spring学习(四)
声明:该内容来源于动力节点,本人在学习spring过程中参考该内容,并自己做了部分笔记,但个人觉得本人做的笔记不如动力节点做的好,故使用动力节点的笔记作为后续spring的复习。
十二、Spring IoC注解式开发
12.1 回顾注解
注解的存在主要是为了简化XML的配置。Spring6倡导全注解开发。
我们来回顾一下:
- 第一:注解怎么定义,注解中的属性怎么定义?
- 第二:注解怎么使用?
- 第三:通过反射机制怎么读取注解?
注解怎么定义,注解中的属性怎么定义?
package com.powernode.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
String value();
}
以上是自定义了一个注解:Component
该注解上面修饰的注解包括:Target注解和Retention注解,这两个注解被称为元注解。
Target注解用来设置Component注解可以出现的位置,以上代表表示Component注解只能用在类和接口上。
Retention注解用来设置Component注解的保持性策略,以上代表Component注解可以被反射机制读取。
String value(); 是Component注解中的一个属性。该属性类型String,属性名是value。
注解怎么使用?
package com.powernode.bean;
import com.powernode.annotation.Component;
@Component(value = "userBean")
public class User {
}
用法简单,语法格式:@注解类型名(属性名=属性值, 属性名=属性值, 属性名=属性值…)
userBean为什么使用双引号括起来,因为value属性是String类型,字符串。
另外如果属性名是value,则在使用的时候可以省略属性名,例如:
package com.powernode.bean;
import com.powernode.annotation.Component;
//@Component(value = "userBean")
@Component("userBean")
public class User {
}
通过反射机制怎么读取注解?
接下来,我们来写一段程序,当Bean类上有Component注解时,则实例化Bean对象,如果没有,则不实例化对象。
我们准备两个Bean,一个上面有注解,一个上面没有注解。
package com.powernode.bean;
import com.powernode.annotation.Component;
@Component("userBean")
public class User {
}
package com.powernode.bean;
public class Vip {
}
假设我们现在只知道包名:com.powernode.bean。至于这个包下有多少个Bean我们不知道。哪些Bean上有注解,哪些Bean上没有注解,这些我们都不知道,如何通过程序全自动化判断。
package com.powernode.test;
import com.powernode.annotation.Component;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Test
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 存放Bean的Map集合。key存储beanId。value存储Bean。
Map<String,Object> beanMap = new HashMap<>();
String packageName = "com.powernode.bean";
String path = packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/");
URL url = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResource(path);
File file = new File(url.getPath());
File[] files = file.listFiles();
Arrays.stream(files).forEach(f -> {
String className = packageName + "." + f.getName().split("\\.")[0];
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
if (clazz.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)) {
Component component = clazz.getAnnotation(Component.class);
String beanId = component.value();
Object bean = clazz.newInstance();
beanMap.put(beanId, bean);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
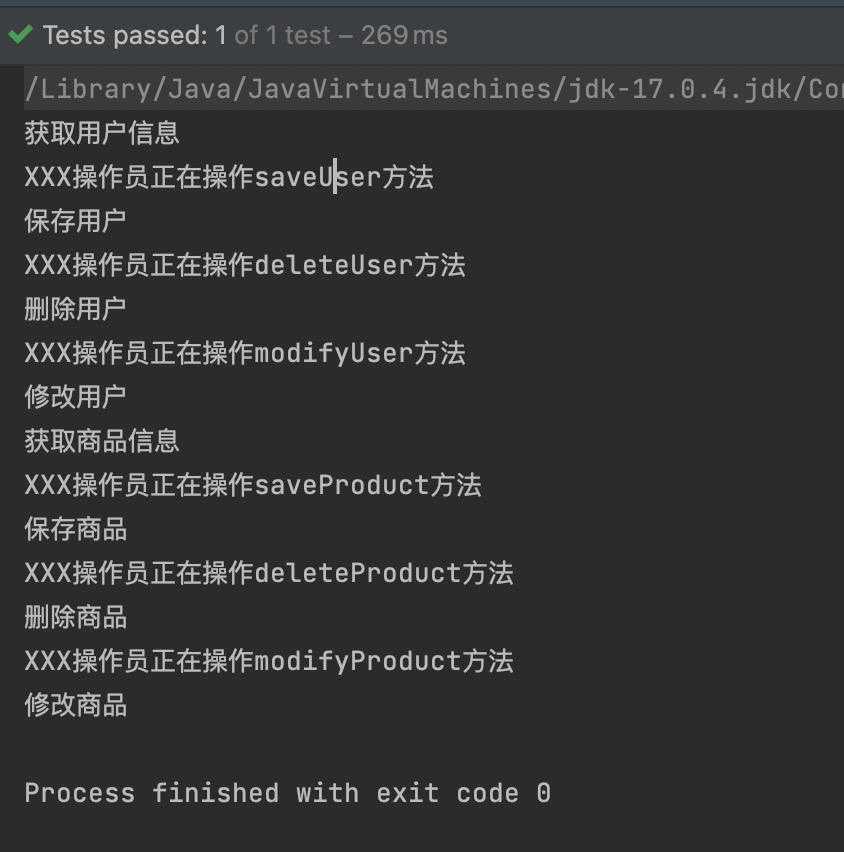
System.out.println(beanMap);
}
}
执行结果:
12.2 声明Bean的注解
负责声明Bean的注解,常见的包括四个:
- @Component
- @Controller
- @Service
- @Repository
源码如下:
package com.powernode.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Component {
String value();
}
package org.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Controller {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
package org.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Service {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
package org.springframework.stereotype;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Repository {
@AliasFor(
annotation = Component.class
)
String value() default "";
}
通过源码可以看到,@Controller、@Service、@Repository这三个注解都是@Component注解的别名。
也就是说:这四个注解的功能都一样。用哪个都可以。
只是为了增强程序的可读性,建议:
- 控制器类上使用:Controller
- service类上使用:Service
- dao类上使用:Repository
他们都是只有一个value属性。value属性用来指定bean的id,也就是bean的名字。

12.3 Spring注解的使用
如何使用以上的注解呢?
- 第一步:加入aop的依赖
- 第二步:在配置文件中添加context命名空间
- 第三步:在配置文件中指定扫描的包
- 第四步:在Bean类上使用注解
第一步:加入aop的依赖
我们可以看到当加入spring-context依赖之后,会关联加入aop的依赖。所以这一步不用做。
第二步:在配置文件中添加context命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
</beans>
第三步:在配置文件中指定要扫描的包
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.bean"/>
</beans>
第四步:在Bean类上使用注解
package com.powernode.spring6.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component(value = "userBean")
public class User {
}
编写测试程序:
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.bean.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testBean(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
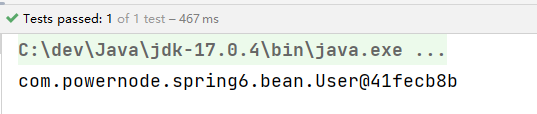
User userBean = applicationContext.getBean("userBean", User.class);
System.out.println(userBean);
}
}
执行结果:
如果注解的属性名是value,那么value是可以省略的。
package com.powernode.spring6.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("vipBean")
public class Vip {
}
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.bean.Vip;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testBean(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
Vip vipBean = applicationContext.getBean("vipBean", Vip.class);
System.out.println(vipBean);
}
}
执行结果:
如果把value属性彻底去掉,spring会被Bean自动取名吗?会的。并且默认名字的规律是:Bean类名首字母小写即可。
package com.powernode.spring6.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BankDao {
}
也就是说,这个BankDao的bean的名字为:bankDao
测试一下
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.bean.BankDao;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testBean(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
BankDao bankDao = applicationContext.getBean("bankDao", BankDao.class);
System.out.println(bankDao);
}
}
执行结果:
我们将Component注解换成其它三个注解,看看是否可以用:
package com.powernode.spring6.bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller
public class BankDao {
}
执行结果:
剩下的两个注解大家可以测试一下。
如果是多个包怎么办?有两种解决方案:
- 第一种:在配置文件中指定多个包,用逗号隔开。
- 第二种:指定多个包的共同父包。
先来测试一下逗号(英文)的方式:
创建一个新的包:bean2,定义一个Bean类。
package com.powernode.spring6.bean2;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class Order {
}
配置文件修改:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.bean,com.powernode.spring6.bean2"/>
</beans>
测试程序:
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.bean.BankDao;
import com.powernode.spring6.bean2.Order;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AnnotationTest {
@Test
public void testBean(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
BankDao bankDao = applicationContext.getBean("bankDao", BankDao.class);
System.out.println(bankDao);
Order order = applicationContext.getBean("order", Order.class);
System.out.println(order);
}
}
执行结果:
我们再来看看,指定共同的父包行不行:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6"/>
</beans>
执行测试程序:
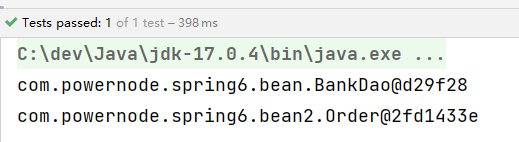
12.4 选择性实例化Bean
假设在某个包下有很多Bean,有的Bean上标注了Component,有的标注了Controller,有的标注了Service,有的标注了Repository,现在由于某种特殊业务的需要,只允许其中所有的Controller参与Bean管理,其他的都不实例化。这应该怎么办呢?
