// 叔节点存在,并且为红色
// 将父节点和叔节点均染成黑色
parent.setColor(BLACK);
uncle.setColor(BLACK);
// 并且将爷爷节点染成红色
parent.getParent().setColor(RED);
// 以爷爷节点作为当前节点进行下一轮处理
node = parent.getParent();
parent = node.getParent();
}
}
// 根节点为黑色
this.root.setColor(BLACK);
// 根节点的父节点设置为 null
this.root.setParent(null);
}
/**
* 删除节点
* |---1:没有找到删除节点则直接返回
* |---2:如果删除的是唯一的根节点,则将 root 置空,返回
* |---3:删除叶子节点
* |---3.1:对要删除的黑色叶子节点进行调整
* |---3.2:删除红黑两种叶子节点
* |---4:删除只有一个子节点的节点
* |---4.1:将红色子节点拷贝到父节点
* |---4.2:将删除节点转换为删除红色叶子节点,即 3.2
* |---5:删除两个子节点的节点
* |---5.1:使用前驱或后继节点作为替换的删除节点
* |---5.2:将删除节点指向替换节点,转为3或4处理
*/
public TreeNode<K, V> removeNode(K key) {
TreeNode<K, V> node = findTreeNode(key);
if (node == null) {
System.out.println("Not find node by key ~~");
return null;
}
TreeNode<K, V> delNode = node;
// 判断需要删除的节点是否为唯一的根节点
if (node == root && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
// 将根节点置空
root = null;
size--;
return delNode;
}
// 替换节点
TreeNode<K, V> replaceNode = null;
// 双子节点置换为前驱节点或后继节点
if (node.right != null && node.left != null) {
// 获取替代节点
replaceNode = this.getReplaceNode(node);
// 置换删除节点与替换节点的键值
node.key = replaceNode.getKey();
node.value = replaceNode.getValue();
// 删除节点指向替代节点
node = replaceNode;
}
// 有一个红色节点的黑节点置换为红色叶子节点的删除
if ((node.left != null && node.right == null) || (node.left == null && node.right != null)) {
// 获得替换的红叶子节点
replaceNode = node.left == null ? node.right : node.left;
// 置换删除节点与替换节点的键值
node.key = replaceNode.getKey();
node.value = replaceNode.getValue();
// 删除节点指向替代节点
node = replaceNode;
}
// 叶子节点的删除
if (node.color == BLACK) {
// 需要进行平衡调整
fixRemove(node);
}
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
if (node == parent.getLeft()) {
// 删除的节点为左子节点
parent.setLeft(null);
} else {
// 删除的节点为右子节点
parent.setRight(null);
}
node.parent = null;
return delNode;
}
/**
* 删除平衡
* |---1:只有一个根节点,直接删除
* |---2:兄弟节点为黑色
* |---2.1:兄弟节点有红色子节点
* |---2.1.1:兄弟节点有红色左子节点
* LL型,该兄弟节点的父节点和左子节点染为黑色,兄弟节点染为父节点的颜色,以父节点右旋
* |---2.1.2:兄弟节点有红色右子节点
* LR型,该兄弟节点的右子节点染为父节点的颜色,父节点染为黑色,以兄弟节点先左旋,再以父节点右旋
* |---2.2:兄弟节点无红色子节点
* |---2.2.1:父节点是红色
* 父节点染为黑色,兄弟节点染为红色
* |---2.2.2:父节点是黑色
* 将兄弟节点染红,把父节点当作新的被删节点,递归调用前面方法,进行相应处理,直至遇到红色父节点并将其染黑,或遇到根节点
* |---3:兄弟为红色节点
* 删除右子节点,需要右旋,兄弟节点和右侄颜色互换
*/
private static final int LL = 1;
private static final int LR = 2;
private static final int RR = 3;
private static final int RL = 4;
private void fixRemove(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
if (root == node) {
root.color = BLACK;
return;
}
// 获取该节点的兄弟节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
TreeNode<K, V> brother = getBrother(node);
if (brother == null) return;
if (brother.color == BLACK) {
// 兄弟节点为黑色
switch (getRemoveRotateType(brother)) {
case LL:
// 兄弟节点旋转后取代父节点颜色
brother.color = parent.color;
// 父节点和侄节点变黑
parent.color = BLACK;
brother.left.color = BLACK;
// 以父节点右旋
rotateRight(parent);
break;
case LR:
// 侄节点变为父节点颜色
brother.right.color = parent.color;
// 父节点变为黑色
parent.color = BLACK;
// 以兄弟节点左旋
rotateLeft(brother);
// 以父节点右旋
rotateRight(parent);
break;
case RR:
// 兄弟节点旋转后取代父节点颜色
brother.color = parent.color;
// 父节点和侄节点变黑
parent.color = BLACK;
brother.left.color = BLACK;
// 以父节点右旋
rotateLeft(parent);
break;
case RL:
// 侄节点变为父节点颜色
brother.left.color = parent.color;
// 父节点变为黑色
parent.color = BLACK;
// 以兄弟节点右旋
rotateRight(brother);
// 以父节点左旋
rotateLeft(parent);
break;
default:
// 兄弟节点无子节点
if (parent.color == RED) {
// 父节点为红色,改变父节点和兄弟节点的颜色
parent.color = BLACK;
brother.color = RED;
} else {
// 父节点为黑色
brother.color = RED;
this.fixRemove(parent);
}
}
} else {
// 兄弟节点为红色
