使用coco数据集进行语义分割(1):数据预处理,制作ground truth
如何coco数据集进行目标检测的介绍已经有很多了,但是关于语义分割几乎没有。本文旨在说明如何处理 stuff_train2017.json stuff_val2017.json panoptic_train2017.json panoptic_val2017.json,将上面那些json中的dict转化为图片的label mask,也就是制作图片像素的标签的ground truth。
首先下载图片和annotation文件(也就是json文件)
2017 Train Images和2017 Val Images解压得到这两个文件夹,里面放着的是所有图片。
annotation下载下来有4个json文件
以及两个压缩包
这两个压缩包里面是panoptic segmentation的mask,用于制作ground truth。
首先说明一下那四个json文件的含义,stuff是语义分割,panoptic是全景分割。二者的区别在与

语义分割只区别种类,全景分割还区分个体。上图中,中间的语义分割将所有的人类视作同一个种类看待,而右边的全景分割还将每一个个体区分出来。
做语义分割,可以使用stuff_train2017.json生成ground truth。但是即便是只做语义分割,不做全景分割,在只看语义分割的情况下,stuff的划分精度不如panoptic,因此建立即使是做语义分割也用panoptic_train2017.json。本文中将两种json都进行说明。
stuff_train2017.json
下面这段代码是处理stuff_train2017.json生成ground truth
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
import os
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def convert_coco2mask_show(image_id):
print(image_id)
img = coco.imgs[image_id]
image = np.array(Image.open(os.path.join(img_dir, img['file_name'])))
plt.imshow(image, interpolation='nearest')
# cat_ids = coco.getCatIds()
cat_ids = list(range(183))
anns_ids = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id'], catIds=cat_ids, iscrowd=None)
anns = coco.loadAnns(anns_ids)
mask = np.zeros((image.shape[0], image.shape[1]))
for i in range(len(anns)):
tmp = coco.annToMask(anns[i]) * anns[i]["category_id"]
mask += tmp
print(np.max(mask), np.min(mask))
# 绘制二维数组对应的颜色图
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 6))
plt.imshow(mask, cmap='viridis', vmin=0, vmax=182)
plt.colorbar(ticks=np.linspace(0, 182, 6), label='Colors') # 添加颜色条
# plt.savefig(save_dir + str(image_id) + ".jpg")
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
Dataset_dir = "/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/"
coco = COCO("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/stuff_train2017.json")
# createIndex
# coco = COCO("/home/robotics/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/annotations/panoptic_val2017.json")
img_dir = os.path.join(Dataset_dir, 'train2017')
save_dir = os.path.join(Dataset_dir, "Mask/stuff mask/train")
if not os.path.isdir(save_dir):
os.makedirs(save_dir)
image_id = 9
convert_coco2mask_show(image_id)
