单目相机标定实现--张正友标定法
文章目录
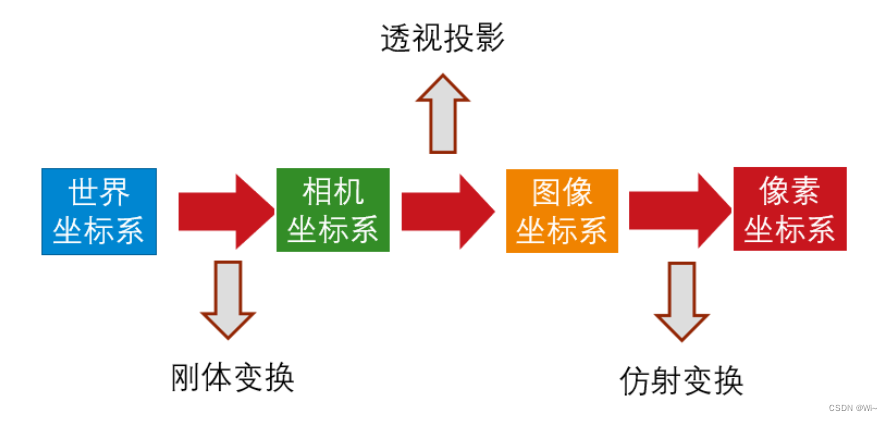
- 一:相机坐标系,像素平面坐标系,世界坐标系,归一化坐标系介绍
- 1:概述
- 公式
- 二:实现
- 1:整体流程
- 4:求出每张图像的单应性矩阵并用LMA优化
- 5:求解理想无畸变情况下的摄像机的内参数和外参数
- 6:应用最小二乘求出实际的畸变系数
- 7:综合内参,外参,畸变系数,使用极大似然法(LMA),优化估计,提升估计精度
- 8:得出相机的内参,外参和畸变系数
- 9:OpenCV模型
- 三:畸变修复(去畸变)
- 四:总结
原文链接:地址
个人笔记:
本次介绍针对于单目相机标定,实现方法:张正友标定法。
一:相机坐标系,像素平面坐标系,世界坐标系,归一化坐标系介绍
1:概述
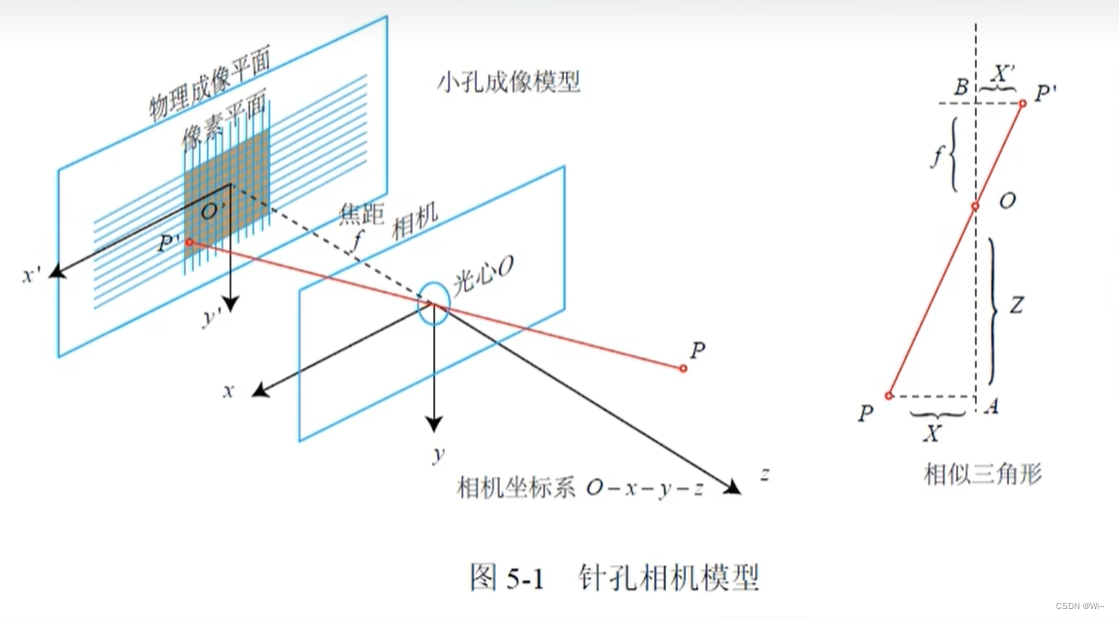
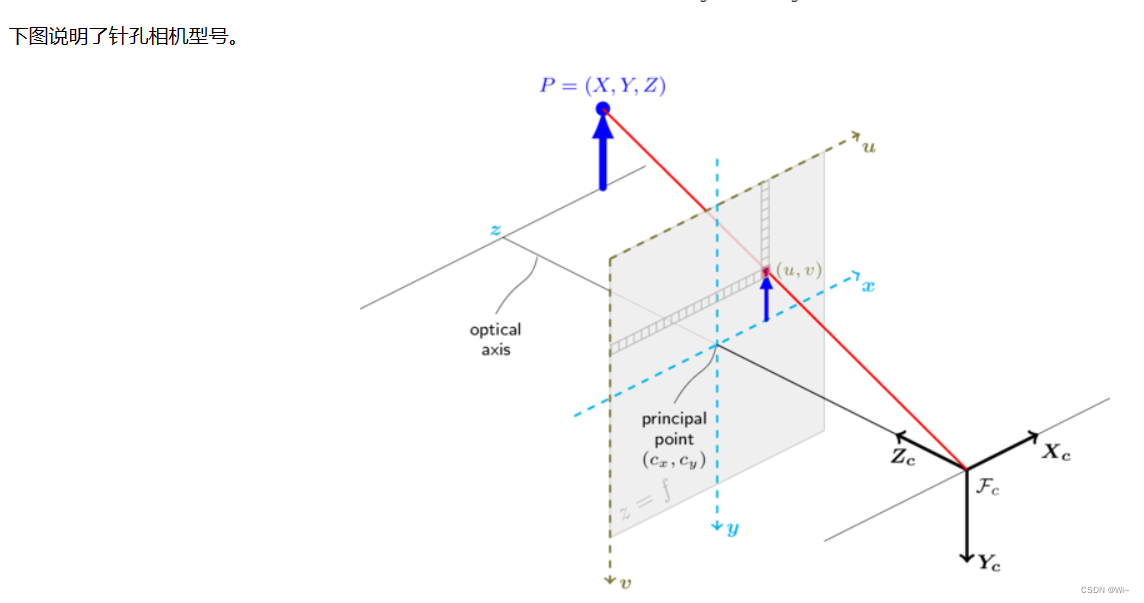
如图,现实世界中有一个P点和一个相机(光心),描述这个P点的空间坐标首先得有一个坐标系,那么以光心为原点O建一个坐标系,叫相机坐标系。
那么就可以在相机坐标系下,设
P
坐
标
(
X
,
Y
,
Z
)
P坐标(X,Y,Z)
P坐标(X,Y,Z)和P的投影点
P
′
(
x
′
,
y
′
,
z
′
)
P'(x',y',z')
P′(x′,y′,z′)。值得一提的是,
P
′
(
x
′
,
y
′
,
z
′
)
P'(x',y',z')
P′(x′,y′,z′)坐落在物理成像平面和像素平面。
物理成像平面,像素平面是二维的,他们的坐标系并不一样:
物理成像平面在
O
′
(
x
′
,
y
′
)
O'(x',y')
O′(x′,y′)平面上;
像素平面的原点在那个黑灰色图的左上角(图片的左上角),横轴向右称为
u
u
u轴,纵轴向下称为
v
v
v轴。
这样就得到了
P
′
P'
P′的像素坐标
P
(
u
,
v
)
P(u,v)
P(u,v),称为
P
u
v
Puv
Puv。
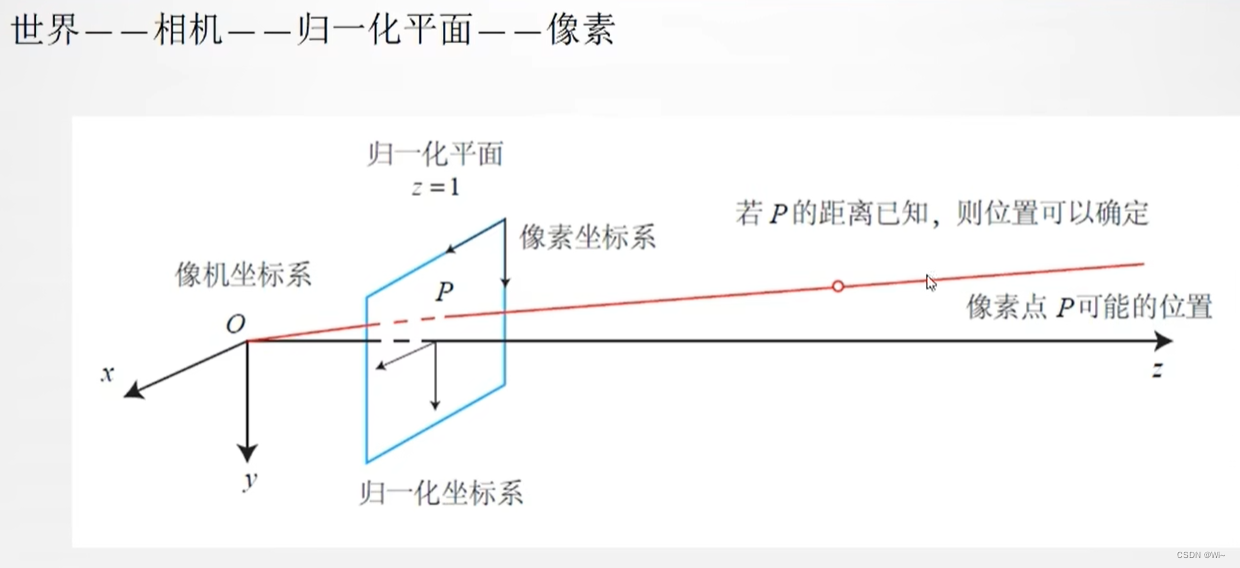 所谓的归一化的成像平面,就是将三维空间点的坐标都除以Z,在相机坐标系下,P有X, Y, Z 三个量,如果把它们投影到归一化平面 Z = 1 上,就会得到P的归一化坐标P(X/Z, Y/Z, 1)。
所谓的归一化的成像平面,就是将三维空间点的坐标都除以Z,在相机坐标系下,P有X, Y, Z 三个量,如果把它们投影到归一化平面 Z = 1 上,就会得到P的归一化坐标P(X/Z, Y/Z, 1)。
公式

[
X
Y
Z
1
]
−
>
\left[\begin{array}{c} X \\ Y \\ Z \\ 1 \end{array}\right]->
⎣⎢⎢⎡XYZ1⎦⎥⎥⎤−>物体坐标.
[ R T 0 1 ] − > \left[\begin{array}{cc} R & T \\ 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]-> [R0T1]−>外参
[ α γ u 0 0 0 β v 0 0 0 0 1 0 ] − > \left[\begin{array}{cccc} \alpha & \gamma & u_{0} & 0 \\ 0 & \beta & v_{0} & 0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 & 0 \end{array}\right]-> ⎣⎡α00γβ0u0v01000⎦⎤−>内参
[ u v 1 ] − > \left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{array}\right]-> ⎣⎡uv1⎦⎤−>像素坐标
其中外参
T
T
T是平移向量
(
t
1
,
t
2
,
t
3
)
T
(t1,t2,t3)^T
(t1,t2,t3)T.