if (node == parent.getLeft()) {
brother.color = BLACK;
brother.left.color = RED;
rotateLeft(parent);
} else {
brother.color = BLACK;
brother.right.color = RED;
rotateRight(parent);
}
}
}
private int getRemoveRotateType(TreeNode<K,V> brotherNode) {
if ( brotherNode.parent != null && brotherNode == brotherNode.parent.left) {
if (brotherNode.left != null && brotherNode.left.color == RED) {
return LL;
}
if (brotherNode.right != null && brotherNode.right.color == RED) {
return LR;
}
} else {
if (brotherNode.right != null && brotherNode.right.color == RED) {
return RR;
}
if (brotherNode.left != null && brotherNode.left.color == RED) {
return RL;
}
}
return 0;
}
/**
* 获取叔节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> getUncle(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 获取父节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
// 获取爷爷节点
TreeNode<K, V> ancestor = parent.getParent();
if (ancestor == null) {
// 如果没有爷爷节点则说明父节点为根节点,无叔节点
return null;
}
if (parent == ancestor.getLeft()) {
// 说明爷爷节点的左节点是父节点,则爷爷节点的右节点为叔节点
return ancestor.getRight();
} else {
// 说明爷爷节点的右节点是父节点,则爷爷节点的左节点为叔节点
return ancestor.getLeft();
}
}
/**
* 获取兄弟节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> getBrother(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
// 获取父节点
TreeNode<K, V> parent = node.getParent();
if (parent == null) {
// 如果没有父节点,则说明该节点为根节点,无兄弟节点
return null;
}
return node == parent.getLeft() ? parent.getRight() : parent.getLeft();
}
/**
* 找到节点 node 的父节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> findParentNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> dataRoot = root;
TreeNode<K, V> child = dataRoot;
while (child != null) {
int cr = child.getKey().compareTo(node.getKey());
if (cr == 0) {
return child;
} else if (cr > 0) {
dataRoot = child;
child = child.getLeft();
} else {
dataRoot = child;
child = child.getRight();
}
}
return dataRoot;
}
/**
* 根据 key 查询某个节点
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> findTreeNode(K key) {
// 从根节点开始
TreeNode<K,V> temp = root;
// 节点不为 null 则进行循环查找
while (temp != null) {
int cr = temp.getKey().compareTo(key);
if (cr == 0) {
return temp;
} else if (cr > 0) {
// 往左边找
temp = temp.left;
} else {
// 往右边找
temp = temp.right;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* 获取前驱节点:比当前节点小的最大值
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> provNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> temp = node.getLeft();
if (temp == null) {
// 如果当前节点没有左子节点,则它的前驱节点为它的父节点
return node.getParent();
}
while (temp.right != null) {
temp = temp.right;
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 获取后继节点:比当前节点大的最小值
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> successNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> temp = node.getRight();
while (temp.left != null) {
temp = temp.left;
}
return temp;
}
/**
* 获取替代节点
* 该方法的目的是为了减少调整的次数
* 先找前驱,如果找到以下两种则返回前驱
* ① 红色叶子节点
* ② 有一个红色叶子节点的黑节点
* 否则返回后继
*/
private TreeNode<K,V> getReplaceNode(TreeNode<K,V> node) {
TreeNode<K, V> provNode = this.provNode(node);
if (provNode != null) {
if (provNode.color == RED || provNode.left != null) {
return provNode;
}
}
return this.successNode(node);
}
}
五、测试
1. 红黑树打印类
public class TreeOperation {
/*
树的结构示例:
1
/ \
2 3
/ \ / \
4 5 6 7
*/
// 用于获得树的层数
public static <K extends Comparable<K>,V> int getTreeDepth(RedBlackTree.TreeNode<K,V> root) {
return root == null ? 0 : (1 + Math.max(getTreeDepth(root.getLeft()), getTreeDepth(root.getRight())));
}
private static <K extends Comparable<K>,V> void writeArray(RedBlackTree.TreeNode<K,V> currNode, int rowIndex, int columnIndex, String[][] res, int treeDepth) {
// 保证输入的树不为空
if (currNode == null) return;
// 先将当前节点保存到二维数组中
res[rowIndex][columnIndex] = String.valueOf(currNode.getKey() + "-" + (currNode.isColor() ? "R" : "B") + "");
// 计算当前位于树的第几层
int currLevel = ((rowIndex + 1) / 2);
// 若到了最后一层,则返回
if (currLevel == treeDepth) return;
// 计算当前行到下一行,每个元素之间的间隔(下一行的列索引与当前元素的列索引之间的间隔)
int gap = treeDepth - currLevel - 1;
// 对左儿子进行判断,若有左儿子,则记录相应的"/"与左儿子的值
if (currNode.getLeft() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex - gap] = "/";
writeArray(currNode.getLeft(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex - gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
// 对右儿子进行判断,若有右儿子,则记录相应的"\"与右儿子的值
if (currNode.getRight() != null) {
res[rowIndex + 1][columnIndex + gap] = "\\";
writeArray(currNode.getRight(), rowIndex + 2, columnIndex + gap * 2, res, treeDepth);
}
}
public static <K extends Comparable<K>,V> void show(RedBlackTree.TreeNode<K,V> root) {
if (root == null) System.out.println("EMPTY!");
// 得到树的深度
int treeDepth = getTreeDepth(root);
// 最后一行的宽度为2的(n - 1)次方乘3,再加1
// 作为整个二维数组的宽度
int arrayHeight = treeDepth * 2 - 1;
int arrayWidth = (2 << (treeDepth - 2)) * 3 + 1;
// 用一个字符串数组来存储每个位置应显示的元素
String[][] res = new String[arrayHeight][arrayWidth];
// 对数组进行初始化,默认为一个空格
for (int i = 0; i < arrayHeight; i ++) {
for (int j = 0; j < arrayWidth; j ++) {
res[i][j] = " ";
}
}
// 从根节点开始,递归处理整个树
// res[0][(arrayWidth + 1)/ 2] = (char)(root.val + '0');
writeArray(root, 0, arrayWidth/ 2, res, treeDepth);
// 此时,已经将所有需要显示的元素储存到了二维数组中,将其拼接并打印即可
for (String[] line: res) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < line.length; i ++) {
sb.append(line[i]);
if (line[i].length() > 1 && i <= line.length - 1) {
i += line[i].length() > 4 ? 2: line[i].length() - 1;
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}
2. 测试代码
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class RBTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
RedBlackTree<Integer, String> tree = new RedBlackTree<>();
boolean selectFlag = false;
boolean insert = true;
while (true) {
if (!selectFlag) {
if (insert) {
System.out.println("请输入当前要添加的节点(整数值):");
} else {
System.out.println("请输入当前要删除的节点(整数值):");
}
String next = scanner.next();
Integer key = null;
try {
key = Integer.valueOf(next);
} catch (Exception e) {
break;
}
System.out.println();
if (insert) {
tree.addNode(key,null);
} else {
tree.removeNode(key);
}
selectFlag = true;
// 打印树
TreeOperation.show(tree.getRoot());
} else {
System.out.println("请输出您要进行的操作(A为添加操作,R为删除操作):");
String next = scanner.next();
if ("A".equals(next)) {
insert = true;
selectFlag = false;
} else if ("R".equals(next)) {
insert = false;
selectFlag = false;
} else {
System.out.println("选择操作有误!");
}
}
}
// 中序遍历
List<RedBlackTree.TreeNode<Integer, String>> list = tree.infixOrder();
for (RedBlackTree.TreeNode<Integer, String> node : list) {
System.out.println("key:" + node.getKey() + " ,value=" + node.getValue());
}
}
}
3. 测试结果

参考:
红黑树详解:https://blog.csdn.net/c15158032319/article/details/103148119
java 打印红黑树TreeOperation()类:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_42428778/article/details/120106144
视频-红黑树详解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV15P4y1v7dE?p=1&vd_source=11e08f3dedd62039a273f8675fa5988c
视频-红黑树源码讲解:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1UJ411J7CU/?spm_id_from=333.337.search-card.all.click&vd_source=11e08f3dedd62039a273f8675fa5988c