package com.powernode.spring6.bean3;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Component
public class A {
public A() {
System.out.println("A的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Controller
class B {
public B() {
System.out.println("B的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Service
class C {
public C() {
System.out.println("C的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Repository
class D {
public D() {
System.out.println("D的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Controller
class E {
public E() {
System.out.println("E的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
@Controller
class F {
public F() {
System.out.println("F的无参数构造方法执行");
}
}
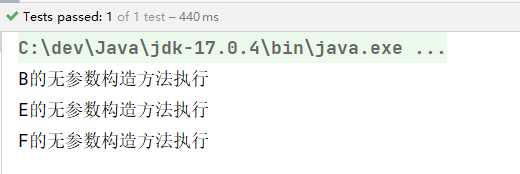
我只想实例化bean3包下的Controller。配置文件这样写:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.bean3" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
</beans>
use-default-filters=“true” 表示:使用spring默认的规则,只要有Component、Controller、Service、Repository中的任意一个注解标注,则进行实例化。
use-default-filters=“false” 表示:不再spring默认实例化规则,即使有Component、Controller、Service、Repository这些注解标注,也不再实例化。
<context:include-filter type=“annotation” expression=“org.springframework.stereotype.Controller”/> 表示只有Controller进行实例化。
@Test
public void testChoose(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-choose.xml");
}
执行结果:
也可以将use-default-filters设置为true(不写就是true),并且采用exclude-filter方式排出哪些注解标注的Bean不参与实例化:
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.bean3">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Repository"/>
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/>
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
执行测试程序:
12.5 负责注入的注解
@Component @Controller @Service @Repository 这四个注解是用来声明Bean的,声明后这些Bean将被实例化。接下来我们看一下,如何给Bean的属性赋值。给Bean属性赋值需要用到这些注解:
- @Value
- @Autowired
- @Qualifier
- @Resource
12.5.1 @Value
当属性的类型是简单类型时,可以使用@Value注解进行注入。
package com.powernode.spring6.bean4;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
@Value(value = "zhangsan")
private String name;
@Value("20")
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
开启包扫描:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.bean4"/>
</beans>
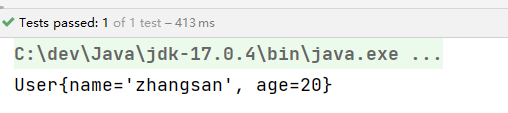
@Test
public void testValue(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-injection.xml");
Object user = applicationContext.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user);
}
执行结果:
通过以上代码可以发现,我们并没有给属性提供setter方法,但仍然可以完成属性赋值。
如果提供setter方法,并且在setter方法上添加@Value注解,可以完成注入吗?尝试一下:
package com.powernode.spring6.bean4;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
@Value("李四")
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Value("30")
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
执行结果:
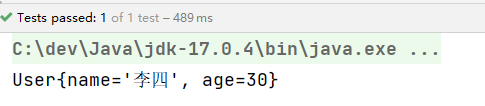
通过测试可以得知,@Value注解可以直接使用在属性上,也可以使用在setter方法上。都是可以的。都可以完成属性的赋值。
为了简化代码,以后我们一般不提供setter方法,直接在属性上使用@Value注解完成属性赋值。
出于好奇,我们再来测试一下,是否能够通过构造方法完成注入:
package com.powernode.spring6.bean4;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
public User(@Value("隔壁老王") String name, @Value("33") int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
执行结果:
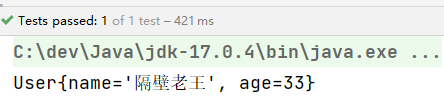
通过测试得知:@Value注解可以出现在属性上、setter方法上、以及构造方法的形参上。可见Spring给我们提供了多样化的注入。太灵活了。
12.5.2 @Autowired与@Qualifier
@Autowired注解可以用来注入非简单类型。被翻译为:自动连线的,或者自动装配。
单独使用@Autowired注解,默认根据类型装配。【默认是byType】
看一下它的源码:
package org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target({ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
boolean required() default true;
}
源码中有两处需要注意:
- 第一处:该注解可以标注在哪里?
- 构造方法上
- 方法上
- 形参上
- 属性上
- 注解上
- 第二处:该注解有一个required属性,默认值是true,表示在注入的时候要求被注入的Bean必须是存在的,如果不存在则报错。如果required属性设置为false,表示注入的Bean存在或者不存在都没关系,存在的话就注入,不存在的话,也不报错。
我们先在属性上使用@Autowired注解:
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
public interface UserDao {
void insert();
}
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository //纳入bean管理
public class UserDaoForMySQL implements UserDao{
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向mysql数据库插入User数据");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service // 纳入bean管理
public class UserService {
@Autowired // 在属性上注入
private UserDao userDao;
// 没有提供构造方法和setter方法。
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.dao,com.powernode.spring6.service"/>
</beans>
@Test
public void testAutowired(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-injection.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
执行结果:
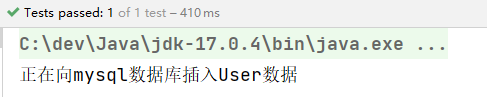
以上构造方法和setter方法都没有提供,经过测试,仍然可以注入成功。
接下来,再来测试一下@Autowired注解出现在setter方法上:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:
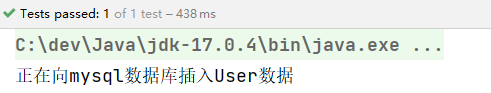
我们再来看看能不能出现在构造方法上:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:

再来看看,这个注解能不能只标注在构造方法的形参上:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(@Autowired UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:
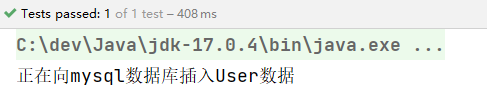
还有更劲爆的,当有参数的构造方法只有一个时,@Autowired注解可以省略。
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:
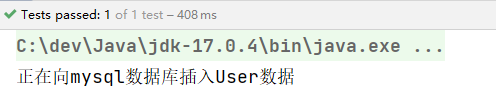
当然,如果有多个构造方法,@Autowired肯定是不能省略的。
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public UserService(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public UserService(){
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:
到此为止,我们已经清楚@Autowired注解可以出现在哪些位置了。
@Autowired注解默认是byType进行注入的,也就是说根据类型注入的,如果以上程序中,UserDao接口还有另外一个实现类,会出现问题吗?
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository //纳入bean管理
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao{
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据");
}
}
当你写完这个新的实现类之后,此时IDEA工具已经提示错误信息了:

错误信息中说:不能装配,UserDao这个Bean的数量大于1.
怎么解决这个问题呢?当然要byName,根据名称进行装配了。
@Autowired注解和@Qualifier注解联合起来才可以根据名称进行装配,在@Qualifier注解中指定Bean名称。
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository // 这里没有给bean起名,默认名字是:userDaoForOracle
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao{
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("userDaoForOracle") // 这个是bean的名字。
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:

总结:
- @Autowired注解可以出现在:属性上、构造方法上、构造方法的参数上、setter方法上。
- 当带参数的构造方法只有一个,@Autowired注解可以省略。
- @Autowired注解默认根据类型注入。如果要根据名称注入的话,需要配合@Qualifier注解一起使用。
12.5.3 @Resource
@Resource注解也可以完成非简单类型注入。那它和@Autowired注解有什么区别?
- @Resource注解是JDK扩展包中的,也就是说属于JDK的一部分。所以该注解是标准注解,更加具有通用性。(JSR-250标准中制定的注解类型。JSR是Java规范提案。)
- @Autowired注解是Spring框架自己的。
- @Resource注解默认根据名称装配byName,未指定name时,使用属性名作为name。通过name找不到的话会自动启动通过类型byType装配。
- @Autowired注解默认根据类型装配byType,如果想根据名称装配,需要配合@Qualifier注解一起用。
- @Resource注解用在属性上、setter方法上。
- @Autowired注解用在属性上、setter方法上、构造方法上、构造方法参数上。
@Resource注解属于JDK扩展包,所以不在JDK当中,需要额外引入以下依赖:【如果是JDK8的话不需要额外引入依赖。高于JDK11或低于JDK8需要引入以下依赖。】
<dependency>
<groupId>jakarta.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>jakarta.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1</version>
</dependency>
一定要注意:如果你用Spring6,要知道Spring6不再支持JavaEE,它支持的是JakartaEE9。(Oracle把JavaEE贡献给Apache了,Apache把JavaEE的名字改成JakartaEE了,大家之前所接触的所有的 javax. 包名统一修改为 jakarta.包名了。)
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.annotation</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.annotation-api</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
@Resource注解的源码如下:
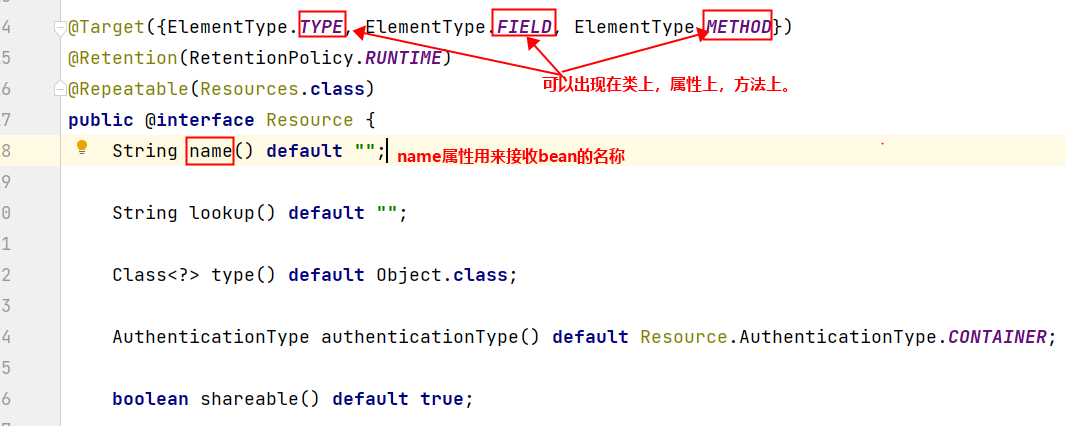
测试一下:
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("xyz")
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao{
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource(name = "xyz")
private UserDao userDao;
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行测试程序:
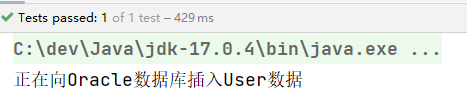
我们把UserDaoForOracle的名字xyz修改为userDao,让这个Bean的名字和UserService类中的UserDao属性名一致:
package com.powernode.spring6.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository("userDao")
public class UserDaoForOracle implements UserDao{
@Override
public void insert() {
System.out.println("正在向Oracle数据库插入User数据");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao;
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行测试程序:
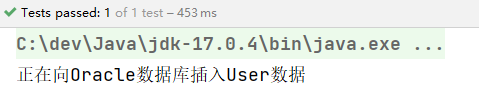
通过测试得知,当@Resource注解使用时没有指定name的时候,还是根据name进行查找,这个name是属性名。
接下来把UserService类中的属性名修改一下:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Resource
private UserDao userDao2;
public void save(){
userDao2.insert();
}
}
执行结果:
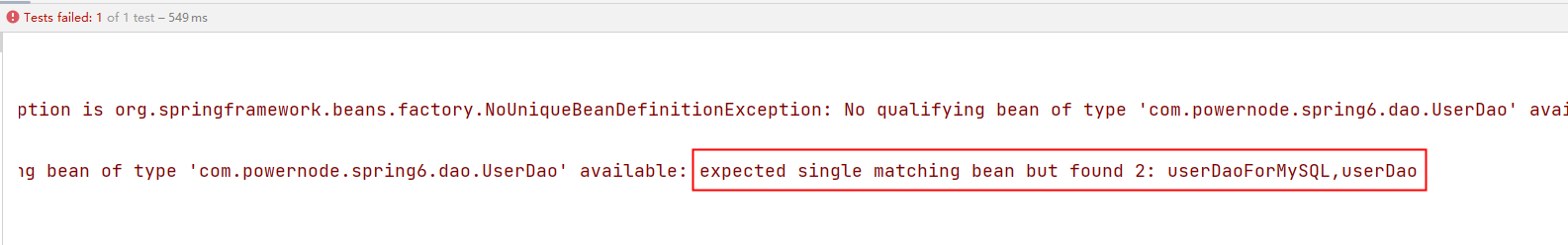
根据异常信息得知:显然当通过name找不到的时候,自然会启动byType进行注入。以上的错误是因为UserDao接口下有两个实现类导致的。所以根据类型注入就会报错。
我们再来看@Resource注解使用在setter方法上可以吗?
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Resource
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
注意这个setter方法的方法名,setUserDao去掉set之后,将首字母变小写userDao,userDao就是name
执行结果:
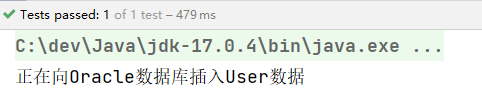
当然,也可以指定name:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import com.powernode.spring6.dao.UserDao;
import jakarta.annotation.Resource;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
@Resource(name = "userDaoForMySQL")
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void save(){
userDao.insert();
}
}
执行结果:
一句话总结@Resource注解:默认byName注入,没有指定name时把属性名当做name,根据name找不到时,才会byType注入。byType注入时,某种类型的Bean只能有一个。
12.6 全注解式开发
所谓的全注解开发就是不再使用spring配置文件了。写一个配置类来代替配置文件。
package com.powernode.spring6.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScans;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.powernode.spring6.dao", "com.powernode.spring6.service"})
public class Spring6Configuration {
}
编写测试程序:不再new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext()对象了。
@Test
public void testNoXml(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Configuration.class);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.save();
}
执行结果:
十三、JdbcTemplate
JdbcTemplate是Spring提供的一个JDBC模板类,是对JDBC的封装,简化JDBC代码。
当然,你也可以不用,可以让Spring集成其它的ORM框架,例如:MyBatis、Hibernate等。
接下来我们简单来学习一下,使用JdbcTemplate完成增删改查。
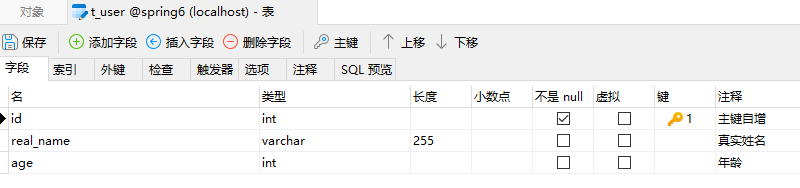
13.1 环境准备
数据库表:t_user
IDEA中新建模块:spring6-007-jdbc
引入相关依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.powernode</groupId>
<artifactId>spring6-007-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>repository.spring.milestone</id>
<name>Spring Milestone Repository</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
</repository>
</repositories>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13.2</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--新增的依赖:mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.30</version>
</dependency>
<!--新增的依赖:spring jdbc,这个依赖中有JdbcTemplate-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>17</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>17</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
</project>
准备实体类:表t_user对应的实体类User。
package com.powernode.spring6.bean;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className User
* @since 1.0
**/
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String realName;
private Integer age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", realName='" + realName + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public User() {
}
public User(Integer id, String realName, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.realName = realName;
this.age = age;
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getRealName() {
return realName;
}
public void setRealName(String realName) {
this.realName = realName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
编写Spring配置文件:
JdbcTemplate是Spring提供好的类,这类的完整类名是:org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate
我们怎么使用这个类呢?new对象就可以了。怎么new对象,Spring最在行了。直接将这个类配置到Spring配置文件中,纳入Bean管理即可。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"></bean>
</beans>
我们来看一下这个JdbcTemplate源码:
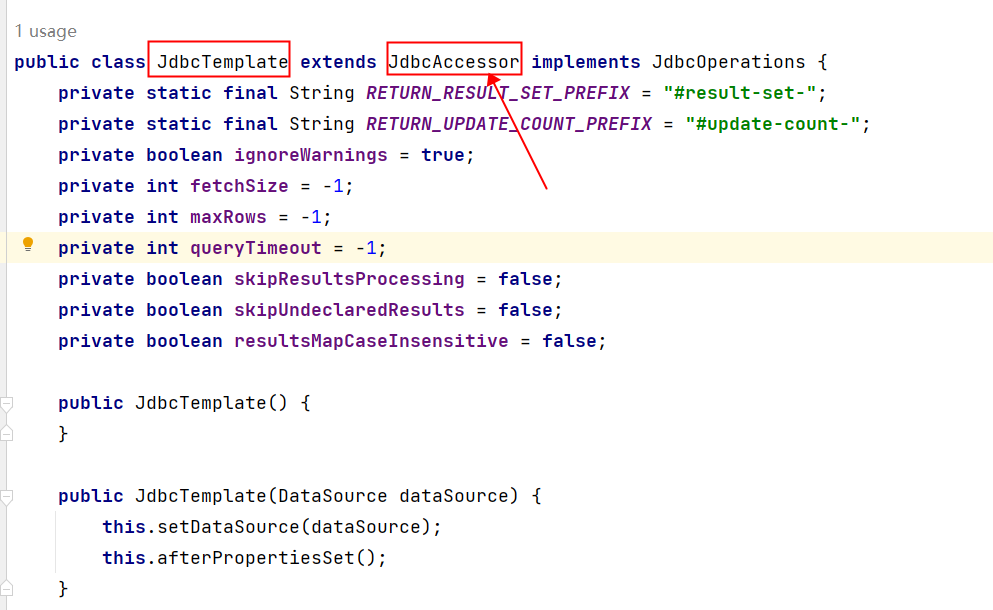
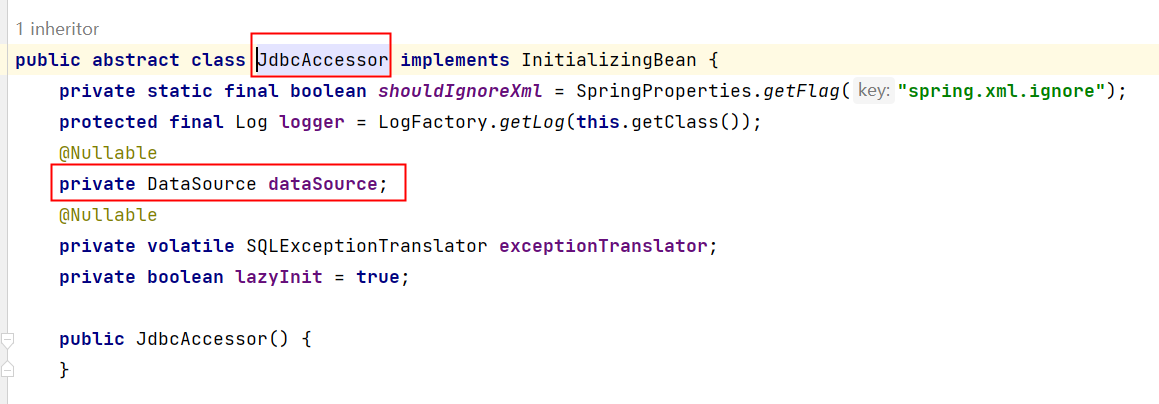
可以看到JdbcTemplate中有一个DataSource属性,这个属性是数据源,我们都知道连接数据库需要Connection对象,而生成Connection对象是数据源负责的。所以我们需要给JdbcTemplate设置数据源属性。
所有的数据源都是要实现javax.sql.DataSource接口的。这个数据源可以自己写一个,也可以用写好的,比如:阿里巴巴的德鲁伊连接池,c3p0,dbcp等。我们这里自己先手写一个数据源。
package com.powernode.spring6.jdbc;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.SQLFeatureNotSupportedException;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className MyDataSource
* @since 1.0
**/
public class MyDataSource implements DataSource {
// 添加4个属性
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
// 提供4个setter方法
public void setDriver(String driver) {
this.driver = driver;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
// 重点写怎么获取Connection对象就行。其他方法不用管。
@Override
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
try {
Class.forName(driver);
Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
return conn;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public PrintWriter getLogWriter() throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public void setLogWriter(PrintWriter out) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public void setLoginTimeout(int seconds) throws SQLException {
}
@Override
public int getLoginTimeout() throws SQLException {
return 0;
}
@Override
public Logger getParentLogger() throws SQLFeatureNotSupportedException {
return null;
}
@Override
public <T> T unwrap(Class<T> iface) throws SQLException {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isWrapperFor(Class<?> iface) throws SQLException {
return false;
}
}
写完数据源,我们需要把这个数据源传递给JdbcTemplate。因为JdbcTemplate中有一个DataSource属性:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="myDataSource" class="com.powernode.spring6.jdbc.MyDataSource">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="myDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
到这里环境就准备好了。
13.2 新增
编写测试程序:
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className JdbcTest
* @since 1.0
**/
public class JdbcTest {
@Test
public void testInsert(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执行插入操作
// 注意:insert delete update的sql语句,都是执行update方法。
String sql = "insert into t_user(id,real_name,age) values(?,?,?)";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, null, "张三", 30);
System.out.println("插入的记录条数:" + count);
}
}
update方法有两个参数:
- 第一个参数:要执行的SQL语句。(SQL语句中可能会有占位符 ? )
- 第二个参数:可变长参数,参数的个数可以是0个,也可以是多个。一般是SQL语句中有几个问号,则对应几个参数。
13.3 修改
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执行更新操作
String sql = "update t_user set real_name = ?, age = ? where id = ?";
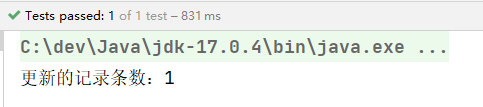
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "张三丰", 55, 1);
System.out.println("更新的记录条数:" + count);
}
执行结果:
13.4 删除
@Test
public void testDelete(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执行delete
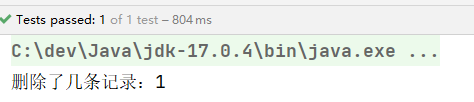
String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ?";
int count = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, 1);
System.out.println("删除了几条记录:" + count);
}
执行结果:
13.5 查询一个对象
@Test
public void testSelectOne(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执行select
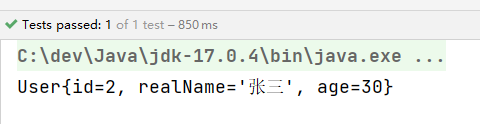
String sql = "select id, real_name, age from t_user where id = ?";
User user = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class), 2);
System.out.println(user);
}
执行结果:
queryForObject方法三个参数:
- 第一个参数:sql语句
