【数据结构】实现二叉树的基本操作
目录
1. 二叉树的基本操作
2. 具体实现
2.1 创建BinaryTree类以及简单创建一棵树
2.2 前序遍历
2.3 中序遍历
2.4 后序遍历
2.5 层序遍历
2.6 获取树中节点的个数
2.7 获取叶子节点的个数
2.8 获取第K层节点的个数
2.9 获取二叉树的高度
2.10 检测值为val的元素是否存在
2.11 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
3. 整体代码 + 测试代码
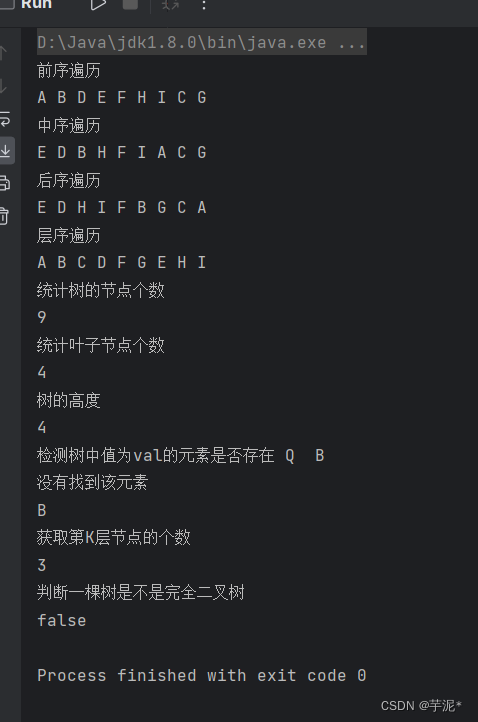
测试结果:
上一篇已经了解了一些二叉树的基本内容,这篇来讲二叉树的基本操作。
1. 二叉树的基本操作
// 前序遍历
void preOrder(TreeNode root);
// 中序遍历
void inOrder(TreeNode root);
// 后序遍历
void postOrder(TreeNode root);
// 获取树中节点的个数:遍历思路
public static int nodeSize;
void size(TreeNode root);
// 获取节点的个数:子问题的思路
int size2(TreeNode root);
//获取叶子节点的个数:遍历思路
public static int leafSize = 0;
void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root);
// 获取叶子节点的个数:子问题
int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root);
// 获取第K层节点的个数
int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k);
// 获取二叉树的高度,时间复杂度:O(N)
int getHeight(TreeNode root);
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val);
//层序遍历
void levelOrder(TreeNode root);
// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root);2. 具体实现
2.1 创建BinaryTree类以及简单创建一棵树

public class MyBinTree {
private class TreeNode {
char val;
TreeNode left;// 左孩子的引用,常常代表左孩子为根的整棵左子树
TreeNode right;// 右孩子的引用,常常代表右孩子为根的整棵右子树
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
public TreeNode createTree() {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode('A');
TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode('B');
TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode('C');
TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode('D');
TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode('E');
TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode('F');
TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode('G');
TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode('H');
TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode('I');
root.left = node1;
root.right = node2;
node1.left = node3;
node1.right = node5;
node2.right = node6;
node3.left = node4;
node5.left = node7;
node5.right = node8;
return root;
}
}2.2 前序遍历
"根左右":从树根开始,先遍历根节点,继续递归的遍历左子树,最后再递归的遍历右子树。
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
// 1.base case
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 根
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
// 左
preOrder(root.left);
//右
preOrder(root.right);
}2.3 中序遍历
"左根右":先递归的访问左子树,然后访问根节点,最后递归的访问右子树。
// 中序遍历
public void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 先左子树的中序
inOrder(root.left);
// 根
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
// 再右子树的中序
inOrder(root.right);
}2.4 后序遍历
"左右根":先递归的访问左子树,然后递归的访问右子树,最后访问根节点。
// 后序遍历
public void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return;
}
// 先左子树的后序
postOrder(root.left);
// 再右子树的后序
postOrder(root.right);
// 根
