二叉树的前中后序遍历以及求深度、叶子节点和二叉树的重建
目录
二叉树
二叉树的创建和嵌套打印
创建二叉树
嵌套打印
二叉树的前中后序遍历
前中后序遍历
层次遍历
二叉树的深度和叶子节点的个数
演示各个遍历后的结果以及深度和叶子节点的个数
二叉树的重建
二叉树
二叉树是一种数据结构,由节点(node)组成,每个节点最多有两个子节点,分别称为左子节点(left child)和右子节点(right child)。一个节点也可以没有子节点,这时该节点就是叶子节点(leaf node)。
二叉树有许多不同的类型,其中比较常见的包括二叉搜索树、平衡二叉树、红黑树等。二叉搜索树的特点是,对于每个节点,它的左子树中所有节点的值都小于它的值,而右子树中所有节点的值都大于它的值。这使得二叉搜索树可以快速地查找、插入和删除节点,时间复杂度为O(log n)。
二叉树的创建和嵌套打印
首先用一个类来封装二叉树的节点
public class TreeNode {
int data;//数据
TreeNode left;//左子节点
TreeNode right;//右子节点
public TreeNode(){};
//构造函数
public TreeNode(int data, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}创建二叉树
public class BinaryTree {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
TreeNode root = null;//二叉树的根,默认为空
public TreeNode createBinaryTree() {//创建二叉树
TreeNode t;//当前树的根
int x = scanner.nextInt();//输入当前节点的值,如果为0则表示空节点
if (x == 0) {
t = null;
} else {
t = new TreeNode();
t.data = x;//data为往前节点的数值
t.left = createBinaryTree();
t.right = createBinaryTree();
}
return t;
}
}嵌套打印
public void printTree(TreeNode t) {//嵌套打印
if (t != null) {
System.out.print(t.data);//输出根节点
if (t.left != null || t.right != null) {
//只要左子节点和右子节点有一个不为空就输出
System.out.print("(");
printTree(t.left);//递归调用左子节点
if (t.right != null) {
System.out.print(",");
}
printTree(t.right);
System.out.print(")");
}
}
}二叉树的前中后序遍历
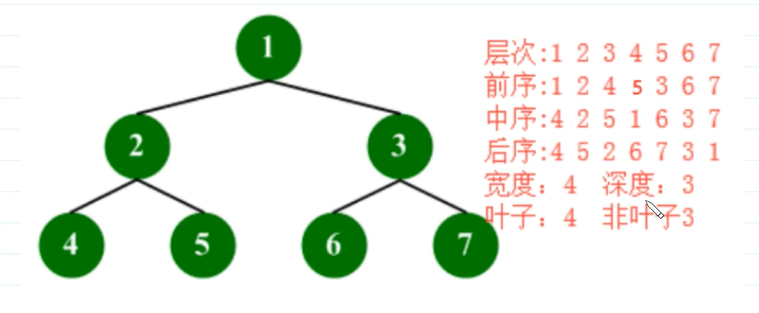
二叉树的遍历是指按照一定的顺序访问树中的每个节点。二叉树的三种遍历方式分别为前序遍历(pre-order traversal)、中序遍历(in-order traversal)和后序遍历(post-order traversal)。其中前序遍历的顺序是根节点-左子树-右子树,中序遍历的顺序是左子树-根节点-右子树,后序遍历的顺序是左子树-右子树-根节点。
前中后序遍历
public void preOrder(TreeNode root) {//前序遍历 根节点-左子树-右子树
if (root != null) {
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
}
public void midOrder(TreeNode root) {//中序遍历 左子树-根节点-右子树
if (root != null) {
midOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
midOrder(root.right);
}
}
public void postOrder(TreeNode root) {//后序遍历 左子树-右子树-根节点
if (root != null) {
postOrder(root.left);
postOrder(root.right);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
}
}层次遍历
public void leverOrder(TreeNode root) {//层次遍历
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
if (root == null) return;
queue.offer(root);//根入列
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode head = queue.poll();//弹出列头
System.out.print(head.data + " ");
if (head.left != null) {
queue.offer(head.left);
}
if (head.right != null) {
queue.offer(head.right);
}
}
}二叉树的深度和叶子节点的个数
public int treeDepth(TreeNode root) {//求二叉树的深度