- 第二个参数:Bean属性值和数据库记录行的映射对象。在构造方法中指定映射的对象类型。
- 第三个参数:可变长参数,给sql语句的占位符问号传值。
13.6 查询多个对象
@Test
public void testSelectAll(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 执行select
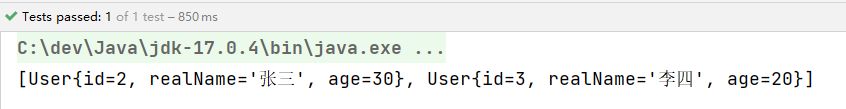
String sql = "select id, real_name, age from t_user";
List<User> users = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(User.class));
System.out.println(users);
}
执行结果:
13.7 查询一个值
@Test
public void testSelectOneValue(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
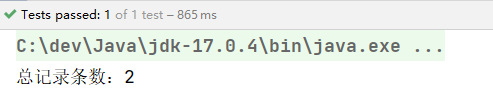
// 执行select
String sql = "select count(1) from t_user";
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, int.class); // 这里用Integer.class也可以
System.out.println("总记录条数:" + count);
}
执行结果:
13.8 批量添加
@Test
public void testAddBatch(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
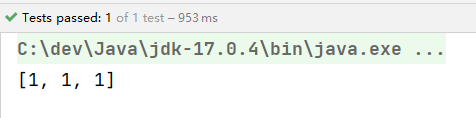
// 批量添加
String sql = "insert into t_user(id,real_name,age) values(?,?,?)";
Object[] objs1 = {null, "小花", 20};
Object[] objs2 = {null, "小明", 21};
Object[] objs3 = {null, "小刚", 22};
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(objs1);
list.add(objs2);
list.add(objs3);
int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
}
执行结果:
13.9 批量修改
@Test
public void testUpdateBatch(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 批量修改
String sql = "update t_user set real_name = ?, age = ? where id = ?";
Object[] objs1 = {"小花11", 10, 2};
Object[] objs2 = {"小明22", 12, 3};
Object[] objs3 = {"小刚33", 9, 4};
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(objs1);
list.add(objs2);
list.add(objs3);
int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
}
执行结果:
13.10 批量删除
@Test
public void testDeleteBatch(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
// 批量删除
String sql = "delete from t_user where id = ?";
Object[] objs1 = {2};
Object[] objs2 = {3};
Object[] objs3 = {4};
List<Object[]> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(objs1);
list.add(objs2);
list.add(objs3);
int[] count = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(count));
}
执行结果:
13.11 使用回调函数
使用回调函数,可以参与的更加细节:
@Test
public void testCallback(){
// 获取JdbcTemplate对象
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = applicationContext.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
String sql = "select id, real_name, age from t_user where id = ?";
User user = jdbcTemplate.execute(sql, new PreparedStatementCallback<User>() {
@Override
public User doInPreparedStatement(PreparedStatement ps) throws SQLException, DataAccessException {
User user = null;
ps.setInt(1, 5);
ResultSet rs = ps.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
user = new User();
user.setId(rs.getInt("id"));
user.setRealName(rs.getString("real_name"));
user.setAge(rs.getInt("age"));
}
return user;
}
});
System.out.println(user);
}
执行结果:
13.12 使用德鲁伊连接池
之前数据源是用我们自己写的。也可以使用别人写好的。例如比较牛的德鲁伊连接池。
第一步:引入德鲁伊连接池的依赖。(毕竟是别人写的)
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.8</version>
</dependency>
第二步:将德鲁伊中的数据源配置到spring配置文件中。和配置我们自己写的一样。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring6"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
</beans>
测试结果:
十四、GoF之代理模式
14.1 对代理模式的理解
生活场景1:牛村的牛二看上了隔壁村小花,牛二不好意思直接找小花,于是牛二找来了媒婆王妈妈。这里面就有一个非常典型的代理模式。牛二不能和小花直接对接,只能找一个中间人。其中王妈妈是代理类,牛二是目标类。王妈妈代替牛二和小花先见个面。(现实生活中的婚介所)【在程序中,对象A和对象B无法直接交互时。】
生活场景2:你刚到北京,要租房子,可以自己找,也可以找链家帮你找。其中链家是代理类,你是目标类。你们两个都有共同的行为:找房子。不过链家除了满足你找房子,另外会收取一些费用的。(现实生活中的房产中介)【在程序中,功能需要增强时。】
西游记场景:八戒和高小姐的故事。八戒要强抢民女高翠兰。悟空得知此事之后怎么做的?悟空幻化成高小姐的模样。代替高小姐与八戒会面。其中八戒是客户端程序。悟空是代理类。高小姐是目标类。那天夜里,在八戒眼里,眼前的就是高小姐,对于八戒来说,他是不知道眼前的高小姐是悟空幻化的,在他内心里这就是高小姐。所以悟空代替高小姐和八戒亲了嘴儿。这是非常典型的代理模式实现的保护机制。代理模式中有一个非常重要的特点:对于客户端程序来说,使用代理对象时就像在使用目标对象一样。【在程序中,目标需要被保护时】
业务场景:系统中有A、B、C三个模块,使用这些模块的前提是需要用户登录,也就是说在A模块中要编写判断登录的代码,B模块中也要编写,C模块中还要编写,这些判断登录的代码反复出现,显然代码没有得到复用,可以为A、B、C三个模块提供一个代理,在代理当中写一次登录判断即可。代理的逻辑是:请求来了之后,判断用户是否登录了,如果已经登录了,则执行对应的目标,如果没有登录则跳转到登录页面。【在程序中,目标不但受到保护,并且代码也得到了复用。】
代理模式是GoF23种设计模式之一。属于结构型设计模式。
代理模式的作用是:为其他对象提供一种代理以控制对这个对象的访问。在某些情况下,一个客户不想或者不能直接引用一个对象,此时可以通过一个称之为“代理”的第三者来实现间接引用。代理对象可以在客户端和目标对象之间起到中介的作用,并且可以通过代理对象去掉客户不应该看到的内容和服务或者添加客户需要的额外服务。 通过引入一个新的对象来实现对真实对象的操作或者将新的对象作为真实对象的一个替身,这种实现机制即为代理模式,通过引入代理对象来间接访问一个对象,这就是代理模式的模式动机。
代理模式中的角色:
- 代理类(代理主题)
- 目标类(真实主题)
- 代理类和目标类的公共接口(抽象主题):客户端在使用代理类时就像在使用目标类,不被客户端所察觉,所以代理类和目标类要有共同的行为,也就是实现共同的接口。
代理模式的类图:
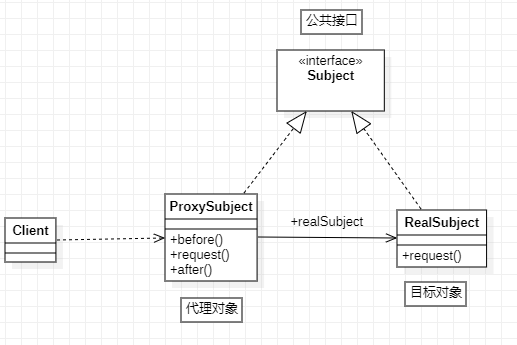
代理模式在代码实现上,包括两种形式:
- 静态代理
- 动态代理
14.2 静态代理
现在有这样一个接口和实现类:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
/**
* 订单接口
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderService
* @since 1.0
**/
public interface OrderService {
/**
* 生成订单
*/
void generate();
/**
* 查看订单详情
*/
void detail();
/**
* 修改订单
*/
void modify();
}
package com.powernode.mall.service.impl;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderServiceImpl
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
public void generate() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1234);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单已生成");
}
@Override
public void detail() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2541);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单信息如下:******");
}
@Override
public void modify() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1010);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单已修改");
}
}
其中Thread.sleep()方法的调用是为了模拟操作耗时。
项目已上线,并且运行正常,只是客户反馈系统有一些地方运行较慢,要求项目组对系统进行优化。于是项目负责人就下达了这个需求。首先需要搞清楚是哪些业务方法耗时较长,于是让我们统计每个业务方法所耗费的时长。如果是你,你该怎么做呢?
第一种方案:直接修改Java源代码,在每个业务方法中添加统计逻辑,如下:
package com.powernode.mall.service.impl;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderServiceImpl
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
public void generate() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1234);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单已生成");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时长"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
@Override
public void detail() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(2541);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单信息如下:******");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时长"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
@Override
public void modify() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
Thread.sleep(1010);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单已修改");
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时长"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
}
需求可以满足,但显然是违背了OCP开闭原则。这种方案不可取。
第二种方案:编写一个子类继承OrderServiceImpl,在子类中重写每个方法,代码如下:
package com.powernode.mall.service.impl;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderServiceImplSub
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderServiceImplSub extends OrderServiceImpl{
@Override
public void generate() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
super.generate();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
@Override
public void detail() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
super.detail();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
@Override
public void modify() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
super.modify();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
}
这种方式可以解决,但是存在两个问题:
- 第一个问题:假设系统中有100个这样的业务类,需要提供100个子类,并且之前写好的创建Service对象的代码,都要修改为创建子类对象。
- 第二个问题:由于采用了继承的方式,导致代码之间的耦合度较高。
这种方案也不可取。
第三种方案:使用代理模式(这里采用静态代理)
可以为OrderService接口提供一个代理类。
package com.powernode.mall.service;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderServiceProxy
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderServiceProxy implements OrderService{ // 代理对象
// 目标对象
private OrderService orderService;
// 通过构造方法将目标对象传递给代理对象
public OrderServiceProxy(OrderService orderService) {
this.orderService = orderService;
}
@Override
public void generate() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行目标对象的目标方法
orderService.generate();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
@Override
public void detail() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行目标对象的目标方法
orderService.detail();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
@Override
public void modify() {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 执行目标对象的目标方法
orderService.modify();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
}
这种方式的优点:符合OCP开闭原则,同时采用的是关联关系,所以程序的耦合度较低。所以这种方案是被推荐的。
编写客户端程序:
package com.powernode.mall;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderServiceProxy;
import com.powernode.mall.service.impl.OrderServiceImpl;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Client
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建目标对象
OrderService target = new OrderServiceImpl();
// 创建代理对象
OrderService proxy = new OrderServiceProxy(target);
// 调用代理对象的代理方法
proxy.generate();
proxy.modify();
proxy.detail();
}
}
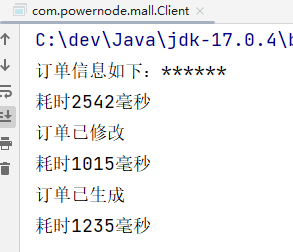
运行结果:
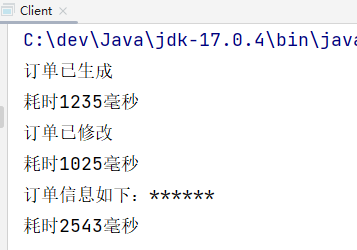
以上就是代理模式中的静态代理,其中OrderService接口是代理类和目标类的共同接口。OrderServiceImpl是目标类。OrderServiceProxy是代理类。
大家思考一下:如果系统中业务接口很多,一个接口对应一个代理类,显然也是不合理的,会导致类爆炸。怎么解决这个问题?动态代理可以解决。因为在动态代理中可以在内存中动态的为我们生成代理类的字节码。代理类不需要我们写了。类爆炸解决了,而且代码只需要写一次,代码也会得到复用。
14.3 动态代理
在程序运行阶段,在内存中动态生成代理类,被称为动态代理,目的是为了减少代理类的数量。解决代码复用的问题。
在内存当中动态生成类的技术常见的包括:
-
JDK动态代理技术:只能代理接口。
-
CGLIB动态代理技术:CGLIB(Code Generation Library)是一个开源项目。是一个强大的,高性能,高质量的Code生成类库,它可以在运行期扩展Java类与实现Java接口。它既可以代理接口,又可以代理类,底层是通过继承的方式实现的。性能比JDK动态代理要好。(底层有一个小而快的字节码处理框架ASM。)
-
Javassist动态代理技术:Javassist是一个开源的分析、编辑和创建Java字节码的类库。是由东京工业大学的数学和计算机科学系的 Shigeru Chiba (千叶 滋)所创建的。它已加入了开放源代码JBoss 应用服务器项目,通过使用Javassist对字节码操作为JBoss实现动态"AOP"框架。
( )
14.3.1 JDK动态代理
我们还是使用静态代理中的例子:一个接口和一个实现类。
package com.powernode.mall.service;
/**
* 订单接口
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderService
* @since 1.0
**/
public interface OrderService {
/**
* 生成订单
*/
void generate();
/**
* 查看订单详情
*/
void detail();
/**
* 修改订单
*/
void modify();
}
package com.powernode.mall.service.impl;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className OrderServiceImpl
* @since 1.0
**/
public class OrderServiceImpl implements OrderService {
@Override
public void generate() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1234);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单已生成");
}
@Override
public void detail() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2541);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单信息如下:******");
}
@Override
public void modify() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1010);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("订单已修改");
}
}
我们在静态代理的时候,除了以上一个接口和一个实现类之外,是不是要写一个代理类UserServiceProxy呀!在动态代理中UserServiceProxy代理类是可以动态生成的。这个类不需要写。我们直接写客户端程序即可:
package com.powernode.mall;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
import com.powernode.mall.service.impl.OrderServiceImpl;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Client
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 第一步:创建目标对象
OrderService target = new OrderServiceImpl();
// 第二步:创建代理对象
OrderService orderServiceProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), 调用处理器对象);
// 第三步:调用代理对象的代理方法
orderServiceProxy.detail();
orderServiceProxy.modify();
orderServiceProxy.generate();
}
}
以上第二步创建代理对象是需要大家理解的:
OrderService orderServiceProxy = Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), 调用处理器对象);
这行代码做了两件事:
- 第一件事:在内存中生成了代理类的字节码
- 第二件事:创建代理对象
Proxy类全名:java.lang.reflect.Proxy。这是JDK提供的一个类(所以称为JDK动态代理)。主要是通过这个类在内存中生成代理类的字节码。
其中newProxyInstance()方法有三个参数:
- 第一个参数:类加载器。在内存中生成了字节码,要想执行这个字节码,也是需要先把这个字节码加载到内存当中的。所以要指定使用哪个类加载器加载。
- 第二个参数:接口类型。代理类和目标类实现相同的接口,所以要通过这个参数告诉JDK动态代理生成的类要实现哪些接口。
- 第三个参数:调用处理器。这是一个JDK动态代理规定的接口,接口全名:java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler。显然这是一个回调接口,也就是说调用这个接口中方法的程序已经写好了,就差这个接口的实现类了。
所以接下来我们要写一下java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler接口的实现类,并且实现接口中的方法,代码如下:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className TimerInvocationHandler
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TimerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return null;
}
}
InvocationHandler接口中有一个方法invoke,这个invoke方法上有三个参数:
- 第一个参数:Object proxy。代理对象。设计这个参数只是为了后期的方便,如果想在invoke方法中使用代理对象的话,尽管通过这个参数来使用。
- 第二个参数:Method method。目标方法。
- 第三个参数:Object[] args。目标方法调用时要传的参数。
我们将来肯定是要调用“目标方法”的,但要调用目标方法的话,需要“目标对象”的存在,“目标对象”从哪儿来呢?我们可以给TimerInvocationHandler提供一个构造方法,可以通过这个构造方法传过来“目标对象”,代码如下:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className TimerInvocationHandler
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TimerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
// 目标对象
private Object target;
// 通过构造方法来传目标对象
public TimerInvocationHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
return null;
}
}
有了目标对象我们就可以在invoke()方法中调用目标方法了。代码如下:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className TimerInvocationHandler
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TimerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
// 目标对象
private Object target;
// 通过构造方法来传目标对象
public TimerInvocationHandler(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 目标执行之前增强。
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用目标对象的目标方法
Object retValue = method.invoke(target, args);
// 目标执行之后增强。
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
// 一定要记得返回哦。
return retValue;
}
}
到此为止,调用处理器就完成了。接下来,应该继续完善Client程序:
package com.powernode.mall;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
import com.powernode.mall.service.TimerInvocationHandler;
import com.powernode.mall.service.impl.OrderServiceImpl;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Client
* @since 1.0
**/
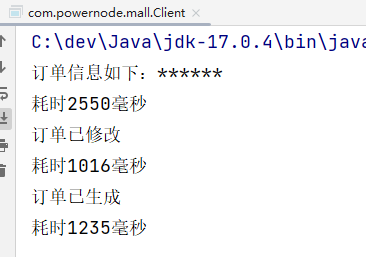
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建目标对象
OrderService target = new OrderServiceImpl();
// 创建代理对象
OrderService orderServiceProxy = (OrderService) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new TimerInvocationHandler(target));
// 调用代理对象的代理方法
orderServiceProxy.detail();
orderServiceProxy.modify();
orderServiceProxy.generate();
}
}
大家可能会比较好奇:那个InvocationHandler接口中的invoke()方法没看见在哪里调用呀?
注意:当你调用代理对象的代理方法的时候,注册在InvocationHandler接口中的invoke()方法会被调用。也就是上面代码第24 25 26行,这三行代码中任意一行代码执行,注册在InvocationHandler接口中的invoke()方法都会被调用。
执行结果:
学到这里可能会感觉有点懵,折腾半天,到最后这不是还得写一个接口的实现类吗?没省劲儿呀?
你要这样想就错了!!!
我们可以看到,不管你有多少个Service接口,多少个业务类,这个TimerInvocationHandler接口是不是只需要写一次就行了,代码是不是得到复用了!!!!
而且最重要的是,以后程序员只需要关注核心业务的编写了,像这种统计时间的代码根本不需要关注。因为这种统计时间的代码只需要在调用处理器中编写一次即可。
到这里,JDK动态代理的原理就结束了。
不过我们看以下这个代码确实有点繁琐,对于客户端来说,用起来不方便:
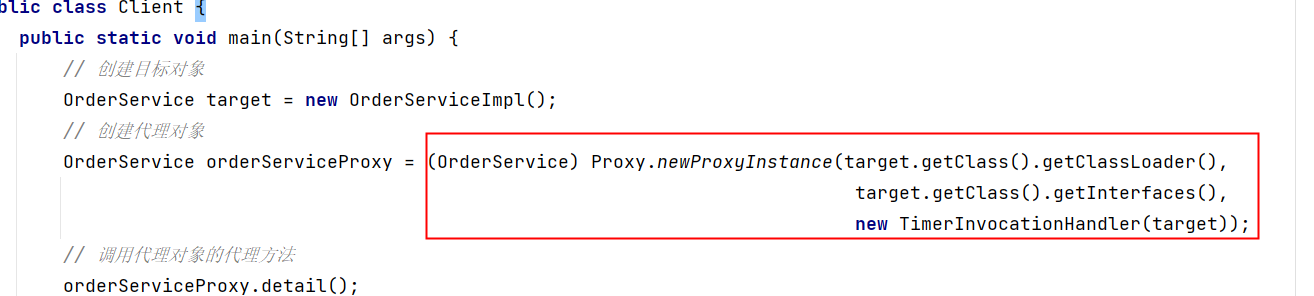
我们可以提供一个工具类:ProxyUtil,封装一个方法:
package com.powernode.mall.util;
import com.powernode.mall.service.TimerInvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className ProxyUtil
* @since 1.0
**/
public class ProxyUtil {
public static Object newProxyInstance(Object target) {
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.getClass().getClassLoader(),
target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new TimerInvocationHandler(target));
}
}
这样客户端代码就不需要写那么繁琐了:
package com.powernode.mall;
import com.powernode.mall.service.OrderService;
import com.powernode.mall.service.TimerInvocationHandler;
import com.powernode.mall.service.impl.OrderServiceImpl;
import com.powernode.mall.util.ProxyUtil;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Client
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建目标对象
OrderService target = new OrderServiceImpl();
// 创建代理对象
OrderService orderServiceProxy = (OrderService) ProxyUtil.newProxyInstance(target);
// 调用代理对象的代理方法
orderServiceProxy.detail();
orderServiceProxy.modify();
orderServiceProxy.generate();
}
}
执行结果:
14.3.2 CGLIB动态代理
CGLIB既可以代理接口,又可以代理类。底层采用继承的方式实现。所以被代理的目标类不能使用final修饰。
使用CGLIB,需要引入它的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>3.3.0</version>
</dependency>
我们准备一个没有实现接口的类,如下:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className UserService
* @since 1.0
**/
public class UserService {
public void login(){
System.out.println("用户正在登录系统....");
}
public void logout(){
System.out.println("用户正在退出系统....");
}
}
使用CGLIB在内存中为UserService类生成代理类,并创建对象:
package com.powernode.mall;
import com.powernode.mall.service.UserService;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Client
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建字节码增强器
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 告诉cglib要继承哪个类
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserService.class);
// 设置回调接口
enhancer.setCallback(方法拦截器对象);
// 生成源码,编译class,加载到JVM,并创建代理对象
UserService userServiceProxy = (UserService)enhancer.create();
userServiceProxy.login();
userServiceProxy.logout();
}
}
和JDK动态代理原理差不多,在CGLIB中需要提供的不是InvocationHandler,而是:net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor
编写MethodInterceptor接口实现类:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className TimerMethodInterceptor
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TimerMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object target, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
return null;
}
}
MethodInterceptor接口中有一个方法intercept(),该方法有4个参数:
第一个参数:目标对象
第二个参数:目标方法
第三个参数:目标方法调用时的实参
第四个参数:代理方法
在MethodInterceptor的intercept()方法中调用目标以及添加增强:
package com.powernode.mall.service;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className TimerMethodInterceptor
* @since 1.0
**/
public class TimerMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object target, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
// 前增强
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
// 调用目标
Object retValue = methodProxy.invokeSuper(target, objects);
// 后增强
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时" + (end - begin) + "毫秒");
// 一定要返回
return retValue;
}
}
回调已经写完了,可以修改客户端程序了:
package com.powernode.mall;
import com.powernode.mall.service.TimerMethodInterceptor;
import com.powernode.mall.service.UserService;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
/**
* @author 动力节点
* @version 1.0
* @className Client
* @since 1.0
**/
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建字节码增强器
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 告诉cglib要继承哪个类
enhancer.setSuperclass(UserService.class);
// 设置回调接口
enhancer.setCallback(new TimerMethodInterceptor());
// 生成源码,编译class,加载到JVM,并创建代理对象
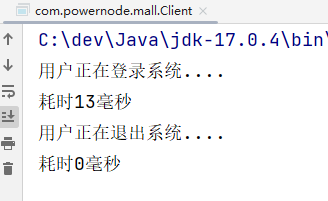
UserService userServiceProxy = (UserService)enhancer.create();
userServiceProxy.login();
userServiceProxy.logout();
}
}
对于高版本的JDK,如果使用CGLIB,需要在启动项中添加两个启动参数:
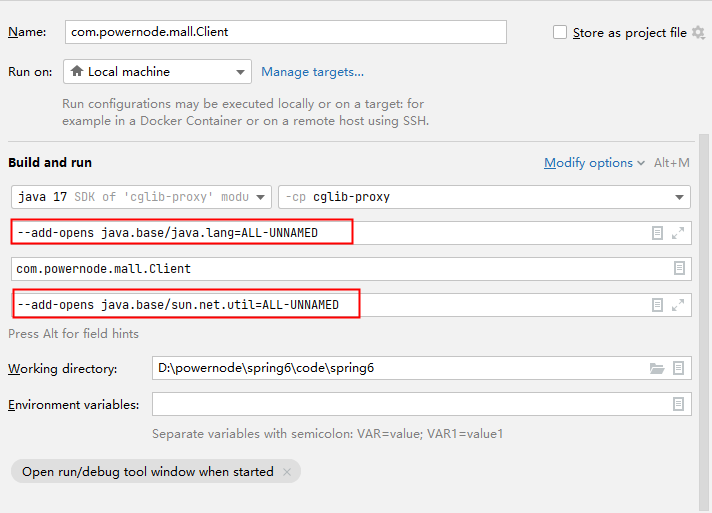
- –add-opens java.base/java.lang=ALL-UNNAMED
- –add-opens java.base/sun.net.util=ALL-UNNAMED
执行结果:
十五、面向切面编程AOP
IoC使软件组件松耦合。AOP让你能够捕捉系统中经常使用的功能,把它转化成组件。
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):面向切面编程,面向方面编程。(AOP是一种编程技术)
AOP是对OOP的补充延伸。
AOP底层使用的就是动态代理来实现的。
Spring的AOP使用的动态代理是:JDK动态代理 + CGLIB动态代理技术。Spring在这两种动态代理中灵活切换,如果是代理接口,会默认使用JDK动态代理,如果要代理某个类,这个类没有实现接口,就会切换使用CGLIB。当然,你也可以强制通过一些配置让Spring只使用CGLIB。
15.1 AOP介绍
一般一个系统当中都会有一些系统服务,例如:日志、事务管理、安全等。这些系统服务被称为:交叉业务
这些交叉业务几乎是通用的,不管你是做银行账户转账,还是删除用户数据。日志、事务管理、安全,这些都是需要做的。
如果在每一个业务处理过程当中,都掺杂这些交叉业务代码进去的话,存在两方面问题:
- 第一:交叉业务代码在多个业务流程中反复出现,显然这个交叉业务代码没有得到复用。并且修改这些交叉业务代码的话,需要修改多处。
- 第二:程序员无法专注核心业务代码的编写,在编写核心业务代码的同时还需要处理这些交叉业务。
使用AOP可以很轻松的解决以上问题。
请看下图,可以帮助你快速理解AOP的思想:
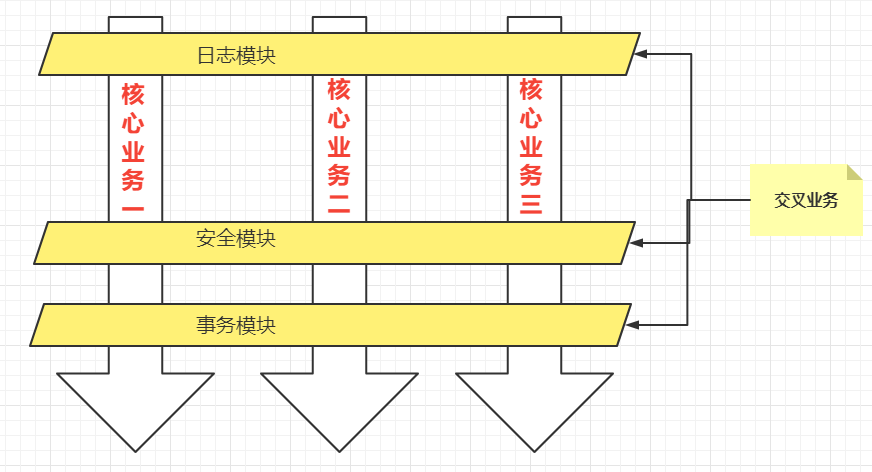
用一句话总结AOP:将与核心业务无关的代码独立的抽取出来,形成一个独立的组件,然后以横向交叉的方式应用到业务流程当中的过程被称为AOP。
AOP的优点:
- 第一:代码复用性增强。
- 第二:代码易维护。
- 第三:使开发者更关注业务逻辑。
15.2 AOP的七大术语
public class UserService{
public void do1(){
System.out.println("do 1");
}
public void do2(){
System.out.println("do 2");
}
public void do3(){
System.out.println("do 3");
}
public void do4(){
System.out.println("do 4");
}
public void do5(){
System.out.println("do 5");
}
// 核心业务方法
public void service(){
do1();
do2();
do3();
do5();
}
}
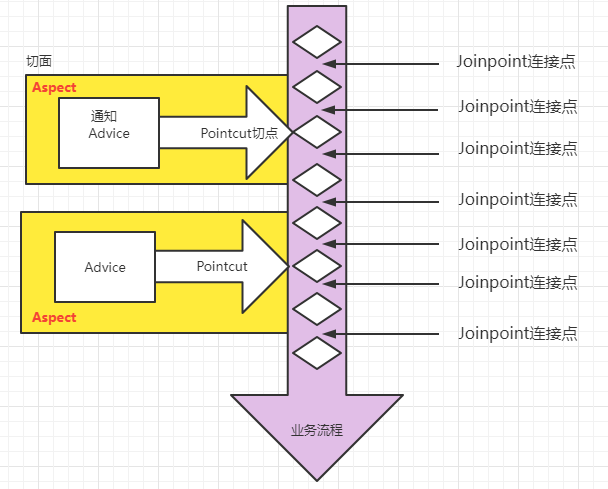
- 连接点 Joinpoint
- 在程序的整个执行流程中,可以织入切面的位置。方法的执行前后,异常抛出之后等位置。
- 切点 Pointcut
- 在程序执行流程中,真正织入切面的方法。(一个切点对应多个连接点)
- 通知 Advice
- 通知又叫增强,就是具体你要织入的代码。
- 通知包括:
- 前置通知
- 后置通知
- 环绕通知
- 异常通知
- 最终通知
- 切面 Aspect
- 切点 + 通知就是切面。
- 织入 Weaving
- 把通知应用到目标对象上的过程。
- 代理对象 Proxy
- 一个目标对象被织入通知后产生的新对象。
- 目标对象 Target
- 被织入通知的对象。
通过下图,大家可以很好的理解AOP的相关术语:
15.3 切点表达式
切点表达式用来定义通知(Advice)往哪些方法上切入。
切入点表达式语法格式:
execution([访问控制权限修饰符] 返回值类型 [全限定类名]方法名(形式参数列表) [异常])
访问控制权限修饰符:
- 可选项。
- 没写,就是4个权限都包括。
- 写public就表示只包括公开的方法。
返回值类型:
- 必填项。
-
- 表示返回值类型任意。
全限定类名:
- 可选项。
- 两个点“…”代表当前包以及子包下的所有类。
- 省略时表示所有的类。
方法名:
- 必填项。
- *表示所有方法。
- set*表示所有的set方法。
形式参数列表:
- 必填项
- () 表示没有参数的方法
- (…) 参数类型和个数随意的方法
- (*) 只有一个参数的方法
- (*, String) 第一个参数类型随意,第二个参数是String的。
异常:
- 可选项。
- 省略时表示任意异常类型。
理解以下的切点表达式:
execution(public * com.powernode.mall.service.*.delete*(..))
execution(* com.powernode.mall..*(..))
execution(* *(..))
15.4 使用Spring的AOP
Spring对AOP的实现包括以下3种方式:
- 第一种方式:Spring框架结合AspectJ框架实现的AOP,基于注解方式。
- 第二种方式:Spring框架结合AspectJ框架实现的AOP,基于XML方式。
- 第三种方式:Spring框架自己实现的AOP,基于XML配置方式。
实际开发中,都是Spring+AspectJ来实现AOP。所以我们重点学习第一种和第二种方式。
什么是AspectJ?(Eclipse组织的一个支持AOP的框架。AspectJ框架是独立于Spring框架之外的一个框架,Spring框架用了AspectJ)
AspectJ项目起源于帕洛阿尔托(Palo Alto)研究中心(缩写为PARC)。该中心由Xerox集团资助,Gregor Kiczales领导,从1997年开始致力于AspectJ的开发,1998年第一次发布给外部用户,2001年发布1.0 release。为了推动AspectJ技术和社团的发展,PARC在2003年3月正式将AspectJ项目移交给了Eclipse组织,因为AspectJ的发展和受关注程度大大超出了PARC的预期,他们已经无力继续维持它的发展。
15.4.1 准备工作
使用Spring+AspectJ的AOP需要引入的依赖如下:
<!--spring context依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring aop依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aop</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring aspects依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>6.0.0-M2</version>
</dependency>
Spring配置文件中添加context命名空间和aop命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
</beans>
15.4.2 基于AspectJ的AOP注解式开发
实现步骤
第一步:定义目标类以及目标方法
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
// 目标类
public class OrderService {
// 目标方法
public void generate(){
System.out.println("订单已生成!");
}
}
第二步:定义切面类
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
// 切面类
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
}
第三步:目标类和切面类都纳入spring bean管理
在目标类OrderService上添加**@Component注解。
在切面类MyAspect类上添加@Component**注解。
第四步:在spring配置文件中添加组建扫描
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.service"/>
</beans>
第五步:在切面类中添加通知
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
// 切面类
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
// 这就是需要增强的代码(通知)
public void advice(){
System.out.println("我是一个通知");
}
}
第六步:在通知上添加切点表达式
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
// 切面类
@Aspect
@Component
public class MyAspect {
// 切点表达式
@Before("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
// 这就是需要增强的代码(通知)
public void advice(){
System.out.println("我是一个通知");
}
}
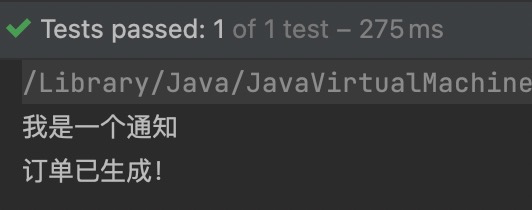
注解@Before表示前置通知。
第七步:在spring配置文件中启用自动代理
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.powernode.spring6.service"/>
<!--开启自动代理-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true"/>
</beans>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class=“true”/> 开启自动代理之后,凡事带有@Aspect注解的bean都会生成代理对象。
proxy-target-class=“true” 表示采用cglib动态代理。
proxy-target-class=“false” 表示采用jdk动态代理。默认值是false。即使写成false,当没有接口的时候,也会自动选择cglib生成代理类。
测试程序:
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest {
@Test
public void testAOP(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-aspectj-aop-annotation.xml");
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
}
运行结果:
通知类型
通知类型包括:
- 前置通知:@Before 目标方法执行之前的通知
- 后置通知:@AfterReturning 目标方法执行之后的通知
- 环绕通知:@Around 目标方法之前添加通知,同时目标方法执行之后添加通知。
- 异常通知:@AfterThrowing 发生异常之后执行的通知
- 最终通知:@After 放在finally语句块中的通知
接下来,编写程序来测试这几个通知的执行顺序:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 切面类
@Component
@Aspect
public class MyAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
// 执行目标方法。
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterReturningAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(){
System.out.println("异常通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 目标类
@Component
public class OrderService {
// 目标方法
public void generate(){
System.out.println("订单已生成!");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest {
@Test
public void testAOP(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-aspectj-aop-annotation.xml");
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
}
执行结果:
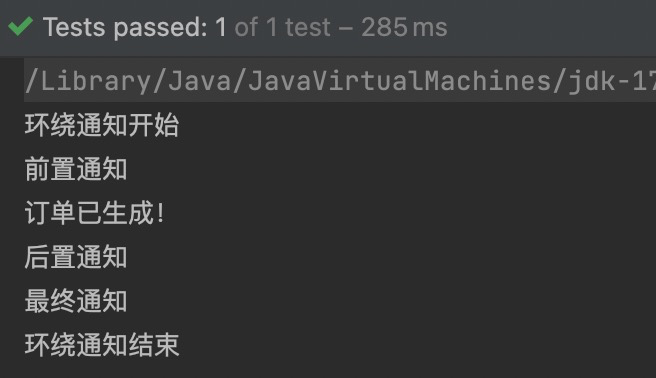
通过上面的执行结果就可以判断他们的执行顺序了,这里不再赘述。
结果中没有异常通知,这是因为目标程序执行过程中没有发生异常。我们尝试让目标方法发生异常:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 目标类
@Component
public class OrderService {
// 目标方法
public void generate(){
System.out.println("订单已生成!");
if (1 == 1) {
throw new RuntimeException("模拟异常发生");
}
}
}
再次执行测试程序,结果如下:
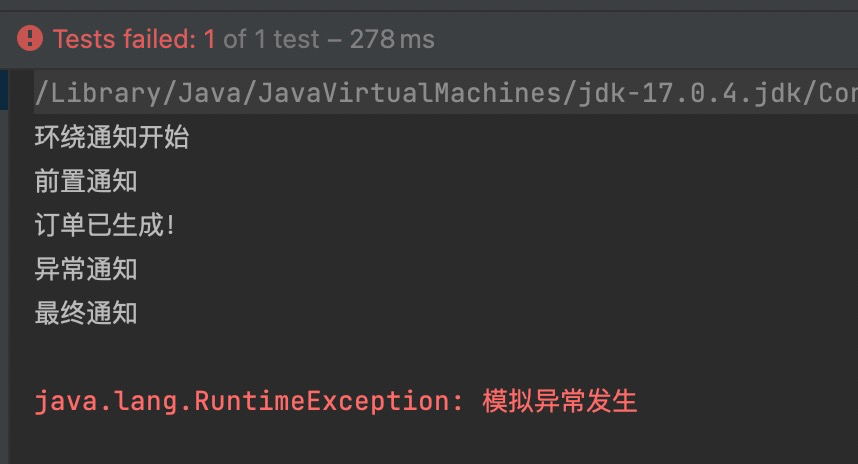
通过测试得知,当发生异常之后,最终通知也会执行,因为最终通知@After会出现在finally语句块中。
出现异常之后,后置通知和环绕通知的结束部分不会执行。
切面的先后顺序
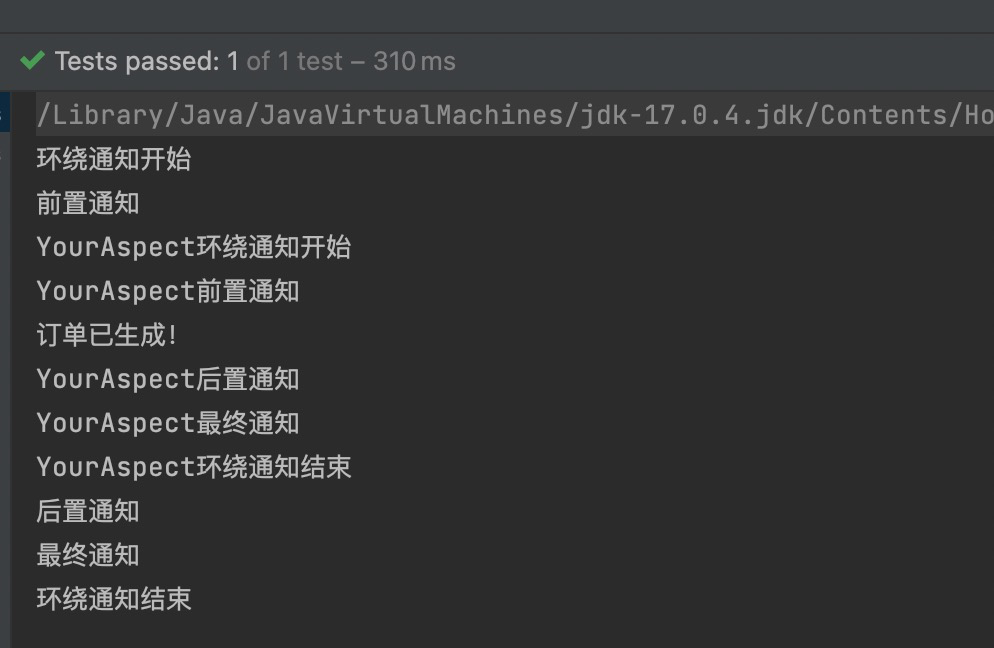
我们知道,业务流程当中不一定只有一个切面,可能有的切面控制事务,有的记录日志,有的进行安全控制,如果多个切面的话,顺序如何控制:可以使用@Order注解来标识切面类,为@Order注解的value指定一个整数型的数字,数字越小,优先级越高。
再定义一个切面类,如下:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
@Order(1) //设置优先级
public class YourAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("YourAspect环绕通知开始");
// 执行目标方法。
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("YourAspect环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("YourAspect前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterReturningAdvice(){
System.out.println("YourAspect后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(){
System.out.println("YourAspect异常通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("YourAspect最终通知");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 切面类
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2) //设置优先级
public class MyAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
// 执行目标方法。
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterReturningAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(){
System.out.println("异常通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
执行测试程序:
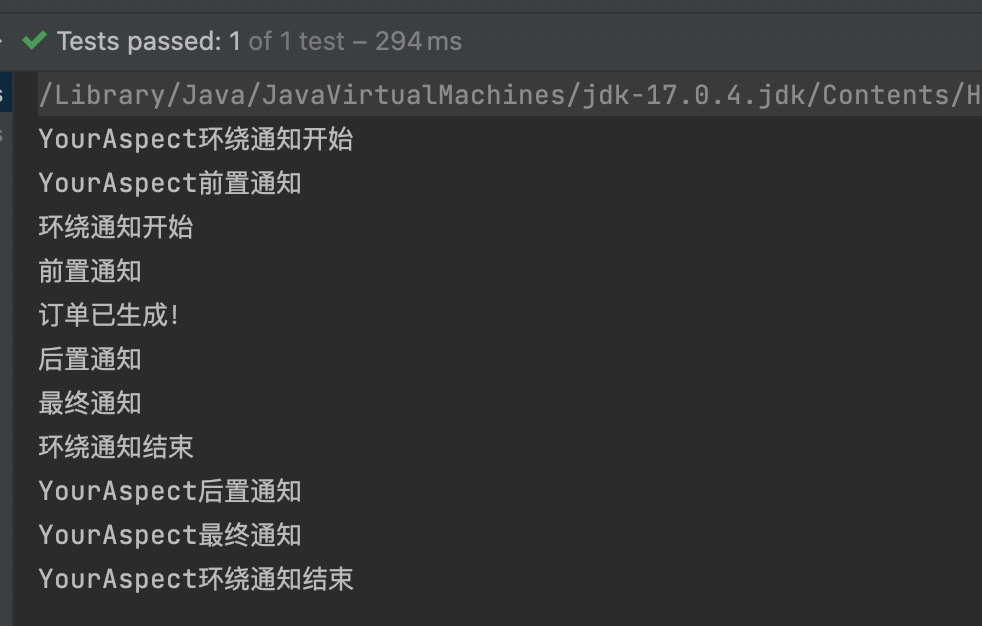
通过修改@Order注解的整数值来切换顺序,执行测试程序:
优化使用切点表达式
观看以下代码中的切点表达式:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 切面类
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class MyAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
// 执行目标方法。
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterReturningAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(){
System.out.println("异常通知");
}
@After("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
缺点是:
- 第一:切点表达式重复写了多次,没有得到复用。
- 第二:如果要修改切点表达式,需要修改多处,难维护。
可以这样做:将切点表达式单独的定义出来,在需要的位置引入即可。如下:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 切面类
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(2)
public class MyAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.OrderService.*(..))")