R
R
R旋转矩阵如下图:
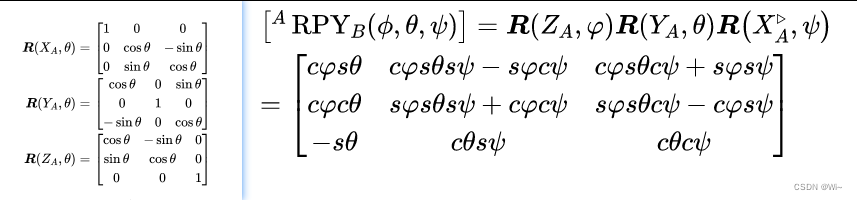
二:实现
1:整体流程
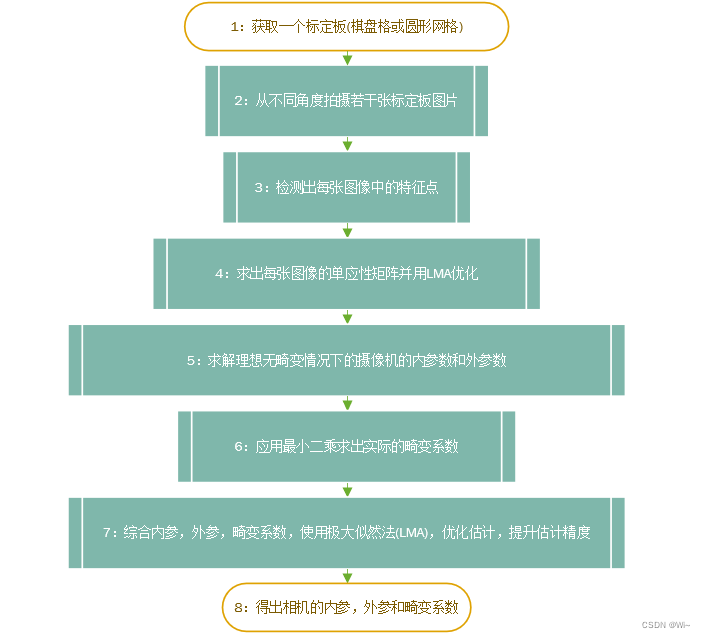
第1步,第2步,第3步 暂不介绍了(可以用halcon算子块或者OpenCV获取特征点坐标),主要介绍获取到特征点以后,优化获取参数部分。
4:求出每张图像的单应性矩阵并用LMA优化
如何计算单应性矩阵:
[
x
b
y
b
w
b
]
=
[
h
1
h
2
h
3
h
4
h
5
h
6
h
7
h
8
h
9
]
[
x
a
y
a
w
a
]
x
b
w
b
=
h
1
x
a
+
h
2
y
a
+
h
3
w
a
h
7
x
a
+
h
8
y
a
+
h
9
w
a
=
h
1
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
2
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
3
h
7
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
8
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
9
y
b
w
b
=
h
4
x
a
+
h
5
y
a
+
h
6
w
a
h
7
x
a
+
h
8
y
a
+
h
9
w
a
=
h
4
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
5
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
6
h
7
x
a
/
w
a
+
h
8
y
a
/
w
a
+
h
9
\begin{array}{c} \left[\begin{array}{l} x_{b} \\ y_{b} \\ w_{b} \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} \mathrm{h}_{1} & \mathrm{~h}_{2} & \mathrm{~h}_{3} \\ \mathrm{~h}_{4} & \mathrm{~h}_{5} & \mathrm{~h}_{6} \\ \mathrm{~h}_{7} & \mathrm{~h}_{8} & \mathrm{~h}_{9} \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{l} x_{a} \\ y_{a} \\ w_{a} \end{array}\right] \\\\ \frac{x_{b}}{w_{b}}=\frac{h_{1} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3} w_{a}}{h_{7} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9} w_{a}}=\frac{h_{1} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3}}{h_{7} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \\ \frac{y_{b}}{w_{b}}=\frac{h_{4} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6} w_{a}}{h_{7} x_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9} w_{a}}=\frac{h_{4} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6}}{h_{7} x_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} y_{a} / w_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \end{array}
⎣⎡xbybwb⎦⎤=⎣⎡h1 h4 h7 h2 h5 h8 h3 h6 h9⎦⎤⎣⎡xayawa⎦⎤wbxb=h7xa+h8ya+h9wah1xa+h2ya+h3wa=h7xa/wa+h8ya/wa+h9h1xa/wa+h2ya/wa+h3wbyb=h7xa+h8ya+h9wah4xa+h5ya+h6wa=h7xa/wa+h8ya/wa+h9h4xa/wa+h5ya/wa+h6
令
u
a
=
x
a
w
a
,
v
a
=
y
a
w
a
,
u
b
=
x
b
w
b
,
v
b
=
y
b
w
b
, 上式化简为
\text { 令 } u_{a}=\frac{x_{a}}{w_{a}}, v_{a}=\frac{y_{a}}{w_{a}}, u_{b}=\frac{x_{b}}{w_{b}}, v_{b}=\frac{y_{b}}{w_{b}} \text {, 上式化简为 }
令 ua=waxa,va=waya,ub=wbxb,vb=wbyb, 上式化简为
u
b
=
h
1
u
a
+
h
2
v
a
+
h
3
h
7
u
a
+
h
8
v
a
+
h
9
v
b
=
h
4
u
a
+
h
5
v
a
+
h
6
h
7
u
a
+
h
8
v
a
+
h
9
\begin{array}{l} u_{b}=\frac{h_{1} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3}}{h_{7} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \\ v_{b}=\frac{h_{4} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6}}{h_{7} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \end{array}
ub=h7ua+h8va+h9h1ua+h2va+h3vb=h7ua+h8va+h9h4ua+h5va+h6
h 1 u a + h 2 v a + h 3 − h 7 u a u b − h 8 v a u b − h 9 u b = 0 h 4 u a + h 5 v a + h 6 − h 7 u a v b − h 8 v a v b − h 9 v b = 0 \begin{array}{c} h_{1} u_{a}+h_{2} v_{a}+h_{3}-h_{7} u_{a} u_{b}-h_{8} v_{a} u_{b}-h_{9} u_{b}=0 \\ h_{4} u_{a}+h_{5} v_{a}+h_{6}-h_{7} u_{a} v_{b}-h_{8} v_{a} v_{b}-h_{9} v_{b}=0 \end{array} h1ua+h2va+h3−h7uaub−h8vaub−h9ub=0h4ua+h5va+h6−h7uavb−h8vavb−h9vb=0
可以直接设
∥
h
∥
2
2
=
1
,此时仍然可以固定住尺度,且有:
\text { 可以直接设 }\|h\|_{2}^{2}=1 \text { ,此时仍然可以固定住尺度,且有: }
可以直接设 ∥h∥22=1 ,此时仍然可以固定住尺度,且有:
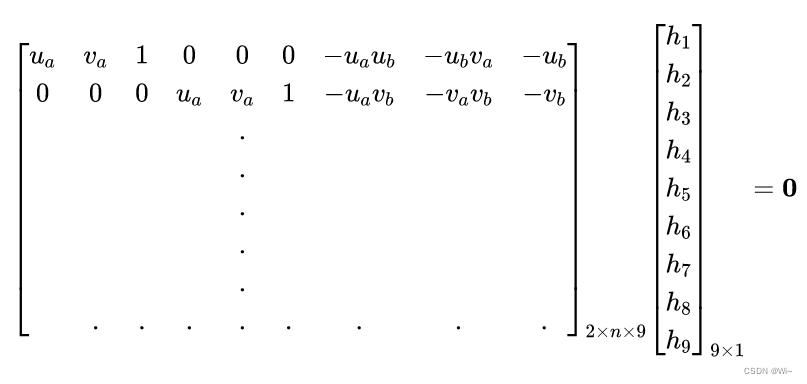
此时系数矩阵秩为8,有线性空间解,解的自由度为1,满足齐次性,又由于限制单位长度,有唯一解,此时仍可以通过SVD分解求解出 h,从而得到单应矩阵。
代码实现:
//获取标准差
double CameraCalibration::StdDiffer(const Eigen::VectorXd& data)
{
//获取平均值
double mean = data.mean();
//std::sqrt((Σ(x-_x)²) / n)
return std::sqrt((data.array() - mean).pow(2).sum() / data.rows());
}
// 归一化
Eigen::Matrix3d CameraCalibration::Normalization (const Eigen::MatrixXd& P)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d T;
double cx = P.col ( 0 ).mean();
double cy = P.col ( 1 ).mean();
double stdx = StdDiffer(P.col(0));
double stdy = StdDiffer(P.col(1));;
double sqrt_2 = std::sqrt ( 2 );
double scalex = sqrt_2 / stdx;
double scaley = sqrt_2 / stdy;
T << scalex, 0, -scalex*cx,
0, scaley, -scaley*cy,
0, 0, 1;
return T;
}
//获取初始矩阵H
Eigen::VectorXd CameraCalibration::GetInitialH (const Eigen::MatrixXd& srcNormal,const Eigen::MatrixXd& dstNormal )
{
Eigen::Matrix3d realNormMat = Normalization(srcNormal);
Eigen::Matrix3d picNormMat = Normalization(dstNormal);
int n = srcNormal.rows();
// 2. DLT
Eigen::MatrixXd input ( 2*n, 9 );
for ( int i=0; i<n; ++i )
{
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::MatrixXd singleSrcCoor(3,1),singleDstCoor(3,1);
singleSrcCoor(0,0) = srcNormal(i,0);
singleSrcCoor(1,0) = srcNormal(i,1);
singleSrcCoor(2,0) = 1;
singleDstCoor(0,0) = dstNormal(i,0);
singleDstCoor(1,0) = dstNormal(i,1);
singleDstCoor(2,0) = 1;
//坐标归一化
Eigen::MatrixXd realNorm(3,1),picNorm(3,1);
realNorm = realNormMat * singleSrcCoor;
picNorm = picNormMat * singleDstCoor;
input ( 2*i, 0 ) = realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 1 ) = realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 2 ) = 1.;
input ( 2*i, 3 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i, 4 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i, 5 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i, 6 ) = -picNorm ( 0, 0 ) * realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 7 ) = -picNorm ( 0, 0 ) * realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i, 8 ) = -picNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 0 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i+1, 1 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i+1, 2 ) = 0.;
input ( 2*i+1, 3 ) = realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 4 ) = realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 5 ) = 1.;
input ( 2*i+1, 6 ) = -picNorm ( 1, 0 ) * realNorm ( 0, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 7 ) = -picNorm ( 1, 0 ) * realNorm ( 1, 0 );
input ( 2*i+1, 8 ) = -picNorm ( 1, 0 );
}
// 3. SVD分解
JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svdSolver ( input, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV );
Eigen::MatrixXd V = svdSolver.matrixV();
Eigen::Matrix3d H = V.rightCols(1).reshaped<RowMajor>(3,3);
//去归一化
H = (picNormMat.inverse() * H) * realNormMat;
H /= H(2,2);
return H.reshaped<RowMajor>(9,1);
}
求出初始单应性矩阵 h h h,然后用 L M A LMA LMA优化,得到具有实际意义的单应性矩阵。
优化代码如下:
求残差值向量:
//单应性残差值向量
class HomographyResidualsVector
{
public:
Eigen::VectorXd operator()(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> &otherArgs)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd inValue = otherArgs.at(0);
Eigen::MatrixXd outValue = otherArgs.at(1);
int dataCount = inValue.rows();
//保存残差值
Eigen::VectorXd residual(dataCount*2) ,residualNew(dataCount*2);
Eigen::Matrix3d HH = parameter.reshaped<RowMajor>(3,3);
//获取预测偏差值 r= ^y(预测值) - y(实际值)
for(int i=0;i<dataCount;++i)
{
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::VectorXd singleRealCoor(3),U(3);
singleRealCoor(0,0) = inValue(i,0);
singleRealCoor(1,0) = inValue(i,1);
singleRealCoor(2,0) = 1;
U = HH * singleRealCoor;
U /= U(2);
residual(i*2) = U(0);
residual(i*2+1) = U(1);
residualNew(i*2) = outValue(i,0);
residualNew(i*2+1) = outValue(i,1);
}
residual -= residualNew;
return residual;
}
};
求雅克比矩阵构建原函数:
u
b
=
h
1
u
a
+
h
2
v
a
+
h
3
h
7
u
a
+
h
8
v
a
+
h
9
v
b
=
h
4
u
a
+
h
5
v
a
+
h
6
h
7
u
a
+
h
8
v
a
+
h
9
\begin{array}{l} u_{b}=\frac{h_{1} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{2} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{3}}{h_{7} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \\ v_{b}=\frac{h_{4} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{5} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{6}}{h_{7} u_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{8} v_{a}+\mathrm{h}_{9}} \end{array}
ub=h7ua+h8va+h9h1ua+h2va+h3vb=h7ua+h8va+h9h4ua+h5va+h6
#define DERIV_STEP 1e-5
//求单应性雅克比矩阵
class HomographyJacobi
{
//求偏导1
double PartialDeriv_1(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,int paraIndex,const Eigen::MatrixXd &inValue,int objIndex)
{
Eigen::VectorXd para1 = parameter;
Eigen::VectorXd para2 = parameter;
para1(paraIndex) -= DERIV_STEP;
para2(paraIndex) += DERIV_STEP;
//逻辑
double obj1 = ((para1(0))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(1)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(2)) / (para1(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(8));
double obj2 = ((para2(0))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(1)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(2)) / (para2(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(8));;
return (obj2 - obj1) / (2 * DERIV_STEP);
}
//求偏导2
double PartialDeriv_2(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,int paraIndex,const Eigen::MatrixXd &inValue,int objIndex)
{
Eigen::VectorXd para1 = parameter;
Eigen::VectorXd para2 = parameter;
para1(paraIndex) -= DERIV_STEP;
para2(paraIndex) += DERIV_STEP;
//逻辑
double obj1 = ((para1(3))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(4)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(5)) / (para1(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para1(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para1(8));
double obj2 = ((para2(3))*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(4)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(5)) / (para2(6)*inValue(objIndex,0) + para2(7)*inValue(objIndex,1) + para2(8));;
return (obj2 - obj1) / (2 * DERIV_STEP);
}
public:
Eigen::MatrixXd operator()(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> &otherArgs)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd inValue = otherArgs.at(0);
int rowNum = inValue.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd Jac(rowNum*2, parameter.rows());
for (int i = 0; i < rowNum; i++)
{
// //第一种方法:直接求偏导
// double sx = parameter(0)*inValue(i,0) + parameter(1)*inValue(i,1) + parameter(2);
// double sy = parameter(3)*inValue(i,0) + parameter(4)*inValue(i,1) + parameter(5);
// double w = parameter(6)*inValue(i,0) + parameter(7)*inValue(i,1) + parameter(8);
// double w2 = w*w;
// Jac(i*2,0) = inValue(i,0)/w;
// Jac(i*2,1) = inValue(i,1)/w;
// Jac(i*2,2) = 1/w;
// Jac(i*2,3) = 0;
// Jac(i*2,4) = 0;
// Jac(i*2,5) = 0;
// Jac(i*2,6) = -sx*inValue(i,0)/w2;
// Jac(i*2,7) = -sx*inValue(i,1)/w2;
// Jac(i*2,8) = -sx/w2;
// Jac(i*2+1,0) = 0;
// Jac(i*2+1,1) = 0;
// Jac(i*2+1,2) = 0;
// Jac(i*2+1,3) = inValue(i,0)/w;
// Jac(i*2+1,4) = inValue(i,1)/w;
// Jac(i*2+1,5) = 1/w;
// Jac(i*2+1,6) = -sy*inValue(i,0)/w2;
// Jac(i*2+1,7) = -sy*inValue(i,1)/w2;
// Jac(i*2+1,8) = -sy/w2;
//第二种方法: 计算求偏导
Jac(i*2,0) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,0,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,1) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,1,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,2) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,2,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,3) = 0;
Jac(i*2,4) = 0;
Jac(i*2,5) = 0;
Jac(i*2,6) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,6,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,7) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,7,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2,8) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,8,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,0) = 0;
Jac(i*2+1,1) = 0;
Jac(i*2+1,2) = 0;
Jac(i*2+1,3) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,3,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,4) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,4,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,5) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,5,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,6) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,6,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,7) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,7,inValue,i);
Jac(i*2+1,8) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,8,inValue,i);
}
return Jac;
}
};
//求具有实际意义单应性矩阵H
Eigen::Matrix3d CameraCalibration::GetHomography(const Eigen::MatrixXd& src,const Eigen::MatrixXd& dst)
{
//获取初始单应性矩阵 -- svd
Eigen::VectorXd H = GetInitialH(src,dst);
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> otherValue{src,dst};
//非线性优化 H 参数 -- LM算法
H =GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->LevenbergMarquardtAlgorithm(H,otherValue,HomographyResidualsVector(),HomographyJacobi());
H /= H(8);
// std::cout<<"H:"<<std::endl<<H<<std::endl;
return H.reshaped<RowMajor>(3,3);
}
LevenbergMarquardtAlgorithm 函数实现地址在这边文章有介绍:LM算法实现
5:求解理想无畸变情况下的摄像机的内参数和外参数
在求取了单应性矩阵后, 还要进一步求出摄像机的内参数。首先令
h
i
h_{i}
hi
表示
H
H
H 的 每一列向量, 于是有:
[ h 1 h 2 h 3 ] = λ K [ r 1 r 2 t ] \left[\begin{array}{lll} h_{1} & h_{2} & h_{3} \end{array}\right]=\lambda K\left[\begin{array}{lll} r_{1} & r_{2} & t \end{array}\right] [h1h2h3]=λK[r1r2t]
又因为 r 1 r_{1} r1 和 r 2 r_{2} r2 是单位正交向量, 所以有 :
h
1
T
K
−
T
K
−
1
h
2
=
0
h
1
T
K
−
T
K
−
1
h
1
=
h
2
T
K
−
T
K
−
1
h
2
\begin{aligned} h_{1}^{T} K^{-T} K^{-1} h_{2} & =0 \\ h_{1}^{T} K^{-T} K^{-1} h_{1} & =h_{2}^{T} K^{-T} K^{-1} h_{2} \end{aligned}
h1TK−TK−1h2h1TK−TK−1h1=0=h2TK−TK−1h2

则:
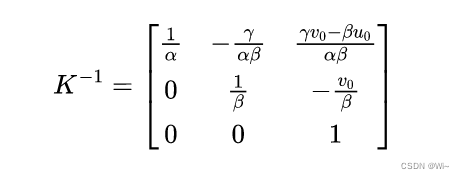
这样就为内参数的求解提供了两个约束方程,令:
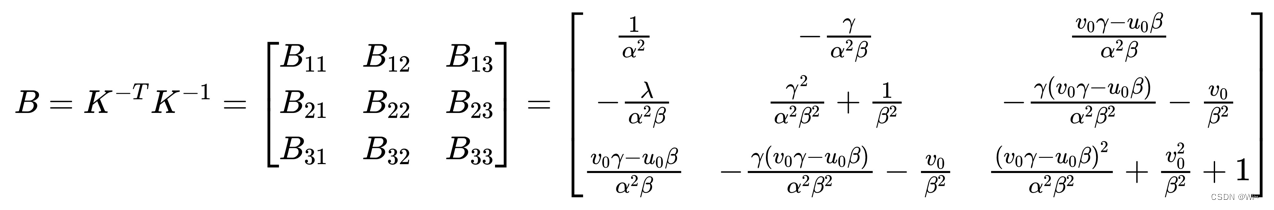 由于
B
B
B 为对称矩阵, 所以它可以由一个 6 维向量来定义, 即:
由于
B
B
B 为对称矩阵, 所以它可以由一个 6 维向量来定义, 即:
b
=
[
B
11
B
12
B
22
B
13
B
23
B
33
]
T
b=\left[\begin{array}{llllll} B_{11} & B_{12} & B_{22} & B_{13} & B_{23} & B_{33} \end{array}\right]^{T}
b=[B11B12B22B13B23B33]T
令
H
的
第
i
列
向
量
为
h
i
=
[
h
i
1
h
i
2
h
i
3
]
T
,
则
:
令 H 的第 i 列向量为 h_{i}=\left[\begin{array}{lll}h_{i 1} & h_{i 2} & h_{i 3}\end{array}\right]^{T} , 则:
令H的第i列向量为hi=[hi1hi2hi3]T,则:
h
i
T
B
h
j
=
V
i
j
T
b
h_{i}^{T} B h_{j}=V_{i j}^{T} b
hiTBhj=VijTb
其中:
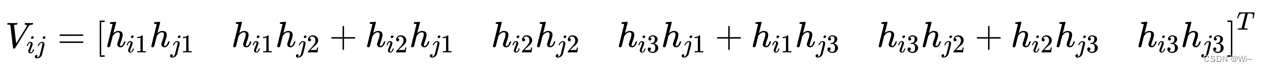
所以组成一个方程组为:
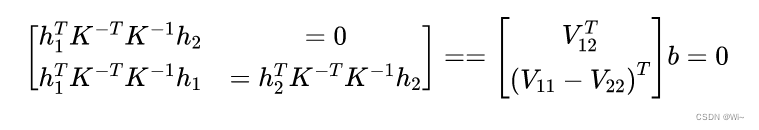 V
为
2
n
∗
6
矩
阵
V为2n*6矩阵
V为2n∗6矩阵。如果
n
>
=
3
n>=3
n>=3,则可以列出6个方程,从而解出6个内参数。这6个解出的内部参数不是唯一的,而是通过了一个比例因子缩放。求出内参:
V
为
2
n
∗
6
矩
阵
V为2n*6矩阵
V为2n∗6矩阵。如果
n
>
=
3
n>=3
n>=3,则可以列出6个方程,从而解出6个内参数。这6个解出的内部参数不是唯一的,而是通过了一个比例因子缩放。求出内参:
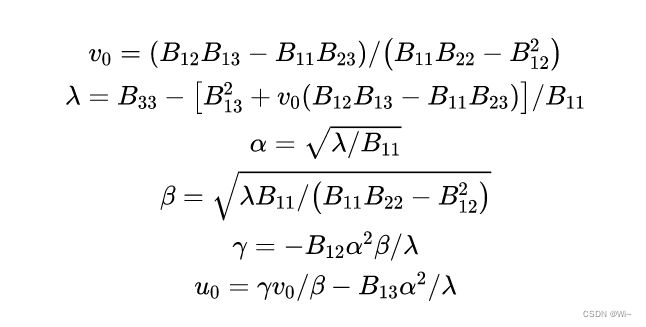
即可求出相机内参矩阵:
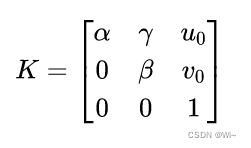
内参求出后,求外参:
再根据
[
h
1
h
2
h
3
]
=
λ
A
[
r
1
r
2
t
]
\left[\begin{array}{lll} \mathbf{h}_{1} & \mathbf{h}_{2} & \mathbf{h}_{3} \end{array}\right]=\lambda \mathbf{A}\left[\begin{array}{lll} \mathbf{r}_{1} & \mathbf{r}_{2} & \mathbf{t} \end{array}\right]
[h1h2h3]=λA[r1r2t]化简可得外部参数,即:
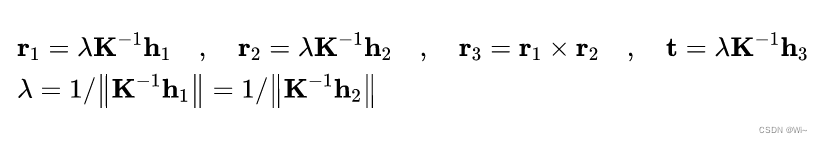
代码实现:
//根据单应性矩阵H返回pq位置对应的v向量
Eigen::VectorXd CameraCalibration::CreateV(int p, int q,const Eigen::Matrix3d& H)
{
Eigen::VectorXd v(6,1);
v << H(0, p) * H(0, q),
H(0, p) * H(1, q) + H(1, p) * H(0, q),
H(1, p) * H(1, q),
H(2, p) * H(0, q) + H(0, p) * H(2, q),
H(2, p) * H(1, q) + H(1, p) * H(2, q),
H(2, p) * H(2, q);
return v;
}
//求相机内参
Eigen::Matrix3d CameraCalibration::GetIntrinsicParameter(const QList<Eigen::Matrix3d>& HList)
{
int HCount = HList.count();
//构建V矩阵
Eigen::MatrixXd V(HCount*2,6);
for(int i=0;i<HCount;++i)
{
V.row(i*2) = CreateV(0, 1, HList.at(i)).transpose();
V.row(i*2+1) = (CreateV(0, 0, HList.at(i)) - CreateV(1, 1, HList.at(i))).transpose();
}
//Vb = 0
//svd分解求x
JacobiSVD<Eigen::MatrixXd> svd(V, Eigen::ComputeFullU | Eigen::ComputeFullV);
//获取V矩阵最后一列就是b的值
Eigen::VectorXd b = svd.matrixV().rightCols(1);
double B11 = b(0);
double B12 = b(1);
double B22 = b(2);
double B13 = b(3);
double B23 = b(4);
double B33 = b(5);
double v0 = (B12*B13 - B11*B23) / (B11*B22 - B12*B12);
double lambda = B33 - (B13*B13 + v0*(B12*B13 - B11*B23))/B11;
//double lambda = 1.0;
double alpha = qSqrt(lambda / B11);
double beta = qSqrt(lambda*B11 / (B11*B22 - B12 *B12));
double gamma = (- B12*alpha*alpha*beta) / lambda;
double u0 = (gamma*v0 / beta) - (B13 * alpha * alpha / lambda);
Eigen::Matrix3d K;
K<<alpha,gamma,u0,
0,beta,v0,
0,0,1;
return K;
}
//求相机外参
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> CameraCalibration::GetExternalParameter(const QList<Eigen::Matrix3d>& HList,const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam)
{
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> exterParame;
//内参逆矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d intrinsicParamInv = intrinsicParam.inverse();
int HCount = HList.count();
for(int i=0;i<HCount;++i)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d H = HList.at(i);
Eigen::Vector3d h0,h1,h2;
h0 = H.col(0);
h1 = H.col(1);
h2 = H.col(2);
Eigen::Vector3d r0,r1,r2,t;
//比例因子λ
double scaleFactor = 1 / (intrinsicParamInv * h0).lpNorm<2>();
r0 = scaleFactor * (intrinsicParamInv * h0);
r1 = scaleFactor * (intrinsicParamInv * h1);
r2 = r0.cross(r1);
t = scaleFactor * (intrinsicParamInv * h2);
Eigen::MatrixXd Rt(3,4);
Rt.col(0) = r0;
Rt.col(1) = r1;
Rt.col(2) = r2;
Rt.col(3) = t;
exterParame.append(Rt);
// std::cout<<"Rt"<<i<<":"<<std::endl<<Rt<<std::endl;
}
return exterParame;
}
//无畸变优化
Eigen::VectorXd disCoeff1(0);
//GetDistortionCoeff(srcL,dstL,A,W,disCoeff);
//OptimizeParameter 优化函数后面会介绍
OptimizeParameter(srcL,dstL,A,disCoeff1,W);
6:应用最小二乘求出实际的畸变系数
相机主要包括径向畸变和切向畸变
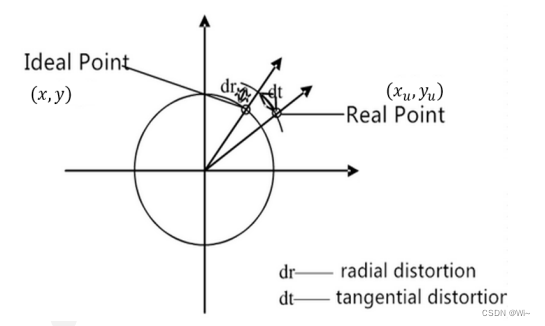
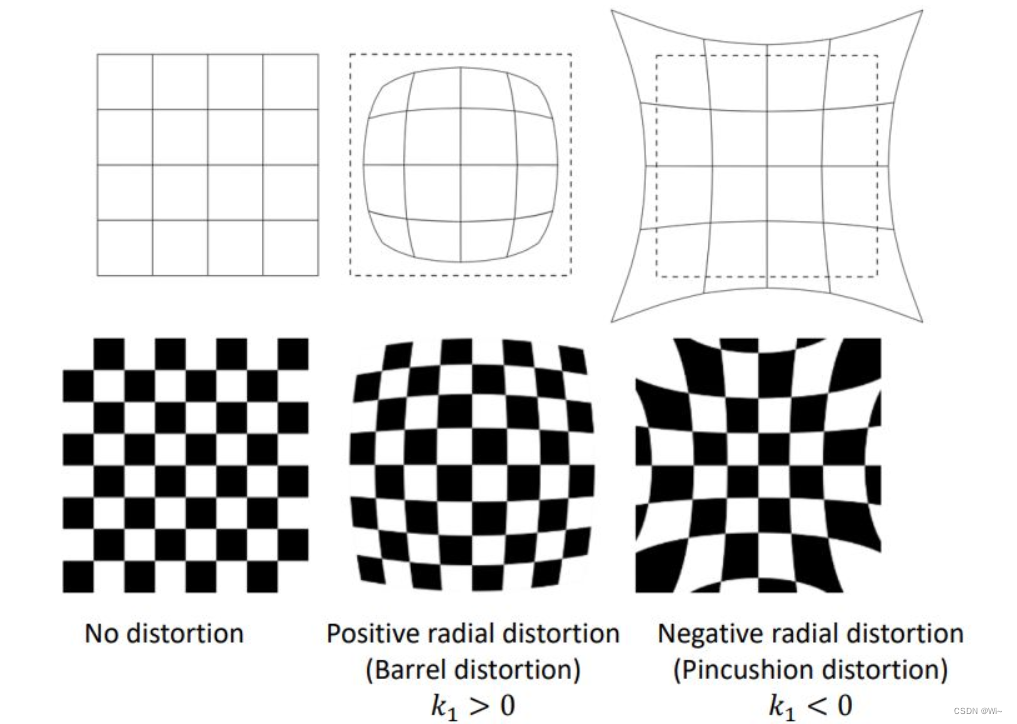
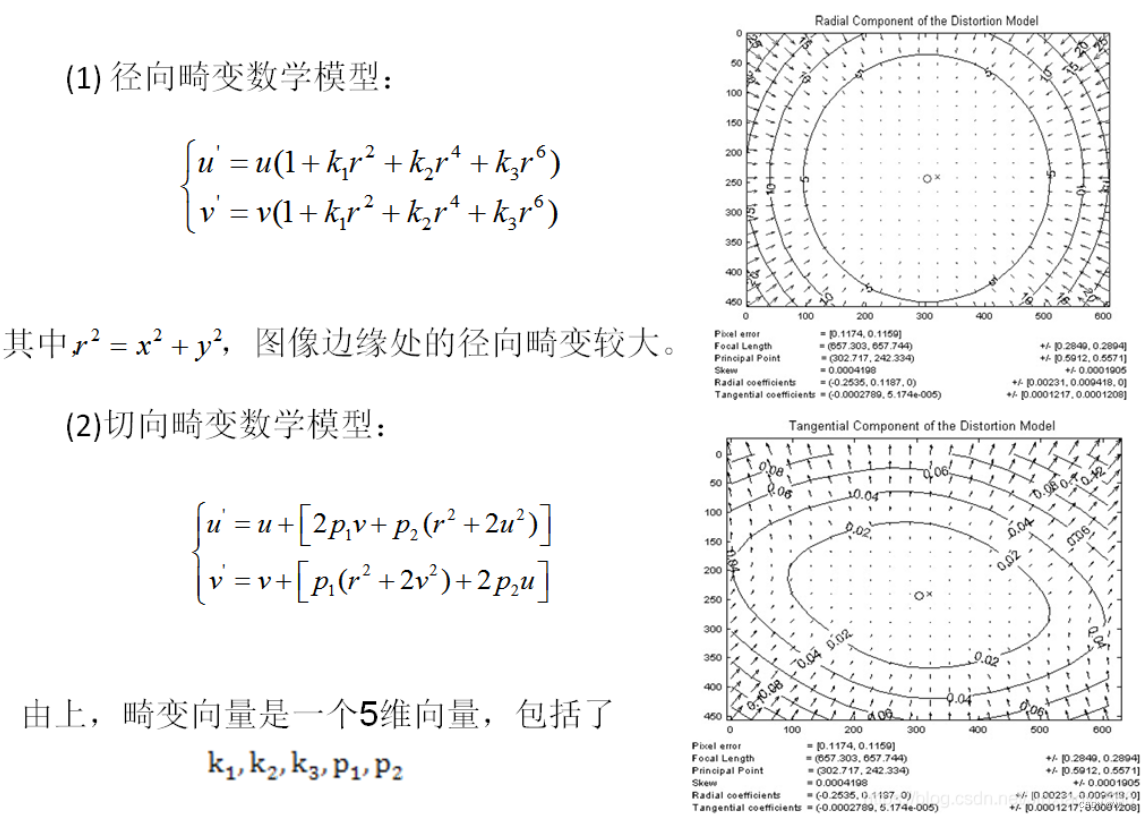

代码实现:
//获取畸变系数 k1,k2,[p1,p2,[k3]]
void CameraCalibration::GetDistortionCoeff(const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& srcL,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& dstL,const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam ,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& externalParams,Eigen::VectorXd & disCoeff)
{
//按照畸变个数获取参数
int disCount = disCoeff.rows();
if(!(disCount == 2 || disCount == 4 || disCount == 5))
{
qDebug()<<QString("畸变参数个数按照数组大小为2或者4或者5,请重新设置数组大小!");
return;
}
int count = srcL.count();
double u0 = intrinsicParam(0,2);
double v0 = intrinsicParam(1,2);
int rowS = 0;
int k = 0;
//获取数据个数
for(int i=0;i<count;++i)
{
rowS += srcL.at(i).rows();
}
//初始化数据大小
Eigen::MatrixXd D(rowS*2,disCount),d(rowS*2,1);
for(int i=0;i<count;++i)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd src = srcL.at(i);
int dataCount = src.rows();
Eigen::MatrixXd dst = dstL.at(i);
Eigen::MatrixXd externalParam = externalParams.at(i);
for(int j=0;j<dataCount;++j)
{
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::VectorXd singleCoor(4);
singleCoor(0) = src(j,0);
singleCoor(1) = src(j,1);
singleCoor(2) = 0.0;
singleCoor(3) = 1.0;
//用现有的内参及外参求估计图像坐标
Eigen::VectorXd imageCoorEstimate = intrinsicParam * externalParam * singleCoor;
//归一化图像坐标
double u_estimate = imageCoorEstimate(0)/imageCoorEstimate(2);
double v_estimate = imageCoorEstimate(1)/imageCoorEstimate(2);
//相机坐标系下的坐标
Eigen::VectorXd normCoor = externalParam * singleCoor;
//归一化坐标
normCoor /= normCoor(2);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(normCoor(0),2) + std::pow(normCoor(1),2));
//k1,k2
if(disCount >= 2)
{
D(k,0) = (u_estimate - u0)*std::pow(r,2);
D(k,1) = (u_estimate - u0)*std::pow(r,4);
D(k+1,0) = (v_estimate - v0)*std::pow(r,2);
D(k+1,1) = (v_estimate - v0)*std::pow(r,4);
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(disCount >= 4)
{
D(k,2) = (u_estimate - u0)*(v_estimate - v0)*2;
D(k,3) = 2 * std::pow((u_estimate - u0),2) + std::pow(r,2);
D(k+1,2) = 2 * std::pow((v_estimate - v0),2) + std::pow(r,2);
D(k+1,3) = (u_estimate - u0)*(v_estimate - v0)*2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(disCount >= 5)
{
D(k,4) = (u_estimate - u0)*std::pow(r,6);
D(k+1,4) = (v_estimate - v0)*std::pow(r,6);
}
d(k,0) = dst(j,0) - u_estimate;
d(k+1,0) = dst(j,1) - v_estimate;
k += 2;
}
}
// 最小二乘求解畸变系数 disCoeff
disCoeff = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->LeastSquares(D,d);
}
LeastSquares函数:最小二乘实现
7:综合内参,外参,畸变系数,使用极大似然法(LMA),优化估计,提升估计精度
构建原函数模型:
min
∑
i
=
1
n
∑
j
=
1
m
∥
m
i
j
−
m
^
∥
2
\min \sum_{i=1}^{n} \sum_{j=1}^{m}\left\|m_{i j}-\hat{m}\right\|^2
min∑i=1n∑j=1m∥mij−m^∥2
其中 m i j m_{ij} mij为实际像素坐标(算法提取到的), m ^ \hat{m} m^为重投影点(利用内参外参畸变计算得到的)
1:如何计算
m
^
\hat{m}
m^
设内参矩阵K =
[
f
x
γ
u
0
0
f
y
v
0
0
0
1
]
\left[\begin{array}{ccc} fx & \gamma & u_{0} \\ 0 & fy & v_{0} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]
⎣⎡fx00γfy0u0v01⎦⎤
旋转向量
r
→
=
[
r
1
,
r
2
,
r
3
]
\overrightarrow{r}=[r1,r2,r3]
r=[r1,r2,r3] (旋转向量有旋转矩阵转换得到实现链接),平移向量
[
t
1
,
t
2
,
t
3
]
[t1,t2,t3]
[t1,t2,t3],令
θ
=
∣
r
→
∣
=
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
\theta=|\overrightarrow{r}|=\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}
θ=∣r∣=r12+r22+r32,记
r
′
→
=
r
⃗
∣
r
⃗
∣
(
单
位
化
)
=
1
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
(
r
→
)
\overrightarrow{r^{\prime}}=\frac{\vec{r}}{|\vec{r}|}(单位化)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}}(\overrightarrow{r})
r′=∣r∣r(单位化)=r12+r22+r321(r)
记某角点世界坐标为
[
X
Y
Z
]
=
P
→
\left[\begin{array}{c} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{array}\right]=\overrightarrow{P}
⎣⎡XYZ⎦⎤=P
则(旋转后):
(
X
r
Y
r
Z
r
)
=
cos
θ
⋅
(
X
Y
Z
)
+
(
1
−
cos
θ
)
⋅
(
p
⃗
⋅
r
′
→
)
r
′
→
+
sin
θ
⋅
r
′
→
×
p
⃗
\left(\begin{array}{l} X_{r} \\ Y_{r} \\ Z_{r} \end{array}\right)=\cos \theta \cdot\left(\begin{array}{l} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{array}\right)+(1-\cos \theta) \cdot\left(\vec{p} \cdot \overrightarrow{r^{\prime}}\right) \overrightarrow{r^{\prime}}+\sin \theta \cdot \overrightarrow{r^{\prime}} \times \vec{p}
⎝⎛XrYrZr⎠⎞=cosθ⋅⎝⎛XYZ⎠⎞+(1−cosθ)⋅(p⋅r′)r′+sinθ⋅r′×p
=
(
cos
θ
⋅
X
cos
θ
⋅
Y
cos
θ
⋅
Z
)
+
(
1
−
cos
θ
)
⋅
r
1
X
+
r
2
Y
+
r
3
Z
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
⋅
1
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
(
r
1
r
2
r
3
)
+
sin
θ
⋅
(
r
1
r
2
r
3
)
⋅
1
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
×
(
X
Y
Z
)
=\left(\begin{array}{l} \cos \theta \cdot X\\ \cos \theta \cdot Y\\ \cos \theta \cdot Z \end{array}\right)+(1-\cos \theta) \cdot\frac{r_1X+r_2Y+r_3Z}{\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}}\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}}\left(\begin{array}{l} r1 \\ r2 \\ r3 \end{array}\right)+\sin \theta \cdot\left(\begin{array}{l} r1 \\ r2 \\ r3 \end{array}\right)\cdot \frac{1}{\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}}×\left(\begin{array}{l} X \\ Y \\ Z \end{array}\right)
=⎝⎛cosθ⋅Xcosθ⋅Ycosθ⋅Z⎠⎞+(1−cosθ)⋅r12+r22+r32r1X+r2Y+r3Z⋅r12+r22+r321⎝⎛r1r2r3⎠⎞+sinθ⋅⎝⎛r1r2r3⎠⎞⋅r12+r22+r321×⎝⎛XYZ⎠⎞
=
(
cos
θ
⋅
X
cos
θ
⋅
Y
cos
θ
⋅
Z
)
+
(
1
−
cos
θ
)
r
1
X
+
r
2
Y
+
r
3
Z
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
(
r
1
r
2
r
3
)
+
sin
θ
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
(
r
2
Z
−
r
3
Y
r
3
X
−
r
1
Z
r
1
Y
−
r
2
X
)
=\left(\begin{array}{c} \cos \theta \cdot X \\ \cos \theta \cdot Y \\ \cos \theta \cdot Z \end{array}\right)+(1-\cos \theta)\frac{r_{1} X+r_{2} Y+r_{3} Z}{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}\left(\begin{array}{l} r_{1} \\ r_{2} \\ r_{3} \end{array}\right)+\frac{\sin \theta}{\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}}\left(\begin{array}{l} r_{2} Z-r_{3} Y \\ r_{3} X-r_{1} Z \\ r_{1} Y-r_{2} X \end{array}\right)
=⎝⎛cosθ⋅Xcosθ⋅Ycosθ⋅Z⎠⎞+(1−cosθ)r12+r22+r32r1X+r2Y+r3Z⎝⎛r1r2r3⎠⎞+r12+r22+r32sinθ⎝⎛r2Z−r3Yr3X−r1Zr1Y−r2X⎠⎞
平移后:
(
X
r
t
Y
r
t
Z
r
t
)
=
(
cos
θ
⋅
X
cos
θ
⋅
Y
cos
θ
⋅
Z
)
+
(
1
−
cos
θ
)
r
1
X
+
r
2
Y
+
r
3
Z
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
(
r
1
r
2
r
3
)
+
sin
θ
r
1
2
+
r
2
2
+
r
3
2
(
r
2
Z
−
r
3
Y
r
3
X
−
r
1
Z
r
1
Y
−
r
2
X
)
+
(
t
1
t
2
t
3
)
\left(\begin{array}{l} X_{rt} \\ Y_{rt} \\ Z_{rt} \end{array}\right)=\left(\begin{array}{c} \cos \theta \cdot X \\ \cos \theta \cdot Y \\ \cos \theta \cdot Z \end{array}\right)+(1-\cos \theta)\frac{r_{1} X+r_{2} Y+r_{3} Z}{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}\left(\begin{array}{l} r_{1} \\ r_{2} \\ r_{3} \end{array}\right)+\frac{\sin \theta}{\sqrt{r_{1}^{2}+r_{2}^{2}+r_{3}^{2}}}\left(\begin{array}{l} r_{2} Z-r_{3} Y \\ r_{3} X-r_{1} Z \\ r_{1} Y-r_{2} X \end{array}\right)+\left(\begin{array}{l} t_{1} \\ t_{2} \\ t_{3} \end{array}\right)
⎝⎛XrtYrtZrt⎠⎞=⎝⎛cosθ⋅Xcosθ⋅Ycosθ⋅Z⎠⎞+(1−cosθ)r12+r22+r32r1X+r2Y+r3Z⎝⎛r1r2r3⎠⎞+r12+r22+r32sinθ⎝⎛r2Z−r3Yr3X−r1Zr1Y−r2X⎠⎞+⎝⎛t1t2t3⎠⎞
(这个公式没有考虑到畸变参数)重投影
m
^
→
=
[
u
v
c
]
=
[
f
x
γ
u
0
0
f
y
v
0
0
0
1
]
⋅
(
X
r
t
Y
r
t
Z
r
t
)
=
[
f
x
⋅
X
r
t
+
Y
r
t
⋅
γ
+
u
0
⋅
Z
r
t
f
y
⋅
Y
r
t
+
v
0
⋅
Z
r
t
Z
r
t
]
\overrightarrow {\hat m} = \left[\begin{array}{l} u \\ v \\ c \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} fx& \gamma & u_{0} \\ 0 & fy & v_{0} \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right] \cdot\left(\begin{array}{l} X_{rt} \\ Y_{rt}\\ Z_{rt} \end{array}\right)=\left[\begin{array}{c} f_{x} \cdot X_{rt}+Y_{rt} \cdot \gamma +u_{0} \cdot Z_{rt} \\ f_y \cdot Y_{rt}+v_{0}\cdot Z_{rt} \\ Z_{rt} \end{array}\right]
m^=⎣⎡uvc⎦⎤=⎣⎡fx00γfy0u0v01⎦⎤⋅⎝⎛XrtYrtZrt⎠⎞=⎣⎡fx⋅Xrt+Yrt⋅γ+u0⋅Zrtfy⋅Yrt+v0⋅ZrtZrt⎦⎤
即:
u
′
=
f
x
⋅
X
r
t
+
Y
r
t
⋅
γ
+
u
0
⋅
Z
r
t
Z
r
t
=
X
r
t
Z
r
t
⋅
f
x
+
Y
r
t
Z
r
t
⋅
γ
+
u
0
v
′
=
f
y
⋅
Y
r
t
+
v
0
⋅
Z
r
t
Z
r
t
=
Y
r
t
Z
r
t
⋅
f
y
+
v
0
\begin{array}{l} u^{\prime}=\frac{f_{x} \cdot X_{rt}+Y_{rt} \cdot \gamma+u_{0} \cdot Z_{rt}}{Z_{rt}}=\frac{X_{rt}}{Z_{rt}} \cdot f_{x}+\frac{Y_{rt}}{Z_{rt}} \cdot \gamma +u_{0}\\ v^{\prime}=\frac{f_{y} \cdot Y_{rt}+v_{0} \cdot Z_{rt}}{Z_{rt}}=\frac{Y_{rt}}{Z_{rt}} \cdot f_{y}+v_{0} \\ \end{array}
u′=Zrtfx⋅Xrt+Yrt⋅γ+u0⋅Zrt=ZrtXrt⋅fx+ZrtYrt⋅γ+u0v′=Zrtfy⋅Yrt+v0⋅Zrt=ZrtYrt⋅fy+v0
完整原函数模型(含畸变):

旋转矩阵和旋转向量互相转换,后面代码会用到
//旋转矩阵 --> 旋转向量 :罗德里格斯公式逆变换
Vector3d Rodrigues(const Matrix3d& R)
{
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotAA2(R);
Vector3d r{rotAA2.angle() * rotAA2.axis()};
// double theta = acos((R.trace() - 1) * 0.5);
// Matrix3d r_hat = (R - R.transpose()) * 0.5 / sin(theta);
// Vector3d r1;
// r1(0) = theta*(r_hat(2,1) - r_hat(1,2))*0.5;
// r1(1) = theta*(r_hat(0,2) - r_hat(2,0))*0.5;
// r1(2) = theta*(r_hat(1,0) - r_hat(0,1))*0.5;
// std::cout<<"R.trace():"<<R.trace()<<" theta: "<<theta<<std::endl<<"r:"<< r <<std::endl<<std::endl<<"r1:"<< r1 <<std::endl;
return r;
}
//旋转向量 --> 旋转矩阵 :罗德里格斯公式
Matrix3d Rodrigues(const Vector3d& _r)
{
// 第1种方法
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotAA{_r.norm(), _r.normalized()};
Matrix3d R {rotAA.toRotationMatrix()};
// // 第2种方法
// double theta = _r.lpNorm<2>();
// Vector3d r = _r / theta;
// Matrix3d r_hat;
// r_hat << 0, -r[2], r[1],
// r[2], 0, -r[0],
// -r[1], r[0], 0;
// Matrix3d R = cos(theta) * Matrix3d::Identity() + (1 - cos(theta)) * r * r.transpose() + sin(theta) * r_hat;
// std::cout << "R :" << R << std::endl;
return R;
}
代码实现:
#define DERIV_STEP 1e-5
#define INTRINSICP_COUNT 5 //内参个数
typedef struct _CameraOtherParameter
{
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> srcL; //物体点
QList<Eigen::MatrixXd> dstL; //图像点
int intrinsicCount; //内参个数
int disCount; //畸变个数 //畸变系数 2:k1,k2,(4:)p1,p2,[(5:)k3]
int imageCount; // 图像个数
}S_CameraOtherParameter;
//相机标定残差值向量 -- 返回所有点的真实世界坐标映射到图像坐标 与 真实图像坐标的残差
class CalibrationResidualsVector
{
//返回从真实世界坐标映射的图像坐标
Eigen::Vector3d getMapCoor(const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam ,const Eigen::VectorXd& distortionCoeff,const Eigen::MatrixXd& externalParam,const Eigen::Vector3d& XYZ)
{
//畸变个数
int disCount = distortionCoeff.rows();
//转换齐次坐标
Eigen::VectorXd singleCoor(4);
singleCoor(0) = XYZ(0);
singleCoor(1) = XYZ(1);
singleCoor(2) = XYZ(2);
singleCoor(3) = 1;
//归一化坐标
Eigen::Vector3d normCoor = externalParam * singleCoor;
normCoor /= normCoor(2);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(normCoor(0),2) + std::pow(normCoor(1),2));
Eigen::Vector3d uv;
uv(0)=0;
uv(1)=0;
uv(2)=1;
//无畸变参数
if(disCount == 0)
{
uv(0) = normCoor(0);
uv(1) = normCoor(1);
}
double u_2=0,v_2=0,u_4=0,v_4=0,u_5=0,v_5=0,u_8=0,v_8=0,u_12=0,v_12=0;
//k1,k2
if(disCount >= 2)
{
u_2 = normCoor(0)*(1+std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(0) + std::pow(r,4) * distortionCoeff(1));
v_2 = normCoor(1)*(1+std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(0) + std::pow(r,4) * distortionCoeff(1));
uv(0) += u_2;
uv(1) += v_2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(disCount >= 4)
{
u_4 = (2*normCoor(0)*normCoor(1)*distortionCoeff(2) + (2*std::pow(normCoor(0),2) + std::pow(r,2))*distortionCoeff(3));
v_4 = ((2*std::pow(normCoor(1),2) + std::pow(r,2))*distortionCoeff(2) + normCoor(0)*normCoor(1)*2*distortionCoeff(3));
uv(0) += u_4;
uv(1) += v_4;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(disCount >= 5)
{
u_5 = normCoor(0)*std::pow(r,6)*distortionCoeff(4);
v_5 = normCoor(1)*std::pow(r,6)*distortionCoeff(4);
uv(0) += u_5;
uv(1) += v_5;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6
if(disCount >= 8)
{
u_8 = (u_2 + u_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(5) + std::pow(r,4) * distortionCoeff(6) + std::pow(r,6)*distortionCoeff(7)) + u_4;
v_8 = (v_2 + v_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(5) + std::pow(r,4) * distortionCoeff(6) + std::pow(r,6)*distortionCoeff(7)) + v_4;
uv(0) = u_8;
uv(1) = v_8;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6,s1,s2,s3,s4
if(disCount >= 12)
{
u_12 = std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(8) + std::pow(r,4)*distortionCoeff(9);
v_12 = std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(10) + std::pow(r,4)*distortionCoeff(11);
uv(0) += u_12;
uv(1) += v_12;
}
uv = intrinsicParam * uv;
return uv;
}
public:
Eigen::VectorXd operator()(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,const S_CameraOtherParameter &otherArgs)
{
//获取数据总个数
int allCount=0;
for(int i=0;i<otherArgs.imageCount;++i)
{
allCount += otherArgs.srcL.at(i).rows();
}
Eigen::VectorXd real_uv(allCount*2),map_uv(allCount*2);
//内参
Eigen::Matrix3d intrinsicParam;
intrinsicParam<<parameter(0),parameter(1),parameter(3),
0,parameter(2),parameter(4),
0,0,1;
//畸变系数
Eigen::VectorXd distortionCoeff(otherArgs.disCount);
for(int i=0;i<otherArgs.disCount;++i)
{
distortionCoeff(i) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+i);
}
//索引k存放数据
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<otherArgs.imageCount;++i)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd src = otherArgs.srcL.at(i);
Eigen::MatrixXd dst = otherArgs.dstL.at(i);
int srcCount = src.rows();
//外参
Eigen::MatrixXd W(3,4);
Eigen::Vector3d r ;
r(0) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6);
r(1) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1);
r(2) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2);
W.block(0,0,3,3) = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->Rodrigues(r);
W(0,3) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+3);
W(1,3) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+4);
W(2,3) = parameter(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5);
//遍历当前图片数据点
for(int j=0;j<srcCount;++j)
{
//物体坐标
Eigen::Vector3d XYZ;
XYZ<<src(j,0),
src(j,1),
0;
Eigen::Vector3d uv = getMapCoor(intrinsicParam,distortionCoeff,W,XYZ);
map_uv(k) = uv(0);
map_uv(k+1) = uv(1);
real_uv(k) = dst(j,0);
real_uv(k+1) = dst(j,1);
k += 2;
}
}
//获取预测偏差值 r= ^y(预测值) - y(实际值)
return map_uv - real_uv;
}
};
//求相机标定雅克比矩阵
class CalibrationJacobi
{
//求偏导1
double PartialDeriv_1(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,int paraIndex, const S_CameraOtherParameter &otherArgs,int i,int j)
{
Eigen::VectorXd para1 = parameter;
Eigen::VectorXd para2 = parameter;
para1(paraIndex) -= DERIV_STEP;
para2(paraIndex) += DERIV_STEP;
double obj1 =0,obj2 =0;
//坐标
double x = otherArgs.srcL.at(i)(j,0);
double y = otherArgs.srcL.at(i)(j,1);
double z = 0;
//旋转向量
double r_1 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6);
double r_2 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1);
double r_3 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2);
//平移向量
double t_1 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+3);
double t_2 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+4);
double t_3 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5);
double x1 = (((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_1*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*x+(sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_2*z-r_3*y))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+t_1)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double y1 = ((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_3*x-r_1*z))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_2*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*y+t_2)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(x1,2)+std::pow(y1,2));
double x11=0,y11=0;
//无畸变参数
if(otherArgs.disCount == 0)
{
x11 = x1;
y11 = y1;
}
double u_2=0,v_2=0,u_4=0,v_4=0,u_5=0,v_5=0,u_8=0,v_8=0,u_12=0,v_12=0;
//k1,k2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 2)
{
u_2 = x1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
v_2 = y1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
x11 += u_2;
y11 += v_2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 4)
{
u_4 = (2*x1*y1*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + (2*std::pow(x1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
v_4 = ((2*std::pow(y1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + x1*y1*2*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
x11 += u_4;
y11 += v_4;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 5)
{
u_5 = x1*std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
v_5 = y1*std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
x11 += u_5;
y11 += v_5;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 8)
{
u_8 = (u_2 + u_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + u_4;
v_8 = (v_2 + v_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + v_4;
x11 = u_8;
y11 = v_8;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6,s1,s2,s3,s4
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 12)
{
u_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+8) + std::pow(r,4)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+9);
v_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+10) + std::pow(r,4)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+11);
x11 += u_12;
y11 += v_12;
}
double f_x = para1(0);
double gam = para1(1);
//double f_y = para1(2);
double u_0 = para1(3);
//double v_0 = para1(4);
obj1 = f_x*x11+gam*y11+u_0;
{
//旋转向量
double r_1 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6);
double r_2 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1);
double r_3 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2);
//平移向量
double t_1 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+3);
double t_2 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+4);
double t_3 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5);
double x1 = (((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_1*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*x+(sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_2*z-r_3*y))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+t_1)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double y1 = ((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_3*x-r_1*z))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_2*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*y+t_2)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(x1,2)+std::pow(y1,2));
double x11=0,y11=0;
//无畸变参数
if(otherArgs.disCount == 0)
{
x11 = x1;
y11 = y1;
}
double u_2=0,v_2=0,u_4=0,v_4=0,u_5=0,v_5=0,u_8=0,v_8=0,u_12=0,v_12=0;
//k1,k2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 2)
{
u_2 = x1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
v_2 = y1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
x11 += u_2;
y11 += v_2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 4)
{
u_4 = (2*x1*y1*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + (2*std::pow(x1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
v_4 = ((2*std::pow(y1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + x1*y1*2*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
x11 += u_4;
y11 += v_4;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 5)
{
u_5 = x1*std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
v_5 = y1*std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
x11 += u_5;
y11 += v_5;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 8)
{
u_8 = (u_2 + u_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + u_4;
v_8 = (v_2 + v_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + v_4;
x11 = u_8;
y11 = v_8;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6,s1,s2,s3,s4
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 12)
{
u_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+8) + std::pow(r,4)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+9);
v_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+10) + std::pow(r,4)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+11);
x11 += u_12;
y11 += v_12;
}
double f_x = para2(0);
double gam = para2(1);
//double f_y = para2(2);
double u_0 = para2(3);
// double v_0 = para2(4);
obj2 = f_x*x11+gam*y11+u_0;
}
return (obj2 - obj1) / (2 * DERIV_STEP);
}
//求偏导2
double PartialDeriv_2(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,int paraIndex, const S_CameraOtherParameter &otherArgs,int i,int j)
{
Eigen::VectorXd para1 = parameter;
Eigen::VectorXd para2 = parameter;
para1(paraIndex) -= DERIV_STEP;
para2(paraIndex) += DERIV_STEP;
double obj1 =0,obj2 =0;
//坐标
double x = otherArgs.srcL.at(i)(j,0);
double y = otherArgs.srcL.at(i)(j,1);
double z = 0;
//旋转向量
double r_1 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6);
double r_2 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1);
double r_3 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2);
//平移向量
double t_1 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+3);
double t_2 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+4);
double t_3 = para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5);
double x1 = (((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_1*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*x+(sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_2*z-r_3*y))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+t_1)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double y1 = ((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_3*x-r_1*z))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_2*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*y+t_2)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(x1,2)+std::pow(y1,2));
double x11=0,y11=0;
//无畸变参数
if(otherArgs.disCount == 0)
{
x11 = x1;
y11 = y1;
}
double u_2=0,v_2=0,u_4=0,v_4=0,u_5=0,v_5=0,u_8=0,v_8=0,u_12=0,v_12=0;
//k1,k2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 2)
{
u_2 = x1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
v_2 = y1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
x11 += u_2;
y11 += v_2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 4)
{
u_4 = (2*x1*y1*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + (2*std::pow(x1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
v_4 = ((2*std::pow(y1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + x1*y1*2*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
x11 += u_4;
y11 += v_4;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 5)
{
u_5 = x1*std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
v_5 = y1*std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
x11 += u_5;
y11 += v_5;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 8)
{
u_8 = (u_2 + u_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + u_4;
v_8 = (v_2 + v_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + v_4;
x11 = u_8;
y11 = v_8;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6,s1,s2,s3,s4
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 12)
{
u_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+8) + std::pow(r,4)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+9);
v_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+10) + std::pow(r,4)*para1(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+11);
x11 += u_12;
y11 += v_12;
}
//double f_x = para1(0);
// double gam = para1(1);
double f_y = para1(2);
//double u_0 = para1(3);
double v_0 = para1(4);
obj1 = f_y*y11+v_0;
{
//旋转向量
double r_1 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6);
double r_2 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1);
double r_3 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2);
//平移向量
double t_1 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+3);
double t_2 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+4);
double t_3 = para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5);
double x1 = (((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_1*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*x+(sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_2*z-r_3*y))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+t_1)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double y1 = ((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_3*x-r_1*z))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_2*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*y+t_2)/((sin(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*(r_1*y-r_2*x))/std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+((1-cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))))*r_3*(r_1*x+r_3*z+r_2*y))/(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2))+cos(std::sqrt(std::pow(r_1,2)+std::pow(r_2,2)+std::pow(r_3,2)))*z+t_3);
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(x1,2)+std::pow(y1,2));
double x11=0,y11=0;
//无畸变参数
if(otherArgs.disCount == 0)
{
x11 = x1;
y11 = y1;
}
double u_2=0,v_2=0,u_4=0,v_4=0,u_5=0,v_5=0,u_8=0,v_8=0,u_12=0,v_12=0;
//k1,k2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 2)
{
u_2 = x1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
v_2 = y1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1));
x11 += u_2;
y11 += v_2;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 4)
{
u_4 = (2*x1*y1*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + (2*std::pow(x1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
v_4 = ((2*std::pow(y1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) + x1*y1*2*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3));
x11 += u_4;
y11 += v_4;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 5)
{
u_5 = x1*std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
v_5 = y1*std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4);
x11 += u_5;
y11 += v_5;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 8)
{
u_8 = (u_2 + u_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + u_4;
v_8 = (v_2 + v_5) / (1+std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) + std::pow(r,4) * para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) + std::pow(r,6)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7)) + v_4;
x11 = u_8;
y11 = v_8;
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6,s1,s2,s3,s4
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 12)
{
u_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+8) + std::pow(r,4)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+9);
v_12 = std::pow(r,2)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+10) + std::pow(r,4)*para2(otherArgs.intrinsicCount+11);
x11 += u_12;
y11 += v_12;
}
//double f_x = para2(0);
//double gam = para2(1);
double f_y = para2(2);
//double u_0 = para2(3);
double v_0 = para2(4);
obj2 = f_y*y11+v_0;
}
return (obj2 - obj1) / (2 * DERIV_STEP);
}
public:
Eigen::MatrixXd operator()(const Eigen::VectorXd& parameter,const S_CameraOtherParameter &otherArgs)
{
//获取数据总个数
int allCount=0;
for(int i=0;i<otherArgs.imageCount;++i)
{
allCount += otherArgs.srcL.at(i).rows();
}
//初始化雅可比矩阵都为0
Eigen::MatrixXd Jac = Eigen::MatrixXd::Zero(allCount*2,parameter.rows());
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<otherArgs.imageCount;++i)
{
Eigen::MatrixXd src = otherArgs.srcL.at(i);
int srcCount = src.rows();
//遍历当前图片数据点
for(int j=0;j<srcCount;++j)
{
//内参偏导
Jac(k,0) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,0,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,1) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,1,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,2) = 0;
Jac(k,3) = 1;
Jac(k,4) = 0;
Jac(k+1,0) = 0;
Jac(k+1,1) = 0;
Jac(k+1,2) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,2,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,3) = 0;
Jac(k+1,4) = 1;
//畸变偏导
//k1,k2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 2)
{
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+1,otherArgs,i,j);
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 4)
{
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+2,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+3,otherArgs,i,j);
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 5)
{
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+4,otherArgs,i,j);
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 8)
{
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+5,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+6,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+7,otherArgs,i,j);
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3,k4,k5,k6,s1,s2,s3,s4
if(otherArgs.disCount >= 12)
{
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+8) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+8,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+9) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+9,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+10) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+10,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+11) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+11,otherArgs,i,j);
}
//外参偏导 r1,r2,r3,t1,t2,t3
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 1) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 2) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 3) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+3,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 4) = 0;
Jac(k,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 5) = PartialDeriv_1(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6,otherArgs,i,j);
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 1) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+1,otherArgs,i,j);;
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 2) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+2,otherArgs,i,j);;
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 3) = 0;
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 4) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+4,otherArgs,i,j);;
Jac(k+1,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount + i*6 + 5) = PartialDeriv_2(parameter,otherArgs.intrinsicCount+otherArgs.disCount+i*6+5,otherArgs,i,j);;
k += 2;
}
}
return Jac;
}
};
//整合所有参数(内参,畸变系数,外参)到一个向量中
Eigen::VectorXd CameraCalibration::ComposeParameter(const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam ,const Eigen::VectorXd& distortionCoeff,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& externalParams)
{
//畸变参数个数
int disCount = distortionCoeff.rows();
//外参个数
int exterCount=0;
for(int i=0;i<externalParams.count();++i)
{
//一张图片的外参个数 R->r(9->3) + t 3 = 6
exterCount += 6;
}
Eigen::VectorXd P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+exterCount);
//整合内参
P(0) = intrinsicParam(0,0);
P(1) = intrinsicParam(0,1);
P(2) = intrinsicParam(1,1);
P(3) = intrinsicParam(0,2);
P(4) = intrinsicParam(1,2);
//整合畸变
for(int i=0;i<disCount;++i)
{
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+i) = distortionCoeff(i);
}
//整合外参
for(int i=0;i<externalParams.count();++i)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d R = externalParams.at(i).block(0,0,3,3);
//旋转矩阵转旋转向量
Eigen::Vector3d r = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->Rodrigues(R);
Eigen::Vector3d t = externalParams.at(i).col(3);
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+i*6) = r(0);
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+i*6+1) = r(1);
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+i*6+2) = r(2);
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+i*6+3) = t(0);
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+i*6+4) = t(1);
P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+disCount+i*6+5) = t(2);
}
return P;
}
//分解所有参数 得到对应的内参,畸变矫正系数,外参
void CameraCalibration::DecomposeParamter(const Eigen::VectorXd &P, Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam , Eigen::VectorXd& distortionCoeff, QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& externalParams)
{
//内参
intrinsicParam << P(0),P(1),P(3),
0,P(2),P(4),
0,0,1;
//畸变
for(int i =0;i<distortionCoeff.rows();++i)
{
distortionCoeff(i) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+i);
}
//外参
for(int i=0;i<externalParams.count();++i)
{
Eigen::Vector3d r,t;
r(0) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6);
r(1) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+1) ;
r(2) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+2);
t(0) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+3) ;
t(1) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+4);
t(2) = P(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+5) ;
Eigen::Matrix3d R = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->Rodrigues(r);
externalParams[i].block(0,0,3,3) = R;
externalParams[i].col(3) = t;
}
}
//优化所有参数 (内参,畸变系数,外参) 返回重投影误差值
double CameraCalibration::OptimizeParameter(const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& srcL,const QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& dstL, Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParam , Eigen::VectorXd& distortionCoeff, QList<Eigen::MatrixXd>& externalParams)
{
//整合参数
Eigen::VectorXd P = ComposeParameter(intrinsicParam,distortionCoeff,externalParams);
S_CameraOtherParameter cameraParam;
cameraParam.dstL = dstL;
cameraParam.srcL = srcL;
cameraParam.imageCount = dstL.count();
cameraParam.intrinsicCount = INTRINSICP_COUNT;
cameraParam.disCount = distortionCoeff.rows();
Eigen::VectorXd P1 = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->LevenbergMarquardtAlgorithm(P,cameraParam,CalibrationResidualsVector(),CalibrationJacobi(),m_epsilon,m_maxIteCount);
//分解参数
DecomposeParamter(P1,intrinsicParam,distortionCoeff,externalParams);
//计算重投影误差
CalibrationResidualsVector reV;
//每张图片重投影误差
m_reprojErrL.clear();
Eigen::VectorXd PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+6);
PP.block(0,0,INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows(),1) = P1.block(0,0,INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows(),1);
for(int i=0;i<externalParams.count();++i)
{
PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows())= P1(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6);
PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+1)= P1(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+1);
PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+2)= P1(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+2);
PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+3)= P1(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+3);
PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+4)= P1(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+4);
PP(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+5)= P1(INTRINSICP_COUNT+distortionCoeff.rows()+i*6+5);
S_CameraOtherParameter cameraParam1;
cameraParam1.dstL.append(dstL.at(i));
cameraParam1.srcL.append(srcL.at(i));
cameraParam1.imageCount = 1;
cameraParam1.intrinsicCount = INTRINSICP_COUNT;
cameraParam1.disCount = distortionCoeff.rows();
Eigen::VectorXd reV1 = reV(PP,cameraParam1);
int pointCount = reV1.rows()/2;
Eigen::VectorXd errorV(pointCount);
for(int i=0,k=0;i<pointCount;++i,k+=2)
{
errorV(i) = std::sqrt(std::pow(reV1(k),2) + std::pow(reV1(k+1),2));
}
m_reprojErrL.append(std::sqrt(errorV.sum()/pointCount));
//qDebug()<<"errorV: "<<errorV.lpNorm<2>()<<" : "<<std::sqrt(errorV.sum()/pointCount)<<" : "<<errorV.maxCoeff()<<" :"<<i;
}
//总重投影误差
Eigen::VectorXd reV1 = reV(P1,cameraParam);
int pointCount = reV1.rows()/2;
Eigen::VectorXd errorV(pointCount);
for(int i=0,k=0;i<pointCount;++i,k+=2)
{
errorV(i) = std::sqrt(std::pow(reV1(k),2) + std::pow(reV1(k+1),2));
}
//qDebug()<<"errorV: "<<errorV.lpNorm<2>()<<" : "<<std::sqrt(errorV.sum()/pointCount)<<" : "<<errorV.maxCoeff();
return std::sqrt(errorV.sum()/pointCount);
}
//带畸变优化
//m_disCount 畸变个数 ,可选 [2,[4,[5]]]
Eigen::VectorXd disCoeff = Eigen::VectorXd::Zero(m_disCount);
//获取初始畸变参数
GetDistortionCoeff(srcL,dstL,K,W,disCoeff);
//优化内参,外参,畸变参数
double reprojErr = OptimizeParameter(srcL,dstL,K,disCoeff,W);
8:得出相机的内参,外参和畸变系数
内参 K,外参 W,畸变参数 disCoeff
9:OpenCV模型
无畸变:
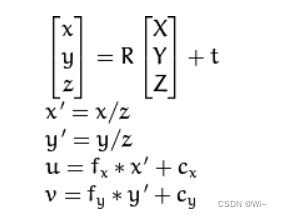
 含畸变:
含畸变:

上面代码实现畸变只包含了:k1,k2,p1,p2,k3。
OpenCV:calibrateCamera函数
三:畸变修复(去畸变)
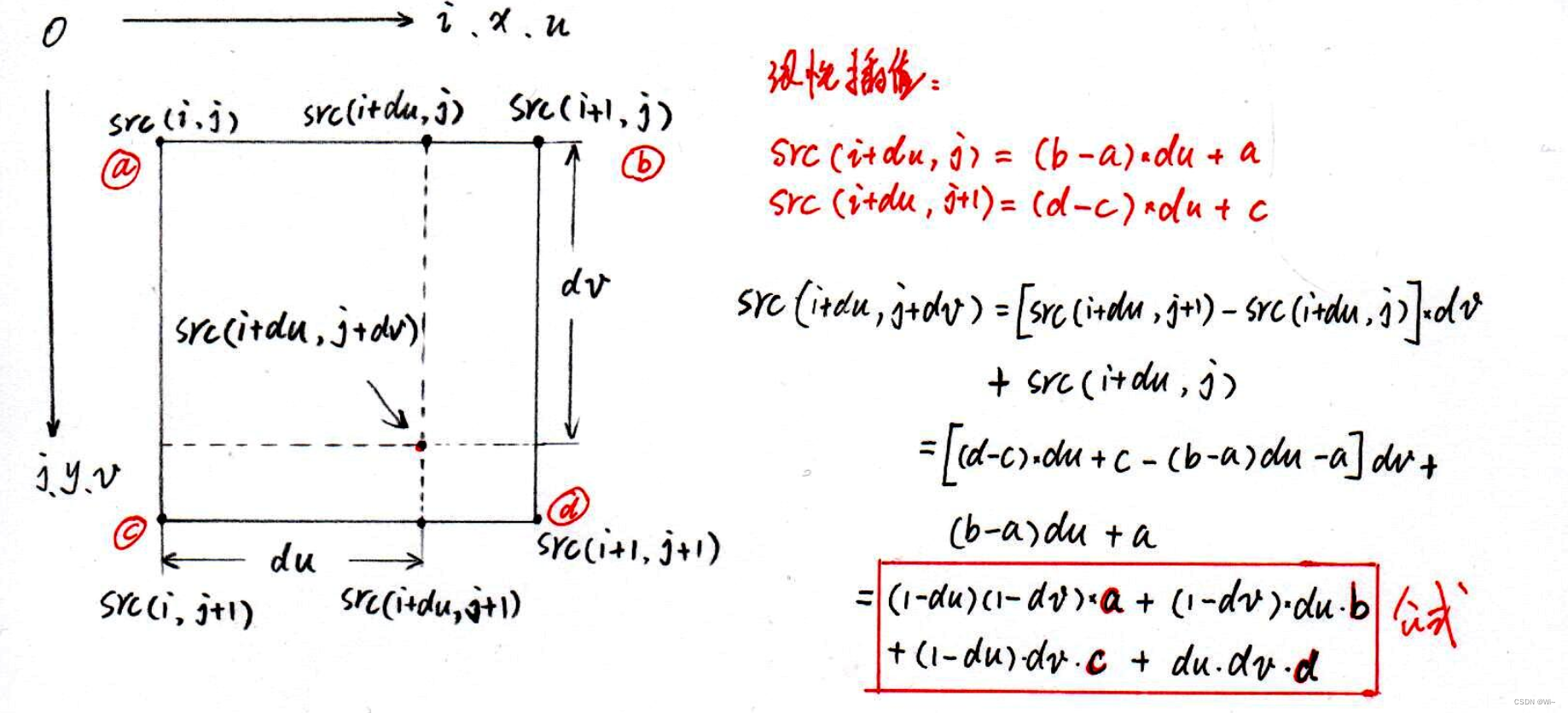
采用双线插值法实现
代码实现:
//矫正图像 根据内参和畸变系数矫正
Eigen::MatrixXi GlobleAlgorithm::RectifiedImage(Eigen::MatrixXi src,Eigen::Matrix3d intrinsicParam , Eigen::VectorXd distortionCoeff )
{
int rowCount = src.rows();
int colCount = src.cols();
int disCount = distortionCoeff.rows();
//无畸变参数
if(disCount == 0)
{
return src;
}
Eigen::MatrixXi dst = Eigen::MatrixXi::Zero(rowCount,colCount);
double f_x = intrinsicParam(0,0);
double gam = intrinsicParam(0,1);
double f_y = intrinsicParam(1,1);
double u_0 = intrinsicParam(0,2);
double v_0 = intrinsicParam(1,2);
for(int i=0;i<rowCount;++i)
{
for(int j=0;j<colCount;++j)
{
double y1 = (j-v_0)/f_y;
double x1 = (i-u_0-y1*gam)/f_x;
double r = std::sqrt(std::pow(x1,2)+std::pow(y1,2));
double x11=0,y11=0;
//k1,k2
if(disCount >= 2)
{
x11 += x1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(0) + std::pow(r,4) * distortionCoeff(1));
y11 += y1*(1+std::pow(r,2)*distortionCoeff(0) + std::pow(r,4) * distortionCoeff(1));
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2
if(disCount >= 4)
{
x11 += (2*x1*y1*distortionCoeff(2) + (2*std::pow(x1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*distortionCoeff(3));
y11 += ((2*std::pow(y1,2) + std::pow(r,2))*distortionCoeff(2) + x1*y1*2*distortionCoeff(3));
}
//k1,k2,p1,p2,k3
if(disCount >= 5)
{
x11 += x1*std::pow(r,6)*distortionCoeff(4);
y11 += y1*std::pow(r,6)*distortionCoeff(4);
}
double ud = f_x*x11 + y11*gam + u_0;
double vd = y11*f_y + v_0;
// 赋值 (双线性插值)
if (ud >= 0 && vd >= 0 && ud < rowCount && vd < colCount)
{
//取整数
quint32 au = (quint32)std::floor(ud);
quint32 av = (quint32)std::floor(vd);
//取小数
double du = ud - au;
double dv = vd - av;
//找出临近的四个数据(像素值)
int a=0,b=0,c=0,d=0;
a = src(au,av);
if(vd+1<colCount)
{
b = src(au,av+1);
}
if(ud+1<rowCount)
{
c = src(au+1,av);
}
if(vd+1<colCount && ud+1<rowCount)
{
d = src(au+1,av+1);
}
dst(i, j) = (1-du)*(1-dv)*a + (1-du)*dv*b + (1-dv)*du*c + du*dv*d;
}
else
{
dst(i, j) = 0;
}
}
}
return dst;
}
//修复图片
QImage ImageCorrectionWidget::RectifiedImage(const QImage& srcImage, const Eigen::Matrix3d& intrinsicParameter,const Eigen::VectorXd& distortionCoeff)
{
int width = srcImage.width (); // 图像宽度
int height = srcImage.height (); // 图像高度
//qDebug()<< srcImage.depth() <<srcImage.allGray()<<" width:"<<width<<" height:"<<height;
//获取rgb数值
Eigen::MatrixXi srcR(height,width),srcG(height,width),srcB(height,width);
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) // 遍历每一行
{
for ( int j = 0; j < width; j++ ) // 遍历每一列
{
QColor color = srcImage.pixelColor(j,i);
srcR(i,j) = color.red();
srcG(i,j) = color.green();
srcB(i,j) = color.blue();
}
}
//rgb数值转换去畸变
Eigen::MatrixXi dstR = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->RectifiedImage(srcR,intrinsicParameter,distortionCoeff);
Eigen::MatrixXi dstG = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->RectifiedImage(srcG,intrinsicParameter,distortionCoeff);
Eigen::MatrixXi dstB = GlobleAlgorithm::getInstance()->RectifiedImage(srcB,intrinsicParameter,distortionCoeff);
QImage dstImage(width,height,srcImage.format());
//填充去畸变图像
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) // 遍历每一行
{
for ( int j = 0; j < width; j++ ) // 遍历每一列
{
dstImage.setPixelColor(j,i,QColor(dstR(i,j),dstG(i,j),dstB(i,j)));
}
}
return dstImage;
}
QStringList m_files;//文件路径列表
for(int i=0;i<m_files.count();++i)
{
QImage srcImage(m_files.at(i));
QImage dstImage = RectifiedImage(srcImage,intrinsicParameter,distortionCoeff);
QString fileName = m_files.at(i).split(QDir::separator()).last();
QString path = m_savePath+QDir::separator()+QDateTime::currentDateTime().toString("yyyy.MM.dd-hh.mm.ss.zzz")+"_"+fileName;
if(dstImage.save(path))
{
m_outTextEdit->append(path+" : 保存成功!");
}
else
{
m_outTextEdit->append(path+" : 保存失败!");
}
}
有畸变:
 去畸变后:
去畸变后:

双线性插值
双线性插值法计算
四:总结
以上所有代码还有优化空间,并未优化。
1:工具:主要Qt + Eigen库
Eigen库是一个用于矩阵计算,代数计算库
2:上面完整代码已上传GitHub
3:参考文献
张正友论文
构建雅可比矩阵模型
Python代码实现
什么是归一化的平面坐标
重投影误差理解
单应矩阵的计算
相机坐标系,像素平面坐标系,世界坐标系,归一化坐标系总结
旋转向量与旋转矩阵的相互转化
原函数模型推导
LM算法实现介绍
相机畸变详解
畸变校正详解