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}2.5 层序遍历
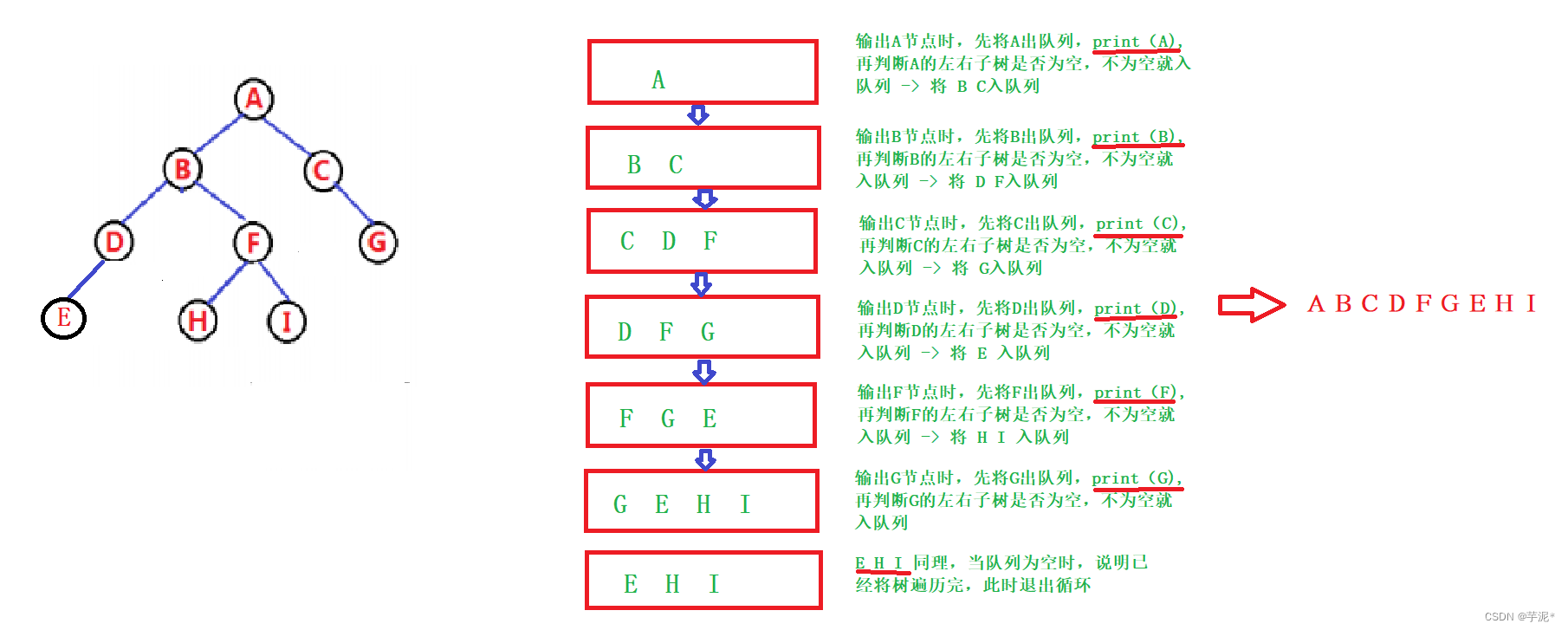
借助队列先进先出的特点来遍历节点:
void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
System.out.println("这是颗空树!!!");
return;
}
// 借助队列来模拟层序遍历的过程
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
// 队列为空,表示所有元素访问完毕
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = queue.pop();
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
// 依次将当前节点的左右子树依次入队
if (cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}2.6 获取树中节点的个数
将问题拆分成根节点与左右子树的问题,解决根节点的问题再递归调用本方法解决左右子树的问题。
第一种:需要一个全局变量来保存节点的个数,每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,否则加上这个节点即nodeSize+1,然后再递归的访问它的左右子树。
第二种:每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,否则返回1 + 左子树的节点个数 + 右子树的节点个数。
public static int nodeSize;
/**
* 获取树中节点的个数:遍历思路
*/
void size(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return;
}
nodeSize ++;
size(root.left);
size(root.right);
}
/**
* 获取节点的个数:子问题的思路
*/
int size2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return size2(root.left) + size2(root.right) + 1;
}2.7 获取叶子节点的个数
与上一个的思路类似,也是拆分成根节点与左右子树的问题再递归调用本方法。
第一种:需要一个全局变量来保存叶子节点的个数,每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,再判断它是否为叶子节点(它的左右子树是否为空),是则leafSize+1,然后再递归的访问它的左右子树。
第二种:每走到一个节点先判断它是否为空,为空返回,再判断它是否为叶子节点(它的左右子树是否为空),是,返回1,否则返回左子树的叶子节点个数 + 右子树的叶子节点个数。
/*
获取叶子节点的个数:遍历思路
*/
public static int leafSize = 0;
void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
leafSize ++;
}
getLeafNodeCount1(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount1(root.right);
}
/*
获取叶子节点的个数:子问题
*/
int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);
}2.8 获取第K层节点的个数
(1)判断根节点是否为空或k是否合法,根节点为空或k不合法返回0
(2)再判断是否到了第k层(k == 1),是,返回1(第k层节点个数+1)
(3)否则(没到第k层)返回根节点的左右子树的叶子节点。
int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null || k <= 0){
return 0;
}
if (k == 1){
return 1;
}
return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k - 1);
}2.9 获取二叉树的高度
(1)判断根节点是否为空,根节点为空,直接返回0
(2)再判断根节点的左右子树是否为空(判断树是否只有一个节点),是,返回1
(3)返回 本层高度1 + 根节点的左右子树中高度较大的数(递归的交给getHeigth方法判断)
/*
获取二叉树的高度
时间复杂度:O(N)
*/
int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return 1;
}
return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left),getHeight(root.right));
}2.10 检测值为val的元素是否存在
前序遍历的思路
第一种:
(1)判断根节点是否为空,根节点为空,直接返回null(不存在)
(2)判断根节点的值是否等于val,是,说明找到了该元素,返回根节点
(3)判断左子树中是否存在val,存在,返回该节点;不存在,再到右子树中寻找。
第二种:
与第一种思路一致,但是返回值使用布尔值,代码更简洁了。
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在1
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val) {
if (root == null){
return null;
}
if (root.val == val){
return root;
}
TreeNode node = find(root.left,val);
if (node != null){
return node;
}
return find(root.right,val);
}
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在2
public boolean contains(TreeNode root,char val){
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val == val){
return true;
}
return contains(root.left,val) || contains(root.right,val);
}2.11 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
按照层序遍历的方式遍历完全二叉树
step1:当前完全二叉树的每个节点都是度为2的节点,碰到第一个叶子节点或者只有左子树没有右子树的节点时转入step2;碰到第一个只有右子树没有左子树的节点直接返回false。
step2:当前完全二叉树全是叶子节点
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean isStep1 = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(isStep1){
if(node.left != null && node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
} else if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
isStep1 = false;
} else if (node.right != null){
return false;
}else {
isStep1 = false;
}
}else {
if(node.left != null || node.right != null){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}3. 整体代码 + 测试代码
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.LinkedList;
public class BinaryTree {
static class TreeNode {
public char val;
public TreeNode left;//左孩子的引用
public TreeNode right;//右孩子的引用
public TreeNode(char val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
/**
* 创建一棵二叉树 返回这棵树的根节点
*
* @return
*/
public TreeNode createTree() {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode('A');
TreeNode node1 = new TreeNode('B');
TreeNode node2 = new TreeNode('C');
TreeNode node3 = new TreeNode('D');
TreeNode node4 = new TreeNode('E');
TreeNode node5 = new TreeNode('F');
TreeNode node6 = new TreeNode('G');
TreeNode node7 = new TreeNode('H');
TreeNode node8 = new TreeNode('I');
root.left = node1;
root.right = node2;
node1.left = node3;
node1.right = node5;
node2.right = node6;
node3.left = node4;
node5.left = node7;
node5.right = node8;
return root;
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
// 中序遍历
void inOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
inOrder(root.right);
}
// 后序遍历
void postOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
public static int nodeSize;
/**
* 获取树中节点的个数:遍历思路
*/
void size(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return;
}
nodeSize ++;
size(root.left);
size(root.right);
}
/**
* 获取节点的个数:子问题的思路
*
* @param root
* @return
*/
int size2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return size2(root.left) + size2(root.right) + 1;
}
/*
获取叶子节点的个数:遍历思路
*/
public static int leafSize = 0;
void getLeafNodeCount1(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null){
return;
}
if (root.left == null && root.right == null){
leafSize ++;
}
getLeafNodeCount1(root.left);
getLeafNodeCount1(root.right);
}
/*
获取叶子节点的个数:子问题
*/
int getLeafNodeCount2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) {
return 1;
}
return getLeafNodeCount2(root.left) + getLeafNodeCount2(root.right);
}
/*
获取第K层节点的个数
*/
int getKLevelNodeCount(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null || k <= 0){
return 0;
}
if (k == 1){
return 1;
}