# for keyi, valuei in coco.imgs.items():
# image_id = valuei["id"]
# convert_coco2mask_show(image_id)
解释一下上面的代码。
coco = COCO("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/stuff_train2017.json")从coco的官方库中导入工具,读取json。会得到这样的字典结构
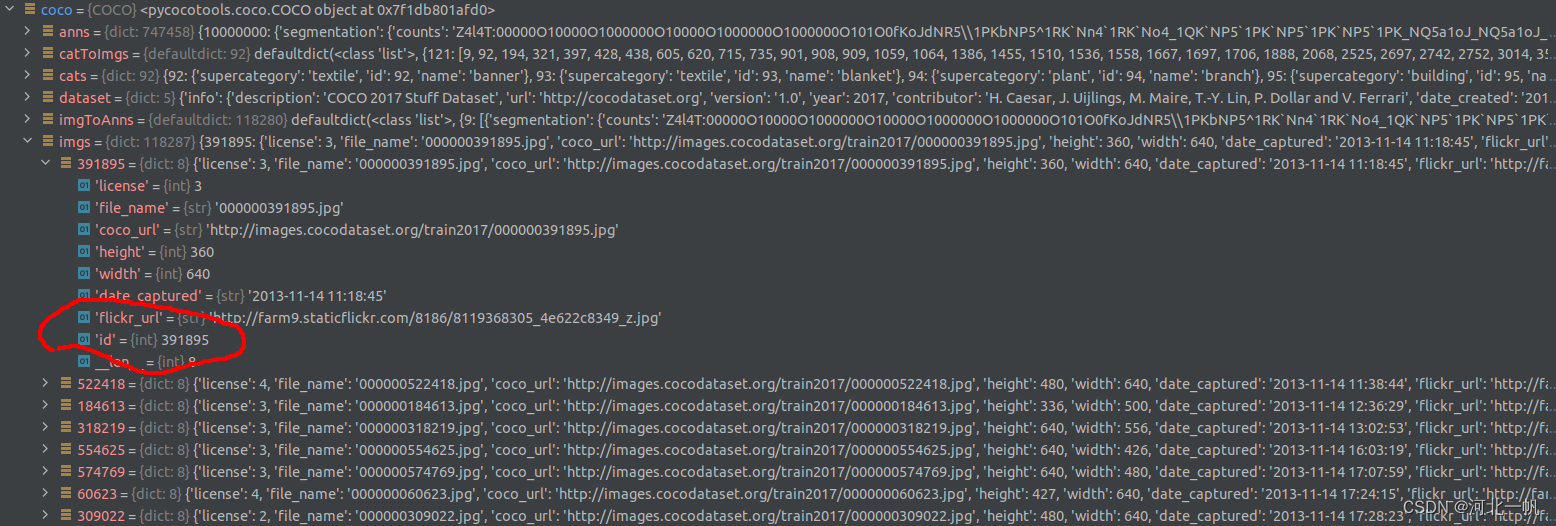
在 coco.imgs ,找到 "id" 对应的value,这个就是每个图片唯一的编号,根据这个编号,到 coco.anns 中去索引 segmentation
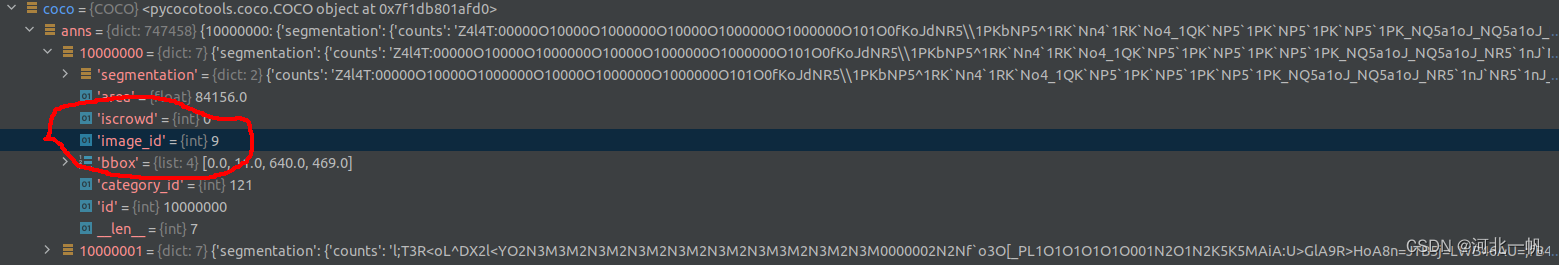
注意 coco.imgs 的 id 对应的是 anns 中的 image_id,这个也是 train2017 文件夹中图片的文件名。
# cat_ids = coco.getCatIds()
cat_ids = list(range(183))网上的绝大多数教程都写的是上面我注释的那行代码,那行代码会得到91个类,那个只能用于图像检测,但对于图像分割任务,包括的种类是182个和一个未归类的0类一共183个类。
tmp = coco.annToMask(anns[i]) * anns[i]["category_id"]上面那行代码就是提取每一个类所对应的id,将所有的类都加进一个二维数组,就制作完成了ground truth。
panoptic_train2017.json
上面完成了通过stuff的json文件自作ground truth,那么用panoptic的json文件制作ground truth,是不是只要把
coco = COCO("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/stuff_train2017.json")换为
coco = COCO("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/annotations/panoptic_val2017.json")就行了呢?
答案是不行!会报错
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "/home/xxxx/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/IPython/core/interactiveshell.py", line 3508, in run_code
exec(code_obj, self.user_global_ns, self.user_ns)
File "<ipython-input-4-66f5c6e7dbe4>", line 1, in <module>
coco = COCO("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/panoptic_val2017.json")
File "/home/robotics/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pycocotools/coco.py", line 86, in __init__
self.createIndex()
File "/home/xxxx/.local/lib/python3.8/site-packages/pycocotools/coco.py", line 96, in createIndex
anns[ann['id']] = ann
KeyError: 'id'用官方的库读官方的json还报错,真是巨坑!关键还没有官方的文档教你怎么用,只能一点点摸索,非常浪费时间精力。
制作panoptic的ground truth,用到了Meta公司的detectron2这个库
# Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
import copy
import json
import os
from detectron2.data import MetadataCatalog
from detectron2.utils.file_io import PathManager
def load_coco_panoptic_json(json_file, image_dir, gt_dir, meta):
"""
Args:
image_dir (str): path to the raw dataset. e.g., "~/coco/train2017".
gt_dir (str): path to the raw annotations. e.g., "~/coco/panoptic_train2017".
json_file (str): path to the json file. e.g., "~/coco/annotations/panoptic_train2017.json".
Returns:
list[dict]: a list of dicts in Detectron2 standard format. (See
`Using Custom Datasets </tutorials/datasets.html>`_ )
"""
def _convert_category_id(segment_info, meta):
if segment_info["category_id"] in meta["thing_dataset_id_to_contiguous_id"]:
segment_info["category_id"] = meta["thing_dataset_id_to_contiguous_id"][
segment_info["category_id"]
]
segment_info["isthing"] = True
else:
segment_info["category_id"] = meta["stuff_dataset_id_to_contiguous_id"][
segment_info["category_id"]
]
segment_info["isthing"] = False
return segment_info
with PathManager.open(json_file) as f:
json_info = json.load(f)
ret = []
for ann in json_info["annotations"]:
image_id = int(ann["image_id"])
# TODO: currently we assume image and label has the same filename but
# different extension, and images have extension ".jpg" for COCO. Need
# to make image extension a user-provided argument if we extend this
# function to support other COCO-like datasets.
image_file = os.path.join(image_dir, os.path.splitext(ann["file_name"])[0] + ".jpg")
label_file = os.path.join(gt_dir, ann["file_name"])
segments_info = [_convert_category_id(x, meta) for x in ann["segments_info"]]
ret.append(
{
"file_name": image_file,
"image_id": image_id,
"pan_seg_file_name": label_file,
"segments_info": segments_info,
}
)
assert len(ret), f"No images found in {image_dir}!"
assert PathManager.isfile(ret[0]["file_name"]), ret[0]["file_name"]
assert PathManager.isfile(ret[0]["pan_seg_file_name"]), ret[0]["pan_seg_file_name"]
return ret
if __name__ == "__main__":
from detectron2.utils.logger import setup_logger
from detectron2.utils.visualizer import Visualizer
import detectron2.data.datasets # noqa # add pre-defined metadata
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
logger = setup_logger(name=__name__)
meta = MetadataCatalog.get("coco_2017_train_panoptic")
dicts = load_coco_panoptic_json("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/panoptic_train2017.json",
"/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/train2017",
"/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/Mask/panoptic mask/panoptic_train2017", meta.as_dict())
logger.info("Done loading {} samples.".format(len(dicts)))
dirname = "coco-data-vis"
os.makedirs(dirname, exist_ok=True)
new_dic = {}
num_imgs_to_vis = 100
for i, d in enumerate(dicts):
img = np.array(Image.open(d["file_name"]))
visualizer = Visualizer(img, metadata=meta)
pan_seg, segments_info = visualizer.draw_dataset_dict(d)
seg_cat = {0: 0}
for segi in segments_info:
seg_cat[segi["id"]] = segi["category_id"]
mapped_seg = np.vectorize(seg_cat.get)(pan_seg)
# 保存数组为txt文件
save_name = "/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/Mask/panoptic label/train/" + str(d["image_id"]) + ".txt"
np.savetxt(save_name, mapped_seg, fmt='%i')
new_dic[d["image_id"]] = {"image_name": d["file_name"], "label_name": save_name}
# # 将numpy数组转换为PIL Image对象
# img1 = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(mapped_seg))
# # 缩放图片
# img_resized = img1.resize((224, 224))
# # 将PIL Image对象转换回numpy数组
# mapped_seg_resized = np.array(img_resized)
# # 创建一个新的图形
# plt.figure(figsize=(6, 8))
# # 使用imshow函数来显示数组,并使用cmap参数来指定颜色映射
# plt.imshow(mapped_seg_resized, cmap='viridis')
# # 显示图形
# plt.show()
# fpath = os.path.join(dirname, os.path.basename(d["file_name"]))
# # vis.save(fpath)
if i + 1 >= num_imgs_to_vis:
# 将字典转换为json字符串
json_data = json.dumps(new_dic)
# 将json字符串写入文件
with open('/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/data_for_train.json', 'w') as f:
f.write(json_data)
break
dicts = load_coco_panoptic_json("/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/annotations/panoptic_train2017.json",
"/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/train2017",
"/home/xxxx/Downloads/coco2017/Mask/panoptic mask/panoptic_train2017", meta.as_dict())load_coco_panoptic_json的第三个参数,就是下载panoptic的annotations时,里面包含的两个压缩包。
上面这段代码,还需要修改一下detectron2库内部的文件
pan_seg, segments_info = visualizer.draw_dataset_dict(d)进入 draw_dataset_dict这个函数内部,将两个中间结果拿出来
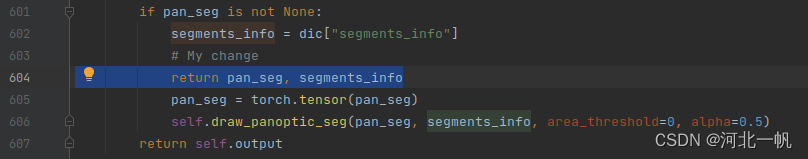
603行和604行是我自己加的代码。
这两个中间结果拿出来后,pan_seg是图片每个像素所属的种类,但是这个种类不是coco分类的那183个类
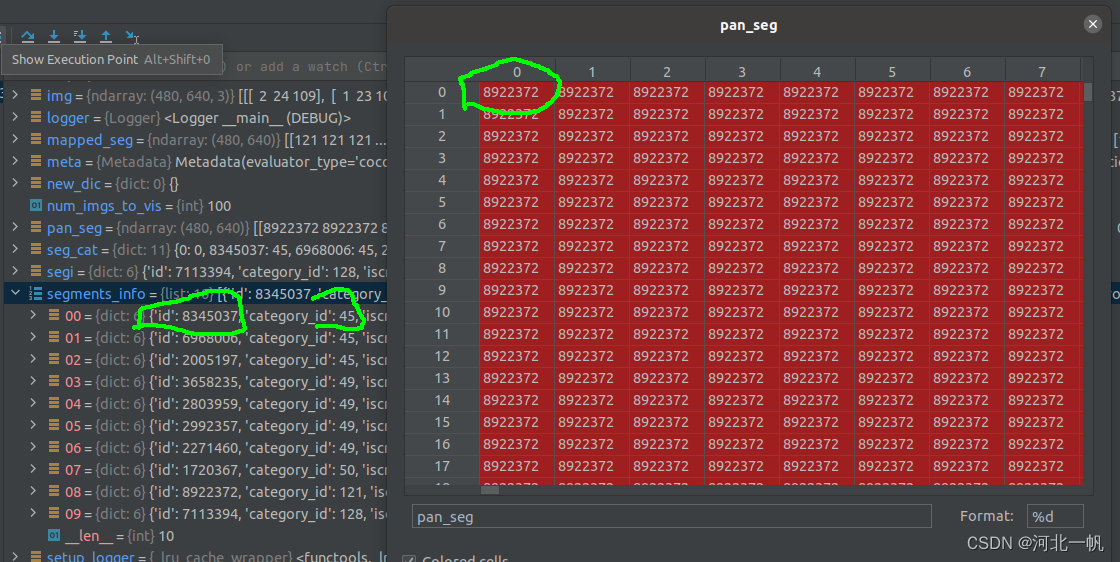
pan_seg中的数,要映射到segments_info中的 category_id,这个才是coco数据集所规定的183个类 。下图节选了183个中的前10个展示
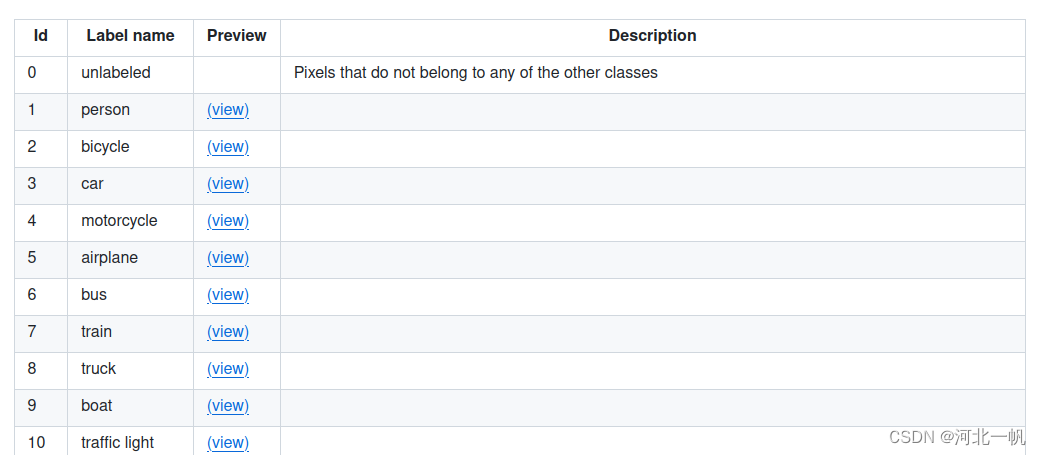
mapped_seg = np.vectorize(seg_cat.get)(pan_seg)上面这行代码就是完成pan_seg中的数,映射到segments_info中的 category_id。不要用两层的for循环,太低效了,numpy中有函数可以完成数组的映射。
这样就得到了语义分割的ground truth,也就是每个像素所属的种类。
