stack_queue | priority_queue | 仿函数
文章目录
- 1. stack 的使用
- 2. stack的模拟实现
- 3. queue的使用
- 4. queue的模拟实现
- 5. deque ——双端队列
- deque优缺点
- 6. priority_queue ——优先级队列
- 1. priority_queue的使用
- 2. priority_queue的模拟实现
- push——插入
- pop ——删除
- top —— 堆顶
- 仿函数问题
- 完整代码实现
1. stack 的使用
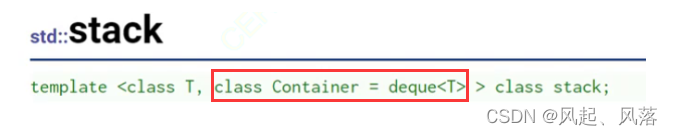
栈不在是一个容器,而是一个容器适配器 ,
stack的模板中第二个deque暂时不知道干什么的,后面会说

说明stack是一个容器适配器,并且为了保证严格的先进后出,所以不存在迭代器
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
stack<int>v;
v.push(1);
v.push(2);
v.push(3);
v.push(4);
while (!v.empty())//后进先出的原则
{
cout << v.top() << " ";//4 3 2 1
v.pop();
}
return 0;
}
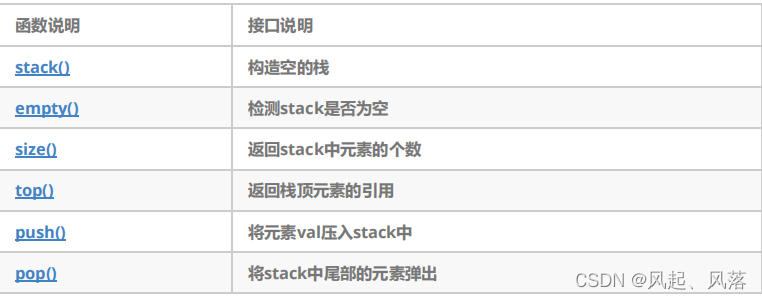
2. stack的模拟实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<list>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
namespace yzq
{
//适配器模式
template<class T, class Container = deque<T>>//给与缺省值
//deque 作为一个双端队列,可以非常适用与大量 头插 头删 尾插 尾删 的情况
class stack
{
public:
void push(const T& x)//插入
{
_con.push_back(x);//尾插
}
void pop()//删除栈顶元素
{
_con.pop_back();
}
const T& top()//栈顶
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()//大小
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()//判空
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;//Container 是一个符合要求的容器
};//适配器模式
void test()
{
yzq::stack<int>v;
v.push(1);
v.push(2);
v.push(3);
v.push(4);
while (!v.empty())
{
cout << v.top() << " ";
v.pop();
}
cout << endl;
}
}
这里假设我们不认识 deque,那么如果stack频繁使用pop尾删,将vector< T >设置成缺省值也是非常适合的
3. queue的使用
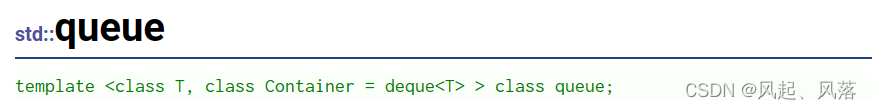
队列同样不在是一个容器,而是一个容器适配器

说明queue为了保证严格的先进先出,所以不存在迭代器

#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
queue<int>v;
v.push(1);
v.push(2);
v.push(3);
v.push(4);
while (!v.empty())//符合先进先出的原则
{
cout << v.front() << " ";//1 2 3 4
v.pop();
}
return 0;
}
4. queue的模拟实现
#pragma once
namespace yzq
{
template<class T, class Container=deque<T>>//给与缺省值,默认使用list<T>
class queue
{
public:
void push(const T& x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
}
void pop()
{
_con.pop_front(); //vector没有头删,强行使用erase 效率太低
}
const T& front()
{
return _con.front();
}
const T& back()
{
return _con.back();
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;//Container 是一个符合要求的容器
};
}
这里假设我们不认识 deque,那么如果stack频繁使用pop头删,将 list< T >设置成缺省值也是非常适合的
5. deque ——双端队列
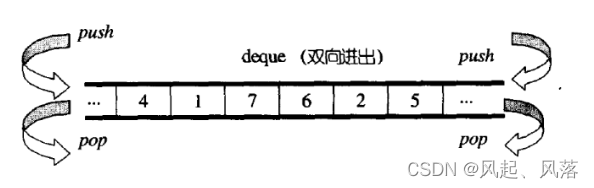
可以在头尾双端进行插入和删除的操作,且时间复杂度为O(1),与vetcor比较,头插效率高,不需要移动元素,
与list比较,空间利用比较高

而deque就是要综合两者的优点 (想法很美好)
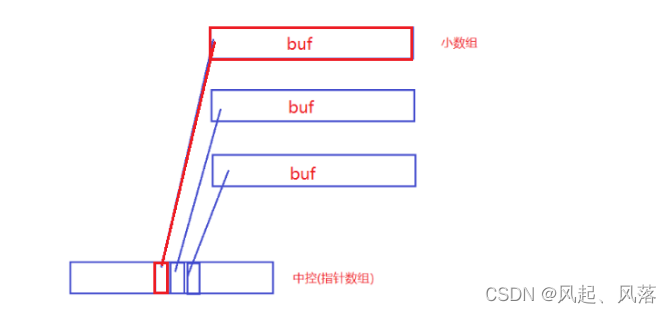
deque并不是真正的连续的空间,而是由一段段连续的小空间拼接而成的
一段段的小数组,若满了不扩容,在开辟一块空间,通过中控(指针数组)的方式将一个个小数组管理起来
第一个buf数组,开的是中控指针数组中间的位置
头插:
尾插:
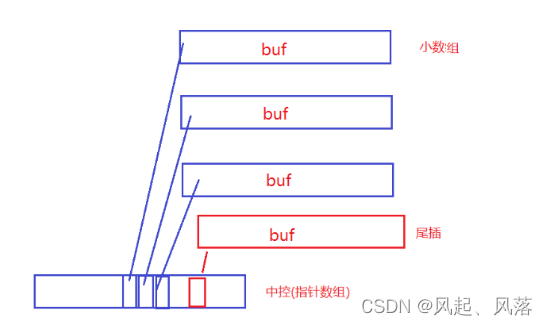
若中控满了,就要扩容,但是扩容代价低
若为vector,本来为100个int空间,需要200个空间,就需要扩容2倍
而 中控是一个指针数组,里面都是指针,可能只需要20个指针就搞定了,所以扩容代价相对于低一些
deque优缺点
优点:
1.相比于vector,扩容代价低
2. 头插 头删,尾插尾删效率高
3. 支持随机访问
缺点:
1.中间插入删除很难搞
若中间插入删除效率高,会影响随机访问的效率,牺牲中间插入删除的效率,随机访问效率就变高了
2.没有vector和list优点极致
deque你说它跟vector比随机访问,速度不如vector,跟list比任意位置插入删除,效率没list高 ,这种就搞的很难啦,哪一项都不突出,但是都会一点
栈和队列都是需要大量的头插头删,尾插尾删的,而deque在这个场景下效率很高,所以deque被当作栈和队列的默认适配容器
6. priority_queue ——优先级队列
1. priority_queue的使用
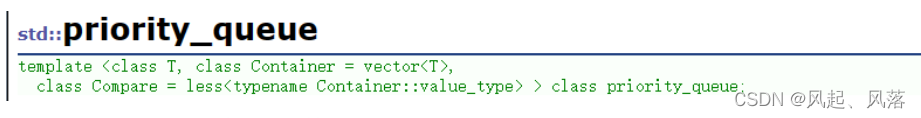
底层是一个堆,默认容器使用vector, 最后一个模板参数代表仿函数 默认使用 less 代表小于 (后面会讲)

#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<functional>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int, vector<int>>v;
//默认为大堆,数据大的优先级高
v.push(4);
v.push(8);
v.push(6);
v.push(2);
while (!v.empty())
{
cout << v.top() << " "; //8 6 4 2
v.pop();
}
return 0;
}
正常来说,默认建立大堆,所以数据大的优先级高
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<functional>
int main()
{
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>>v;//greater作为仿函数
//设置小堆,让小的优先级高
v.push(4);
v.push(8);
v.push(6);
v.push(2);
while (!v.empty())
{
cout << v.top() << " "; //2 4 6 8
v.pop();
}
return 0;
}
但若加入仿函数 greater 后,则会建立小堆,所以数据小的优先级高
2. priority_queue的模拟实现
由于是自己实现的所以要加上命名空间,避免冲突
push——插入
void adjustup(int child)//向上调整算法
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//建大堆
if (com(_con[parent] ,_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T&x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjustup(_con.size() - 1);//向上调整算法
}
由于是堆的插入,而堆本身也是由数组的数据构成的,所以数组加入一个数据相当于在堆最后插入一个数据,在通过向上调整算法依次交换, 不懂向上调整算法的点击这里
pop ——删除
void adjustdown(int parent)//向下调整算法
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2+1;//假设为左孩子
while (child<_con.size())
{
//建大堆
if (child+1 < _con.size()&&com(_con[child],_con[child + 1]))
//child+1是防止右孩子不存在导致越界
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent] ,_con[child]))//将两者换一种说法,使之能=能够调用<即可
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);//首尾交换
_con.pop_back();//尾删
adjustdown(0);//向下调整算法
}
由于要删除堆顶的数据,所以交换堆尾与堆顶数据,在删除堆尾数据,默认容器为vector,所以有pop_back 尾删的功能,而此时堆顶的数据不符合当前的位置,所以需要借助向下调整算法把该数据调整到合适的位置 不懂向下调整算法的点击这里
top —— 堆顶
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
堆是借助数组来实现的,所以堆顶的数据就是当前的第一个数据
仿函数问题
template <class T>
struct Less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template <class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
仿函数主要是借助两个类 来重载 运算符 ( ) ,
而 Less ( x<y) 用于 建立大堆 ,greater (x>y) 用于建立小堆
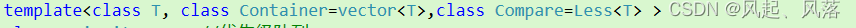
Less / greater 分别都是类名 ,而模板参数 Compare 需要类型
所以 都需要加上 ,即 Less< T> / greater < T >
通过该类型在向上/向下调整算法中分别建立对象,通过对象调用对应类less/greater的重载()从而达到目的