return getKLevelNodeCount(root.left,k - 1) + getKLevelNodeCount(root.right,k - 1);
}
/*
获取二叉树的高度
时间复杂度:O(N)
*/
int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
return 0;
}
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
return 1;
}
return 1 + Math.max(getHeight(root.left),getHeight(root.right));
}
// 检测值为value的元素是否存在1
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, char val) {
if (root == null){
return null;
}
if (root.val == val){
return root;
}
TreeNode node = find(root.left,val);
if (node != null){
return node;
}
return find(root.right,val);
}
// 检测树中值为val的元素是否存在2
public boolean contains(TreeNode root,char val){
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
if (root.val == val){
return true;
}
return contains(root.left,val) || contains(root.right,val);
}
//层序遍历
void levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null){
System.out.println("这是颗空树!!!");
return;
}
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = queue.pop();
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
if (cur.left != null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null){
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
// 判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树
boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
boolean isStep1 = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if(isStep1){
if(node.left != null && node.right != null){
queue.offer(node.left);
queue.offer(node.right);
} else if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
isStep1 = false;
} else if (node.right != null){
return false;
}else {
isStep1 = false;
}
}else {
if(node.left != null || node.right != null){
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree tree = new BinaryTree();
TreeNode root = tree.createTree();
System.out.println("前序遍历");
tree.preOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("中序遍历");
tree.inOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("后序遍历");
tree.postOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("层序遍历");
tree.levelOrder(root);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("统计树的节点个数");
tree.size(root);
System.out.println(nodeSize);
System.out.println("统计叶子节点个数");
tree.getLeafNodeCount1(root);
System.out.println(leafSize);
System.out.println("树的高度");
System.out.println(tree.getHeight(root));
System.out.println("检测树中值为val的元素是否存在");
// System.out.println(tree.find(root,'x').val);
if (tree.find(root,'Q') == null){
System.out.println("没有找到该元素");
}else {
System.out.println(tree.find(root,'x').val);
}
if (tree.find(root,'B') == null){
System.out.println("没有找到该元素");
}else {
System.out.println(tree.find(root,'B').val);
}
System.out.println("获取第K层节点的个数");
System.out.println(tree.getKLevelNodeCount(root,3));
System.out.println("判断一棵树是不是完全二叉树");
System.out.println(tree.isCompleteTree(root));
}
}
测试结果: