C#中的异常
目录
一、什么是异常
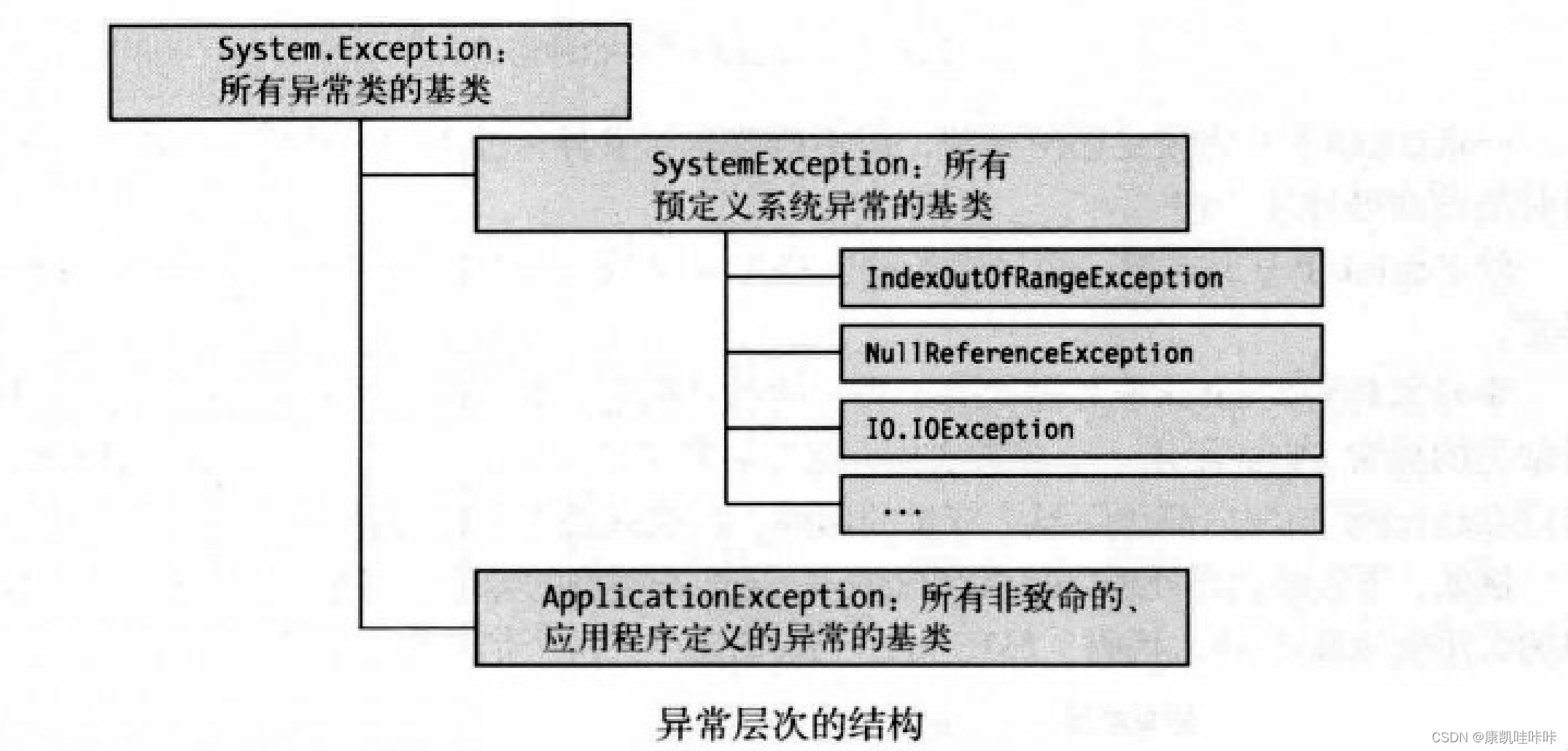
二、异常类
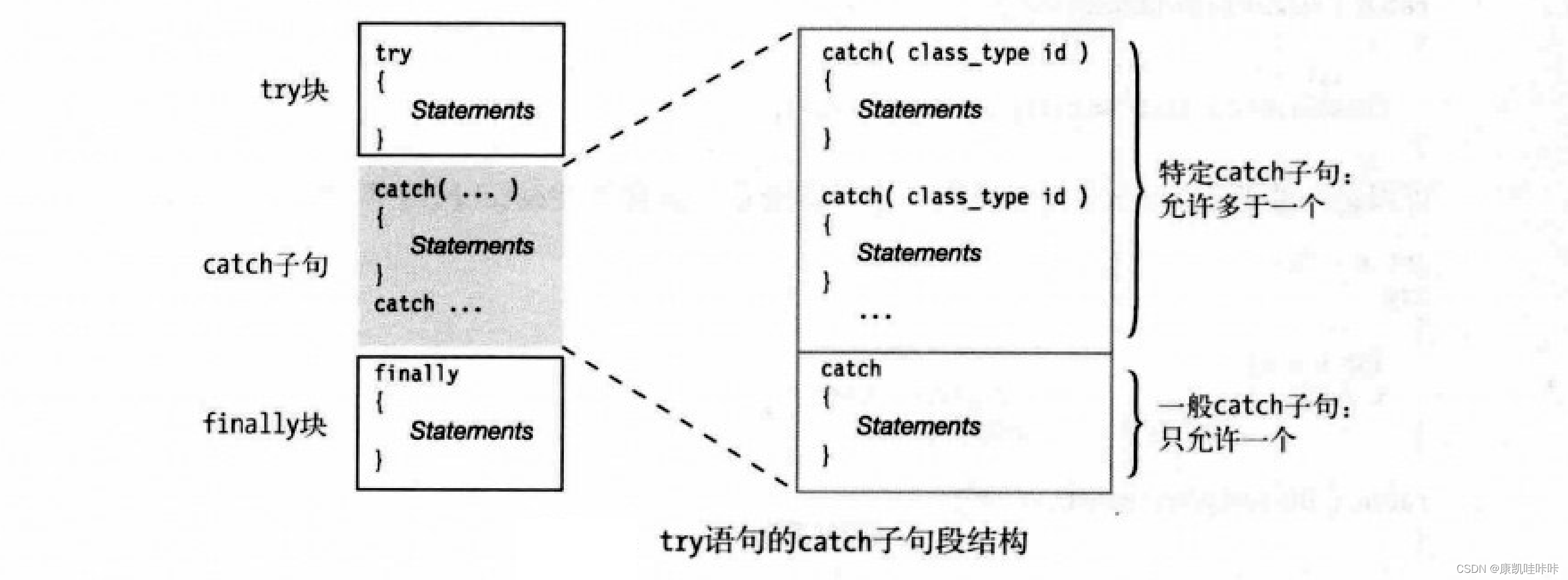
三、catch子句
1.catch的三种形式
2. 使用特定catch子句
1. 捕获指定异常
2.带对象的特定catch子句
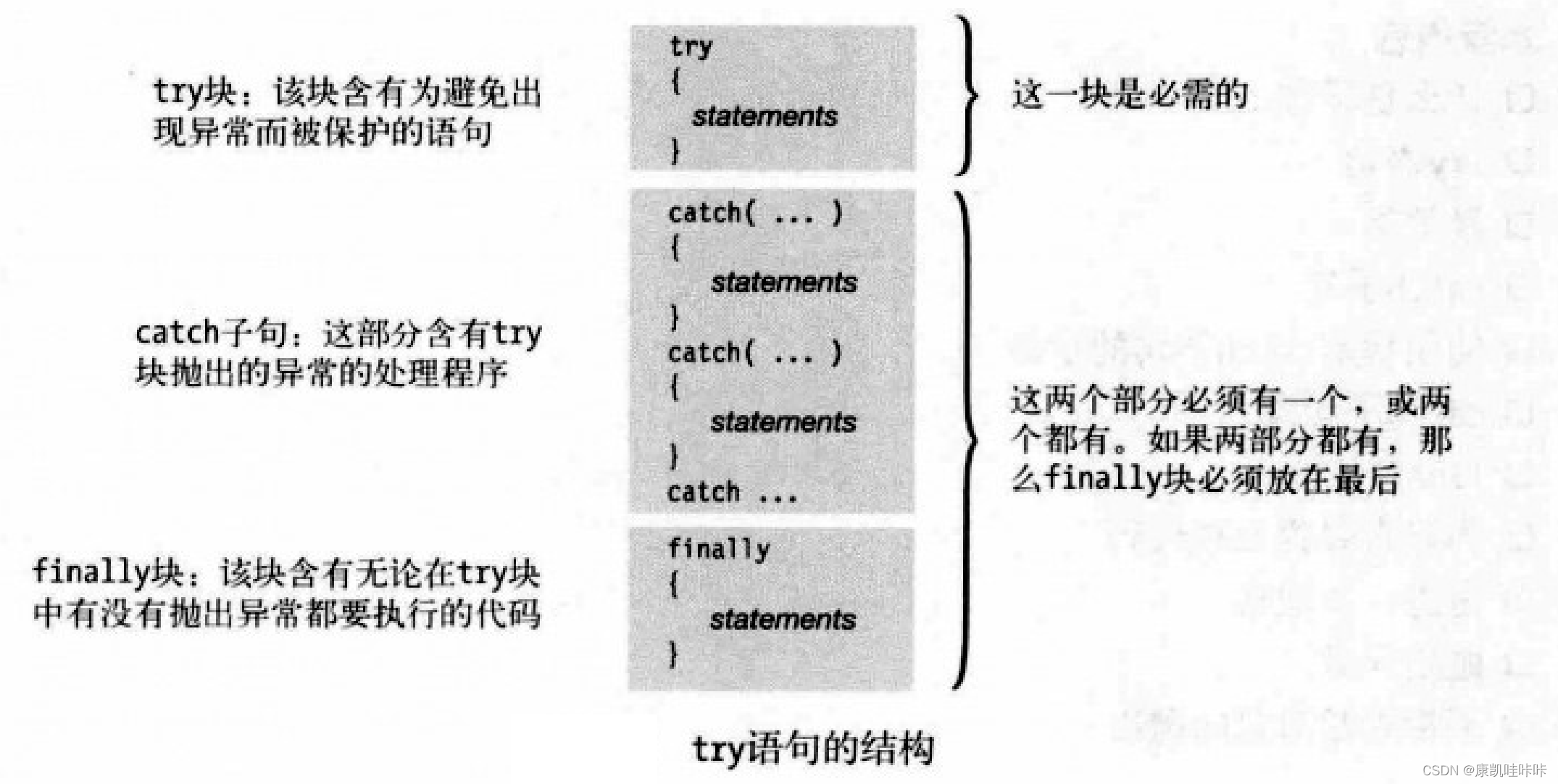
四、finally块
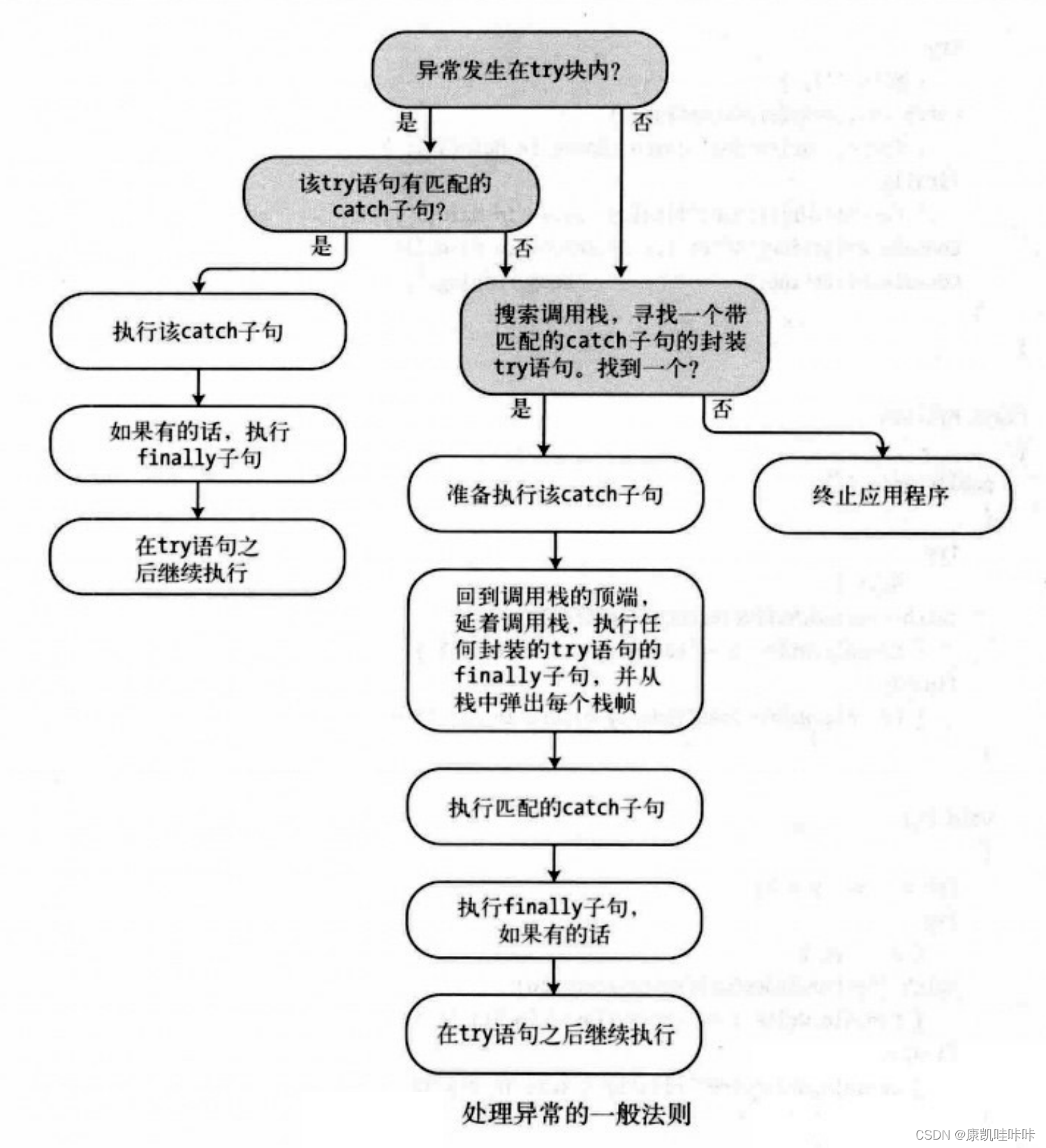
五、为异常寻找处理程序
1.try块寻找异常处理程序流程
2.按顺序搜索调用栈寻找异常处理程序
3.处理异常的一般法则
六、抛出异常
1. 异常对象的抛出
2.不带异常对象的抛出
一、什么是异常
异常是程序中的运行时错误。如果没有特定的程序来捕获并处理异常,程序将被挂起。
static void Main
{
int x = 10;
int y = 0;
x /= y; //抛出一个异常
}我们可以使用try...catch...fianlly...语句来处理异常。
- try块包含为避免出现异常而被保护的代码。
- catch块可以有一个或多个,是异常处理程序。
- finally块无论异常是否发生都需要执行的代码。
处理异常示例:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 10;