if (root == null) return 0;
return Math.max(treeDepth(root.left), treeDepth(root.right)) + 1;
}
public int treeLeaf(TreeNode root) {//求二叉树的叶子数量
if (root == null) return 0;
else if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
else return treeLeaf(root.left) + treeLeaf(root.right);
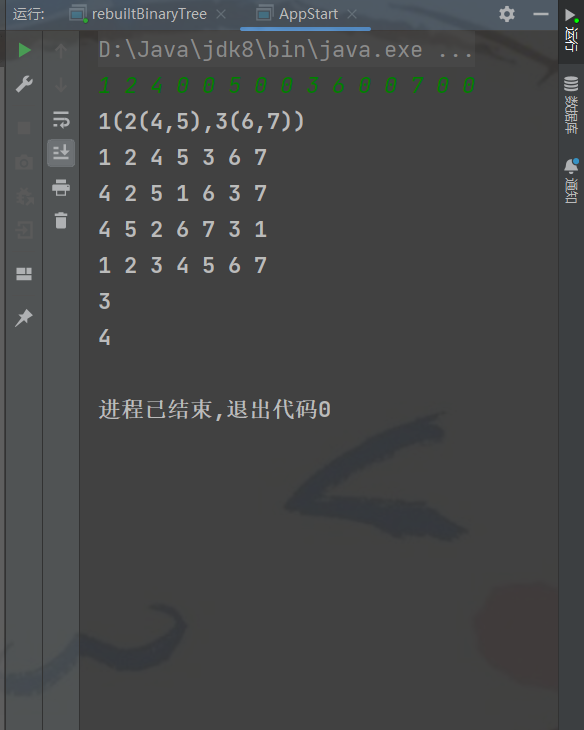
}演示各个遍历后的结果以及深度和叶子节点的个数
public class AppStart {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
binaryTree.root = binaryTree.createBinaryTree();
binaryTree.printTree(binaryTree.root);//嵌套打印
System.out.println();//换行
binaryTree.preOrder(binaryTree.root);//前序遍历
System.out.println();
binaryTree.midOrder(binaryTree.root);//中序遍历
System.out.println();
binaryTree.postOrder(binaryTree.root);//后序遍历
System.out.println();
binaryTree.leverOrder(binaryTree.root);//层次遍历
System.out.println();
System.out.println(binaryTree.treeDepth(binaryTree.root));//深度
System.out.println(binaryTree.treeLeaf(binaryTree.root));//叶子个数
}
}输入的数据为1 2 4 0 0 5 0 0 3 6 0 0 7 0 0,是因为4 5 6 7为叶子,没有子叶
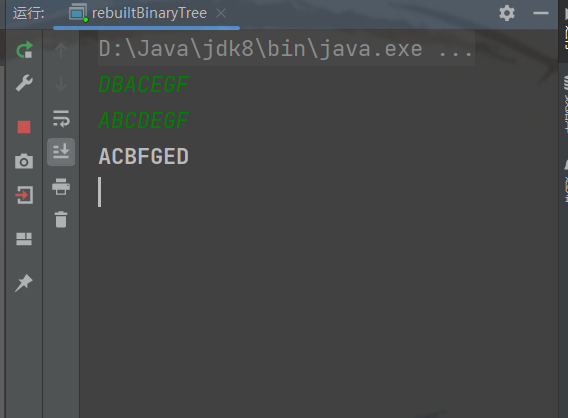
二叉树的重建
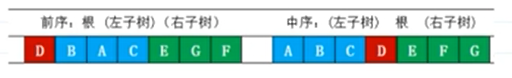
二叉树的重建是指根据已知的二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历序列,重新构建出二叉树的过程。具体过程如下:
(1)根据前序遍历序列,第一个元素为根节点,将其插入二叉树中。
(2)根据中序遍历序列,找到根节点在其中的位置,将中序遍历序列划分为左子树和右子树的序列。
(3)对于前序遍历序列,左子树序列的下一个元素即为左子树的根节点,右子树序列的下一个元素即为右子树的根节点。将它们插入二叉树中。
(4)递归处理左子树和右子树,重复步骤2和步骤3,直到序列为空或者只剩下一个元素。
import java.util.Scanner;
public class rebuiltBinaryTree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
String pre,mid;//定义前序和中序变量
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
pre = scanner.next();
mid = scanner.next();
System.out.println(f(pre,mid));
}
}
public static String f(String pre, String mid) {
if (pre.length() == 0) return "";
else if (pre.length() == 1) return pre;
else {
int pos = mid.indexOf(pre.charAt(0));//根据前序的根去中序里分左右
/*
public int indexOf(int ch)
返回指定字符在此字符串中第一次出现处的索引。
如果在此 String 对象表示的字符序列中出现值为 ch 的字符,则返回第一次出现该字符的索引
*/
String left = f(pre.substring(1, pos + 1), mid.substring(0, pos));
/*
public String substring(int beginIndex,int endIndex)
返回一个新字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。该子字符串从指定的 beginIndex 处开始,
直到索引 endIndex - 1 处的字符。因此,该子字符串的长度为 endIndex-beginIndex
*/
String right = f(pre.substring(pos + 1), mid.substring(pos + 1));
/*
public String substring(int beginIndex)
返回一个新的字符串,它是此字符串的一个子字符串。
该子字符串从指定索引处的字符开始,直到此字符串末尾。
*/
return left + right + pre.charAt(0);//前序的第一个字符是根
}
}
}