若为默认类型Less,则调用x <y ,从而建大堆
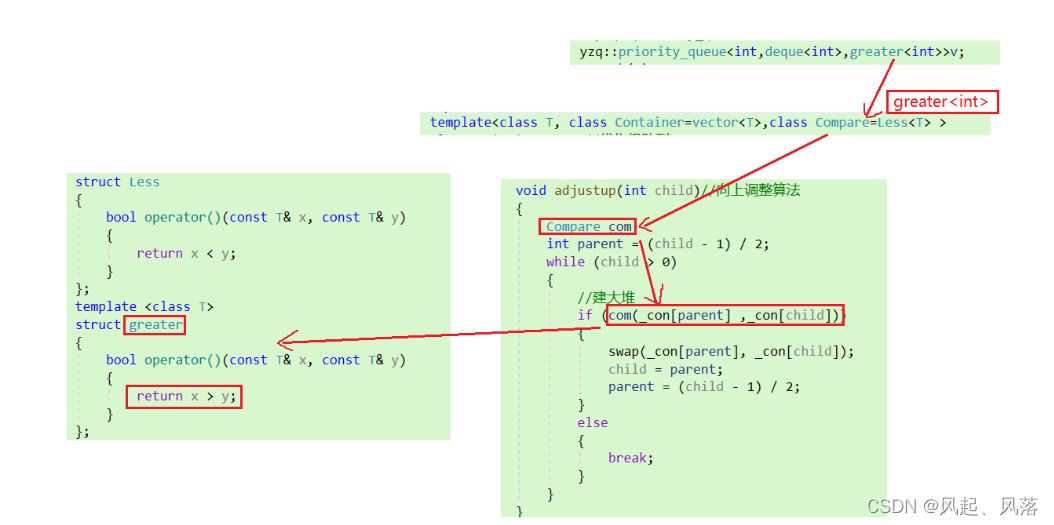
当传入greater< T >类型后,调用对象,找到对应greater类型的重载() ,调用 x >y ,从而建小堆
完整代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
namespace yzq
{
template <class T>
struct Less
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x < y;
}
};
template <class T>
struct greater
{
bool operator()(const T& x, const T& y)
{
return x > y;
}
};
template<class T, class Container=vector<T>,class Compare=Less<T> >
class priority_queue//优先级队列
{
public:
void adjustup(int child)//向上调整算法
{
Compare com;
int parent = (child - 1) / 2;
while (child > 0)
{
//建大堆
if (com(_con[parent] ,_con[child]))
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
child = parent;
parent = (child - 1) / 2;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void adjustdown(int parent)//向下调整算法
{
Compare com;
int child = parent * 2+1;//假设为左孩子
while (child<_con.size())
{
//建大堆
if (child+1 < _con.size()&&com(_con[child],_con[child + 1]))
//child+1是防止右孩子不存在导致越界
{
child++;
}
if (com(_con[parent] ,_con[child]))//将两者换一种说法,使之能=能够调用<即可
{
swap(_con[parent], _con[child]);
parent = child;
child = parent * 2 + 1;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
}
void push(const T&x)
{
_con.push_back(x);
adjustup(_con.size() - 1);//向上调整算法
}
void pop()
{
swap(_con[0], _con[_con.size() - 1]);//首尾交换
_con.pop_back();//尾删
adjustdown(0);//向下调整算法
}
const T& top()
{
return _con[0];
}
size_t size()
{
return _con.size();
}
bool empty()
{
return _con.empty();
}
private:
Container _con;//使用vector实现
};
}
int main()
{
//yzq::priority_queue<int>v;
yzq::priority_queue<int,deque<int>,greater<int>>v;
v.push(1);
v.push(5);
v.push(8);
v.push(4);
while (!v.empty())
{
cout << v.top() << " ";
v.pop();
}
return 0;
}