int y = 0;
try
{
x /= y; //需要避免发生异常的代码
}
catch (Exception ex) //捕获异常
{
y = 2; //处理异常
x /= y;
}
finally //无论是否发生异常都会被调用
{
Console.WriteLine("finally被调用了");
}
Console.WriteLine(x);
}二、异常类
有许多不同类型的异常可在程序中发生。BCL定义了许多不同类型的异常,当异常发生时CLR:
- 创建该类型的异常对象。
- 寻找适当的catch子句以处理异常。
- 所有异常类从根本上派生自System.Exception类。
三、catch子句
1.catch的三种形式
catch子句处理异常。有以下三种形式:
- 一般catch子句:能接受任何异常,但不能确定引发异常的类型。
- 特定catch子句:捕获指定异常类或派生自它的异常类。
- 带对象的特定catch子句:可通过异常变量访问详细的异常信息。

2. 使用特定catch子句
1. 捕获指定异常
代码示例:指定捕获DivideByZeroException异常
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 10;
int y = 0;
string[] strs = new string[10];
try
{
//x /= y; //DivideByZeroException类型的异常
string str = strs[10];//IndexOutOfRangeException数组下标越界异常
}
catch (DivideByZeroException) //只捕获DivideByZeroException的异常
{
y = 2;
x /= y;
}
Console.WriteLine(x);
}2.带对象的特定catch子句
代码示例:可以通过异常变量访问一些信息
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int x = 10;
int y = 0;
try
{
x /= y; //DivideByZeroException类型的异常
}
catch (DivideByZeroException e) //e为异常变量
{
//访问异常变量
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
Console.WriteLine(e.Source);
Console.WriteLine(e.StackTrace);
}
}
四、finally块
如果控制流进入了一个带fianlly块的try语句,那么finally始终会被执行。即使在try块中有一条return语句或在catch中抛出一个异常,也不会饶过fianlly块。
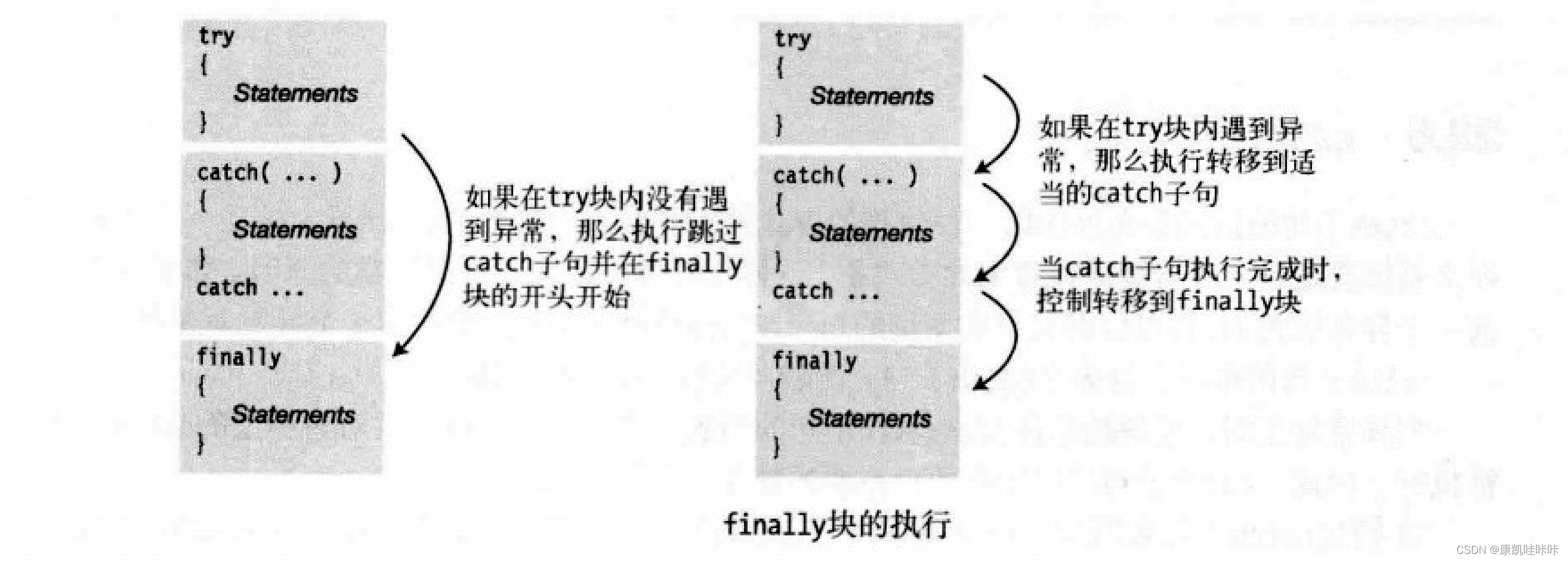
五、为异常寻找处理程序
1.try块寻找异常处理程序流程

2.按顺序搜索调用栈寻找异常处理程序
3.处理异常的一般法则
搜索调用栈来寻找异常处理程序的代码示例:
//B方法中有个异常,B被A调用,A被Main方法调用,搜索调用栈来为B方法中的异常寻找异常处理程序
class MyClass
{
public void A()
{
try
{
B();
} catch (IndexOutOfRangeException)
{
Console.WriteLine("执行A方法中的catch");
} finally
{
Console.WriteLine("执行A方法中的fianlly");
}
}
public void B()
{
int x = 10;
int y = 0;
try
{
x /= y; //DivideByZeroException类型的异常
}
catch (NullReferenceException)
{
Console.WriteLine("执行B方法中的catch");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("执行B方法中的fianlly");
}
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClass myClass = new MyClass();
try
{
myClass.A();
}
catch (DivideByZeroException)
{
Console.WriteLine("执行Main方法中的catch");
}
finally
{
Console.WriteLine("执行Main方法中的fianlly");
}
}
}代码图解示例:
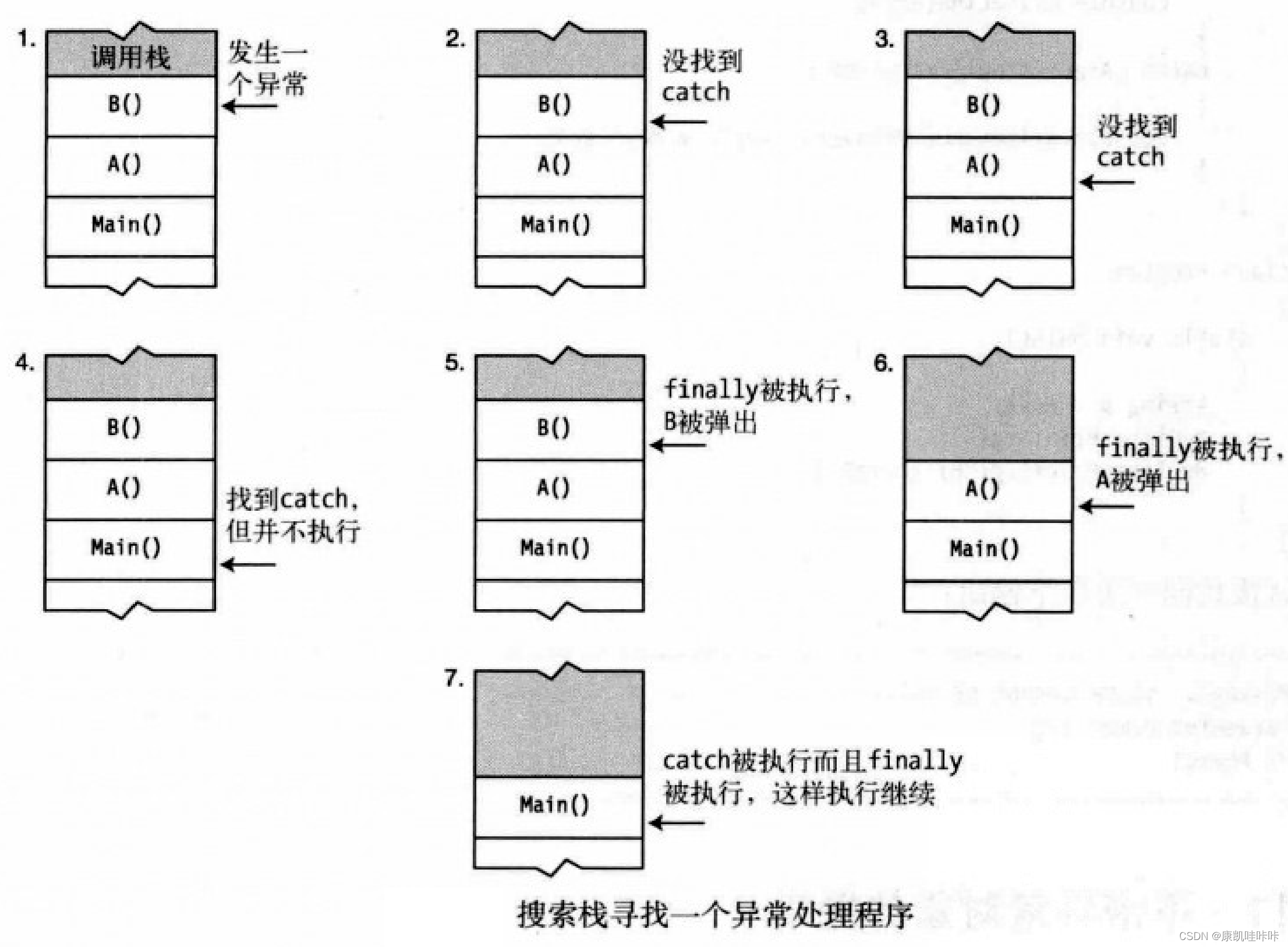
六、抛出异常
可以使用throw语句显示地引发一个异常。
1. 异常对象的抛出
class MyClass
{
public static void PrintArg(string arg)
{
try
{
if (arg == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("arg");
Console.WriteLine(arg);
}
catch (ArgumentNullException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("Message:{0}",e.Message);
}
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClass.PrintArg(null);
MyClass.PrintArg("Hello");
}
}2.不带异常对象的抛出
throw语句还可以不带异常对象使用,在catch块内部使用。
- 这种形式重新抛出当前异常,系统继续它的搜索,为该异常寻找另外的处理代码。
- 这种形式只能用在catch语句内部。
class MyClass
{
public static void PrintArg(string arg)
{
try
{
try
{
if (arg == null)
throw new ArgumentNullException("arg");
Console.WriteLine(arg);
}
catch (ArgumentNullException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("内部catch捕获异常,Message:{0}", e.Message);
throw;//重新抛出异常,没有附加参数
}
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("外部catch捕获异常:捕获内部重新抛出的异常");
}
}
}
internal class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
MyClass.PrintArg(null);
MyClass.PrintArg("Hello");
}
}(注:本章内容学习总结自《C#图解教程》)