【计算机视觉】24-Object Detection
文章目录
- 24-Object Detection
- 1. Introduction
- 2. Methods
- 2.1 Sliding Window
- 2.2 R-CNN: Region-Based CNN
- 2.3 Fast R-CNN
- 2.4 Faster R-CNN: Learnable Region Proposals
- 2.5 Results of objects detection
- 3. Summary
- Reference
24-Object Detection
1. Introduction
-
Task Definition
Input: Single RGB Image
Output: A set of detected objects;
For each object predict:
-
Category label (from fixed, known set of categories)
-
Bounding box(four numbers: x, y, width, height)
-
-
Challenges
- Multiple outputs: Need to output variable numbers of objects per image
- Multiple types of output: Need to predict ”what” (category label) as well as “where” (bounding box)
- Large images: Classification works at 224x224; need higher resolution for detection, often ~800x600
-
Detecting a single object
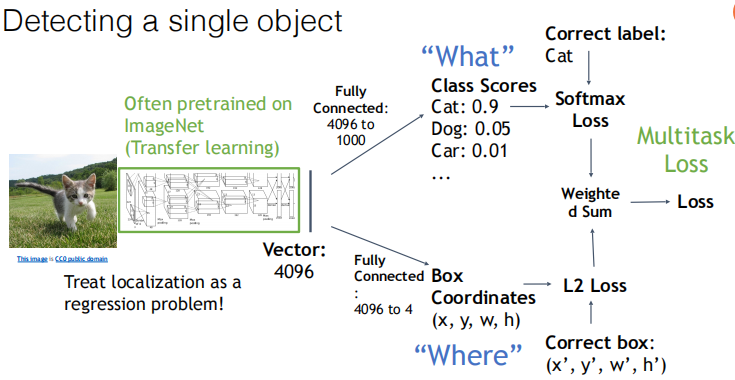
With two branches, outputting label, and box
Problem: Images can have more than one object! And if we use multiple single object detection, it will decrease the efficiency.
2. Methods
2.1 Sliding Window
Apply a CNN to many different crops of the image, CNN classifies each crop as an object or background:
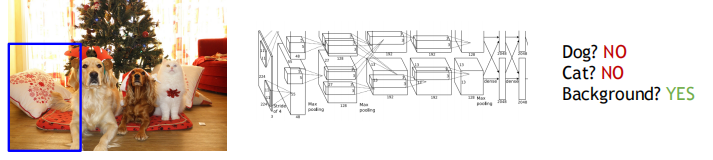
Problem: Need too many calculations
- Consider an image of size H*W and a box of size h*w
- Total possible boxes: ∑ h = 1 H ∑ w = 1 W ( W − w + 1 ) ( H − h + 1 ) = H ( H + 1 ) 2 W ( W + 1 ) 2 \sum_{h=1}^{H}\sum_{w=1}^{W}(W-w+1)(H-h+1)=\frac{H(H+1)}{2}\frac{W(W+1)}{2} ∑h=1H∑w=1W(W−w+1)(H−h+1)=2H(H+1)2W(W+1)
- 800 x 600 image has ~58M boxes! No way we can evaluate them all.
2.2 R-CNN: Region-Based CNN
-
Region Proposals(Selective Search)
Selective Search is a region proposal algorithm used in object detection. It is based on computing hierarchical grouping of similar regions based on color, texture, size and shape compatibility.
Selective Search starts by over-segmenting the image based on intensity of the pixels using a graph-based segmentation method by Felzenszwalb and Huttenlocher.

Selective Search algorithm takes these oversegments as initial input and performs the following steps
- Add all bounding boxes corresponding to segmented parts to the list of regional proposals
- Group adjacent segments based on similarity
- Go to step 1
At each iteration, larger segments are formed and added to the list of region proposals. Hence we create region proposals from smaller segments to larger segments in a bottom-up approach.
As for the calculation of similarity measures based on color, texture, size and shape compatibility, please refer to Selective Search for Object Detection (C++ / Python) | LearnOpenCV
-
Architecture of the network
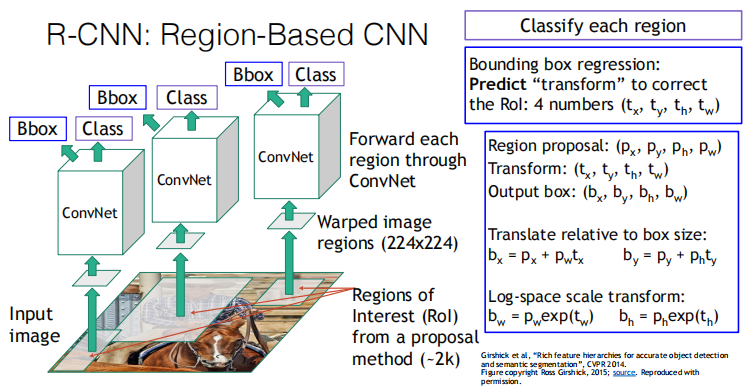
On two thousand selected regions, we narrow them down to the size required for classification, and after passing through the convolutional network, we output the category along with the box offset
-
Steps
- Run region proposal method to compute ~2000 region proposals
- Resize each region to 224x224 and run independently through CNN to predict class scores and bbox transform
- Use scores to select a subset of region proposals to output (Many choices here: threshold on background, or per-category? Or take top K proposals per image?)
- Compare with ground-truth boxes
-
Details(Focus on step3 and 4)
-
Intersection over Union (IoU)
I o U = Area of Intersection Area of Union IoU=\frac{\color{yellow}{\text{Area of Intersection}}}{\color{purple}{\text{Area of Union}}} IoU=Area of UnionArea of Intersection

-
Non-Max Suppression (NMS)
-
Select next highest-scoring box
-
Eliminate lower-scoring boxes(Comparing the highest-scoring box to all the others ) with IoU > threshold (e.g. 0.7)
-
If any boxes remain, GOTO 1
Problem: NMS may eliminate ”good” boxes when objects are highly overlapping:
-
-

-
Mean Average Precision (mAP)

Use the gif to understand it(but I only have the final image):
 For example, the mAP in COCO dataset is 0.4.
For example, the mAP in COCO dataset is 0.4.
-
Problem: Very slow! Need to do ~2k forward passes for each image!
Solution: Run CNN before warping!
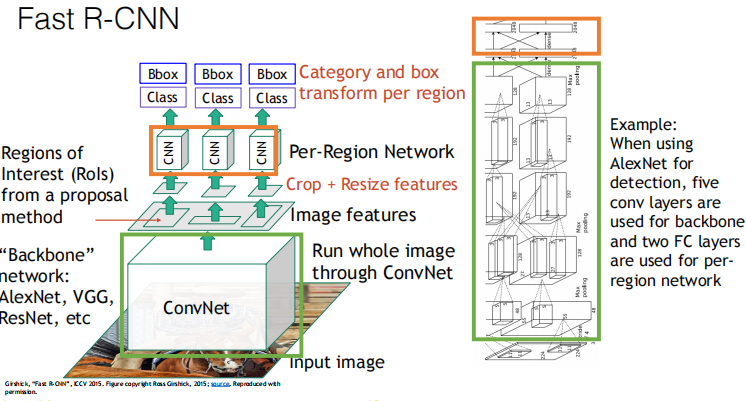
2.3 Fast R-CNN
-
Architecture:
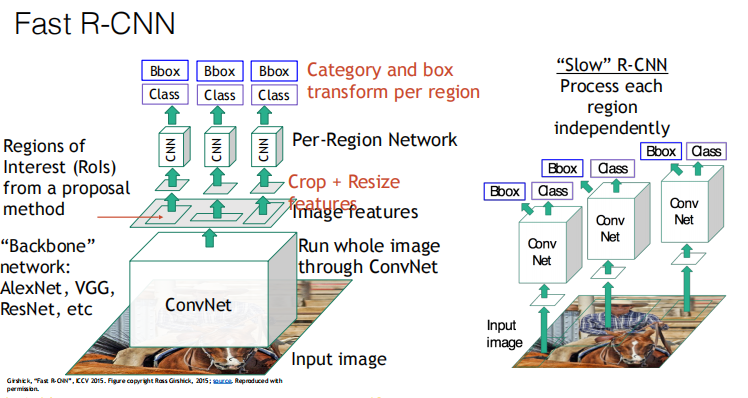
-
Most of the computation happens in the backbone network; this saves work for overlapping region proposals
-
Per-Region network is relatively lightweight
-
-
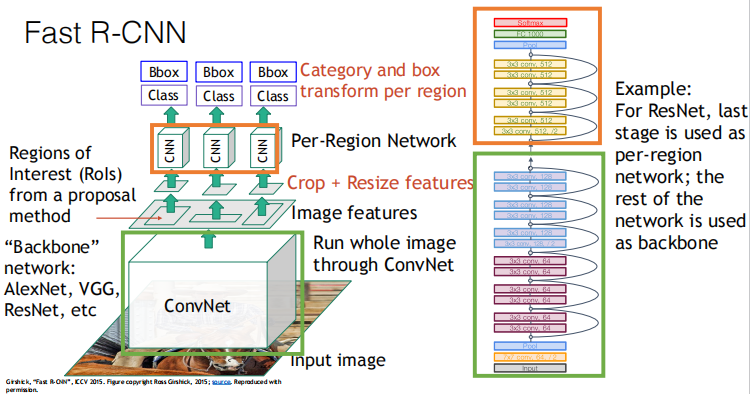
The concrete architecture in Alexnet and Resnet:
-
Details:
How to crop features?
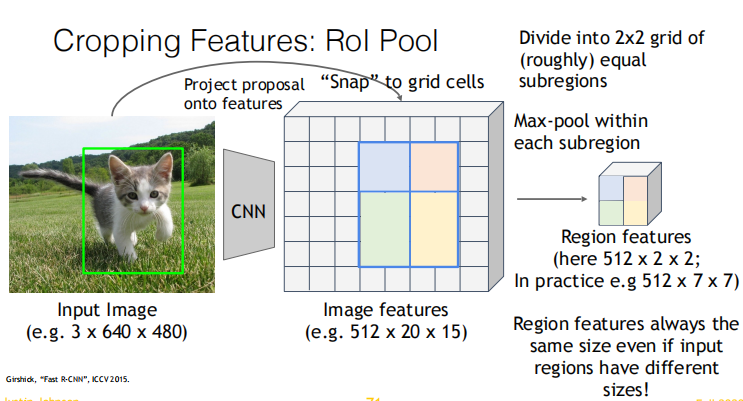
In this process, there are two errors:

如下图,假设输入图像经过一系列卷积层下采样32倍后输出的特征图大小为8x8,现有一 RoI 的左上角和右下角坐标(x, y 形式)分别为(0, 100) 和 (198, 224),映射至特征图上后坐标变为(0, 100 / 32)和(198 / 32,224 / 32),由于像素点是离散的,因此向下取整后最终坐标为(0, 3)和(6, 7),这里产生了第一次量化误差。
假设最终需要将 RoI 变为固定的2x2大小,那么将 RoI 平均划分为2x2个区域,每个区域长宽分别为 (6 - 0 + 1) / 2 和 (7 - 3 + 1) / 2 即 3.5 和 2.5,同样,由于像素点是离散的,因此有些区域的长取3,另一些取4,而有些区域的宽取2,另一些取3,这里产生了第二次量化误差。
-
RoI Align in Mask R-CNN

Notice: RoI Align needs to set a hyperparameter to represent the number of sampling points in each region, which is usually 4.
-
Speed

It has an enormous increase from R-CNN. But we can find that region proposals costs lots of time.
2.4 Faster R-CNN: Learnable Region Proposals
-
Architecture:
Insert Region Proposal Network (RPN) to predict proposals from feature

-
Details:
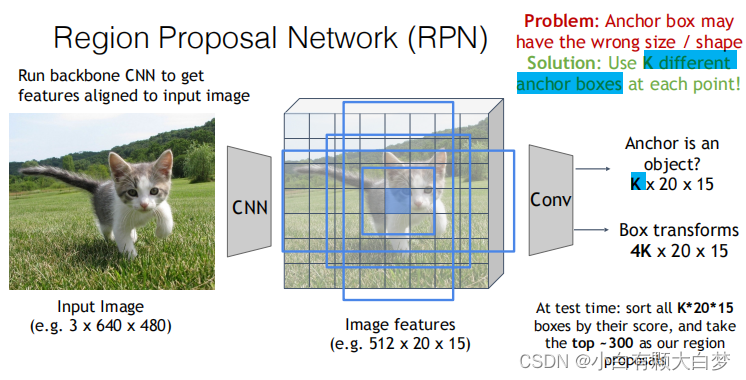
At each point, predict whether the corresponding anchor contains an object. And we use logistic regression to express the error. predict scores with conv layer
- Evaluation

-
Improvement
Faster R-CNN is a Two-stage object detector:

But we want to design the structure of end to end, eliminating the second stage. So we change the function of region proposal network to predict the class label.

2.5 Results of objects detection

- Two-stage method (Faster R-CNN) gets the best accuracy but are slower.
- Single-stage methods (SSD) are much faster but don’t perform as well
- Bigger backbones improve performance, but are slower
- Diminishing returns for slower methods

These results are a few years old …since then GPUs have gotten faster, and we’ve improved performance with many tricks:
- Train longer!
- Multiscale backbone: Feature
Pyramid Networks - Better backbone: ResNeXt
- Single-Stage methods have improved
- Very big models work better
- Test-time augmentation pushes
numbers up - Big ensembles, more data, etc
3. Summary

Reference
[1] RoI Pooling 系列方法介绍(文末附源码) - 知乎 (zhihu.com)
[2] Selective Search for Object Detection (C++ / Python) | LearnOpenCV