public void pointcut(){}
@Around("pointcut()")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕通知开始");
// 执行目标方法。
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕通知结束");
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void beforeAdvice(){
System.out.println("前置通知");
}
@AfterReturning("pointcut()")
public void afterReturningAdvice(){
System.out.println("后置通知");
}
@AfterThrowing("pointcut()")
public void afterThrowingAdvice(){
System.out.println("异常通知");
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void afterAdvice(){
System.out.println("最终通知");
}
}
使用@Pointcut注解来定义独立的切点表达式。
注意这个@Pointcut注解标注的方法随意,只是起到一个能够让@Pointcut注解编写的位置。
执行测试程序:
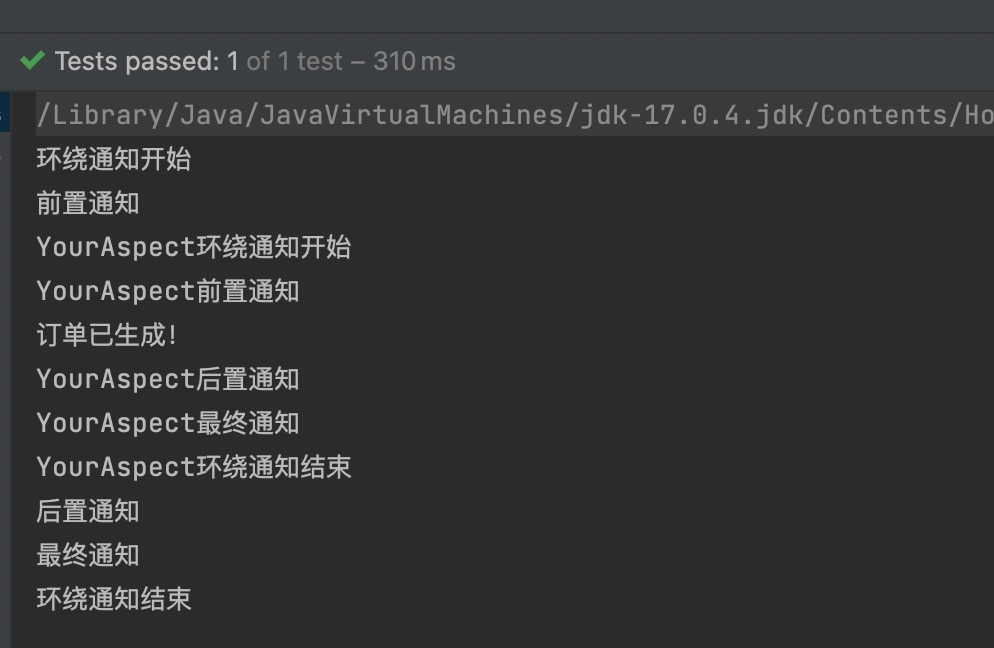
全注解式开发AOP
就是编写一个类,在这个类上面使用大量注解来代替spring的配置文件,spring配置文件消失了,如下:
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.powernode.spring6.service")
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class Spring6Configuration {
}
测试程序也变化了:
@Test
public void testAOPWithAllAnnotation(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Configuration.class);
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
orderService.generate();
}
执行结果如下:
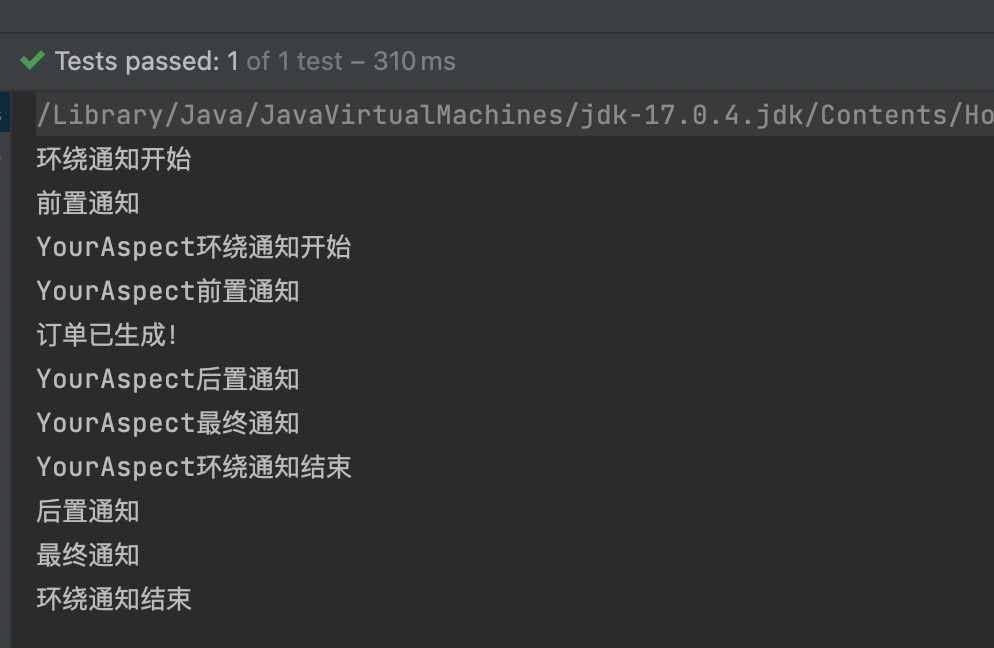
15.4.3 基于XML配置方式的AOP(了解)
第一步:编写目标类
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
// 目标类
public class VipService {
public void add(){
System.out.println("保存vip信息。");
}
}
第二步:编写切面类,并且编写通知
package com.powernode.spring6.service;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
// 负责计时的切面类
public class TimerAspect {
public void time(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
long begin = System.currentTimeMillis();
//执行目标
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗时"+(end - begin)+"毫秒");
}
}
第三步:编写spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--纳入spring bean管理-->
<bean id="vipService" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.VipService"/>
<bean id="timerAspect" class="com.powernode.spring6.service.TimerAspect"/>
<!--aop配置-->
<aop:config>
<!--切点表达式-->
<aop:pointcut id="p" expression="execution(* com.powernode.spring6.service.VipService.*(..))"/>
<!--切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="timerAspect">
<!--切面=通知 + 切点-->
<aop:around method="time" pointcut-ref="p"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
测试程序:
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.service.VipService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest3 {
@Test
public void testAOPXml(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-aop-xml.xml");
VipService vipService = applicationContext.getBean("vipService", VipService.class);
vipService.add();
}
}
执行结果:
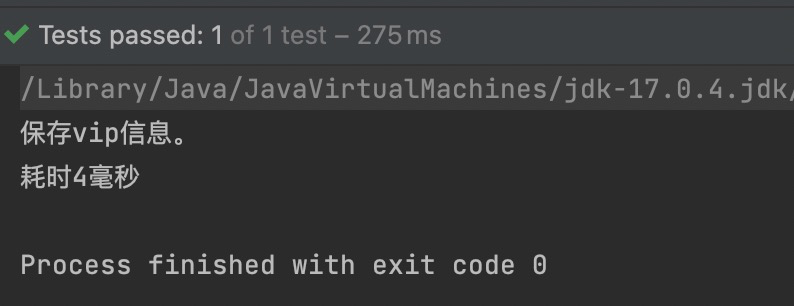
15.5 AOP的实际案例:事务处理
项目中的事务控制是在所难免的。在一个业务流程当中,可能需要多条DML语句共同完成,为了保证数据的安全,这多条DML语句要么同时成功,要么同时失败。这就需要添加事务控制的代码。例如以下伪代码:
class 业务类1{
public void 业务方法1(){
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法2(){
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法3(){
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
}
class 业务类2{
public void 业务方法1(){
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法2(){
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
public void 业务方法3(){
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
step1();
step2();
step3();
....
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
}
}
//......
可以看到,这些业务类中的每一个业务方法都是需要控制事务的,而控制事务的代码又是固定的格式,都是:
try{
// 开启事务
startTransaction();
// 执行核心业务逻辑
//......
// 提交事务
commitTransaction();
}catch(Exception e){
// 回滚事务
rollbackTransaction();
}
这个控制事务的代码就是和业务逻辑没有关系的“交叉业务”。以上伪代码当中可以看到这些交叉业务的代码没有得到复用,并且如果这些交叉业务代码需要修改,那必然需要修改多处,难维护,怎么解决?可以采用AOP思想解决。可以把以上控制事务的代码作为环绕通知,切入到目标类的方法当中。接下来我们做一下这件事,有两个业务类,如下:
package com.powernode.spring6.biz;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
// 业务类
public class AccountService {
// 转账业务方法
public void transfer(){
System.out.println("正在进行银行账户转账");
}
// 取款业务方法
public void withdraw(){
System.out.println("正在进行取款操作");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.biz;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
// 业务类
public class OrderService {
// 生成订单
public void generate(){
System.out.println("正在生成订单");
}
// 取消订单
public void cancel(){
System.out.println("正在取消订单");
}
}
注意,以上两个业务类已经纳入spring bean的管理,因为都添加了@Component注解。
接下来我们给以上两个业务类的4个方法添加事务控制代码,使用AOP来完成:
package com.powernode.spring6.biz;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Aspect
@Component
// 事务切面类
public class TransactionAspect {
@Around("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.biz..*(..))")
public void aroundAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint){
try {
System.out.println("开启事务");
// 执行目标
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("提交事务");
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.out.println("回滚事务");
}
}
}
你看,这个事务控制代码是不是只需要写一次就行了,并且修改起来也没有成本。编写测试程序:
package com.powernode.spring6.test;
import com.powernode.spring6.biz.AccountService;
import com.powernode.spring6.biz.OrderService;
import com.powernode.spring6.service.Spring6Configuration;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class AOPTest2 {
@Test
public void testTransaction(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Configuration.class);
OrderService orderService = applicationContext.getBean("orderService", OrderService.class);
AccountService accountService = applicationContext.getBean("accountService", AccountService.class);
// 生成订单
orderService.generate();
// 取消订单
orderService.cancel();
// 转账
accountService.transfer();
// 取款
accountService.withdraw();
}
}
执行结果:
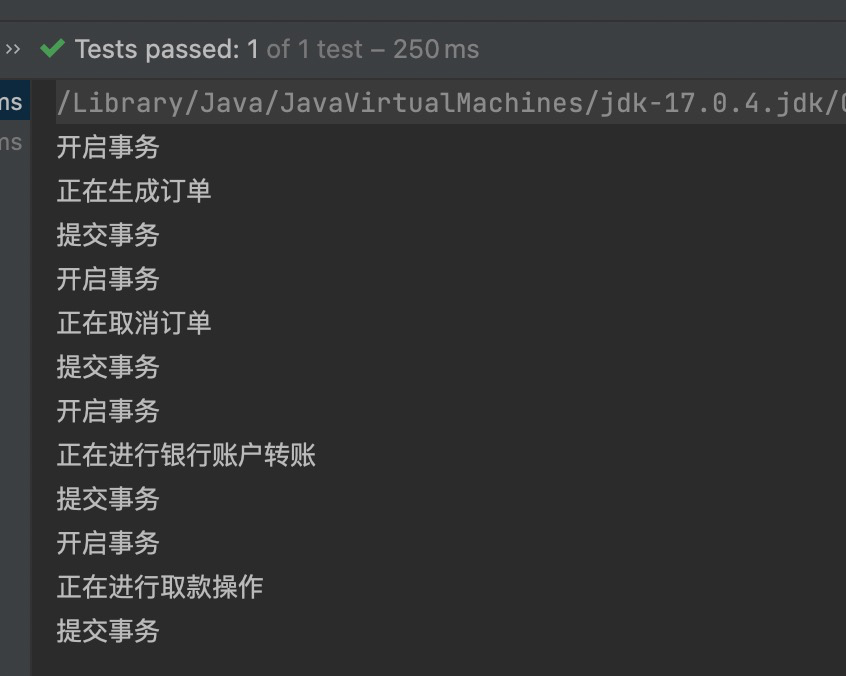
通过测试可以看到,所有的业务方法都添加了事务控制的代码。
15.6 AOP的实际案例:安全日志
需求是这样的:项目开发结束了,已经上线了。运行正常。客户提出了新的需求:凡事在系统中进行修改操作的,删除操作的,新增操作的,都要把这个人记录下来。因为这几个操作是属于危险行为。例如有业务类和业务方法:
package com.powernode.spring6.biz;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
//用户业务
public class UserService {
public void getUser(){
System.out.println("获取用户信息");
}
public void saveUser(){
System.out.println("保存用户");
}
public void deleteUser(){
System.out.println("删除用户");
}
public void modifyUser(){
System.out.println("修改用户");
}
}
package com.powernode.spring6.biz;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
// 商品业务类
@Component
public class ProductService {
public void getProduct(){
System.out.println("获取商品信息");
}
public void saveProduct(){
System.out.println("保存商品");
}
public void deleteProduct(){
System.out.println("删除商品");
}
public void modifyProduct(){
System.out.println("修改商品");
}
}
注意:已经添加了@Component注解。
接下来我们使用aop来解决上面的需求:编写一个负责安全的切面类
package com.powernode.spring6.biz;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class SecurityAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.biz..save*(..))")
public void savePointcut(){}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.biz..delete*(..))")
public void deletePointcut(){}
@Pointcut("execution(* com.powernode.spring6.biz..modify*(..))")
public void modifyPointcut(){}
@Before("savePointcut() || deletePointcut() || modifyPointcut()")
public void beforeAdivce(JoinPoint joinpoint){
System.out.println("XXX操作员正在操作"+joinpoint.getSignature().getName()+"方法");
}
}
@Test
public void testSecurity(){
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Spring6Configuration.class);
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
ProductService productService = applicationContext.getBean("productService", ProductService.class);
userService.getUser();
userService.saveUser();
userService.deleteUser();
userService.modifyUser();
productService.getProduct();
productService.saveProduct();
productService.deleteProduct();
productService.modifyProduct();
}
执行结果: