GraphHopper调研笔记
一、 GraphHopper
GraphHopper是一种快速且内存有效的Java导航引擎,默认使用OSM和GTFS数据,也可导入其他的数据源。支持CH(Contraction Hierarchies)、A*、Dijkstra算法。
1、应用介绍
graphhopper有以下几种常见的地图应用:
(1) 把一个GPS点垂直投影到最近的道路上
(2)根据输入的两个GPS点进行路径规划,支持设置起点的离开方向和终点的到达方向
(3)根据一个GPS点和给定的时间范围给出等时圈的点
2、功能介绍
2.1 创建地图
2.1.1 示例代码
ghLoc是OSM格式的地图路径
cachePath是读取OSM地图之后的地图缓存,下次可以直接使用缓存中的地图
static GraphHopper createGraphHopperInstance(String ghLoc,String cachePath) {
GraphHopper hopper = new GraphHopper();
// OSM 文件路径
hopper.setOSMFile(ghLoc);
// 读取完OSM数据之后会构建路线图,此处配置图的存储路径
hopper.setGraphHopperLocation(cachePath);
hopper.setProfiles(new Profile("car").setVehicle("car").setWeighting("fastest").setTurnCosts(false));
hopper.importOrLoad();
return hopper;
}
2.2点投影到路上的Node
2.2.1 示例代码
EncodingManager encodingManager = hopper.getEncodingManager();
BooleanEncodedValue accessEnc = encodingManager.getBooleanEncodedValue(VehicleAccess.key("car"));
DecimalEncodedValue speedEnc = encodingManager.getDecimalEncodedValue(VehicleSpeed.key("car"));
// snap some GPS coordinates to the routing graph and build a query graph
FastestWeighting weighting = new FastestWeighting(accessEnc, speedEnc);
Snap snap = hopper.getLocationIndex().findClosest(24.48183200, 118.18120700, new DefaultSnapFilter(weighting, encodingManager.getBooleanEncodedValue(Subnetwork.key("car"))));
System.out.println(snap.getClosestNode());
BaseGraph baseGraph = hopper.getBaseGraph();
NodeAccess nodeAccess = baseGraph.getNodeAccess();
double lon = nodeAccess.getLon(4312);
double lat = nodeAccess.getLat(4312);
System.out.println(lon+","+lat+";");
2.3路径规划
2.3.1示例代码
public static void routing(GraphHopper hopper, String from, String to) {
String[] fromPoint = from.split(",");
double fromLon = Double.parseDouble(fromPoint[0]);
double fromLat = Double.parseDouble(fromPoint[1]);
String[] toPoint = to.split(",");
double toLon = Double.parseDouble(toPoint[0]);
double toLat = Double.parseDouble(toPoint[1]);
// simple configuration of the request object
GHRequest req = new GHRequest(fromLat, fromLon, toLat, toLon).
// note that we have to specify which profile we are using even when there is only one like here
setProfile("car").
// define the language for the turn instructions
setLocale(Locale.CHINA);
GHResponse rsp = hopper.route(req);
// handle errors
if (rsp.hasErrors())
throw new RuntimeException(rsp.getErrors().toString());
// use the best path, see the GHResponse class for more possibilities.
ResponsePath path = rsp.getBest();
// 导航结果点位集合
PointList pointList = path.getPoints();
// 总距离 m
double distance = path.getDistance();
// 总耗时 ms
long timeInMs = path.getTime();
System.out.println("路线点位: ");
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < pointList.size(); ++i) {
if (i > 0) {
sb.append("; ");
}
sb.append(pointList.getLon(i));
sb.append(',');
sb.append(pointList.getLat(i));
if (pointList.is3D()) {
sb.append(',');
sb.append(pointList.getEle(i));
}
}
System.out.println(sb.toString()+"\n------------------------");
System.out.println("总距离: " + distance + ", 总用时: " + timeInMs);
Translation tr = hopper.getTranslationMap().getWithFallBack(Locale.CHINA);
InstructionList il = path.getInstructions();
// iterate over all turn instructions
for (Instruction instruction : il) {
System.out.println("distance " + instruction.getDistance() + " for instruction: " + instruction.getTurnDescription(tr));
}
}
测试类
public static void main(String[] args) {
String osmFilePath = "D:\\work\\CODE\\soft2study/GraphHopper_study/xiamen.osm";
//加载地图
GraphHopper hopper = createGraphHopperInstance(osmFilePath);
String from = "118.15531256,24.51429705";
String to = "118.08894888,24.47891989";
routing(hopper, from, to);
}
2.4等时圈计算
2.3.1示例代码
2.3.2结果示例
官网的等时圈示例
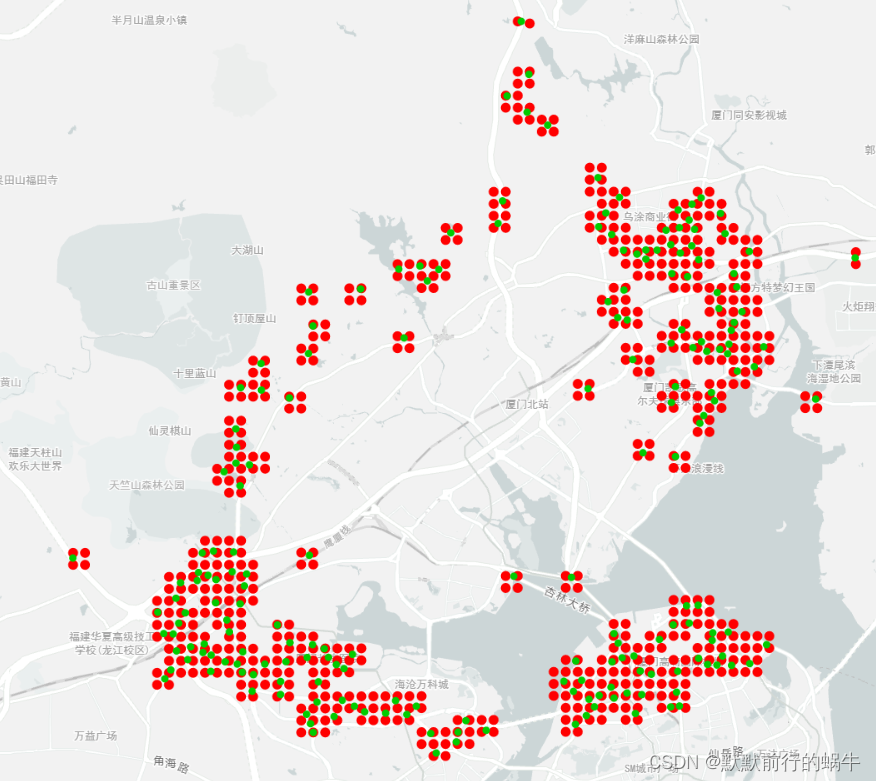
厦门以软三为中心点 15分钟驾车的等时圈示例,红色为100m的网格端点,绿色为等时圈的点
3、graphhopper应用与公共交通
谷歌推出了通用公交数据标准GTFS,主要是使用固定的文本格式和字符对公交数据进行标准化
General Transit Feed Specification
它是一个可预见的中转站位置和时间的结构化数据列表。
3.1.组成元素
agency.txt (机构,运行商)必须
stops.txt (站点,出入口)必须 对应公交站点
routes.txt (路线)必须 对应公交线路
trips.txt (路趟----每一趟车)必须 对应公交时刻表
如果把route表示每一条线路,那么trip就是跑在每一个线路上的车。
比如同是地铁5号线,3点一班车,5点一班车,那么就是两个trip表示。还有上下行车次,区间车等等情况。
frequencies.txt (频率)可选
引入频率,更好的表示trip,如频率表示:7am~9am 每3分钟一趟车。而Trip直接引用frequency即可。
calendar.txt (日历)必须
日历的作用是定义trip的生效日期,比如一个trip规定一个车,在工作日是一个频率,在周末是另一个频率,日期参数就很有用了。
calendar_dates.txt (日历-日期)可选
日期的特殊情况-----节假日,在日期规定了每个工作日都是一个频率,但是偏偏周一是清明节(放假),那么这一天也是按照周末的频率来的。calendar_dates定义假期,当假期与calendar有重叠,会以calendar_dates为准。
stop_times.txt (停车-时间)必须
这是一个与trip相关的表,表示站点的到站时间,离站时间,上下车属性等等。
fare_rules.txt (票价-规定)可选
公交必定是要收费的,这个表规定收费规则。
fare_attributes.txt (票价-属性)可选
表示收费的具体规则对应的钱是多少。
shapes.txt (形状)可选
一般地图信息,都会存储一个形状信息,用于展示(渲染),形状是用经纬度点组成的数组来表示的。
transfers.txt (转车)可选
4、利用源码本地搭建graphhopper
下载源码,源码中有一个web项目,有一个Application
根据官网上的指导说明,需要增加两个参数,一个是server 一个是配置文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
args = new String[2];
args[0] = "server";
args[1]="config.yml";
new GraphHopperApplication().run(args);
}
重点是配置文件config.yml,下载的源码中有一个config-example.yml,复制重命名为自己的配置文件,我这里命名为config.yml
修改了地图的路径和缓存的路径
# OpenStreetMap input file PBF or XML, can be changed via command line -Ddw.graphhopper.datareader.file=some.pbf
datareader.file: "core/files/xiamen.osm"
# Local folder used by graphhopper to store its data
graph.location: target/isochrone-graph-cache
其中datareader.file 表示地图的路径,我这里用的osm的格式
graph.location 表示地图加载之后缓存到本地的路径
完成上面的配置之后,启动GraphHopperApplication,看到了graphhopper的图形
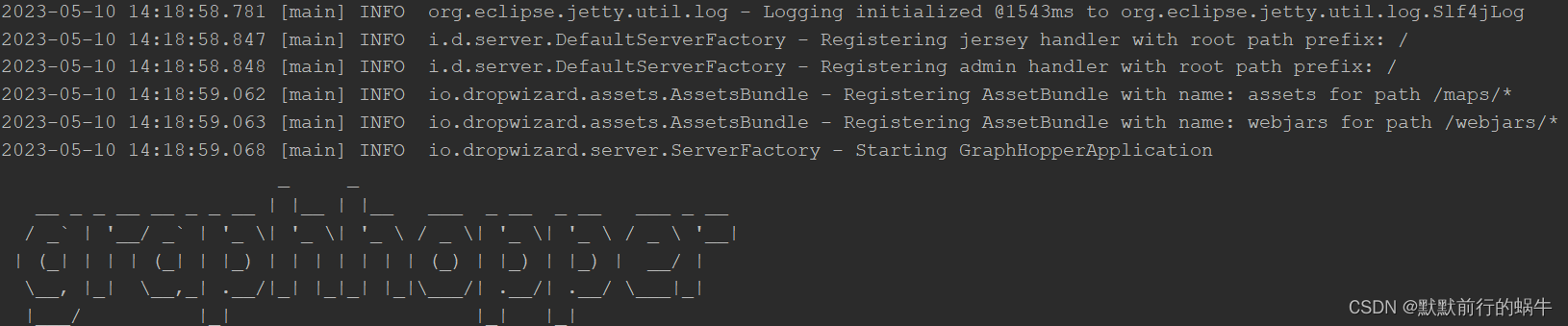

看到了最下面的Started… 表示启动成功
在浏览器中输入:http://localhost:8989/

空白一大片,F12查看原因,发现是在国内请求OpenStreedMap失败的原因。
路径规划的API
http://localhost:8989/route?point=24.51429705,118.15531256&point=24.47891989,118.08894888&profile=car&type=json&points_encoded=false
API参数说明参考https://blog.csdn.net/haochajin/article/details/99963678
返回的结果示例:

